Solución de problemas de GuestShell en plataformas Catalyst 9K
Opciones de descarga
-
ePub (152.3 KB)
Visualice en diferentes aplicaciones en iPhone, iPad, Android, Sony Reader o Windows Phone -
Mobi (Kindle) (123.4 KB)
Visualice en dispositivo Kindle o aplicación Kindle en múltiples dispositivos
Lenguaje no discriminatorio
El conjunto de documentos para este producto aspira al uso de un lenguaje no discriminatorio. A los fines de esta documentación, "no discriminatorio" se refiere al lenguaje que no implica discriminación por motivos de edad, discapacidad, género, identidad de raza, identidad étnica, orientación sexual, nivel socioeconómico e interseccionalidad. Puede haber excepciones en la documentación debido al lenguaje que se encuentra ya en las interfaces de usuario del software del producto, el lenguaje utilizado en función de la documentación de la RFP o el lenguaje utilizado por un producto de terceros al que se hace referencia. Obtenga más información sobre cómo Cisco utiliza el lenguaje inclusivo.
Acerca de esta traducción
Cisco ha traducido este documento combinando la traducción automática y los recursos humanos a fin de ofrecer a nuestros usuarios en todo el mundo contenido en su propio idioma. Tenga en cuenta que incluso la mejor traducción automática podría no ser tan precisa como la proporcionada por un traductor profesional. Cisco Systems, Inc. no asume ninguna responsabilidad por la precisión de estas traducciones y recomienda remitirse siempre al documento original escrito en inglés (insertar vínculo URL).
Contenido
Introducción
Este documento describe cómo resolver problemas con el shell de invitado en los switches Cat9K.
Prerequisites
Requirements
- Conocimientos básicos del software Cisco IOS® XE
- Sistemas de archivos Linux
- Comandos de Linux
Componentes Utilizados
La información que contiene este documento se basa en las siguientes versiones de software y hardware.
- Catalyst 9200
- Catalyst 9300
- Catalyst 9400
- Catalyst 9500
- Catalyst 9600
- Cisco IOS XE 17.9.1 y versiones posteriores
La información que contiene este documento se creó a partir de los dispositivos en un ambiente de laboratorio específico. Todos los dispositivos que se utilizan en este documento se pusieron en funcionamiento con una configuración verificada (predeterminada). Si tiene una red en vivo, asegúrese de entender el posible impacto de cualquier comando.
Antecedentes
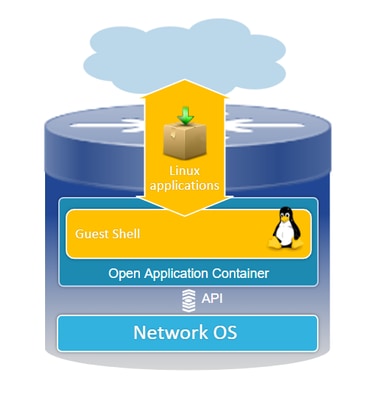
Descripción general de Guest Shell
- El shell de invitado ofrece un entorno de ejecución aislado que funciona dentro de un contenedor Linux (LXC).
- Acceso a la red: Los administradores pueden conectarse a la red a través de interfaces de red Linux, lo que permite una conectividad y gestión sólidas.
- Acceso Bootflash: Existe acceso directo al almacenamiento bootflash, lo que facilita una administración de archivos y operaciones del sistema eficientes.
- Acceso CLI de Cisco IOS: Los administradores tienen la capacidad de interactuar directamente con la interfaz de línea de comandos de Cisco IOS, lo que permite una integración y un control sin problemas.
- Ejecución de scripts: El entorno admite la instalación y ejecución de scripts Python, lo que permite la automatización y la personalización.
- Compatibilidad con aplicaciones: Tanto las aplicaciones Linux de 32 bits como las de 64 bits se pueden instalar y ejecutar, lo que ofrece flexibilidad y una amplia gama de posibilidades funcionales.
Resolución de problemas
.
Configuración
1. Active IOX.
Switch#conf terminal Switch(config)#iox Switch(config)#
Espere de 1 a 5 minutos para que IOX se inicialice. Asegúrese de que IOX esté operativo. Puede verificar los mensajes mostrados durante la sesión CLI o revisando el resultado del comando show.
*Mar 10 15:35:40.206: %UICFGEXP-6-SERVER_NOTIFIED_START: Switch 1 R0/0: psd: Server iox has been notified to start *Mar 10 15:35:51.186: %IOX-3-PD_PARTITION_CREATE: Switch 1 R0/0: run_ioxn_caf: IOX may take upto 5 mins to be ready. Wait for iox to be ready before installing the apps *Mar 10 15:37:56.643: %IOX-3-IOX_RESTARTABITLITY: Switch 1 R0/0: run_ioxn_caf: Stack is in N+1 mode, disabling sync for IOx restartability *Mar 10 15:38:05.835: %IM-6-IOX_ENABLEMENT: Switch 1 R0/0: ioxman: IOX is ready. Switch#show iox-service IOx Infrastructure Summary: --------------------------- IOx service (CAF) : Running IOx service (HA) : Running IOx service (IOxman) : Running IOx service (Sec storage) : Running Libvirtd 5.5.0 : Running Dockerd v19.03.13-ce : Running Sync Status : Disabled
2. Configuración de la red.
Este ejemplo utiliza la interfaz AppGigabitEthernet para proporcionar acceso a la red.
! interface AppGigabitEthernet1/0/1 switchport trunk allowed vlan 50 switchport mode trunk ! app-hosting appid guestshell app-vnic AppGigabitEthernet trunk vlan 50 guest-interface 0 guest-ipaddress 192.168.10.10 netmask 255.255.255.0 name-server0 192.168.10.254 end !

Nota: GuestShell utiliza una dirección IP estática, ya que no incluye el servicio de cliente DHCP de forma predeterminada. Puede instalar el servicio de cliente DHCP para obtener una dirección IP dinámicamente.
Este ejemplo utiliza la interfaz de administración (Gi0/0) para proporcionar acceso a la red. En el modo de administración, guestshell utiliza el puerto de administración para la red. La dirección IP del puerto de administración configurado por Cisco IOS actúa como gateway.
! app-hosting appid guestshell app-vnic management guest-interface 0 name-server0 8.8.8.8 !

Nota: Cuando utiliza la interfaz de administración, la configuración predeterminada para la interfaz eth0 de Guestshell está codificada en la dirección IP 192.168.30.2.
Puede configurar la interfaz del grupo de puertos virtuales:
- Configuración del grupo de puertos virtuales: Establezca un grupo de puertos virtuales con una dirección IP estática.
- Conexión a Internet: Asegúrese de que la interfaz del puerto frontal esté conectada a Internet para permitir el acceso externo.
- Configuración de NAT: Configure NAT entre el grupo de puertos virtuales y el puerto frontal para facilitar la traducción de direcciones de red.
- Asignación de IP de GuestShell: Asigne una dirección IP a GuestShell dentro de la misma subred que la interfaz del grupo de puertos virtuales.
! interface VirtualPortGroup0 ip address 192.168.35.1 255.255.255.0 ip nat inside ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3 no switchport ip address 192.168.100.10 255.255.255.0 ip nat outside ! ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.100.254 ip route vrf Mgmt-vrf 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.10.254 ip nat inside source static tcp 192.168.35.2 7023 192.168.100.10 7023 extendable ! ! ip access-list standard NAT_ACL 10 permit 192.168.0.0 0.0.255.255 ! app-hosting appid guestshell app-vnic gateway1 virtualportgroup 0 guest-interface 0 guest-ipaddress 192.168.35.2 netmask 255.255.255.0 app-default-gateway 192.168.35.1 guest-interface 0 name-server0 8.8.8.8 end
3. Activar guest shell.
Switch#guestshell enable Interface will be selected if configured in app-hosting Please wait for completion guestshell installed successfully Current state is: DEPLOYED guestshell activated successfully Current state is: ACTIVATED guestshell started successfully Current state is: RUNNING Guestshell enabled successfully

Nota: El comando guestshell enable es la única manera de instalar guestshell. El uso de la activación/desactivación/desactivación de CLI de alojamiento de aplicaciones se puede utilizar para controlar el shell de invitado. Se recomienda que en su lugar utilice la CLI exec de guestshell.
Ciclo de vida de invitado
Inhabilitación de invitado: Desactivar guesthell elimina el acceso a guestshell y elimina las sesiones actuales. Los archivos/datos se conservan, puede utilizar guestshell enable para restaurar el acceso.
Switch#guestshell disable Guestshell disabled successfully
Guestshell destruir: Esto elimina el sistema de archivos del shell de invitado de forma irreversible. Todos los archivos/datos/scripts/settinguestshell/ paquetes y módulos instalados.
Switch#guestshell destroy Guestshell destroyed successfully

Nota: Cuando ejecuta este comando, todos los datos se pierden de forma irreversible.
Ejecución de invitado: Guestshell ejecuta el comando guestshell run bash para crear un shell dentro del shell de invitado, lo que le permite utilizar cualquier binario de Linux en /bin y /sbin.
Switch#guestshell run bash [guestshell@guestshell ~]$ ping 192.168.10.1 PING 192.168.10.1 (192.168.10.1) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 192.168.10.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=254 time=0.517 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.10.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=254 time=0.552 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.10.1: icmp_seq=4 ttl=254 time=0.447 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.10.1: icmp_seq=5 ttl=254 time=0.549 ms
Python de ejecución de invitado: Utilice este comando para iniciar el intérprete de python interactivo.
Switch#guestshell run python3 Python 3.6.8 (default, Dec 22 2020, 19:04:08) [GCC 8.4.1 20200928 (Red Hat 8.4.1-1)] on linux Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. >>>
Validaciones
Puede utilizar estos comandos para validar el Guestshell:
Switch#show app-hosting detail appid guestshell
App id : guestshell
Owner : iox
State : RUNNING
Application
Type : lxc
Name : GuestShell
Version : 3.3.0
Description : Cisco Systems Guest Shell XE for x86_64
Author : Cisco Systems
Path : /guestshell/:guestshell.tar
URL Path :
Multicast : yes
Activated profile name : custom
Resource reservation
Memory : 256 MB
Disk : 1 MB
CPU : 800 units
CPU-percent : 11 %
VCPU : 1
Platform resource profiles
Profile Name CPU(unit) Memory(MB) Disk(MB)
--------------------------------------------------------------
Attached devices
Type Name Alias
---------------------------------------------
serial/shell iox_console_shell serial0
serial/aux iox_console_aux serial1
serial/syslog iox_syslog serial2
serial/trace iox_trace serial3
Network interfaces
---------------------------------------
eth0:
MAC address : 52:54:dd:5b:c4:b8
IPv4 address : 192.168.30.2
IPv6 address : ::
Network name : mgmt-bridge200
Port forwarding
Table-entry Service Source-port Destination-port
---------------------------------------------------
Switch#show app-hosting list
App id State
---------------------------------------------------------
guestshell RUNNING
Switch#guestshell run sudo ifconfig
eth0: flaguestshell=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.10.10 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.10.255
inet6 fe80::5054:ddff:fece:a7c9 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20
ether 52:54:dd:ce:a7:c9 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 3 bytes 266 (266.0 B)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 9 bytes 726 (726.0 B)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
lo: flaguestshell=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> mtu 65536
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10
loop txqueuelen 1000 (Local Loopback)
RX packets 338 bytes 74910 (73.1 KiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 338 bytes 74910 (73.1 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
Redimensionamiento de recursos
! app-hosting appid guestshell app-vnic management guest-interface 0 app-resource profile custom cpu 1000 memory 512
persist-disk 200 !
Debe deshabilitar y habilitar el shell de invitado para que los cambios surtan efecto.
Switch#guestshell disable Guestshell disabled successfully Switch#guestshell enable *Mar 11 01:17:46.841: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by coguestshell enable Interface will be selected if configured in app-hosting Please wait for completion guestshell activated successfully Current state is: ACTIVATED guestshell started successfully Current state is: RUNNING Guestshell enabled successfully Switch#show app-hosting detail appid guestshell | sec Resource reservation Resource reservation Memory : 512 MB Disk : 200 MB CPU : 1110 units CPU-percent : 15 % VCPU : 1

Nota: En los switches, la plataforma permite cambiar el tamaño de los recursos hasta el máximo permitido. Consulte Recursos de hardware de la plataforma Cisco Catalyst 9000 para aplicaciones.
Escenarios de ejemplo
Configuración DHCP
Problema: El archivo binario del cliente DHCP (DHCLIENT) no está presente.
Solución
Puede instalar el cliente DHCP mediante la utilidad Yum con el comando sudo yum install dhcp-client. Sin embargo, tenga en cuenta que los repositorios para CentOS Stream 8 ya no están disponibles.
1. Debe evitar configurar la dirección IP en el alojamiento de aplicaciones para permitir que DHCP funcione.
! interface AppGigabitEthernet1/0/1 switchport trunk allowed vlan 50 switchport mode trunk ! app-hosting appid guestshell app-vnic AppGigabitEthernet trunk vlan 50 guest-interface 0 name-server0 8.8.8.8 !
2. Cambie la lista espejo a baseurl vault en yum repo.
Switch#guestshell run bash
[guestshell@guestshell ~]$ sudo find /etc/yum.repos.d/ -type f -exec sed -i 's/mirrorlist=/#mirrorlist=/g' {} +
[guestshell@guestshell ~]$ sudo find /etc/yum.repos.d/ -type f -exec sed -i 's/#baseurl=/baseurl=/g' {} +
[guestshell@guestshell ~]$ sudo find /etc/yum.repos.d/ -type f -exec sed -i 's/mirror.centos.org//g' {} +
[guestshell@guestshell ~]$ cat /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Stream-RealTime.reporepo
# CentOS-Stream-RealTime.repo
# The mirrorlist system uses the connecting IP address of the client and the
# update status of each mirror to pick current mirrors that are geographically
# close to the client. You should use this for CentOS updates unless you are
# manually picking other mirrors.
#
# If the mirrorlist does not work for you, you can try the commented out
# baseurl line instead.
[rt]
name=CentOS Stream $releasever - RealTime
#mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$stream&arch=$basearch&repo=RT&infra=$infra
baseurl=http:///$contentdir/$stream/RT/$basearch/os/
gpgcheck=1
enabled=0
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-centosofficial
3. Instale los paquetes.
guestshell@guestshell ~]$ sudo yum install dhcp-client ast metadata expiration check: 0:50:34 ago on Wed Mar 12 17:44:46 2025. Dependencies resolved. ================================================================================ Package Architecture Version Repository Size ================================================================================ Installing: dhcp-client x86_64 12:4.3.6-50.el8 baseos 319 k Installing dependencies: bind-export-libs x86_64 32:9.11.36-13.el8 baseos 1.1 M dhcp-common noarch 12:4.3.6-50.el8 baseos 208 k dhcp-libs x86_64 12:4.3.6-50.el8 baseos 148 k Transaction Summary ================================================================================ Install 4 Packages Total download size: 1.8 M Installed size: 3.9 M Is this ok [y/N]: y Downloading Packages: (1/4): dhcp-client-4.3.6-50.el8.x86_64.rpm 284 kB/s | 319 kB 00:01 (2/4): dhcp-common-4.3.6-50.el8.noarch.rpm 171 kB/s | 208 kB 00:01 (3/4): dhcp-libs-4.3.6-50.el8.x86_64.rpm 572 kB/s | 148 kB 00:00 (4/4): bind-export-libs-9.11.36-13.el8.x86_64.r 577 kB/s | 1.1 MB 00:02 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total 908 kB/s | 1.8 MB 00:02 CentOS Stream 8 - BaseOS 1.6 MB/s | 1.6 kB 00:00 Importing GPG key 0x8483C65D: Userid : "CentOS (CentOS Official Signing Key) <CentOS Official Signing Key>" Fingerprint: 99DB 70FA E1D7 CE22 7FB6 4882 05B5 55B3 8483 C65D From : /etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-centosofficial Is this ok [y/N]: y Key imported successfully Running transaction check Transaction check succeeded. Running transaction test Transaction test succeeded. Running transaction Preparing : 1/1 Installing : dhcp-libs-12:4.3.6-50.el8.x86_64 1/4 Installing : dhcp-common-12:4.3.6-50.el8.noarch 2/4 Installing : bind-export-libs-32:9.11.36-13.el8.x86_64 3/4 Running scriptlet: bind-export-libs-32:9.11.36-13.el8.x86_64 3/4 Installing : dhcp-client-12:4.3.6-50.el8.x86_64 4/4 Running scriptlet: dhcp-client-12:4.3.6-50.el8.x86_64 4/4 Verifying : bind-export-libs-32:9.11.36-13.el8.x86_64 1/4 Verifying : dhcp-client-12:4.3.6-50.el8.x86_64 2/4 Verifying : dhcp-common-12:4.3.6-50.el8.noarch 3/4 Verifying : dhcp-libs-12:4.3.6-50.el8.x86_64 4/4 Installed: bind-export-libs-32:9.11.36-13.el8.x86_64 dhcp-client-12:4.3.6-50.el8.x86_64 dhcp-common-12:4.3.6-50.el8.noarch dhcp-libs-12:4.3.6-50.el8.x86_64 Complete!

Nota: (PARA CALO) Es posible configurar un proxy para Yum. Esto permite a Yum conectarse a través de un servidor proxy para descargas de paquetes:
[guestshell@guestshell ~]$ echo "proxy=http://<dirección_IP:puerto>/" | sudo tee -a /etc/yum.conf > /dev/null
4. .Solicite una dirección IP DHCP para eth0.
[guestshell@guestshell ~]$ sudo dhclient eth0
5. Compruebe si el cliente DHCP funciona comprobando la asignación de la dirección IP.
Switch#guestshell run ifconfig
eth0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.10.2 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.10.255
inet6 fe80::5054:ddff:fea0:4aef prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20
ether 52:54:dd:a0:4a:ef txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 1516 bytes 2009470 (1.9 MiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 687 bytes 54603 (53.3 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> mtu 65536
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10
loop txqueuelen 1000 (Local Loopback)
RX packets 773 bytes 90658 (88.5 KiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 773 bytes 90658 (88.5 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
Error al actualizar DNF Packet Manager
Problema: No se puede completar la actualización de sudo dnf -y en Guestshell debido al error:
[guestshell@guestshell ~]$ sudo dnf upgrade --refresh Warning: failed loading '/etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo', skipping.
Solución
1. Reinstale y actualice los paquetes RPM.
! Clean packages [guestshell@guestshell ~]$ sudo dnf clean all ! Reinstall and update the tpm2-tss package: [guestshell@guestshell ~]$ sudo dnf install tpm2-tss-2.3.2-3.el8 [guestshell@guestshell ~]$ sudo dnf upgrade rpm
2. Instale el paquete git por separado.
[guestshell@guestshell ~]$ sudo dnf install git -y
Acceso de invitado perdido después de la actualización
Problema: Después de la actualización a la versión 17.08.01 o superior, el shell de invitado se vuelve inaccesible, lo que provoca la incapacidad de ejecutar scripts.
Switch#guestshell run bash Switch#
Solución
El problema está relacionado con el ID de bug de Cisco CSCwi63075  , que se activa durante una actualización cuando FIPS está activado en el switch.
, que se activa durante una actualización cuando FIPS está activado en el switch.
1. Desactive FIPS.
Switch#configure terminal Switch(config)#no fips authorization-key FIPS: Authorization-key erased ONLY from the Flash. But the authorization-key is still operational. Use "reload" command for complete removal of key and to enter into non fips-mode. Make sure to remove fips key from all the members of the stack individually
2. Puede actualizar a una de las versiones que incluyen la corrección, la versión 17.12.04 o cualquier versión posterior.
Restringir el direccionamiento IPv6
Problema: El problema tiene que ver con direcciones IPv6 no deseadas que aparecen en las interfaces del entorno Cisco Guestshell. Aunque no se ha configurado intencionadamente.
La configuración observada en el switch con IPV4 es:
! app-hosting appid guestshell app-vnic AppGigabitEthernet trunk vlan 50 guest-interface 0 guest-ipaddress 192.168.20.10 netmask 255.255.255.0 <-- IPv4 address configured app-default-gateway 192.168.20.1 guest-interface 0 app-resource profile custom name-server1 192.168.20.1 !
Cuando se ejecuta el comando ifconfig en el entorno Guestshell, se hacen visibles las direcciones IPv4 e IPv6.
lat1-2-ssw01.gts#guestshell run bash
[guestshell@guestshell ~]$ sudo ifconfig
eth0: flags=4163 mtu 1500
inet 192.168.20.10 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.20.255
inet6 2620:119:5022:515:5054:ddff:fe41:c643 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x0
inet6 fe80::5054:ddff:fe41:c643 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20
ether 52:54:dd:41:c6:43 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 7829 bytes 1750981 (1.6 MiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 5551 bytes 744320 (726.8 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
lo: flags=73 mtu 65536
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10
loop txqueuelen 1000 (Local Loopback)
RX packets 292 bytes 63812 (62.3 KiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 292 bytes 63812 (62.3 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
Solución
Paso 1: Desactive el enrutamiento y el direccionamiento IPv6 en Guestshell.
lat1-2-ssw01.gts#guestshell run bash [guestshell@guestshell ~]$ sudo sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6=1 [guestshell@guestshell ~]$ sudo sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6=1 [guestshell@guestshell ~]$ sudo sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.lo.disable_ipv6=1
Paso 2: Compruebe que IPv6 está desactivado.
[guestshell@guestshell ~]$ /sbin/ifconfig
eth0: flags=4163 mtu 1500
inet 192.168.20.10 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.20.255
ether 52:54:dd:41:c6:43 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 7829 bytes 1750981 (1.6 MiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 5551 bytes 744320 (726.8 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
lo: flags=73 mtu 65536
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
loop txqueuelen 1000 (Local Loopback)
RX packets 292 bytes 63812 (62.3 KiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 292 bytes 63812 (62.3 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
Errores de espacio en disco al ejecutar scripts Python
Problema: El problema implica la ejecución de un script Python en Embedded Event Manager (EEM) dentro de Guestshell. La secuencia de comandos falla debido a que se está quedando sin espacio en disco con el error:
guestshell run python3 /flash/guest-share/monitoring.py -rt True -bgp True
---- pushing bgp status ----
OSError: [Errno 28] No space left on device
During handling of the above exception, another exception occurred:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/flash/guest-share/monitoring_periodic_tasks.py", line 18, in
print(bgp_status())
File "/bootflash/guest-share/monitoring_bgp_status.py", line 15, in bgp_status
vrf = cli.cli('show vrf')
File "/usr/lib/python3.6/site-packages/cli/__init__.py", line 311, in cli
_log_to_file("CLI execution invoked for '" + command + "'")
File "/usr/lib/python3.6/site-packages/cli/__init__.py", line 87, in _log_to_file
logfile.close()
OSError: [Errno 28] No space left on device
! This error indicates that the disk space allocated for logging command executions within the Guestshell environment has been exhausted.
Solución
Para resolver el problema de quedarse sin espacio en disco, debe aumentar el tamaño del disco persistente para el entorno Guestshell:
1. Modifique el perfil de recursos de aplicación para aumentar el tamaño del disco persistente.
Switch(config-app-hosting)# app-resource profile custom Switch(config-app-hosting-profile)# persist-disk 100 Switch(config-app-hosting-profile)# cpu 800 Switch(config-app-hosting-profile)# memory 256 Switch(config-app-hosting-profile)# end
2. Guarde la configuración y active/desactive el shell de invitado.
Switch# write memory Switch#guestshell disable Guestshell disabled successfully Switch#guestshell enable Interface will be selected if configured in app-hosting Please wait for completion guestshell installed successfully Current state is: DEPLOYED guestshell activated successfully Current state is: ACTIVATED guestshell started successfully Current state is: RUNNING Guestshell enabled successfully
Registro de Syslog
Puede ejecutar estos comandos en guestshell para mostrar los mensajes de syslog :
[guestshell@guestshell ~]$ sudo logger -p 1 "Priority 1" [guestshell@guestshell ~]$ sudo cat /var/log/messages Mar 11 02:05:24 localhost systemd[248]: user@0.service: Failed at step PAM spawning /usr/lib/systemd/systemd: Operation not permitted Mar 11 02:05:24 localhost systemd[1]: user@0.service: Failed with result 'protocol'. Mar 11 02:05:24 localhost systemd[1]: Failed to start User Manager for UID 0. Mar 11 02:05:24 localhost systemd[1]: Stopping /run/user/0 mount wrapper... Mar 11 02:05:24 localhost systemd[1]: run-user-0.mount: Succeeded. Mar 11 02:05:24 localhost systemd[1]: user-runtime-dir@0.service: Succeeded. Mar 11 02:05:24 localhost systemd[1]: Stopped /run/user/0 mount wrapper. Mar 11 02:05:24 localhost root[250]: Priority 1 [guestshell@guestshell ~]$ sudo cat /var/log/secure Mar 11 02:05:24 localhost systemd[248]: pam_unix(systemd-user:account): expired password for user root (root enforced) Mar 11 02:05:24 localhost sudo[246]: pam_systemd(sudo:session): Failed to create session: Start job for unit user@0.service failed with 'failed' Mar 11 02:05:24 localhost sudo[246]: pam_unix(sudo:session): session opened for user root by (uid=0)
Tracelog
Puede utilizar app-hosting move appid guestshell log to bootflash:folder_name para rotar el archivo. Se puede utilizar para rotar a un directorio de destino, pero también rota al directorio traceloguestshell.
Switch#app-hosting move appid guestshell log to bootflash: Successfully moved tracelog to flash:/ioxapploguestshell/iox_R0-0_R0-0.14195_0.20250311023831.bin.gz

Nota: IOX guestshell.log es siempre el archivo tracelog activo bajo /tmp/rp/trace · Cuando este archivo alcanza 1MB, se rota automáticamente a bootflash:traceloguestshell/ con una marca de tiempo, y se inicia uno nuevo.
Información Relacionada
- Informe técnico sobre el alojamiento de aplicaciones en switches Catalyst de Cisco serie 9000
- Guía de instalación de hardware de los switches Catalyst de Cisco serie 9300
- Guía de configuración de capacidad de programación, Cisco IOS XE 17.9.x
- Informe técnico de la arquitectura del sistema Catalyst 9300 StackWise
- ID de bug de Cisco CSCwi63075 - Guestshell no es accesible a través de CLI después de una actualización a 17.08.01 o posterior si el modo FIPS está habilitado
- Soporte Técnico y Documentación - Cisco Systems
Historial de revisiones
| Revisión | Fecha de publicación | Comentarios |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
17-Mar-2025
|
Versión inicial |
Con la colaboración de ingenieros de Cisco
- Christopher Martinez BarriosIngeniero de consultoría técnica
Contacte a Cisco
- Abrir un caso de soporte

- (Requiere un Cisco Service Contract)
 Comentarios
Comentarios