- Preface
- Overview
- Adding and Deleting Mobility Services Engines and Licenses
- Synchronizing Mobility Services Engines
- Configuring and Viewing System Properties
- Working with Maps
- Configuring wIPS and Profiles
- Monitoring the System and Services
- wIPS Policy Alarm Encyclopedia
- Rogue Management
- Configuring and Deploying wIPS Solution
- Index
Cisco Wireless Intrusion Prevention System Configuration Guide, Release 7.5
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- Updated:
- July 31, 2013
Chapter: Monitoring the System and Services
- Working with Alarms
- Working with Events
- Working with Logs
- Monitoring Access Points Details
- Generating Reports
Monitoring the System and Services
This chapter describes how to monitor the Mobility Services Engine by configuring and viewing alarms, events, and logs and how to generate reports on system use and element counts (tags, clients, rogue clients, interferers, and access points). This chapter also describes how to use the Prime Infrastructure to monitor clients (wired and wireless), tags, chokepoints, and Wi-Fi TDOA receivers.
This chapter contains the following sections:
- Working with Alarms
- Working with Events
- Working with Logs
- Monitoring Access Points Details
- Generating Reports
- Creating a Device Utilization Report
- Client Support on the MSE
- Monitoring Geo-Location
- Ekahau Site Survey Integration
- AirMagnet Survey and Planner Integration
- Interpreting Security Dashboard
Working with Alarms
This section describes how to view, assign, and clear alarms on a Mobility Services Engine using the Prime Infrastructure. It also describes how to define alarm notifications (all, critical, major, minor, warning) and how to e-mail those alarm notifications.
This section contains the following topics:
- Guidelines and Limitations
- Viewing Alarms
- wIPS Alarm Consolidation
- Monitoring Cisco Adaptive wIPS Alarm Details
- Assigning and Unassigning Alarms
- Deleting and Clearing Alarms
- E-mailing Alarm Notifications
Guidelines and Limitations
Once the severity is cleared, the alarm is deleted from the Prime Infrastructure after 30 days.
Viewing Alarms
To view Mobility Services Engine alarms, follow these steps:
| Step 1 | Choose Monitor > Alarms. | ||
| Step 2 | Click the Advanced Search link in the navigation bar. A configurable search dialog box for alarms appears. | ||
| Step 3 | Choose Alarms from the Search Category drop-down list. | ||
| Step 4 | Choose the severity of alarms from the Severity drop-down list. The options are All Severities, Critical, Major, Minor, Warning, or Clear. | ||
| Step 5 | Choose Mobility Service from the Alarm Category drop-down list. | ||
| Step 6 | Choose the Condition from the Condition combo box. Alternatively, you can enter the condition in the Condition text box. | ||
| Step 7 | From the Time Period
drop-down list, choose the time frame for which you want to review alarms.
The options range from minutes (5, 15, and 30) to hours (1 and 8) to days (1 and 7). To display all, choose Any time. | ||
| Step 8 | Select the Acknowledged State check box to exclude the acknowledged alarms and their count in the Alarm Summary page. | ||
| Step 9 | Select the Assigned State check box to exclude the assigned alarms and their count in the Alarm Summary page. | ||
| Step 10 | From the Items per page drop-down list, choose the number of alarms to display in each page. | ||
| Step 11 | To save the search criteria
for later use, select the
Save Search check box and
enter a name for the search.
| ||
| Step 12 | Click
Go. The alarms summary
dialog box appears with search results.
| ||
| Step 13 | Repeat Step 2 to Step 12 to see Context-Aware Service notifications for the Mobility Services Engine. Enter Context Aware Notifications as the alarm category in Step 5. |
wIPS Alarm Consolidation
The wIPS alarm consolidation feature is introduced in Release 7.5. The wIPS alarm consolidation aggregates different wireless intrusion incidents reported by access points and provides a concise meaningful alarm. This helps you to quickly separate the potential security issues and concerns. Alarm consolidation is performed at wIPS services module in the MSE. After the consolidation rule is triggered in MSE, the MSE notifies the Prime Infrastructure by sending an SNMP trap.
The following three attack consolidation categories are created:
- Beacon flood—The system detects a number of out of sequence beacon frames sent from a device. By sending fake beacon frames, the hacker can advertise false access point configuration and settings such as supported data rate, SSID, and channel information. The following alarms are included in this alarm consolidation category:
- De-auth flood—This is a type of denial-of-service attack. The traffic pattern matches with the denial-of-service attack that uses spoofed de-authentication frames to break the association between an access point and its client stations. The following alarms are included in this alarm consolidation category:
- MDK3-Destruction attack—This causes all clients that is associated or trying to associate with the AP to fail. The following alarms are included in this consolidation category:
Monitoring Cisco Adaptive wIPS Alarm Details
-
General
Properties—The general information might vary depending on the type of alarm.
For example, some alarm details might include location and switch port tracing
information. The following table describes the general parameters associated
with the MSE Alarm and wIPS Traps condition.
- Detected By wIPS AP—The access point that detected the alarm.
- wIPS AP IP Address—The IP address of the wIPS access point.
- Owner—Name of person to which this alarm is assigned or left blank.
- Acknowledged—Displays whether or not the alarm is acknowledged by the user.
- Category—For wIPS, the alarm category is Security.
- Created—Month, day, year, hour, minute, second, AM or PM that the alarm was created.
- Modified—Month, day, year, hout, minute, second, AM or PM that the alarm was last modified.
- Generated By—Indicates how the alarm event was generated (either NMS or from a trap). NMS (Network Management System - Prime Infrastructure—Generated through polling. Prime Infrastructure periodically polls the controllers and generates events. Prime Infrastructure generates events when the traps are disabled or when the traps are lost for those events. in this case, "Generated by" NMS. Trap—Generated by the controller. Prime Infrastructure process these traps and raises corresponding events for them. In this case, "Generated by" is controller.
- Severity—Level of severity including critical, major, minor, warning, and clear.
- Last Disappeared—The date and time that the potential attack last disappeared.
- Channel—The channel on which the potential attack occurred.
- Attacker Client/AP MAC—The MAC address of the client or access point that initiated the attack.
- Attacker Client/AP IP Address—The IP address of the client or access point that initiated the attack.
- Target Client/AP IP Address—The IP address of the client or access point targeted by the attacker.
- Controller IP Address—The IP address of the controller to which the access point is associated.
- MSE—The IP address of the associated Mobility Services Engine.
- Controller MAC address—The MAC address of the controller to which the access point is associated.
- wIPS access point MAC address
- Forensic File
- Event History—Takes you to the Monitoring Alarms page to view all events for this alarm.
- Annotations—Enter any new notes in this text box and click Add to update the alarm. Notes appear in the "Annotations" display area.
- Messages—Displays the alarm name.
- Description—Displays the consolidated information about the alarm.
- Mitigation Status—Displays what mitigation action was initiated against the attack.
-
Audit
Report—Click to view config audit alarm details. This report is only available
for Config Audit alarms.
Configuration
audit alarms are generated when audit discrepancies are enforced on config
groups.

Note
If enforcement fails, a critical alarm is generated on the config group. If enforcement succeeds, a minor alarm is generated on the config group. The alarms have links to the audit report where you can view a list of discrepancies for each controller.
- Event History—Opens the MSE Alarm Events page to view events for this alarm. When there are multiple alarm pages, the page numbers appear at the top of the page with a scroll arrow on each side. Use these scroll arrows to view additional alarms.
- Rogue Clients—If the failure object is a rogue access point, information about rogue clients is displayed.
- Map Location—Displays the map location for the alarm.
- Related Alarm List—Lists all the alarms related to a particular attack. This shows what consolidation rule was used to consolidate the alarms.
Assigning and Unassigning Alarms
Deleting and Clearing Alarms
If you delete an alarm, the Prime Infrastructure removes it from its database. If you clear an alarm, it remains in the Prime Infrastructure database, but in the Clear state. You should clear an alarm when the condition that caused it no longer exists.
To delete or clear an alarm from a Mobility Services Engine, follow these steps:
E-mailing Alarm Notifications
The Prime Infrastructure lets you send alarm notifications to a specific e-mail address. Sending notifications through e-mail enables you to take prompt action when needed.
You can choose the alarm severity types (critical, major, minor, and warning) to have e-mailed to you.
| Step 1 | Choose Monitor > Alarms. | ||
| Step 2 |
From the Select a command
drop-down list, choose
Email Notification. Click
Go. The Email
Notification page appears.
| ||
| Step 3 | Select the
Enabled check box next to
the Mobility Service.
| ||
| Step 4 | Click the Mobility Service link. The page for configuring the alarm severity types that are reported for the Mobility Services Engine appears. | ||
| Step 5 | Select the check box next to all the alarm severity types for which you want e-mail notifications sent. | ||
| Step 6 | In the To text box, enter the e-mail address or addresses to which you want the e-mail notifications sent. Separate e-mail addresses by commas. | ||
| Step 7 | Click
Save.
You are returned to the Alarms > Notification page. The changes to the reported alarm severity levels and the recipient e-mail address for e-mail notifications are displayed. |
Working with Events
You can use Prime Infrastructure to view the Mobility Services Engine and location notification events. You can search and display events based on their severity (critical, major, minor, warning, clear, and info) and their category.
This section contains Displaying location notification events procedure.
Displaying Location Notification Events
To display location notification events, follow these steps:
| Step 1 | Choose Monitor > Events. | ||
| Step 2 | In the Events page, you can perform the following:
| ||
| Step 3 | If Prime Infrastructure finds events that match the search criteria, it shows a list of these events.
|
Working with Logs
This section describes how to configure logging options and how to download log files.
This section contains the following topics:
Guidelines and Limitations
Configuring Logging Options
You can use Prime Infrastructure to specify the logging level and types of messages to log.
| Step 1 | Choose Services > Mobility Services. | ||
| Step 2 | Click the name of the Mobility Services Engine that you want to configure. | ||
| Step 3 | From the System menu, choose Logs. The logging options for the selected Mobility Services Engine appear. | ||
| Step 4 | Choose the appropriate
options from the Logging Level drop-down list.
There are four logging options: Off, Error, Information, and Trace. All log records with a log level of Error or above are logged to a new error log file locserver-error-%u-%g.log. This is an additional log file maintained along with the location server locserver-%u-%g.log log file. The error log file consists of logs of Error level along with their context information. The contextual information consists of 25 log records prior to the error. You can maintain up to 10 error log files. The maximum size allowed for each log file is 10 MB.
| ||
| Step 5 | Select the Enabled check box next to each element listed in that section to begin logging of its events. | ||
| Step 6 | Select the
Enable check box under
Advanced Parameters to enable advanced debugging. By default, this option is
disabled.
| ||
| Step 7 | To download log files from the server, click Download Logs. For more information, see the Downloading Log Files, page 10-9. | ||
| Step 8 | In the Log File group box, enter the following: | ||
| Step 9 | In the MAC Address Based
Logging page, do the following:
| ||
| Step 10 | Click Save to apply your changes. |
MAC address-based Logging
This feature allows you to create log files that are specific to an entity whose MAC address is specified. The log files are created in the locserver directory under the following path:
/opt/mse/logs/locserver
A maximum of 5 MAC addresses can be logged at a time. The log file format for MAC address aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff is:
macaddress-debug-aa-bb-cc-dd-ee-ff.log
You can create a maximum of two log files for a MAC address. The two log files may consist of one main and one back up or rollover log file.
The minimum size of a MAC log file is 10 MB. The maximum size allowed is 20 MB per MAC address. The MAC log files which are not updated for more than 24 hours are pruned.
Downloading Log Files
If you need to analyze Mobility Services Engine log files, you can use Prime Infrastructure to download them to your system. The Prime Infrastructure downloads a .zip file containing the log files.
To download a .zip file containing the log files, follow these steps:
| Step 1 | Choose Services > Mobility Services. |
| Step 2 | Click the name of the Mobility Services Engine to view its status. |
| Step 3 | From the left sidebar menu, choose Logs. |
| Step 4 | Click Download Logs. |
| Step 5 | Follow the instructions in the File Download dialog box to view the file or save the .zip file to your system. |
Monitoring Access Points Details
The Access Points Details page enables you to view access point information for a single AP.
Choose Monitor > Access Points and click an item in the AP Name column to access this page. Depending on the type of access point, the following tabs might be displayed. This section provides the detailed information regarding each Access Points Details page tab and contains the following topics:
- General Tab
- Interfaces Tab
- CDP Neighbors Tab
- Current Associated Clients Tab
- SSID Tab
- Clients Over Time Tab
General Tab
 Note | The General tab fields differ between lightweight and autonomous access points. |
General—Lightweight Access Points
Table 5-47 lists the General (for Lightweight Access Points) Tab fields.
AP IP address, Ethernet MAC address, and Base Radio MAC address |
|||||
The codes of the supported countries. Up to 20 countries can be supported per controller.
|
|||||
You can configure link latency on the controller to measure the link between an access point and the controller. See the Configuring Link Latency Settings for Access Points for more information.
|
|||||
Displays how long the LWAPP/CAPWAP connection has been active. |
|||||
Displays how long the LWAPP/CAPWAP connection has been joined. |
|||||
The administration state of the access point as either enabled or disabled. |
|||||
Default mode. Data clients are serviced while configured channels are scanned for noise and rogues. The access point goes off-channel for 50 ms and listens for rogues. It cycles through each channel for the period specified under the Auto RF configuration.
|
|||||
Radio receive only mode. The access point scans all configured channels every 12 seconds. Only deauthenticated packets are sent in the air with an access point configured this way. A monitor mode access point can connect as a client to a rogue access point.
|
|||||
The access point radio is turned off and the access point listens to wired traffic only. The controllers that operate in this mode monitor the rogue access points. The controller sends all the rogue access point and client MAC address lists to the rogue detector, and the rogue detector forwards this information to the WLC. The MAC address list is compared to what the WLC access points heard over the network. If the MAC addresses match, you can determine which rogue access points are connected on the wired network. |
|||||
The access point captures and forwards all the packets on a particular channel to a remote machine that runs AiroPeek. These packets contain information such as timestamp, signal strength, packet size, and so on. This feature can only be enabled if you run AiroPeek, which is a third-party network analyzer software that supports the decoding of data packets. |
|||||
Enables FlexConnect for up to six access points. The FlexConnect access points can switch client data traffic locally and perform client authentication locally when their connection to the controller is lost.
|
|||||
This is a special mode where an autonomous access point functions as a wireless client and connects to a lightweight access point. The bridge and its wired clients are listed as client in the Prime Infrastructure if the AP mode is set to Bridge, and the access point is bridge capable. |
|||||
This mode allows a CleanAir-enabled access point to be used extensively for interference detection on all monitored channels. All other functions such as IDS scanning and Wi-Fi are suspended. |
|||||
Enabled or Disabled, to enable the monitoring of the security attacks using Cisco Adaptive wIPS feature. |
|||||
Registered or Not Registered, as determined by the controller. |
|||||
The controller to which the access point is registered. Click to display the registered controller details. See the “Monitoring System Summary” section on page 5-4 for more information. |
|||||
The SNMP name of the access point primary controller. The access point attempts to associate with this controller first for all network operations and in the event of a hardware reset. |
|||||
Displays how long the access point has been active to receive and transmit. |
|||||
Customer-definable location name for the access point. Click to look at the actual location on a map. Choose Monitor > Access Points > name > Map Location for more information. |
|||||
The physical location where the access point is placed (or Unassigned). |
|||||
This counter sets the time in seconds that the access point sends its DOT11 statistics to the controller. |
|||||
The power over ethernet status of the access point. The possible values include the following:
|
|||||
Indicates whether or not Rogue Detection is enabled.
|
|||||
Indicates whether or not the access point is enabled as an OfficeExtend access point. The default is Enabled. |
|||||
Indicates whether or not encryption is enabled.
|
|||||
The access point switches from a priority order search (primary, secondary, and then tertiary controller) to a search for the controller with the best latency measurement (least latency). The controller with the least latency provides the best performance. |
|||||
Indicates whether or not SSH is enabled.
|
|||||
The operating system release.version.dot.maintenance number of the code currently running on the controller. |
|||||
Click the user-assigned profile name to view wIPS profile details. |
|||||
Serial Number |
Unique product serial number. |
||||
Run Ping Test Link— Click to ping the access point. The results are displayed in a pop-up dialog box. The below are the parameters associated: |
|||||
Alarms Link— Click to display alarms associated with this access point. |
|||||
Events Link— Click to display events associated with this access point. |
|||||
General—Autonomous
 Note | For autonomous clients, the Prime Infrastructure only collects client counts. The client counts in the Monitor page and reports have autonomous clients included. Client search, client traffic graphs, or other client reports (such as Unique Clients, Busiest Clients, Client Association) do not include clients from autonomous access points. |
Table 5-48 lists the General (for Autonomous Access Points) tab fields.
Indicates how long the access point has been up in number of days, hours, minutes, and seconds. |
|
Customer-definable location name for the access point. Click to look at the actual location on a map. |
|
Indicates whether or not the access point is in work group bridge mode. |
|
|
The system device type and current version of firmware. The physical location of the device, such as a building name or room in which it is installed. The name of the system administrator responsible for the device. |
|
The operating system release.version.dot.maintenance number of the code currently running on the controller. |
|
Displays the maximum, average, and minimum CPU utilization over the specified amount of time. |
|
Displays the maximum, average, and minimum memory utilization over the specified amount of time. |
|
 Note | Memory and CPU utilization charts are displayed. |
 Note | Click Alarms to display the alarms associated with the access point. Click Events to display events associated with the access point. |
Interfaces Tab
Table 5-49 lists the Interfaces tab fields.
Indicates the channel on which the Cisco Radio is broadcasting. |
|
Indicates the secondary channel on which Cisco radio is broadcasting. |
|
Access Point transmit power level: 1 = Maximum power allowed per Country Code setting, 2 = 50% power, 3 = 25% power, 4 = 6.25 to 12.5% power, and 5 = 0.195 to 6.25% power. |
|
Indicates the channel bandwidth for this radio interface. See the Configuring 802.11a/n RRM Dynamic Channel Allocation for more information on configuring channel bandwidth. Minimum (default) setting is 20 MHz. Maximum setting is the maximum channel width supported by this radio. |
|
Click an interface name to view its properties (see Table 5-50).
Indicates the total number of bytes in the error-free packets received on the interface. |
|
Indicates the total number of unicast packets received on the interface. |
|
Indicates the total number of non-unicast or mulitcast packets received on the interface. |
|
Indicates the total number of CRC error in packets received on the interface. |
|
Indicates the sum of all errors in the packets while receiving on the interface. |
|
Indicates the number of times the receiver hardware was incapable of handing received data to a hardware buffer because the input rate exceeded the receiver capability to handle the data. |
|
Indicates the total number of resource errors in packets received on the interface. |
|
Indicates the number of packets that are discarded because they are smaller than the medium minimum packet size. |
|
Indicates the total number of times the interface advised a sending NIC that it was overwhelmed by packets being sent and to slow the pace of delivery. |
|
Indicates the total number of packet retransmitted due to an Ethernet collision. |
|
Indicates the total number of resource errors in packets transmitted on the interface. |
|
Indicates the sum of all errors that prevented the final transmission of packets out of the interface. |
|
Indicates the operational state of the physical Ethernet interface on the AP. |
|
Indicates the total number of bytes in the error-free packets transmitted on the interface. |
|
Indicates the total number of unicast packets transmitted on the interface. |
|
Indicates the total number of non-unicast or mulitcast packets transmitted on the interface. |
|
Indicates the total number of packet aborted while receiving on the interface. |
|
Indicates the total number of packet received incorrectly having a CRC error and a non-integer number of octets on the interface. |
|
Indicates the total number of packets dropped while receiving on the interface because the queue was full. |
|
Indicates the total number of packet discarded on the interface due to an unknown protocol. |
|
Indicates the number of packets that are discarded because they exceed the maximum packet size of the medium. |
|
Indicates the number of times that an interface has been completely reset. |
|
Indicates the total number of packets discarded because there was no buffer space. |
|
Indicates the number of times the transmitter has been running faster than the router can handle. |
|
Indicates the total number of packets dropped while transmitting from the interface because the queue was full. |
CDP Neighbors Tab
Table 5-51 lists the CDP Neighbors tab fields.
 Note | This tab is visible only when the CDP is enabled. |
Current Associated Clients Tab
Table 5-52 lists the Current Associated Clients tab fields.
 Note | This tab is visible only when there are clients associated to the AP (CAPWAP or Autonomous AP). |
Click the username to view the Monitor Client Details page for this client. See the Monitoring Clients and Users for more information. |
|
Click the client MAC address to view the Monitor Client Details page for this client. |
|
This indicates the total amount of data that has passed through the Ethernet interface either way. |
|
This indicate the total amount of data that has been received through the Ethernet interface either way |
|
When the access point is not associated with the controller, then the database is used to retrieve the data (rather than the controller itself). If the access point is not associated, the following fields appear. |
|
 Note | Click the Edit View link to add, remove or reorder columns in the Current Associated Clients table. See the “Configuring the List of Access Points Display” section on page 5-47 for adding a new field using the Edit View. |
SSID Tab
Table 5-53 lists the SSID tab fields.
 Note | This tab is visible only when the access point is Autonomous AP and there are SSIDs configured on the AP. |
Service Set Identifier being broadcast by the access point radio. |
|
SSID on an access point is configured to recognize a specific VLAN ID or name. |
|
SSID on an access point is configured to recognize a specific VLAN ID or name. |
|
SSID broadcast disabled essentially makes your Access Point invisible unless a wireless client already knows the SSID, or is using tools that monitor or 'sniff' traffic from an AP's associated clients. |
|
Within this specified time period, internal communication within the SSID continues to work. |
Clients Over Time Tab
 Note | The information that appears in the above charts is presented in a time-based graph. For graphs that are time-based, there is a link bar at the top of the graph page that displays 6h, 1d, 1w, 2w, 4w, 3m, 6m, 1y, and Custom. When selected, the data for that time frame is retrieved and the corresponding graph is displayed. See the “Time-Based Graphs” section on page 6-71 for more information. |
Generating Reports
In the Prime Infrastructure, you can generate various kinds of reports. This section explains how to generate Context Aware reports using the Prime Infrastructure Report Launch Pad. By default, reports are stored on the Prime Infrastructure server.
Once you define the report criteria, you can save the reports for future diagnostic use and run them on either an ad hoc or scheduled basis.
You can define the following criteria for the reports:
Report Launch Pad
The report launch pad provides access to all the Prime Infrastructure reports from a single page. In this page, you can view current reports, open specific types of reports, create and save new reports, and manage scheduled runs. You can access the ContextAware reports section in the Report Launch Pad to generate ContextAware reports.
 Tip | Hover your mouse cursor over the tool tip next to the report type to view more report details. |
This section contains the following topics:
- Creating and Running a New Report
- Managing Current Reports
- Managing Scheduled Run Results
- Managing Saved Reports
Creating and Running a New Report
To create and run a new report, follow these steps:
| Step 1 | Choose
Reports
>
Report Launch
Pad.
The reports are listed by category in the main section of the page and on the left sidebar menu. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Step 2 | Find the
appropriate report in the main section of the Report Launch Pad.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Step 3 | Click New. The Report Details page appears. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Step 4 | In the Report
Details page, enter the following Settings parameters:
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Step 5 | If you plan to
run this report at a later time or as a recurring report, enter the Schedule
parameters. The Schedule parameters allow you to control when and how often the
report runs.
The Create Custom Report page allows you to customize the report results. The following table specifies which reports are customizable, which have multiple sub-reports, and which report views are available. In future releases, all reports are customizable.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Step 6 | Click
Customize
to open a separate Create Custom Report page.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Step 7 | When all
report parameters have been set, choose one of the following:
|
Managing Current Reports
If a report has been saved for a specific report type, you can access the current reports from the Report Launch Pad.
When a new chokepoint is created, it is available in all the virtual domains. After placing it on a floor, it is updated so that it is available in the same virtual domain as that of a floor. When a chokepoint is removed from a floor, it will be available in all the virtual domains again.
To access current or saved reports from the Report Launch Pad, follow these steps:
| Step 1 | Choose Reports > Report Launch Pad |
| Step 2 | Choose the specific report from the left sidebar menu or from the main section of the Report Launch Pad. The Report Launch Pad page displays a list of current reports for this report type. To view a list of saved reports, choose Reports > Saved Reports. |
Managing Scheduled Run Results
 Note | The list of scheduled runs can be sorted by report category, report type, and time frame. |
Managing Saved Reports
In the Saved Reports page, you can create and manage saved reports. To open this page in the Prime Infrastructure, choose Reports > Saved Reports.
 Note | The list of saved reports can be sorted by report category, report type, and scheduled status (enabled, disabled, or expired). |
The Saved Reports page shows the following information:
- Report Title—Identifies the user-assigned report name. Click the report title to view the details for this report.
- Report Type—Identifies the specific report type.
- Scheduled—Indicates whether this report is enabled or disabled.
- Next Schedule On—Indicates the date and time of the next scheduled run for this report.
- Last Run—Indicates the date and time of the most recent scheduled run for this report.
- Download—Click the Download icon to open or save a .csv file of the report results.
- Run Now—Click the Run Now icon to immediately run the current report.
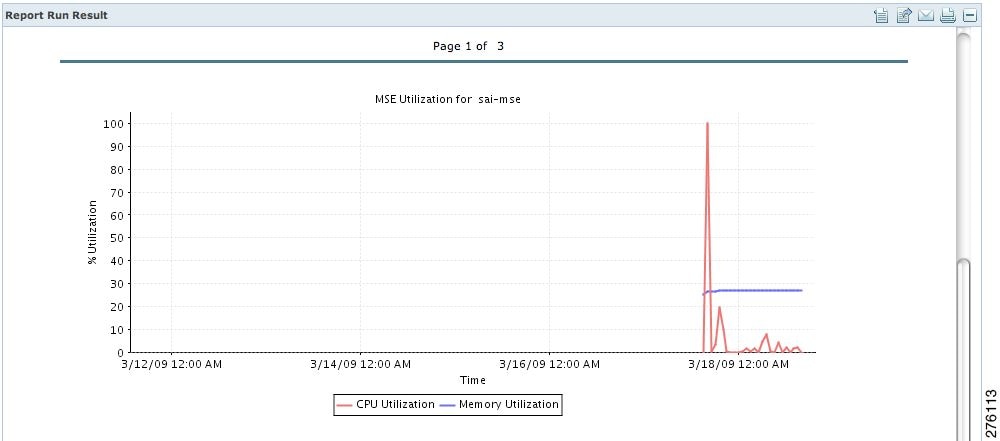
Creating a Device Utilization Report
To create a device utilization report for the Mobility Services Engine, follow these steps:
| Step 1 | Choose Reports > Report Launch Pad. | ||||
| Step 2 | Choose Device > Utilization. | ||||
| Step 3 | Click New. The Utilization Report Details page appears. | ||||
| Step 4 | In the Reports Details page,
enter the following Settings parameters:
| ||||
| Step 5 | In the Schedule group box, select the Enable Schedule check box. | ||||
| Step 6 | Choose the report format (CSV or PDF) from the Export Report drop-down list. | ||||
| Step 7 | Select either
File or
Email
as the destination of the report.
| ||||
| Step 8 | Enter a start date (MM:DD:YYYY), or click the Calendar icon to select a date. | ||||
| Step 9 | Specify a start time using the hour and minute drop-down lists. | ||||
| Step 10 | Select the
Recurrence radio button to determine how often you want to
run the report. The possible values follow:
| ||||
| Step 11 | When finished
with
Step 1 to
Step 10, do one of
the following:
If the report is scheduled, it is shown as enabled and the next scheduled run date is noted. If the report has run and is not scheduled to run again, it is shown as expired. If the report has run and is scheduled to run again, it is shown as disabled. | ||||
| Step 12 | To enable, disable, or delete a report, select the check box next to the report title, and click the appropriate option. |
Viewing Saved Utilization Reports
Viewing Scheduled Utilization Runs
To review the status for a scheduled report, follow these steps:
Client Support on the MSE
You can use the Prime Infrastructure Advanced Search feature to narrow the client list based on specific categories and filters. You can also filter the current list using the Show drop-down list.
- Searching a Wireless Client from the Prime Infrastructure on the MSE by IPv6 Address
- Viewing the Clients Detected by the MSE
Searching a Wireless Client from the Prime Infrastructure on the MSE by IPv6 Address
To search for an MSE-located client using the Prime Infrastructure Advanced Search feature, follow these steps:
| Step 1 | Click Advanced Search located in the top right corner of the Prime Infrastructure UI. | ||
| Step 2 | In the New Search dialog, choose Clients as the search category from the Search Category drop-down list. | ||
| Step 3 | From the Media Type drop-down list, choose Wireless Clients.
| ||
| Step 4 | From the Wireless Type drop-down list, choose any of the following types: All, Lightweight, or Autonomous Clients. | ||
| Step 5 | From the Search By drop-down list, choose IP Address.
| ||
| Step 6 | From the Clients Detected By drop-down list, choose clients detected by MSE. This shows clients located by Context-Aware Service in the MSE by directly communicating with the controllers. | ||
| Step 7 | From the Last detected within drop-down list, choose the time within which the client was detected. | ||
| Step 8 | Enter the client IP address in the Client IP Address text box. You can enter wither a partial or full IPv6 address.
| ||
| Step 9 | From the Client States drop-down list, choose the client states. The possible values for wireless clients are All States, Idle, Authenticated, Associated, Probing, or Excused. The possible values for wired clients are All States, Authenticated, and Associated. | ||
| Step 10 | From the Posture Status drop-down list, choose the posture status to know if the devices are clean or not. The possible values are All, unknown, Passed, and Failed. | ||
| Step 11 | Select the CCX Compatible check box to search for clients that are compatible with Cisco Client Extensions. The possible values are All Versions, V1, V2, V3, V4, V5, and V6. | ||
| Step 12 | Select the E2E Compatible check box to search for clients that are End to End compatible. The possible values are All Versions, V1, and V2. | ||
| Step 13 | Select the NAC State check box to search for clients identified by a certain Network Admission Control (NAC) state. The possible values are Quarantine, Access, Invalid, and Not Applicable. | ||
| Step 14 | Select the Include Disassociated check box to include clients that are no longer on the network but for which Prime Infrastructure has historical records. | ||
| Step 15 | From the Items per page drop-down list, choose the number of records to be displayed in the search results page. | ||
| Step 16 | Select the Save Search check box to save the selected search option. | ||
| Step 17 | Click Go. The Clients and Users page appears with all the clients detected by the MSE. |
Viewing the Clients Detected by the MSE
To view all the clients detected by MSE, follow these steps:
| Step 1 | Choose Monitor > Clients and Users to view both wired and wireless clients information. The Client and Users page appears. The Clients and Users table shows a few column by default. If you want to display the additional columns that are available, click | ||||||||
| Step 2 | Filter the current list to choose all the clients that are detected by MSE by choosing Clients detected by MSE from the Show drop-down list. All the clients detected by MSE including wired and wireless appear. All the clients detected by MSE including wired and wireless appear. The following different parameters are available in the Clients Detected by MSE table:
When you choose a client from the Clients and Users list, the following client details are displayed. Clients are identified using the MAC address.
The Statistics group box contains the following information for the selected client:
This information is presented in interactive graphs. Client IPV6 Addresses The Client IPv6 Address group box contains the following information for the selected client:
The Events group box in the Client Details page displays all events for this client including the event type as well as the date and time of the event: Click View Location History to view the location history details of wired and wireless clients. The following location history information is displayed for a wired or wireless client: |
Monitoring Geo-Location
The MSE provides physical location of wired clients, wired endpoints, switches, controllers, and access points present in a wireless network deployment. Currently, MSE provides location information in geo-location format to the external entities through northbound and southbound entities.
To improve the accuracy of the geo-location information provided by MSE, this feature aims to transform the geometric location co-ordinates of a device to geo-location coordinates (latitude and longitude) and provides it to the external entities through northbound and southbound interfaces.
 Note | At least three GPS markers are required for geo-location calculation. The maximum number of GPS markers that you can add is 20. |
This section contains the following topics:
Adding a GPS Marker to a Floor Map
To add a GPS marker to a floor map, follow these steps:
| Step 1 | Choose Monitor > Site Maps to display the Maps page. | ||
| Step 2 | Choose Campus Name > Building Name > Floor Name. | ||
| Step 3 | Choose the Add/Edit GPS Markers Information menu option on the top left menu to open the Add/Edit GPS page. A GPS Marker icon appears on the top left corner of the map (X=0 Y=0). | ||
| Step 4 | You can drag the GPS Marker icon and place it in the desired location on the map or enter the X and Y position values in the GPS Marker Details table on the left sidebar menu to move the marker to the desired position.
| ||
| Step 5 | Enter the Latitude and Longitude degrees for the selected GPS Marker icon in the left sidebar menu. | ||
| Step 6 | Click Save. The GPS Marker information is saved to the database. | ||
| Step 7 | Click Apply to other Floors of Building to copy GPS markers on one floor of a building to all the remaining floors of that building. |
Editing a GPS Marker
To edit a GPS marker present on the floor, follow these steps:
| Step 1 | Choose Monitor > Site Maps to display the Maps page. |
| Step 2 | Choose Campus Name > Building Name > Floor Name. |
| Step 3 | Choose the Add/Edit GPS Markers Information menu option to open the Add/Edit GPS page. |
| Step 4 | Select an existing GPS Marker which is present on the floor from the left sidebar menu. |
| Step 5 | From the left sidebar menu, you can change the Latitude, Longitude, X Position, and Y Position which is associated with the GPS marker. |
| Step 6 | Click Save. The modified GPS marker information is now saved to the database. |
Deleting a GPS Marker From the Floor
To delete a GPS marker from the floor, follow these steps:
| Step 1 | Choose Monitor > Site Maps to display the Maps page. | ||
| Step 2 | Choose Campus Name > Building Name > Floor Name. | ||
| Step 3 | Choose the Add/Edit GPS Markers Information menu option to open the Add/Edit GPS page. | ||
| Step 4 | Select an existing GPS marker that is present on the floor from the left sidebar menu.
| ||
| Step 5 | Click Delete GPS Marker. The selected GPS marker is deleted from the database. |
Ekahau Site Survey Integration
Ekahau Site Survey (ESS) tool is used for designing, deploying, maintaining, and troubleshooting high performance Wi-Fi networks. ESS works over any 802.11 network and is optimized for centrally managed 802.11n Wi-Fi networks.
You can use the ESS tool to import the existing floor maps from the Prime Infrastructure and export the project to the Prime Infrastructure. For more information, see the Cisco Prime Infrastructure Integration section in the ESS online help.
 Note | The Prime Infrastructure site survey calibration requires that you have collected at least 150 survey data points at 50 distinct locations. If you do not have enough survey data points, a warning is given when trying to export the survey data. |
 Note | If there are no access points in the Prime Infrastructure during the site survey, the site survey will not happen. |
 Note | If the floor map scales are incorrect in the Prime Infrastructure, the visualizations in the ESS will be distorted. |
AirMagnet Survey and Planner Integration
AirMagnet survey and AirMagnet planner is integrated with the Cisco Prime Infrastructure. This integration increases the operational efficiencies by eliminating the need to repeat the wireless planning and site survey tasks commonly associated with deployment and management of wireless LAN networks.
The AirMagnet survey tool allows you to export real world survey data to the Prime Infrastructure for calibrating planner modeling. With the AirMagnet planner, you can create and export planner projects directly to the Prime Infrastructure. This enables the Prime Infrastructure to create its own project directly from the imported AirMagnet Planner tool. For more information, see the AirMagnet Survey and Planning documentation which is available at Fluke Networks website.
Interpreting Security Dashboard
The Prime Infrastructure Security Dashboard have the following features added to it:
All the above features falls under the Client Classification table on the security dashboard. Hyperlinks are provided for the counts of Rogue APs. By clicking on the hyperlinks provided in the table, you will be able to view the details of Soft AP, GGGB and Valid Client on Rogue.
Viewing the Rogue APs
To view the Rogue Access Points (APs), perform the following steps:
1. Click the Valid Client connected to Rogue AP number to view the clients who were previously associated with the enterprise network but are now associated with Rogue APs.
2. This page displays the following items:
3. Click the Soft AP number to view the clients who were previously probing but are now rogue APs.
4. This page displays the following items:
5. Click the Good Guy Gone Bad number to view the clients who were previously associated but are now Rogue APs.
6. This page displays the following items:
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | Click the Valid Client connected to Rogue AP number to view the clients who were previously associated with the enterprise network but are now associated with Rogue APs. | |
| Step 2 | This page displays the following items: |
|
| Step 3 | Click the Soft AP number to view the clients who were previously probing but are now rogue APs. | |
| Step 4 | This page displays the following items: |
|
| Step 5 | Click the Good Guy Gone Bad number to view the clients who were previously associated but are now Rogue APs. | |
| Step 6 | This page displays the following items: |
Client Classification
There are three clients:
Valid Client Connected to Rogue AP: When a client associates with rogue AP, MSE will check whether the client is a valid client. For valid clients, an entry is added to the Rogue AP table with the MAC addresses of both the devices. Depending on the containment action taken, containment fields are updated. The following scenarios needs to be considered:
- Client associates and then disappears
- Client dissociation information is available
- Incomplete Containment
Soft AP: A Soft Access Point (Soft AP) is set-up on a Wi-Fi adapter without the need of a physical Wi-Fi router. It is easy to set-up a Soft AP on the Windows 7 or Windows Vista Machine with Windows 7 virtual Wi-Fi capabilities. Once up and running, it is easy to share the network access available on a machine to other Wi-Fi users that will connect to the Soft AP. If an employee sets up a soft Access Point on his machine inside the corporate premises, and share the corporate network through it, then this soft AP behaves as Rogue AP. You can also turn on Wi-Fi tethering on your smartphone and act as a rogue AP. MSE detects this scenario of soft rogue AP and sends response to Controller for auto containment.
Good Guy Gone Bad: When a valid client turns into a Soft AP, it is a greater threat which need s immediate action. MSE detect s these scenarios and report s a good guy gone bad.
 Feedback
Feedback