Managed Objects (MO) are abstractions
of Cisco UCS domain resources, such as fabric interconnects, chassis, blades,
and rack-mounted servers. Managed Objects represent any physical or logical
entity that is configured / managed in the Cisco UCS MIT. For example, physical
entities such as Servers, Chassis, I/O cards, Processors and logical entities
such as resource pools, user roles, service profiles, and policies are
represented as managed objects.
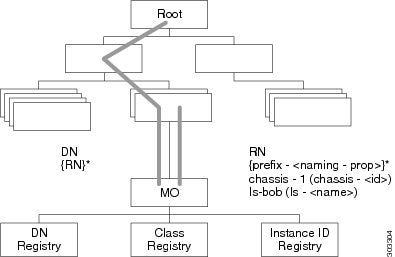
Every managed object is uniquely identified in the tree with its
Distinguished Name (Dn) and can be uniquely identified within the context of
its parent with its Relative Name (Rn). The Dn identifies the place of the MO
in the MIT. A Dn is a concatenation of all the relative names starting from the
root to the MO itself. Essentially, Dn = [Rn]/[Rn]/[Rn]/.../[Rn].
In the example below, Dn provides a fully qualified name for adaptor-1
in the model.
< dn = “sys/chassis-5/blade-2/adaptor-1” />
The above written Dn is composed of the following Rn:
topSystem MO: rn="sys" equipmentChassis MO: rn="chassis-<id>"
computeBlade MO: rn ="blade-<slotId>" adaptorUnit MO:
rn="adaptor-<id>"
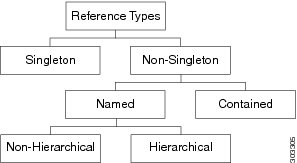
A Relative Name (Rn) may have the value of one or more of the MO’s
properties embedded in it. This allows in differentiating multiple MOs of the
same type within the context of the parent. Any properties that form part of
the Rn as described earlier are referred to as Naming properties.
For instance, multiple blade MOs reside under a chassis MO. The blade
MO contains the blade identifier as part of its Rn (blade-[Id]), thereby
uniquely identifying each blade MO in the context of a chassis.

 Feedback
Feedback