Configurazione della ridistribuzione delle route BGP interne in IGP
Opzioni per il download
Linguaggio senza pregiudizi
La documentazione per questo prodotto è stata redatta cercando di utilizzare un linguaggio senza pregiudizi. Ai fini di questa documentazione, per linguaggio senza di pregiudizi si intende un linguaggio che non implica discriminazioni basate su età, disabilità, genere, identità razziale, identità etnica, orientamento sessuale, status socioeconomico e intersezionalità. Le eventuali eccezioni possono dipendere dal linguaggio codificato nelle interfacce utente del software del prodotto, dal linguaggio utilizzato nella documentazione RFP o dal linguaggio utilizzato in prodotti di terze parti a cui si fa riferimento. Scopri di più sul modo in cui Cisco utilizza il linguaggio inclusivo.
Informazioni su questa traduzione
Cisco ha tradotto questo documento utilizzando una combinazione di tecnologie automatiche e umane per offrire ai nostri utenti in tutto il mondo contenuti di supporto nella propria lingua. Si noti che anche la migliore traduzione automatica non sarà mai accurata come quella fornita da un traduttore professionista. Cisco Systems, Inc. non si assume alcuna responsabilità per l’accuratezza di queste traduzioni e consiglia di consultare sempre il documento originale in inglese (disponibile al link fornito).
Introduzione
In questo documento viene descritto come ridistribuire le route Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) interne nel processo OSPF (Open Shortest Path First).
Prerequisiti
Requisiti
Cisco raccomanda la conoscenza della configurazione BGP di base e la comprensione dei protocolli di routing di:
- BGP
- OSPF
- Protocollo EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol)
- Protocollo RIP (Routing Information Protocol)
Per ulteriori informazioni, fare riferimento ai casi di studio di BGP e alla configurazione di BGP.
Componenti usati
Per la stesura del documento, è stato usato il software Cisco IOS® versione 15.1(4)M5.
Le informazioni discusse in questo documento fanno riferimento a dispositivi usati in uno specifico ambiente di emulazione. Su tutti i dispositivi menzionati nel documento la configurazione è stata ripristinata ai valori predefiniti. Se la rete è operativa, valutare attentamente eventuali conseguenze derivanti dall'uso dei comandi.
Premesse
Come in altri protocolli IGP (Interior Gateway Protocol) per la ridistribuzione IGP, il comportamento è diverso quando il protocollo IBGP (Internal BGP) viene ridistribuito in OSPF. Le route apprese IBGP non vengono inoltrate a un protocollo di routing IGP tramite il comando redistribute. Usare il comando bgp redistribute-internal nel processo BGP sul router che esegue la ridistribuzione.
Configurazione
Esempio di rete
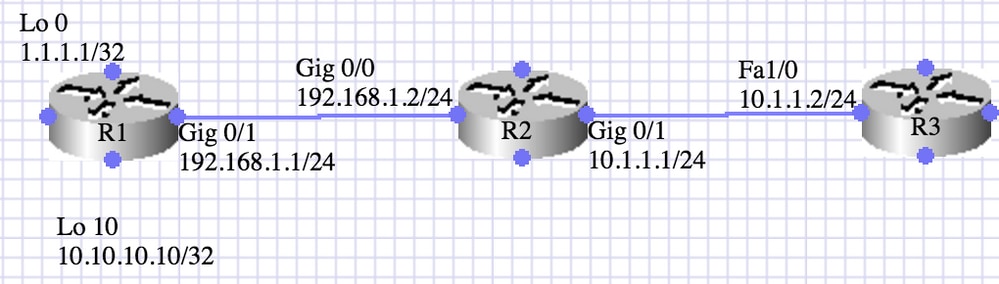
Configurare OSPF tra R2 e R3
Nello scenario illustrato di seguito, i router R1 e R2 eseguono IBGP e i router R2 o R3 eseguono l'area OSPF 0. R1 annuncia due route (1.1.1.1 /32 e 10.10.10.10/32) tramite il comando network.
R2 ridistribuisce BGP nell'area OSPF 0. È necessario ridistribuire le route interne selezionate (10.10.10.10/32).
L'operazione viene eseguita utilizzando prefix-list e route-map.
R1:
interface Loopback0 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 ! interface Loopback10 ip address 10.10.10.10 255.255.255.255 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ! router bgp 10 no synchronization bgp router-id 1.1.1.1 bgp log-neighbor-changes network 1.1.1.1 mask 255.255.255.255 network 10.10.10.10 mask 255.255.255.255 neighbor 192.168.1.2 remote-as 100 no auto-summary
R1#show ip bgp summary BGP router identifier 10.10.10.10, local AS number 10 BGP table version is 3, main routing table version 3 2 network entries using 296 bytes of memory 2 path entries using 128 bytes of memory 1/1 BGP path/bestpath attribute entries using 136 bytes of memory 0 BGP route-map cache entries using 0 bytes of memory 0 BGP filter-list cache entries using 0 bytes of memory BGP using 560 total bytes of memory BGP activity 2/0 prefixes, 2/0 paths, scan interval 60 secs Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd 192.168.1.2 4 10 6 7 3 0 0 00:03:10 0
R2:
interface Loopback0 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto !
router ospf 1 router-id 2.2.2.2 log-adjacency-changes redistribute bgp 100 metric 100 metric-type 1 subnets route-map BGP-To_OSPF network 10.1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 0
R2#show ip ospf neighbor Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface 3.3.3.3 1 FULL/BDR 00:00:38 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1
router bgp 10 no synchronization bgp router-id 2.2.2.2 bgp log-neighbor-changes bgp redistribute-internal neighbor 192.168.12.1 remote-as 10 no auto-summary ! ip prefix-list BGP-to-ospf seq 5 permit 172.16.0.0/16 ! route-map BGP-To_OSPF permit 10 match ip address prefix-list BGP-to-ospf
R2#show ip bgp summary BGP router identifier 192.168.1.2, local AS number 10 BGP table version is 3, main routing table version 3 2 network entries using 272 bytes of memory 2 path entries using 112 bytes of memory 1/1 BGP path/bestpath attribute entries using 128 bytes of memory 0 BGP route-map cache entries using 0 bytes of memory 0 BGP filter-list cache entries using 0 bytes of memory BGP using 512 total bytes of memory BGP activity 2/0 prefixes, 2/0 paths, scan interval 60 secs Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd 192.168.1.1 4 10 8 7 3 0 0 00:03:52 2 R2#show ip bgp BGP table version is 3, local router ID is 192.168.1.2 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, x best-external, f RT-Filter Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *>i1.1.1.1/32 192.168.1.1 0 100 0 i *>i10.10.10.10/32 192.168.1.1 0 100 0 i
R2#show ip route 1.1.1.1 Routing entry for 1.1.1.1/32 Known via "bgp 10", distance 200, metric 0, type internal Last update from 192.168.1.1 00:04:53 ago Routing Descriptor Blocks: * 192.168.1.1, from 192.168.1.1, 00:04:53 ago Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1 AS Hops 0 MPLS label: none R2#show ip route 10.10.10.10 Routing entry for 10.10.10.10/32 Known via "bgp 10", distance 200, metric 0, type internal Last update from 192.168.1.1 00:04:56 ago Routing Descriptor Blocks: * 192.168.1.1, from 192.168.1.1, 00:04:56 ago Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1 AS Hops 0 MPLS label: none
R3:
interface FastEthernet1/0 ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto
router ospf 1 log-adjacency-changes network 10.1.1.2 0.0.0.0 area 0
R3#show ip ospf neighbor Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface 192.168.1.2 1 FULL/DR 00:00:36 10.1.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1
La tabella di routing in R3 prima della ridistribuzione BGP - internal viene aggiunta in R2 con il router BGP 10:
R3#show ip route Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP + - replicated route, % - next hop override Gateway of last resort is not set 3.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets C 3.3.3.3 is directly connected, Loopback0 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks C 10.1.1.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 L 10.1.1.2/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
R2:
router bgp 10 bgp redistribute-internal
Verifica
R3:
La tabella di routing per R3 dopo la ridistribuzione BGP - interna viene aggiunta su R2 con il router BGP 10:
R3#show ip route Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP + - replicated route, % - next hop override Gateway of last resort is not set 3.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets C 3.3.3.3 is directly connected, Loopback0 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 2 masks C 10.1.1.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 L 10.1.1.2/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 O E1 10.10.10.10/32 [110/11] via 10.1.1.1, 00:00:06, GigabitEthernet0/1
Configurare EIGRP tra R2 e R3:
Nello scenario illustrato di seguito, i router R1 e R2 eseguono IBGP e i router R2 o R3 eseguono EIGRP Autonomous System (AS) 1. R1 annuncia due route (1.1.1.1 /32 e 10.10.10.10/32) tramite il comando network.
R2 ridistribuisce BGP in EIGRP AS 1. È necessario ridistribuire le route interne selezionate (10.10.10.10/32).
L'operazione viene eseguita utilizzando prefix-list e route-map.
R2:
router eigrp 1 network 10.0.0.0 redistribute bgp 10 metric 1544 10 255 1 1500 route-map BGP_To_EIGRP eigrp router-id 2.2.2.2
route-map BGP_To_EIGRP, permit, sequence 10 Match clauses: ip address prefix-lists: BGP-to-eigrp Set clauses: Policy routing matches: 0 packets, 0 bytes
ip prefix-list BGP-to-eigrp: 1 entries
seq 1 permit 10.10.10.10/32
R3:
router eigrp 1 network 10.0.0.0 eigrp router-id 3.3.3.3
L'output del comando show IP route su R3 prima della ridistribuzione BGP - internal viene aggiunto su R2 con il router BGP 10:
R3#show ip route Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP + - replicated route, % - next hop override Gateway of last resort is not set 3.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets C 3.3.3.3 is directly connected, Loopback0 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks C 10.1.1.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 L 10.1.1.2/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
R2:
router bgp 10 bgp redistribute-internal
Verifica
L'output del comando show IP route su R3 dopo BGP redistribute-internal viene aggiunto su R2 con il router BGP 10:
R3#show ip route Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP + - replicated route, % - next hop override Gateway of last resort is not set 3.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets C 3.3.3.3 is directly connected, Loopback0 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 2 masks C 10.1.1.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 L 10.1.1.2/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 D EX 10.10.10.10/32 [170/1660672] via 10.1.1.1, 00:00:04, GigabitEthernet0/1
Configurare RIP tra R2 e R3:
Nello scenario illustrato di seguito, i router R1 e R2 eseguono IBGP e i router R2 o R3 eseguono RIPv2.
R1 annuncia due route (1.1.1.1 /32 e 10.10.10.10/32) tramite il comando network.
R2 ridistribuisce BGP in RIPv2. È necessario ridistribuire le route interne selezionate (10.10.10.10/32).
L'operazione viene eseguita utilizzando prefix-list e route-map.
R2:
router rip version 2 redistribute bgp 10 metric 1 route-map BGP_To_RIP network 10.0.0.0 no auto-summary
route-map BGP_To_RIP, permit, sequence 10 Match clauses: ip address prefix-lists: BGP-to-rip Set clauses: Policy routing matches: 0 packets, 0 bytes ip prefix-list BGP-to-rip: 1 entries seq 1 permit 10.10.10.10/32
R3:
router rip version 2 network 10.0.0.0 no auto-summary
Output su R3 prima di abilitare la ridistribuzione BGP-interna su R2 con il router BGP 10:
R3#show ip route Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP + - replicated route, % - next hop override Gateway of last resort is not set 3.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets C 3.3.3.3 is directly connected, Loopback0 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks C 10.1.1.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 L 10.1.1.2/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
R2:
router bgp 10 bgp redistribute-internal
Verifica
Output su R3 dopo aver abilitato la ridistribuzione BGP - interno su R2 con il router BGP 10:
R3#sh ip route Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP + - replicated route, % - next hop override Gateway of last resort is not set 3.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets C 3.3.3.3 is directly connected, Loopback0 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 2 masks C 10.1.1.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 L 10.1.1.2/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 R 10.10.10.10/32 [120/1] via 10.1.1.1, 00:00:09, GigabitEthernet0/1
Risoluzione dei problemi
Al momento non sono disponibili informazioni specifiche per la risoluzione dei problemi di questa configurazione.
Cronologia delle revisioni
| Revisione | Data di pubblicazione | Commenti |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
25-Oct-2016
|
Versione iniziale |
Contributo dei tecnici Cisco
- Gaurav MahajanCisco TAC Engineer
 Feedback
Feedback