Information About ERSPAN
The Cisco NX-OS system supports the Encapsulated Remote Switching Port Analyzer (ERSPAN) feature on both source and destination ports. ERSPAN transports mirrored traffic over an IP network. The traffic is encapsulated at the source router and is transferred across the network. The packet is decapsulated at the destination router and then sent to the destination interface.
ERSPAN consists of an ERSPAN source session, routable ERSPAN generic routing encapsulation (GRE)-encapsulated traffic, and an ERSPAN destination session. You can separately configure ERSPAN source sessions and destination sessions on different switches. You can also configure ERSPAN source sessions to filter ingress traffic by using ACLs.
ERSPAN Sources
-
Ethernet ports and port channels.
-
VLANs—When a VLAN is specified as an ERSPAN source, all supported interfaces in the VLAN are ERSPAN sources.
-
A port configured as a source port cannot also be configured as a destination port.
-
ERSPAN does not monitor any packets that are generated by the supervisor, regardless of their source.
-
Ingress traffic at source ports can be filtered by using ACLs so that they mirror only those packets of information that match the ACL criteria.
ERSPAN Destinations
ERSPAN destination sessions capture packets sent by ERSPAN source sessions on Ethernet ports or port channels and send them to the destination port. Destination ports receive the copied traffic from ERSPAN sources.
ERSPAN destination sessions are identified by the configured source IP address and ERSPAN ID. This allows multiple source sessions to send ERSPAN traffic to the same destination IP and ERSPAN ID and allows you to have multiple sources terminating at a single destination simultaneously.
ERSPAN destination ports have the following characteristics:
-
A port configured as a destination port cannot also be configured as a source port.
-
Destination ports do not participate in any spanning tree instance or any Layer 3 protocols.
-
Ingress and ingress learning options are not supported on monitor destination ports.
-
Host Interface (HIF) port channels and fabric port channel ports are not supported as SPAN destination ports.
ERSPAN Sessions
You can create ERSPAN sessions that designate sources and destinations to monitor.
When configuring ERSPAN source sessions, you must configure the destination IP address. When configuring ERSPAN destination sessions, you must configure the source IP address. See ERSPAN Sources for the properties of source sessions and ERSPAN Destinations for the properties of destination sessions.
 Note |
Only two ERSPAN or SPAN source sessions can run simultaneously across all switches. Only 23 ERSPAN destination sessions can run simultaneously across all switches. |
The following figure shows an ERSPAN configuration.
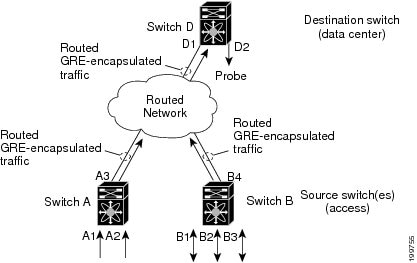
Multiple ERSPAN Sessions
Although you can define up to 18 ERSPAN sessions, only a maximum of four ERSPAN or SPAN sessions can be operational simultaneously. If both receive and transmit sources are configured in the same session, only two ERSPAN or SPAN sessions can be operational simultaneously. You can shut down any unused ERSPAN sessions.
 Note |
The Cisco Nexus 34180YC platform switch supports a total of 32 sessions SPAN and ERSPAN sessions together configured on the switch and, all 32 can be active at the same time. |
For information about shutting down ERSPAN sessions, see Shutting Down or Activating an ERSPAN Session.
High Availability
The ERSPAN feature supports stateless and stateful restarts. After a reboot or supervisor switchover, the running configuration is applied.
 Feedback
Feedback