Prime线缆调配6.1.5 RDU高可用性部署,带Geo模式冗余
下载选项
非歧视性语言
此产品的文档集力求使用非歧视性语言。在本文档集中,非歧视性语言是指不隐含针对年龄、残障、性别、种族身份、族群身份、性取向、社会经济地位和交叉性的歧视的语言。由于产品软件的用户界面中使用的硬编码语言、基于 RFP 文档使用的语言或引用的第三方产品使用的语言,文档中可能无法确保完全使用非歧视性语言。 深入了解思科如何使用包容性语言。
关于此翻译
思科采用人工翻译与机器翻译相结合的方式将此文档翻译成不同语言,希望全球的用户都能通过各自的语言得到支持性的内容。 请注意:即使是最好的机器翻译,其准确度也不及专业翻译人员的水平。 Cisco Systems, Inc. 对于翻译的准确性不承担任何责任,并建议您总是参考英文原始文档(已提供链接)。
目录
简介
本文档介绍在具有地理模式冗余的高可用性(HA)中安装Prime电缆调配6.1.5。
先决条件
要求
Cisco 建议您了解以下主题:
- Redhat Linux对文件系统和分区的了解和理解。
- 在新的主虚拟机和辅助虚拟/物理机上安装6.1.5 RHEL 7.4/内核3.10.0-693.11.6.x86_64。带geo模式的RDU HA仅与此RHEL操作系统和内核版本及其rpm软件包兼容。
- 了解Linux DRBD文件存储复制方法和Corosync-pace maker群集概念。
- 网络配置文件应仅包含系统主机名,而不包含完全限定域名(FQDN)。
组件
本文档中的信息基于以下软件和硬件版本:
- 平台:Red Hat Linux 7.4
- 软件:Prime Cable调配6.1.5映像。
本文档中的信息都是基于特定实验室环境中的设备编写的。本文档中使用的所有设备最初均采用原始(默认)配置。如果您的网络处于活动状态,请确保您了解所有命令的潜在影响。
安装
网络图
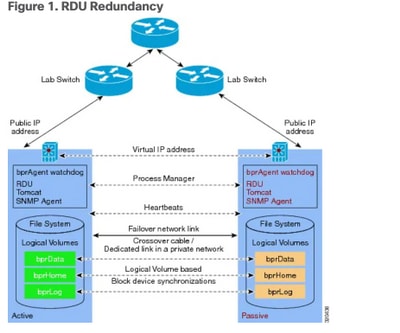
1. LVM在两台服务器上为LVBPRHOME、LVBPRDATA和LVBPRDBLOG创建卷。
2.准备Linux 7.4服务器,以在两台服务器上部署RDU HA。
3.在Geo冗余模式下安装RDU服务器
- 在Geo冗余模式下安装RDU服务器。
- 预先检查HA。 — 主辅模式下的RDU HA设置。
- 安装HA — 安装6.1.5 PCP实例。
- 过帐检查HA。
4.第3层地理冗余部署的路由前提条件。
1. LVM在两台服务器上为LVBPRHOME、LVBPRDATA和LVBPRDBLOG创建卷
此图示为辅助服务器。同样的步骤也需要在主服务器上完成。
- 将新分区添加为sda3,并使用fdisk命令分配磁盘。
[root@pcprdusecondary ~]# fdisk -l
Disk /dev/sda: 107.4 GB, 107374182400 bytes, 209715200 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x00025a26
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 * 2048 2099199 1048576 83 Linux
/dev/sda2 2099200 31211519 14556160 8e Linux LVM
Disk /dev/mapper/rhel-root: 4294 MB, 4294967296 bytes, 8388608 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/mapper/rhel-swap: 8455 MB, 8455716864 bytes, 16515072 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/mapper/rhel-home: 2147 MB, 2147483648 bytes, 4194304 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
[root@pcprdusecondary ~]# fdisk /dev/sda
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2).
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
Be careful before using the write command.
Command (m for help): m
Command action
a toggle a bootable flag
b edit bsd disklabel
c toggle the dos compatibility flag
d delete a partition
g create a new empty GPT partition table
G create an IRIX (SGI) partition table
l list known partition types
m print this menu
n add a new partition
o create a new empty DOS partition table
p print the partition table
q quit without saving changes
s create a new empty Sun disklabel
t change a partition's system id
u change display/entry units
v verify the partition table
w write table to disk and exit
x extra functionality (experts only)
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sda: 107.4 GB, 107374182400 bytes, 209715200 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x00025a26
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 * 2048 2099199 1048576 83 Linux
/dev/sda2 2099200 31211519 14556160 8e Linux LVM
Command (m for help): n
Partition type:
p primary (2 primary, 0 extended, 2 free)
e extended
Select (default p): p
Partition number (3,4, default 3): 3
First sector (31211520-209715199, default 31211520):
Using default value 31211520
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (31211520-209715199, default 209715199):
Using default value 209715199
Partition 3 of type Linux and of size 85.1 GiB is set
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sda: 107.4 GB, 107374182400 bytes, 209715200 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x00025a26
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 * 2048 2099199 1048576 83 Linux
/dev/sda2 2099200 31211519 14556160 8e Linux LVM
/dev/sda3 31211520 209715199 89251840 83 Linux
Command (m for help): t
Partition number (1-3, default 3): 3
Hex code (type L to list all codes): L
0 Empty 24 NEC DOS 81 Minix / old Lin bf Solaris
1 FAT12 27 Hidden NTFS Win 82 Linux swap / So c1 DRDOS/sec (FAT-
2 XENIX root 39 Plan 9 83 Linux c4 DRDOS/sec (FAT-
3 XENIX usr 3c PartitionMagic 84 OS/2 hidden C: c6 DRDOS/sec (FAT-
4 FAT16 <32M 40 Venix 80286 85 Linux extended c7 Syrinx
5 Extended 41 PPC PReP Boot 86 NTFS volume set da Non-FS data
6 FAT16 42 SFS 87 NTFS volume set db CP/M / CTOS / .
7 HPFS/NTFS/exFAT 4d QNX4.x 88 Linux plaintext de Dell Utility
8 AIX 4e QNX4.x 2nd part 8e Linux LVM df BootIt
9 AIX bootable 4f QNX4.x 3rd part 93 Amoeba e1 DOS access
a OS/2 Boot Manag 50 OnTrack DM 94 Amoeba BBT e3 DOS R/O
b W95 FAT32 51 OnTrack DM6 Aux 9f BSD/OS e4 SpeedStor
c W95 FAT32 (LBA) 52 CP/M a0 IBM Thinkpad hi eb BeOS fs
e W95 FAT16 (LBA) 53 OnTrack DM6 Aux a5 FreeBSD ee GPT
f W95 Ext'd (LBA) 54 OnTrackDM6 a6 OpenBSD ef EFI (FAT-12/16/
10 OPUS 55 EZ-Drive a7 NeXTSTEP f0 Linux/PA-RISC b
11 Hidden FAT12 56 Golden Bow a8 Darwin UFS f1 SpeedStor
12 Compaq diagnost 5c Priam Edisk a9 NetBSD f4 SpeedStor
14 Hidden FAT16 61 SpeedStor ab Darwin boot f2 DOS secondary
16 Hidden FAT16 63 GNU HURD or Sys af HFS / HFS+ fb VMware VMFS
17 Hidden HPFS/NTF 64 Novell Netware b7 BSDI fs fc VMware VMKCORE
18 AST SmartSleep 65 Novell Netware b8 BSDI swap fd Linux raid auto
1b Hidden W95 FAT3 70 DiskSecure Mult bb Boot Wizard hid fe LANstep
1c Hidden W95 FAT3 75 PC/IX be Solaris boot ff BBT
1e Hidden W95 FAT1 80 Old Minix
Hex code (type L to list all codes): 8e
Changed type of partition 'Linux' to 'Linux LVM'
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
WARNING: Re-reading the partition table failed with error 16: Device or resource busy.
The kernel still uses the old table. The new table will be used at
the next reboot or after you run partprobe(8) or kpartx(8)
Syncing disks.
此错误消息应为。您需要重新加载Linux计算机,使新更改生效。
[root@pcprdusecondary ~]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/mapper/rhel-root 4.0G 946M 3.1G 24% /
devtmpfs 3.9G 0 3.9G 0% /dev
tmpfs 3.9G 0 3.9G 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 3.9G 8.6M 3.9G 1% /run
tmpfs 3.9G 0 3.9G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/sda1 1014M 143M 872M 15% /boot
/dev/mapper/rhel-home 2.0G 33M 2.0G 2% /home
tmpfs 781M 0 781M 0% /run/user/0
[root@pcprdusecondary ~]# fdisk -l
Disk /dev/sda: 107.4 GB, 107374182400 bytes, 209715200 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x00025a26
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 * 2048 2099199 1048576 83 Linux
/dev/sda2 2099200 31211519 14556160 8e Linux LVM
/dev/sda3 31211520 209715199 89251840 8e Linux LVM
Disk /dev/mapper/rhel-root: 4294 MB, 4294967296 bytes, 8388608 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/mapper/rhel-swap: 8455 MB, 8455716864 bytes, 16515072 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/mapper/rhel-home: 2147 MB, 2147483648 bytes, 4194304 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
- 为sda3创建物理卷。
[root@pcprdusecondary ~]# pvcreate /dev/sda3
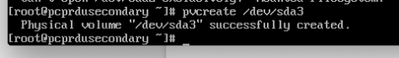
- pvscan — 扫描并列出物理卷组。
- vgscan — 扫描并列出逻辑卷组。
- lvscan — 扫描并列出在卷组下创建的逻辑卷
此Linux LVM创建是RDU服务器安装的先决条件。
- 在主RDU节点和辅助RDU节点上,必须创建一个逻辑卷组,其中有三个逻辑卷。逻辑卷是根据以下规范创建的:
1.<Prime Cable Provisioning安装目录的逻辑卷> — 安装在/bprHome目录上。例如,LVBPRHOME。
2.<Prime Cable Provisioning data directory的逻辑卷> — 安装在/bprData目录上。例如,LVBPRDATA
3.<Prime Cable Provisioning日志目录的逻辑卷> — 装载在/bprLog目录上。例如,LVBPRDBLOG
- 根据需要创建卷组和逻辑卷,并装载到目录/bprData、bprHome和/bprLog目录上。
例如: 此步骤是为具有3 GB磁盘空间的BPRHOME、具有15 GB磁盘空间的BPRDATA和具有5 GB磁盘空间分配的BPRDBLOG创建逻辑卷。您需要根据分配选择要扩展的磁盘空间。
- 创建卷组。
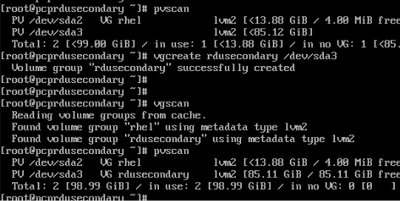
vgcreate <vg_name> <pvname>
[root@pcprdusecondary ~]# vgcreate rdusecondary /dev/sda3
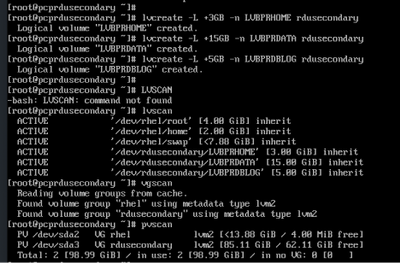
- 创建逻辑卷:
lvcreate -L <GB值> -n <logicalvolumename> <volumegroupname>
[root@pcprdusecondary ~]# lvcreate -L +3GB -n LVBPRHOME rdusecondary
[root@pcprdusecondary ~]# lvcreate -L +15GB -n LVBPRDATA rdusecondary
[root@pcprdusecondary ~]# lvcreate -L +5GB -n LVBPRDBLOG rdusecondary
bprHome — 安装应用程序路径(默认目录 — /opt/CSCObac)
bprData — 安装数据路径。(默认目录 — /var/CSCObac)
Bpr日志 — 安装日志路径。(默认目录 — /var/CSCObac)
- 在lvm分区上创建XFS文件系统。
mkfs.xfs /dev/<volumegroupname>/<logicalvolume>
[root@pcprdusecondary ~]# mkfs.xfs /dev/rdusecondary/LVBPRHOME
[root@pcprdusecondary ~]# mkfs.xfs /dev/rdusecondary/LVBPRDATA
[root@pcprdusecondary ~]# mkfs.xfs /dev/rdusecondary/LVBPRDBLOG
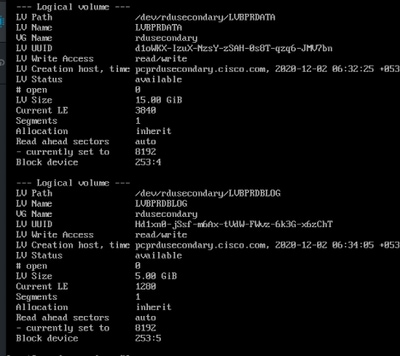
- 创建目录 — bprHome、bprData、bprLog并在这些目录上装载逻辑卷。
[root@pcprdusecondary ~]# mkdir bprHome
[root@pcprdusecondary ~]# mkdir bprData
[root@pcprdusecondary ~]# mkdir bprLog
- 装载在这些目录上创建的逻辑卷。
[root@pcprdusecondary ~]# mount /dev/RDUPRIMARY/LVBPRHOME /bprHome/
[root@pcprdusecondary ~]# mount /dev/RDUPRIMARY/LVBPRDATA /bprData/
[root@pcprdusecondary ~]# mount /dev/RDUPRIMARY/LVBPRDBLOG /bprLog
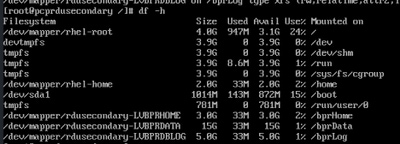
- 这些命令可用于登记和验证新分区状态、新物理和逻辑卷状态、文件系统类型、分配块。
[root@pcprdusecondary ~]# fdisk -l
[root@pcprdusecondary ~]# pvdisplay
[root@pcprdusecondary ~]# vgdisplay
[root@pcprdusecondary ~]# lvdisplay
注意:
-
无需添加逻辑卷的fstab条目。Corosync群集将负责安装卷。过去,由于这些条目,一些客户遇到了问题。在重新启动系统期间,由于计时问题,主卷和辅助卷都会尝试装载卷。
-
卷组名称和逻辑卷(LVBPRHOME、LVBPRDATA、LVBPRDBLOG)在两台服务器上必须相同。两台服务器上应共享相同的磁盘空间。
-
DRBD块设备文件系统同步只在两台服务器上运行磁盘大小相同。
-
CentOS Linux版本必须为7.4,内核必须为3.10.0-693.11.6.el7.x86_64。
-
确保两台服务器对通告VIP的公有IP地址使用相同的接口 — ens192。
2.准备Linux 7.4服务器,在两台服务器上部署RDU HA
3.在地理冗余模式下安装RDU服务器
有关详细信息,请参阅快速入门指南:
4.部署地理冗余的第3层路由前提条件
RDU地理冗余
RDU Geo Redundancy是RHEL 7.4或CentOS 7.4(两者均为64位)上支持的RDU HA的增强功能,其中RDU主节点和辅助节点可以位于不同的地理位置,或者两个节点可以位于不同的子网中。
- 在Geo冗余模式下,VIP可以位于任何子网中,无需在两个节点共同的子网范围内。
- 在Geo冗余模式下,VIP的CIDR值应为32。
- VIP将作为来自活动服务器的RIP通告进行通告,因此需要在两个节点的入口路由器上执行路由注入。
- 在Geo冗余模式下,将使用资源代理(res_VIPArip)监控VIP。
PCP地理冗余要求
虚拟IP(VIP)的路由注入需要在主服务器和辅助服务器连接的入口路由器上完成。
VIP将作为来自活动服务器的RIP2通告进行通告,因此需要对RIP2执行路由重分发,使其重分发到用户环境中运行的动态路由协议。
如何将RIP2路由重分布并通告给OSPF IGRP。同样的重分发也可用于EIGRP/IBGP等其他协议。
对于PCP地理冗余解决方案,VIP的CIDR值应为32。
- 如果通过quagga启用VIP通告,则输入要通过其通告VIP的接口(默认情况下为eth0),请确保主服务器和辅助服务器上的此接口名称相同,并确保此接口连接到执行路由注入的入口路由器。
- 如果禁用通过quagga的VIP通告,则输入VIP的CIDR值
- /etc/quagga/ripd.conf。 — 在Geo模式下添加RIP2 conf的路径。https://www.nongnu.org/quagga/docs/quagga.html#RIP
- RIP邻接关系必须注入到与主服务器和辅助服务器相连的相邻路由器中。此类配置示例:
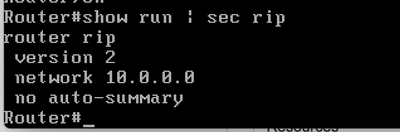
- 邻居对等体的邻接配置。这需要在两台路由器中实施。必须添加VIP和公有IP网络才能通告接口。
- 路由到VIP地址。
- 根据启用的路由通告到外部世界,通过ospf/eigrp/static通告此RIP网络。
Example: Here OSPF is the dynamic protocol
router ospf <processed>
redistribute rip metric-type 1 subnets. For RIP2, it uses metric as hop count.
Example: Here ISIS is the dynamic protocol
router isis
redistribute rip metric
检查后HA
- 使用命令/bprHome/CSCObac/agent/HA/bin/monitor_ha_cluster.sh检查RDU HA集群状态。
- 确保RDU HA工作正常,而不会出现地理冗余模式问题。等待主DRBD和辅助DRBD磁盘同步并显示最新状态(cat /proc/drbd)。
由思科工程师提供
- Renjith GCisco TAC Engineer
 反馈
反馈