Configuring ERSPAN
This module describes how to configure Encapsulated Remote Switched Port Analyzer (ERSPAN). The Cisco ERSPAN feature allows you to monitor traffic on ports or VLANs and send the monitored traffic to destination ports.
Prerequisites for Configuring ERSPAN
-
ERSPAN is supported only with the Network Advantage license level.
-
Access control list (ACL) filter is applied before sending the monitored traffic on to the tunnel.
-
Only supports Type-II ERSPAN header.
Restrictions for Configuring ERSPAN
-
Destination sessions are not supported.
-
A device supports up to 66 sessions. A maximum of 8 source sessions can be configured and the remaining sessions can be configured as RSPAN destinations sessions. A source session can be a local SPAN source session or an RSPAN source session or an ERSPAN source session.
-
You can configure either a list of ports or a list of VLANs as a source, but cannot configure both for a given session.
-
When a session is configured through the ERSPAN CLI, the session ID and the session type cannot be changed. To change them, you must use the no form of the configuration commands to remove the session and then reconfigure the session.
-
ERSPAN source sessions do not copy locally-sourced Remote SPAN (RSPAN) VLAN traffic from source trunk ports that carry RSPAN VLANs.
-
ERSPAN source sessions do not copy locally-sourced ERSPAN GRE-encapsulated traffic from source ports.
Information for Configuring ERSPAN
ERSPAN Overview
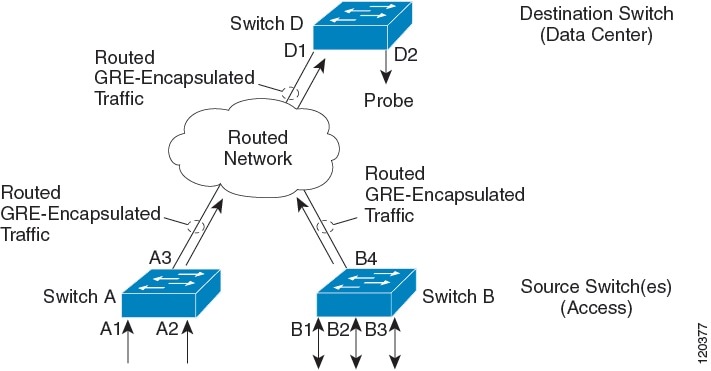
The Cisco ERSPAN feature allows you to monitor traffic on ports or VLANs, and send the monitored traffic to destination ports. ERSPAN sends traffic to a network analyzer, such as a Switch Probe device or a Remote Monitoring (RMON) probe. ERSPAN supports source ports, source VLANs, and destination ports on different devices, which helps remote monitoring of multiple devices across a network.
ERSPAN supports encapsulated packets of up to 9180 bytes. ERSPAN consists of an ERSPAN source session, routable ERSPAN GRE-encapsulated traffic, and an ERSPAN destination session.
ERSPAN consists of an ERSPAN source session, routable ERSPAN GRE-encapsulated traffic, and an ERSPAN destination session. You can configure an ERSPAN source session, an ERSPAN destination session, or both on a device. A device on which only an ERSPAN source session is configured is called an ERSPAN source device, and a device on which only an ERSPAN destination session is configured is called an ERSPAN termination device. A device can act as both; an ERSPAN source device and a termination device.
For a source port or a source VLAN, the ERSPAN can monitor the ingress, egress, or both ingress and egress traffic. By default, ERSPAN monitors all traffic, including multicast, and Bridge Protocol Data Unit (BPDU) frames.
-
A session ID
-
List of source ports or source VLANs to be monitored by the session
-
The destination and origin IP addresses, which are used as the destination and source IP addresses of the generic routing encapsulation (GRE) envelope for the captured traffic, respectively
-
ERSPAN flow ID
-
Optional attributes, such as, IP Time to Live (TTL), related to the GRE envelope
 Note |
ERSPAN source sessions do not copy ERSPAN GRE-encapsulated traffic from source ports. Each ERSPAN source session can have either ports or VLANs as sources, but not both. |
 Note |
Because encapsulation is performed in the hardware, the CPU performance is not impacted. |
ERSPAN Sources
-
Source ports—A source port that is monitored for traffic analysis. Source ports in any VLAN can be configured and trunk ports can be configured as source ports along with nontrunk source ports.
-
Source VLANs—A VLAN that is monitored for traffic analysis.
-
GigabitEthernet
-
PortChannel
-
TenGigabitEthernet
How to Configure ERSPAN
Configuring an ERSPAN Source Session
The ERSPAN source session defines the session configuration parameters and the ports or VLANs to be monitored.
Procedure
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Step 1 |
enable Example: |
|
||
|
Step 2 |
configure terminal Example: |
Enters global configuration mode. |
||
|
Step 3 |
monitor session span-session-number type erspan-source Example: |
|
||
|
Step 4 |
description description Example: |
Describes the ERSPAN source session. |
||
|
Step 5 |
source {interface type number | vlan vlan-ID} [, | -| both | rx | tx] Example: |
Configures the source interface or the VLAN, and the traffic direction to be monitored. |
||
|
Step 6 |
filter {ip access-group {standard-access-list | expanded-access-list | acl-name } | ipv6 access-group acl-name | mac access-group acl-name | vlan vlan-ID [, -]} Example: |
|
||
|
Step 7 |
no shutdown Example: |
Disables the shutting down of the configured session. |
||
|
Step 8 |
destination Example: |
Defines an ERSPAN destination session and enters ERSPAN monitor destination session configuration mode. |
||
|
Step 9 |
ip address ip-address Example: |
Configures an IP address for the ERSPAN destination session. |
||
|
Step 10 |
erspan-id erspan-ID Example: |
Configures the ID used by the destination session to identify the ERSPAN traffic. |
||
|
Step 11 |
origin ip-address Example: |
Configures the IP address used as the destination for the ERSPAN traffic. |
||
|
Step 12 |
ip ttl ttl-value Example: |
Configures Time to Live (TTL) values for packets in the ERSPAN traffic. |
||
|
Step 13 |
end Example: |
Exits ERSPAN monitor destination session configuration mode and returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
Configuration Examples for ERSPAN
Example: Configuring an ERSPAN Source Session
Switch> enable
Switch# configure terminal
Switch(config)# monitor session 1 type erspan-source
Switch(config-mon-erspan-src)# description source1
Switch(config-mon-erspan-src)# source interface fastethernet 0/1 rx
Switch(config-mon-erspan-src)# filter vlan 3
Switch(config-mon-erspan-src)# no shutdown
Switch(config-mon-erspan-src)# destination
Switch(config-mon-erspan-src-dst)# ip address 192.0.2.9
Switch(config-mon-erspan-src-dst)# erspan-id 2
Switch(config-mon-erspan-src-dst)# origin ip-address 203.0.113.2
Switch(config-mon-erspan-src-dst)# ip ttl 32
Switch(config-mon-erspan-src-dst)# end
Verifying ERSPAN
To verify the ERSPAN configuration, use the following commands:
The following is sample output from the show monitor session erspan-source command:
Switch# show monitor session erspan-source session
Type : ERSPAN Source Session
Status : Admin Enabled
Source Ports :
RX Only : Gi1/4/33
Destination IP Address : 192.0.2.1
Destination ERSPAN ID : 110
Origin IP Address : 10.10.10.216
IPv6 Flow Label : None
The following is sample output from the show monitor session erspan-source detail command:
Switch# show monitor session erspan-source detail
Type : ERSPAN Source Session
Status : Admin Enabled
Description : -
Source Ports :
RX Only : Gi1/4/33
TX Only : None
Both : None
Source VLANs :
RX Only : None
TX Only : None
Both : None
Source RSPAN VLAN : None
Destination Ports : None
Filter VLANs : None
Filter Addr Type :
RX Only : None
TX Only : None
Both : None
Filter Pkt Type :
RX Only : None
Dest RSPAN VLAN : None
IP Access-group : None
IPv6 Access-group : None
Destination IP Address : 192.0.2.1
Destination IPv6 Address : None
Destination IP VRF : None
Destination ERSPAN ID : 110
Origin IP Address : 10.10.10.216
IP QOS PREC : 0
IP TTL : 255
The following output from the show capability feature monitor erspan-source command displays information about the configured ERSPAN source sessions:
Switch# show capability feature monitor erspan-source
ERSPAN Source Session Supported: true
No of Rx ERSPAN source session: 8
No of Tx ERSPAN source session: 8
ERSPAN Header Type supported: II
ACL filter Supported: true
Fragmentation Supported: true
Truncation Supported: false
Sequence number Supported: false
QOS Supported: true
The following output from the show capability feature monitor erspan-destination command displays all the configured global built-in templates:
Switch# show capability feature monitor erspan-destination
ERSPAN Destination Session Supported: false
Additional References
RFCs
| Standard/RFC | Title |
|---|---|
|
RFC 2784 |
Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) |
Technical Assistance
| Description | Link |
|---|---|
|
The Cisco Support website provides extensive online resources, including documentation and tools for troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. To receive security and technical information about your products, you can subscribe to various services, such as the Product Alert Tool (accessed from Field Notices), the Cisco Technical Services Newsletter, and Really Simple Syndication (RSS) Feeds. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for Configuring ERSPAN
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to https://cfnng.cisco.com/. An account on Cisco.com is not required.|
Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
|
ERSPAN |
Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.5.1a |
This feature was introduced |
 Feedback
Feedback