Cisco Nexus 1000V Port Profile Configuration Guide, Release 4.2(1)SV2(2.1)
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- Updated:
- June 24, 2013
Chapter: Creating Port Profiles
- Information About Port Profiles
- Guidelines and Limitations for Creating Port Profiles
- Default Settings
- Configuring Port Profiles
- Port Mode Configuration
- Port Binding for vEthernet Port Profiles Configuration
- Enabling a Port Profile
- Removing a Port Profile
- Standards for Creating Port Profiles
- Feature History for Port Profiles
Creating Port Profiles
This chapter contains the following sections:
- Information About Port Profiles
- Guidelines and Limitations for Creating Port Profiles
- Default Settings
- Configuring Port Profiles
- Port Mode Configuration
- Port Binding for vEthernet Port Profiles Configuration
- Enabling a Port Profile
- Removing a Port Profile
- Standards for Creating Port Profiles
- Feature History for Port Profiles
Information About Port Profiles
Information About Port Profile States
The following table describes port profile behavior.
State |
Behavior |
|---|---|
Disabled (the default) |
When disabled, a port profile behaves as follows: |
Enabled |
When enabled, a port profile behaves as follows: |
Information About vEthernet Port Binding
You can configure either static, dynamic, or ephemeral port binding for vEthernet port profiles. The following table shows how this setting controls how ports are assigned in the VMware port group.
Type |
Behavior |
||
|---|---|---|---|
Static (the default) |
A DVPortID is assigned from the port group pool when you first assign the port group to the port. The DVPortID persists for the life of the network adapter. The port group has a fixed number of ports. |
||
Dynamic |
A DVPortID is assigned to a virtual machine only when the virtual machine is powered on and its NIC is in a connected state. The DVPortID is freed when the virtual machine is powered off or the virtual machine's NIC is disconnected. Virtual machines connected to a port group configured with dynamic binding must be powered on and off through the VMware vCenter Server. Dynamic binding can be used in environments where you have more virtual machines than available ports, but do not plan to have a greater number of virtual machines active than you have available ports. For example, if you have 300 virtual machines and 100 ports, but will never have more than 90 virtual machines active at one time, then dynamic binding would be appropriate for your port group. |
||
Ephemeral |
A new DVPortID is assigned to the port every time the VM is powered on. The port keeps this same DVPortID while the VM is up. All available DVS ports are shared. Ports are not allocated from the port group pool.
|
Guidelines and Limitations for Creating Port Profiles
- Once a port profile is created as either an Ethernet or vEthernet type, you cannot change the type.
- In an installation where multiple Ethernet port profiles are active on the same VEM, it is recommended that they do not carry the same VLAN(s). The allowed VLAN list should be mutually exclusive. Overlapping VLANs can be configured but may cause duplicate packets to be received by virtual machines in the network.
- To maintain consistency between the port profile definition and what is applied to an interface, if a port profile modification is rejected by any port, the modification is rejected by the port profile too.
- If you create a port profile with a command error, for example a private VLAN mapping error or service policy map error, then an attempt to apply this port profile to an interface shuts down the interface. The error is not copied to the interface and a system message is generated with details of the error. In this case, you must correct the error in the port profile. Then return the interface to service and apply the corrected port profile using the following command sequence:
For more information, see the Cisco Nexus 1000V Troubleshooting Guide.
- MTU can only be configured for uplink, Ethernet type port profiles.
-
If you configure MTU for an Ethernet port profile, your ESX host may generate the following error:
2010 Nov 15 04:35:27 my-n1k %VEM_MGR-SLOT3-1-VEM_SYSLOG_ALERT: vssnet : sf_platform_set_mtu: Failed setting MTU for VMW port with portID 33554475.
In this case, the MTU value you have set is not supported by the VEM physical NIC. See your VMware documentation for more information about supported MTU for PNIC. - Before configuring a port profile, the Cisco Nexus 1000V software must be initially configured. For information, see the Cisco Nexus 1000V Installation and Upgrade Guide.
- The Cisco Nexus 1000V must be connected to the VMware vCenter Server.
Default Settings
The following table lists the default settings in the port profile configuration.
Parameter |
Default |
|---|---|
capability l3control |
No |
description |
- |
administrative state |
all ports disabled |
switchport mode (access or trunk) |
access |
system vlan vlan_list |
- |
type |
vethernet |
access port vlan |
VLAN 1 |
max-ports |
32 |
min-ports |
32 |
vmware port-group name |
Port profile name |
vEthernet port-bindings |
Static |
Configuring Port Profiles
Creating a Port Profile
1. switch# configure terminal
2. switch(config)# port-profile [type {ethernet | vethernet}] name
3. (Optional) switch(config-port-prof)# description profile_description
4. (Optional) switch(config-port-prof)# show port-profile [brief | expand-interface | usage] [name profile-name]
5. (Optional) switch(config-port-prof)# copy running-config startup-config
DETAILED STEPS
This example shows how to create a new port profile:
switch(config)# port-profile type ethernet AllAccess1 switch(config-port-prof)# description all_access switch(config-port-prof)# show port-profile name AllAccess1 port-profile AllAccess1 description: all_access type: ethernet status: disabled capability l3control: no pinning control-vlan: - pinning packet-vlan: - system vlans: none port-group: max ports: - inherit: config attributes: evaluated config attributes: assigned interfaces: switch(config-port-prof)#
Configuring VMware Attributes
1. switch# configure terminal
2. switch(config)# port-profile [type {ethernet | vethernet}] name
3. switch(config-port-prof)# vmware port-group [pg_name]
4. switch(config-port-prof)# max-ports num
5. (Optional) switch(config-port-prof)# show port-profile [brief | expand-interface | usage] [name profile-name]
6. (Optional) switch(config-port-prof)# copy running-config startup-config
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | switch# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
||
| Step 2 | switch(config)# port-profile [type {ethernet | vethernet}] name | Enters port profile configuration mode for the named port profile. If the port profile does not already exist, it is created using the following characteristics:
|
||
| Step 3 | switch(config-port-prof)# vmware port-group [pg_name] | Designates the port profile as a VMware port group. The port profile is mapped to a VMware port group of the same name unless you specify a name here. When you connect the VSM to vCenter Server, the port group is distributed to the virtual switch on the vCenter Server. |
||
| Step 4 | switch(config-port-prof)# max-ports num | Designates the maximum number of ports that can be assigned to this non-uplink port profile. The default is 32 ports. When the specified maximum number of ports is reached, no more ports can be assigned. |
||
| Step 5 | switch(config-port-prof)# show port-profile [brief | expand-interface | usage] [name profile-name] | (Optional) Displays the configuration for verification. |
||
| Step 6 | switch(config-port-prof)# copy running-config startup-config | (Optional) Saves the change persistently through reboots and restarts by copying the running configuration to the startup configuration. |
Port Mode Configuration
VLAN Ranges
In accordance with the IEEE 802.1Q standard, up to 4094 VLANs are supported. The following table describes the available VLAN ranges and their use.
| VLAN Numbers | Range | Usage |
|---|---|---|
1 |
Normal |
Cisco default. You can use this VLAN, but you cannot modify or delete it. |
2-1005 |
Normal |
You can create, use, modify, and delete these VLANs. |
1006-4094 |
Extended |
You can create, name, and use these VLANs. You cannot change the following parameters: You cannot shut down these VLANs. |
3968-4047 and 4094 |
Internally allocated |
These 80 VLANs, plus VLAN 4094, are allocated for internal device use. You cannot create, delete, or modify any VLANs within the block reserved for internal use. |
Configuring a Trunking Profile
- You are logged in to the CLI in EXEC mode.
- You have already created the port profile using the Creating a Port Profile procedure.
- You know the needed VLAN configuration for this port profile and that it is to be used in trunk mode.
- A VLAN must already be created on the switch before you can assign it to a port profile.
- You know the supported VLAN ranges described in Configuring Port Mode.
1. switch# configure terminal
2. switch(config)# port-profile [type {ethernet | vethernet}] name
3. switch(config-port-prof)# switchport mode trunk
4. switch(config-port-prof)# no shutdown
5. (Optional) switch(config-port-prof)# switchport trunk allowed vlan {allowed-vlans | add add-vlans | except except-vlans | remove remove-vlans | all | none}
6. (Optional) switch(config-port-prof)# switchport trunk native vlan vlan-id
7. (Optional) switch(config-port-prof)# show port-profile [brief | expand-interface | usage] [name profile-name]
8. (Optional) switch(config-port-prof)# copy running-config startup-config
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | switch# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
||
| Step 2 | switch(config)# port-profile [type {ethernet | vethernet}] name | Enters port profile configuration mode for the named port profile. If the port profile does not already exist, it is created using the following characteristics:
|
||
| Step 3 | switch(config-port-prof)# switchport mode trunk | Designates that the interfaces are to be used as a trunking ports. A trunk port transmits untagged packets for the native VLAN and transmits encapsulated, tagged packets for all other VLANs. |
||
| Step 4 | switch(config-port-prof)# no shutdown | Administratively enables all ports in the profile. |
||
| Step 5 | switch(config-port-prof)# switchport trunk allowed vlan {allowed-vlans | add add-vlans | except except-vlans | remove remove-vlans | all | none} | (Optional) Designates the port profile as trunking and defines VLAN access to it as follows:
|
||
| Step 6 | switch(config-port-prof)# switchport trunk native vlan vlan-id | (Optional) Sets the trunking native characteristics when the interface is in trunking mode. If you do not configure a native VLAN, then the default VLAN 1 is used as the native VLAN. |
||
| Step 7 | switch(config-port-prof)# show port-profile [brief | expand-interface | usage] [name profile-name] | (Optional) Displays the configuration for verification. |
||
| Step 8 | switch(config-port-prof)# copy running-config startup-config | (Optional) Saves the running configuration persistently through reboots and restarts by copying it to the startup configuration. |
This example shows how to configure a trunking port profile, allowing all VLANs, and setting VLAN 3 as its native VLAN.
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# port-profile TrunkProf
switch(config-port-prof)# switchport mode trunk
switch(config-port-prof)# no shutdown
switch(config-port-prof)# switchport trunk allowed vlan all
switch(config-port-prof)# switchport trunk native vlan 3
switch(config-port-prof)# show port-profile name TrunkProf
port-profile TrunkProf
description:
type: vethernet
status: disabled
capability l3control: no
pinning control-vlan: -
pinning packet-vlan: -
system vlans: none
port-group:
max ports: 32
inherit:
config attributes:
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk native vlan 3
switchport trunk allowed vlan all
no shutdown
evaluated config attributes:
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk native vlan 3
switchport trunk allowed vlan all
no shutdown
assigned interfaces:
switch(config-port-prof)#
Configuring an Access Profile
An access port transmits packets on only one untagged VLAN. You can specify the VLAN, and it becomes the access VLAN. If you do not specify a VLAN for an access port, that interface carries traffic only on the default VLAN 1.
1. switch# configure terminal
2. switch(config)# port-profile [type {ethernet | vethernet}] name
3. switch(config-port-prof)# switchport mode access
4. switch(config-port-prof)# no shutdown
5. (Optional) switch(config-port-prof)# switchport access vlan [vlan-id-access]
6. (Optional) switch(config-port-prof)# show port-profile [brief | expand-interface | usage] [name profile-name]
7. (Optional) switch(config-port-prof)# copy running-config startup-config
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | switch# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
||
| Step 2 | switch(config)# port-profile [type {ethernet | vethernet}] name | Enters port profile configuration mode for the named port profile. If the port profile does not already exist, it is created using the following characteristics:
|
||
| Step 3 | switch(config-port-prof)# switchport mode access | Designates that the interfaces are to be used as a trunking ports. A trunk port transmits untagged packets for the native VLAN and transmits encapsulated, tagged packets for all other VLANs. |
||
| Step 4 | switch(config-port-prof)# no shutdown | Administratively enables all ports in the profile. |
||
| Step 5 | switch(config-port-prof)# switchport access vlan [vlan-id-access] | (Optional) Assigns an access VLAN ID to this port profile.
|
||
| Step 6 | switch(config-port-prof)# show port-profile [brief | expand-interface | usage] [name profile-name] | (Optional) Displays the configuration for verification. |
||
| Step 7 | switch(config-port-prof)# copy running-config startup-config | (Optional) Saves the change persistently through reboots and restarts by copying the running configuration to the startup configuration. |
This example shows how to configure a port profile with switch access ports, enabling the ports, and then adding an access VLAN:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# port-profile AccessProf
switch(config-port-prof)# switchport mode access
switch(config-port-prof)# no shutdown
switch(config-port-prof)# switchport access vlan 300
switch(config-port-prof)# show port-profile name AccessProf
port-profile AccessProf
description: allaccess4
type: vethernet
status: disabled
capability l3control: no
pinning control-vlan: -
pinning packet-vlan: -
system vlans: none
port-group: AccessProf
max ports: 5
inherit:
config attributes:
switchport mode access
switchport access vlan 300
no shutdown
evaluated config attributes:
switchport mode access
switchport access vlan 300
no shutdown
assigned interfaces:
switch(config-port-prof)#
Clearing a Port Management Policy
You can use this procedure to remove either of the following port management policies from an existing port profile configuration:
 Note |
After removing the configuration for an attribute, the attribute does not appear in show command output. |
1. switch# configure terminal
2. switch(config)# port-profile name
3. default {shutdown | switchport mode}
4. (Optional) switch(config-port-prof)# show port-profile [brief | expand-interface | usage] [name profile-name]
5. (Optional) switch(config-port-prof)# copy running-config startup-config
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | switch# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 | switch(config)# port-profile name | Enters port profile configuration mode for the named port profile. |
| Step 3 | default {shutdown | switchport mode} |
Removes either the shutdown or the switchport mode configuration from the port profile. |
| Step 4 | switch(config-port-prof)# show port-profile [brief | expand-interface | usage] [name profile-name] | (Optional) Displays the configuration for verification. |
| Step 5 | switch(config-port-prof)# copy running-config startup-config | (Optional) Saves the change persistently through reboots and restarts by copying the running configuration to the startup configuration. |
This example shows how to change the administrative state of a port profile back to its default setting (all ports disabled):
switch# configure treminal
switch(config)# port-profile AccessProf
switch(config-port-prof)# default shutdown
switch(config-port-prof)# show port-profile name AccessProf
port-profile AccessProf
description: allaccess4
type: vethernet
status: disabled
capability l3control: no
pinning control-vlan: 8
pinning packet-vlan: 8
system vlans: none
port-group: AccessProf
max ports: 5
inherit:
config attributes:
switchport mode access
evaluated config attributes:
switchport mode access
assigned interfaces:
switch(config-port-prof)#
Port Binding for vEthernet Port Profiles Configuration
Configuring a Default Port Binding Type
You can use this procedure to configure the type of port binding (static, dynamic, or ephemeral) to apply by default to all new vEthernet port profiles.
Before beginning this procedure, you must know or do the following:
1. switch# configure terminal
2. switch(config)# port-profile default port-binding {static [auto] dynamic [auto] | ephemeral}
3. (Optional) switch(config-port-prof)# show running-config
4. (Optional) switch(config-port-prof)# copy running-config startup-config
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | switch# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 | switch(config)# port-profile default port-binding {static [auto] dynamic [auto] | ephemeral} | Configures a default port binding type to be applied automatically to all new vEthernet port profiles unless explicitly configured otherwise:
|
| Step 3 | switch(config-port-prof)# show running-config | (Optional) Displays the configuration for verification. |
| Step 4 | switch(config-port-prof)# copy running-config startup-config | (Optional) Saves the change persistently through reboots and restarts by copying the running configuration to the startup configuration. |
This example shows how to configure the dynamic port binding type as the default for all new vEthernet port profiles created:
switch# configure terminal switch(config)# port-profile default port-binding dynamic switch(config-port-prof)#
Configuring Port Binding for a vEthernet Port Profile
You can use this procedure to configure the type of port binding (static, dynamic, or ephemeral) for an existing vEthernet port profile.
- You are logged in to the CLI in EXEC mode.
- You have already created the vEthernet port profile using Creating a Port Profile.
- You know the type of port binding (static, dynamic, or ephemeral) you want to apply to this vEthernet port profile.
1. switch# configure terminal
2. switch(config)# port-profile [type {vethernet}] profile-name
3. switch(config-port-prof)# port-binding {static [auto] dynamic [auto] | ephemeral}
4. (Optional) switch(config-port-prof)# show port-profile [name profile-name]
5. (Optional) switch(config-port-prof)# copy running-config startup-config
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | switch# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 | switch(config)# port-profile [type {vethernet}] profile-name | Enters port profile configuration mode for the named vEthernet port profile. |
| Step 3 | switch(config-port-prof)# port-binding {static [auto] dynamic [auto] | ephemeral} | Configures a default port binding type to be applied automatically to all new vEthernet port profiles unless explicitly configured otherwise:
|
| Step 4 | switch(config-port-prof)# show port-profile [name profile-name] | (Optional) Displays the configuration for verification. |
| Step 5 | switch(config-port-prof)# copy running-config startup-config | (Optional) Saves the change persistently through reboots and restarts by copying the running configuration to the startup configuration. |
This example shows how to configure the dynamic port binding type for the existing port profile named target-pp.
switch# configure terminal switch(config)# port-profile target-pp switch(config-port-prof)# port-binding dynamic switch(config-port-prof)#
Configuring a Port Profile with Dynamic or Static Port Binding
You can use this procedure to configure a port profile (static or dynamic) with or without the auto option.
You are logged in to the CLI in EXEC mode.
1. switch# configure terminal
2. switch(config)# port-profile [type {vethernet}] profile-name
3. switch(config-port-prof)# vmware port-group [pg_name]
4. switch(config-port-prof)# port-binding {static [auto] dynamic [auto] | ephemeral}
5. switch(config-port-prof)# max-ports number
6. switch(config-port-prof)# min-ports number
7. switch(config-port-prof)# state enabled
8. (Optional) switch(config-port-prof)# copy running-config startup-config
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | switch# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
||
| Step 2 | switch(config)# port-profile [type {vethernet}] profile-name | Enters port profile configuration mode for the named vEthernet port profile. |
||
| Step 3 | switch(config-port-prof)# vmware port-group [pg_name] | Designates the port profile as a VMware port group. The port profile is mapped to a VMware port group of the same name unless you specify a name here. When you connect the VSM to vCenter Server, the port group is distributed to the virtual switch on the vCenter Server. |
||
| Step 4 | switch(config-port-prof)# port-binding {static [auto] dynamic [auto] | ephemeral} | Configures a default port binding type to be applied automatically to all new vEthernet port profiles unless explicitly configured otherwise:
|
||
| Step 5 | switch(config-port-prof)# max-ports number | Designates the maximum number of ports that can be assigned to this non-uplink port profile. The default value is the global default at the time of port profile creation. When the specified maximum number of ports is reached, no more ports can be assigned. The valid range is 1 to 1024.
|
||
| Step 6 | switch(config-port-prof)# min-ports number | Designates the minimum number of ports that can be assigned to this non-uplink port profile. The default value is the global default at the time of port profile creation. The valid range is 1 to 1024.
|
||
| Step 7 | switch(config-port-prof)# state enabled | Enables the port profile and applies its configuration to the assigned ports. If the port profile is a VMware port group, the port group will be created in the vswitch on vCenter Server. |
||
| Step 8 | switch(config-port-prof)# copy running-config startup-config | (Optional) Saves the change persistently through reboots and restarts by copying the running configuration to the startup configuration. |
This example shows how to configure the dynamic auto port binding type:
switch# configure terminal switch(config)# port-profile type vethernet dynamic_auto_pp switch(config-port-prof)# vmware port-group switch(config-port-prof)# port-binding dynamic auto switch(config-port-prof)# max-ports 128 switch(config-port-prof)# min-ports 64 switch(config-port-prof)# state enabled switch(config-port-prof)# copy running-config startup-config
Verifying Port Binding on vCenter Server
You are logged in to vCenter Server on the host.
1. From your DVS in the Networking tab, choose the port group, and then click the Summary tab.
DETAILED STEPS
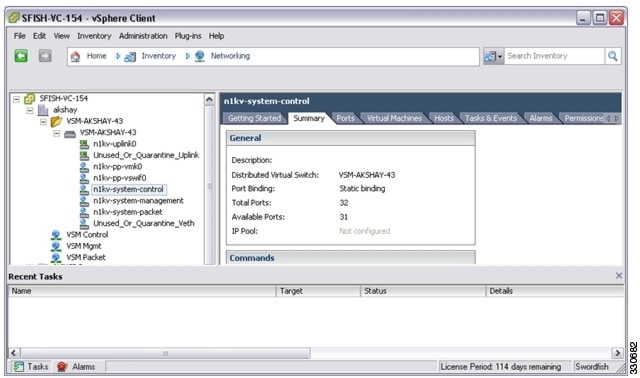
The General section of the Summary tab displays the type of port binding for this port group. |
Enabling a Port Profile
- You are logged in to the CLI in EXEC mode.
- You have already created the port profile using Creating a Port Profile.
1. switch# configure terminal
2. switch(config)# port-profile [type {vethernet}] profile-name
3. switch(config-port-prof)# state enabled
4. switch(config-port-prof)# show port-profile [brief | expand-interface | usage] [name profile-name]
5. (Optional) switch(config-port-prof)# copy running-config startup-config
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | switch# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 2 | switch(config)# port-profile [type {vethernet}] profile-name | Enters port profile configuration mode for the named vEthernet port profile. |
| Step 3 | switch(config-port-prof)# state enabled | Enables the port profile and applies its configuration to the assigned ports. If the port profile is a VMware port group, the port group will be created in the vswitch on vCenter Server. |
| Step 4 | switch(config-port-prof)# show port-profile [brief | expand-interface | usage] [name profile-name] | Displays the configuration for verification. |
| Step 5 | switch(config-port-prof)# copy running-config startup-config | (Optional) Saves the change persistently through reboots and restarts by copying the running configuration to the startup configuration. |
This example shows how to enable a port profile.
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# port-profile AccessProf
switch(config-port-prof)# state enabled
switch(config-port-prof)# show port-profile name AccessProf port-profile AccessProf
description: allaccess4
status: enabled
capability l3control: no
pinning control-vlan: -
pinning packet-vlan: -
system vlans: none
port-group:
max ports: 32
inherit:
config attributes:
channel-group auto mode on
evaluated config attributes:
channel-group auto mode on
assigned interfaces:
switch(config-port-prof)#
Removing a Port Profile
- You are logged in to the CLI in EXEC mode.
- If the port profile is inherited by another port profile, you need to remove the inheritance from the other port profile before removing this port profile. If you do not remove the inheritance first, the procedure fails. See Removing Inherited Policies from a Port Profile.
1. switch# configure terminal
2. (Optional) switch(config)# show port-profile virtual usage name profile_name
3. switch(config)# no port-profile profile_name
4. (Optional) switch(config)# show port-profile [name profile-name]
5. (Optional) switch(config)# copy running-config startup-config
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | switch# configure terminal | Enters global configuration mode. |
||
| Step 2 | switch(config)# show port-profile virtual usage name profile_name | (Optional) Verifies if active interfaces use this port profile.
|
||
| Step 3 | switch(config)# no port-profile profile_name | Removes the port profile configuration and operational settings. When you remove a port profile that is mapped to a VMware port group, the associated port group and settings within the vCenter Server are also removed. |
||
| Step 4 | switch(config)# show port-profile [name profile-name] | (Optional) Displays the configuration for verification. |
||
| Step 5 | switch(config)# copy running-config startup-config | (Optional) Saves the change persistently through reboots and restarts by copying the running configuration to the startup configuration. |
This example shows how to remove a port profile:
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# show port-profile virtual usage name AccessProf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Port Profile Port Adapter Owner
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
n1kv-uplink0 Po1
Eth3/2 vmnic1 localhost.
Eth3/3 vmnic2 localhost.
vlan1767 Veth7 Net Adapter 1 all-tool-7
AccessProf vEth12 vmnic1 localhost.
switch(config)# no port-profile AccessProf
switch(config)# show port-profile name AccessProf
ERROR: port-profile AccessProf does not exist
switch(config)# copy running-config startup-config
switch(config)#
Standards for Creating Port Profiles
No new or modified standards are supported by this feature, and support for existing standards has not been modified by this feature.
Feature History for Port Profiles
Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
Port Binding |
4.2(1)SV1(4a) |
You can configure a static port binding with the auto option. |
Port Binding |
4.2(1)SV1(4a) |
You can configure a port binding with the dynamic [auto] option. |
Atomic Inheritance |
4.2(1)SV1(4) |
Port Profile configuration applied to member interfaces. |
Port Profile Rollback |
4.2(1)SV1(4) |
After configuration failure, a port profile and its member interfaces are rolled back to the last good configuration. |
Interface Quarantine |
4.2(1)SV1(4) |
After a configuration failure, interfaces are shut down to maintain accurate configuration. |
Port Profile Type |
4.0(4)SV1(2) |
Port profiles are configured as either Ethernet or vEthernet type. By default, a port profile is created as vEthernet type. |
[no] capability uplink command |
4.0(4)SV1(2) |
The capability uplink command has been replaced with the port-profile [type {ethernet | vethernet}] name command. To configure a port profile with uplink capability, configure the port profile as an Ethernet type. The no capability uplink command has been removed. |
Port Profiles |
4.0(4)SV1(1) |
This feature was introduced. |
 Feedback
Feedback