Cisco Nexus 1010 Software Configuration Guide, Release 4.2(1)SP1(4)
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- Updated:
- February 20, 2012
Chapter: VSB Backup and Recovery
VSB Backup and Recovery
This chapter describes how to backup and recover a VSB, and includes the following sections:
•![]() Information About VSB Backup and Recovery
Information About VSB Backup and Recovery
•![]() Configuring VSB Backup and Restoration
Configuring VSB Backup and Restoration
•![]() Verifying the Backup and Recovery
Verifying the Backup and Recovery
•![]() Feature History for Export and Import
Feature History for Export and Import
Information About VSB Backup and Recovery
You can create a backup copy of a VSB and store it remotely to use as a recovery mechanism or when you need to move a VSB between Cisco Nexus 1010s.
Figure 6-1 shows the process for backing up and recovering a VSB.
Guidelines and Limitations
The following are guidelines and limitations to use when backing up and recovering a VSB:
•![]() Multiple export files may be created with this process. Do not change the file suffix for numbering purposes. If you change the prefix for one file, then you must change it for all.
Multiple export files may be created with this process. Do not change the file suffix for numbering purposes. If you change the prefix for one file, then you must change it for all.
•![]() You must shut down the VSB before creating the file to export.
You must shut down the VSB before creating the file to export.
•![]() The bootflash: export-import directory must be empty prior to either creating an export file or copying the file back from external storage.
The bootflash: export-import directory must be empty prior to either creating an export file or copying the file back from external storage.
Configuring VSB Backup and Restoration
This section includes the following topics and procedures:
•![]() Flowchart: Backing Up and Restoring a VSB Configuration
Flowchart: Backing Up and Restoring a VSB Configuration
•![]() Exporting a Backup VSB Configuration
Exporting a Backup VSB Configuration
•![]() Recovering a VSM with a Backup Configuration File
Recovering a VSM with a Backup Configuration File
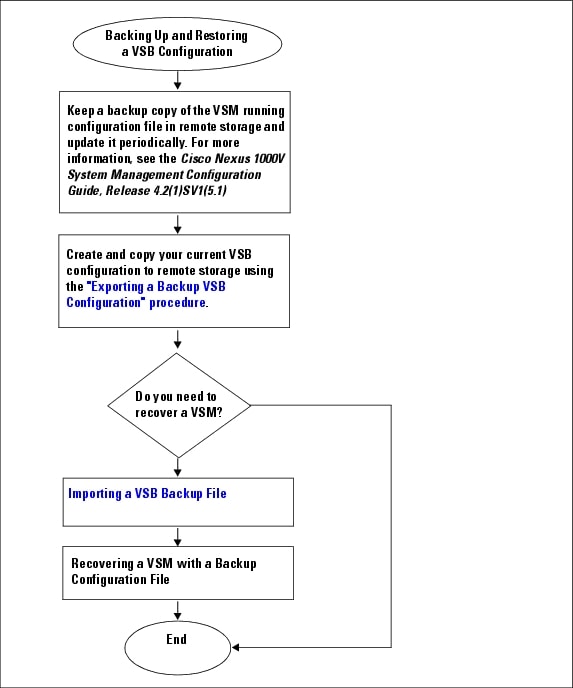
Flowchart: Backing Up and Restoring a VSB Configuration
You can use the following process for backing up and restoring a VSB configuration.
Figure 6-1 Flow Chart: Backing Up and Restoring a VSB Configuration
Exporting a Backup VSB Configuration
You can use the following procedures to create a backup copy of a VSB, store it remotely, and then re-import it to either recover a VSM or move a VSB between Cisco Nexus 1010s.
•![]() Copying the VSB Backup File to External Storage
Copying the VSB Backup File to External Storage
Creating a VSB Backup File
You can use this procedure to create a file for exporting a VSB.
BEFORE YOU BEGIN
Before beginning this procedure, you must know or do the following:
•![]() You are logged in to the CLI of the Cisco Nexus 1010 in EXEC mode.
You are logged in to the CLI of the Cisco Nexus 1010 in EXEC mode.
•![]() You know the name of the VSB for which you are creating a file to export.
You know the name of the VSB for which you are creating a file to export.
•![]() You have verified that the bootflash: export-import directory is empty. If files are present in this directory, you must delete them before starting this procedure.
You have verified that the bootflash: export-import directory is empty. If files are present in this directory, you must delete them before starting this procedure.
•![]() You must shut down the VSB that you want to backup before creating the file to export. This procedure includes a step for shutting down the VSB and then a step to restart the VSB after creating the file.
You must shut down the VSB that you want to backup before creating the file to export. This procedure includes a step for shutting down the VSB and then a step to restart the VSB after creating the file.

Note ![]() Multiple files may be created. Do not change the file suffix for numbering purposes. If you change the prefix for one file, then you must change it for all.
Multiple files may be created. Do not change the file suffix for numbering purposes. If you change the prefix for one file, then you must change it for all.
SUMMARY STEPS
1. ![]() dir export-import
dir export-import
2. ![]() (Optional) delete filename
(Optional) delete filename
3. ![]() config t
config t
4. ![]() virtual-service-blade name
virtual-service-blade name
5. ![]() shutdown [primary | secondary]
shutdown [primary | secondary]
6. ![]() show virtual-service-blade summary
show virtual-service-blade summary
7. ![]() export [primary | secondary]
export [primary | secondary]
8. ![]() dir bootflash:export-import
dir bootflash:export-import
9. ![]() no shutdown [primary | secondary]
no shutdown [primary | secondary]
10. ![]() show virtual-service-blade summary
show virtual-service-blade summary
DETAILED STEPS
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Step 1 |
dir export-import
Example: n1010# dir export-import DOCS-CPPA# dir export-import
Usage for bootflash://sup-local 496164864 bytes used 3495215104 bytes free 3991379968 bytes total n1010# |
Displays the contents of the export-import directory for verification that the directory is empty. If there is anything in this directory, you must use the next step to delete it before proceeding. |
Step 2 |
delete filename
Example: n1010-1(config-vsb-config)# delete bootflash:/export-import/1/*.* n1010-1(config-vsb-config)# delete bootflash:/export-import/1
n1010-1(config-vsb-config)#
|
Deletes the contents of the folder and the parent folder. Note |
Step 3 |
config t
Example: n1010-1# config t n1010-1(config)# |
Enters CLI Global Configuration mode. |
Step 4 |
virtual-service-blade name
Example: n1010-1(config)# virtual-service-blade vsm-1 n1010-1(config-vsb-config)# |
Enters configuration mode for the named virtual service blade. |
Step 5 |
shutdown [primary | secondary]
Example: n1010-1(config-vsb-config)# shutdown secondary
n1010-1(config-vsb-config)# |
Shuts down the VSB you are exporting from. If a redundant pair of Cisco Nexus 1010s, you must specify whether to shut down the primary or secondary. |
Step 6 |
show virtual-service-blade summary |
Displays the virtual service blade configuration for verification. |
Example: n1010-1(config-vsb-config)# show virtual-service-blade summary
------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Name Role State Nexus1010-Module ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- VSM1 PRIMARY VSB POWERED ON Nexus1010-PRIMARY VSM1 SECONDARY VSB POWERED OFF Nexus1010-SECONDARY
|
||
Step 7 |
export [primary | secondary]
Example: n1010-1(config-vsb-config)# export secondary Note: export started.. Note: please be patient.. Note: please be patient.. Note: please be patient.. Note: export completed...n1010-1(config-vsb-config)#
Example: n1010-1(config-vsb-config)# export primary ERROR: Please clean export-import directory first, then proceed. n1010-1(config-vsb-config)#
Example: n1010-1(config-vsb-config)# export secondary ERROR: Cannot export active virtual-service-blade, please shut and retry. |
Creates a directory named for the slot id of the exported VSB containing a compressed tar image of the VSB. If exporting from a redundant pair of Cisco Nexus 1010s, you must specify whether exporting from the primary or secondary. Note |
Step 8 |
dir bootflash:export-import
Example: n1010-1(config-vsb-config)# dir bootflash:export-import 4096 Sep 08 19:12:52 2011 1/
Usage for bootflash://sup-local 310870016 bytes used 3680509952 bytes free 3991379968 bytes total
|
Displays the contents of the bootflash: export-import directory, including the directory name of the folder containing the compressed tar image of the VSB, for verification. Note |
Step 9 |
no shutdown [primary | secondary]
Example: n1010-1(config-vsb-config)# no shutdown secondary
n1010-1(config-vsb-config)# |
Powers on the VSB that was powered off when creating the file for export. If a redundant pair of Cisco Nexus 1010s, you must specify primary or secondary. |
Step 10 |
show virtual-service-blade summary |
Displays the virtual service blade configuration for verification. |
Example: n1010-1(config-vsb-config)# show virtual-service-blade summary
------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Name Role State Nexus1010-Module ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- VSM1 PRIMARY VSB POWERED ON Nexus1010-PRIMARY VSM1 SECONDARY VSB POWERED ON Nexus1010-SECONDARY
|
||
Step 11 |
dir bootflash:export-import
Example: n1010-1(config-vsb-config)# dir bootflash:export-import/1 279955021 Sep 08 19:13:21 2011 Vdisk1.img.tar.00
Usage for bootflash://sup-local 310870016 bytes used 3680509952 bytes free 3991379968 bytes total
|
Displays the contents of the Cisco Nexus 1010 export folder, including the filename of the VSB compressed tar image. Note Note |
Copying the VSB Backup File to External Storage
Use this procedure to copy a VSB configuration file to remote storage and then delete the folder created for this purpose from the Cisco Nexus 1010.
BEFORE YOU BEGIN
Before beginning this procedure, you must know or do the following:
•![]() You have created a file to export using the "Creating a VSB Backup File" procedure and you know the name of this file and the name of the folder it resides in.
You have created a file to export using the "Creating a VSB Backup File" procedure and you know the name of this file and the name of the folder it resides in.

Note ![]() Multiple files may be created. If so, use the first filename in this procedure. Do not change the file suffix for numbering purposes. If you change the prefix for one file, then you must change it for all.
Multiple files may be created. If so, use the first filename in this procedure. Do not change the file suffix for numbering purposes. If you change the prefix for one file, then you must change it for all.
•![]() You are logged in to the CLI of the Cisco Nexus 1010 in EXEC mode.
You are logged in to the CLI of the Cisco Nexus 1010 in EXEC mode.
•![]() You know name of the path to a remote storage location.
You know name of the path to a remote storage location.
•![]() After copying the export backup file, delete the contents, including files and folders, of the export-import directory. Do not delete the export-import folder.
After copying the export backup file, delete the contents, including files and folders, of the export-import directory. Do not delete the export-import folder.
SUMMARY STEPS
1. ![]() copy bootflash:export-import/folder-name/filename ftp:
copy bootflash:export-import/folder-name/filename ftp:
2. ![]() cd /export-import/folder-name
cd /export-import/folder-name
3. ![]() delete filename
delete filename
4. ![]() dir
dir
DETAILED STEPS
Importing a VSB Backup File
You can use the following procedure to import a previously-saved backup copy of a VSB from remote storage to the Cisco Nexus 1010.
BEFORE YOU BEGIN
•![]() You are logged in to the CLI of the active Cisco Nexus 1010 in EXEC mode.
You are logged in to the CLI of the active Cisco Nexus 1010 in EXEC mode.
•![]() You have previously created and saved a copy of the Cisco Nexus 1010 configuration in a remote storage location using the "Exporting a Backup VSB Configuration" procedure.
You have previously created and saved a copy of the Cisco Nexus 1010 configuration in a remote storage location using the "Exporting a Backup VSB Configuration" procedure.

Note ![]() Multiple files may be created. If so, use only the first filename with the import command. Do not change the file suffix for numbering purposes. If you change the prefix for one file, then you must change it for all.
Multiple files may be created. If so, use only the first filename with the import command. Do not change the file suffix for numbering purposes. If you change the prefix for one file, then you must change it for all.
•![]() You know the name of the VSB and the path to the remote storage location.
You know the name of the VSB and the path to the remote storage location.
•![]() You have verified that the bootflash: export-import directory is empty. If files are present in this directory, you must delete them before importing a VSB configuration file.
You have verified that the bootflash: export-import directory is empty. If files are present in this directory, you must delete them before importing a VSB configuration file.
•![]() If an imported VSB role does not match the role of the Nexus1010 on which it is imported, then the VSB role should be changed internally to match the Nexus1010 role.
If an imported VSB role does not match the role of the Nexus1010 on which it is imported, then the VSB role should be changed internally to match the Nexus1010 role.
SUMMARY STEPS
1. ![]() dir export-import
dir export-import
2. ![]() (Optional) delete filename
(Optional) delete filename
3. ![]() copy ftp:filename bootflash:export-import
copy ftp:filename bootflash:export-import
4. ![]() config t
config t
5. ![]() virtual-service-blade name
virtual-service-blade name
6. ![]() import [primary | secondary] filename
import [primary | secondary] filename
7. ![]() show virtual-service-blade summary
show virtual-service-blade summary
8. ![]() show virtual-service-blade name name
show virtual-service-blade name name
9. ![]() copy running-config startup-config
copy running-config startup-config
DETAILED STEPS
Recovering a VSM with a Backup Configuration File
You can use this procedure to recover a VSM using a backup configuration file.
BEFORE YOU BEGIN
Before beginning this procedure, you must know or do the following:
•![]() You have imported your backup copy of the configuration file using the "Importing a VSB Backup File" procedure.
You have imported your backup copy of the configuration file using the "Importing a VSB Backup File" procedure.
•![]() You have a copy of the VSM running configuration in remote storage.
You have a copy of the VSM running configuration in remote storage.
•![]() You are logged in to the CLI of the Cisco Nexus 1010 in EXEC mode.
You are logged in to the CLI of the Cisco Nexus 1010 in EXEC mode.
•![]() This procedure includes a step for updating Cisco Nexus 1000V licenses. For more information, see the Cisco Nexus 1000V License Configuration Guide, Release 4.2(1)SV1(5.1).
This procedure includes a step for updating Cisco Nexus 1000V licenses. For more information, see the Cisco Nexus 1000V License Configuration Guide, Release 4.2(1)SV1(5.1).
•![]() This procedure requires you to shutdown the VSM management and control ports to prevent communication with VEMs and vCenter during the recovery. You need to know the IDs of the VSM control and management ports and the VSB serial port.
This procedure requires you to shutdown the VSM management and control ports to prevent communication with VEMs and vCenter during the recovery. You need to know the IDs of the VSM control and management ports and the VSB serial port.
•![]() This procedure requires you to setup the VSM software. You need to have the following information available for the VSM VSB:
This procedure requires you to setup the VSM software. You need to have the following information available for the VSM VSB:
–![]() Admin password
Admin password
–![]() Domain ID
Domain ID
–![]() HA Role (must be set to the same role as that of the VSM on which it is imported)
HA Role (must be set to the same role as that of the VSM on which it is imported)
–![]() Management 0 IP address
Management 0 IP address
–![]() Management 0 netmask
Management 0 netmask
–![]() Default gateway IP address
Default gateway IP address
For detailed information about setting up the VSM software, see the Cisco Nexus 1000V Getting Started Guide, Release 4.2(1)SV1(5.1)
For detailed information about the vCenter server connection, see the
Step 1 ![]() From the Cisco Nexus 1010, shut down the control and management interfaces of the VSM VSB.
From the Cisco Nexus 1010, shut down the control and management interfaces of the VSM VSB.
config t
interface vethernet slot/port
shut
Example:
n1010-1# config t
n1010-1(config)# interface vethernet1/1
n1010-1(config-if)# shut
The VSM management and control interfaces are no longer communicating with VEMs and vCenter.
Step 2 ![]() Verify that the control and management interfaces are down.
Verify that the control and management interfaces are down.
show virtual-service-blade name name
Example:
n1010-1(config)# show virtual-service-blade name VSM1
virtual-service-blade VSM1
Description:
Slot id: 1
Host Name:
Management IP:
VSB Type Name : VSM-1.1
vCPU: 1
Ramsize: 2048
Disksize: 3
Heartbeat: 0
HA Admin role: Primary
HA Oper role: NONE
Status: VSB POWERED OFF
Location: PRIMARY
SW version:
VsbEthernet1/1/1: control vlan: 1306 state: down
VsbEthernet1/1/2: management vlan: 1304 state: down
VsbEthernet1/1/3: packet vlan: 1307 state: up
Interface: internal vlan: NA state: up
HA Admin role: Secondary
HA Oper role: NONE
Status: VSB POWERED ON
Location: SECONDARY
SW version:
VSB Info:
n1010-1(config)#
Step 3 ![]() Power on the VSB VSM.
Power on the VSB VSM.
virtual-service-blade name
no shutdown [primary | secondary]
Example:
n1010-1(config)# virtual-service-blade VSM1
n1010-1(config)# no shutdown primary
n1010-1(config)#
Step 4 ![]() Log in to Cisco Nexus 1010 serial port of the primary VSM.
Log in to Cisco Nexus 1010 serial port of the primary VSM.
Step 5 ![]() Erase the startup configuration.
Erase the startup configuration.
config t
write erase
Example:
n1000v# config t
n1000v(config)# write erase
Warning: This command will erase the startup-configuration.
Do you wish to proceed anyway? (y/n) [n] y
The previous configuration is erased. You will replace it with the previously-saved backup of your running configuration in Step 11.
Step 6 ![]() Reboot the system.
Reboot the system.
reload
n1000v# reload
This command will reboot the system. (y/n)? [n] y
2009 Oct 30 21:51:34 s1 %$ VDC-1 %$ %PLATFORM-2-PFM_SYSTEM_RESET: Manual system restart
from Command Line Interface
n1000v#
The Cisco Nexus 1010 boots up and the setup wizard starts.
Step 7 ![]() Use the setup wizard to configure the VSM. Accept defaults for all except the following:
Use the setup wizard to configure the VSM. Accept defaults for all except the following:
•![]() Admin password
Admin password
•![]() Domain ID
Domain ID
•![]() HA Role (must be set to the same role as that of the VSM on which it is imported)
HA Role (must be set to the same role as that of the VSM on which it is imported)
•![]() Management 0 IP address
Management 0 IP address
•![]() Management 0 netmask
Management 0 netmask
•![]() Default gateway IP address
Default gateway IP address
Example:
---- System Admin Account Setup ----
Enter the password for "admin":
Confirm the password for "admin":
Enter the domain id<1-4095>: 152
Enter HA role[standalone/primary/secondary]: primary
[#########################################] 100%
---- Basic System Configuration Dialog ----
This setup utility will guide you through the basic configuration of
the system. Setup configures only enough connectivity for management
of the system.
*Note: setup is mainly used for configuring the system initially,
when no configuration is present. So setup always assumes system
defaults and not the current system configuration values.
Press Enter at anytime to skip a dialog. Use ctrl-c at anytime
to skip the remaining dialogs.
Would you like to enter the basic configuration dialog (yes/no): yes
Create another login account (yes/no) [n]: no
Configure read-only SNMP community string (yes/no) [n]: no
Configure read-write SNMP community string (yes/no) [n]: no
Enter the switch name: n1000v
Continue with Out-of-band (mgmt0) management configuration? [yes/no] [y]: yes
Mgmt0 IPv4 address: 172.28.15.152
Mgmt0 IPv4 netmask: 255.255.255.0
Configure the default-gateway: (yes/no) [y]: yes
IPv4 address of the default gateway : 172.23.233.1
Enable the telnet service? (yes/no) [y]: no
Enable the ssh service? (yes/no) [y]: no
Enable the http-server? (yes/no) [y]: no
Configure NTP server? (yes/no) [n]: no
Configure svs domain parameters? (yes/no) [y]: no
Vem feature level will be set to 4.2(1)SV1(4),
Do you want to reconfigure? (yes/no) [n] no
The system summarizes the new setup configuration.
Step 8 ![]() Copy the running configuration to the startup configuration.
Copy the running configuration to the startup configuration.
copy running-config startup-config
Example:
n1000v# copy running-config startup-config
[########################################] 100%
n1000v#
Step 9 ![]() Reopen the management interface of the VSM VSB.
Reopen the management interface of the VSM VSB.
config t
interface vethernet slot/port
no shut
Example:
n1010-1# config t
n1010-1(config)# interface vethernet1/2
n1010-1(config-if)# no shut
The VSM management interface is again communicating with VEMs and vCenter.
Step 10 ![]() Verify that the management interface is up.
Verify that the management interface is up.
show virtual-service-blade name name
Example:
n1010-1(config)# show virtual-service-blade name VSM1
virtual-service-blade VSM1
. . .
VsbEthernet1/1/1: control vlan: 1306 state: down
VsbEthernet1/1/2: management vlan: 1304 state: up
VsbEthernet1/1/3: packet vlan: 1307 state: up
Interface: internal vlan: NA state: up
. . .
n1010-1(config)#
Step 11 ![]() Copy your saved running configuration backup to the VSM bootflash.
Copy your saved running configuration backup to the VSM bootflash.
copy bootflash:filename
Example:
n1010-1(config)# copy bootflash:VSM1-periodic-startup-config.txt running-config
n1010-1(config)#
Step 12 ![]() Copy the running configuration to the startup configuration.
Copy the running configuration to the startup configuration.
copy running-config startup-config
Example:
n1000v# copy running-config startup-config
[########################################] 100%
n1000v#
Step 13 ![]() Reopen the control interface of the VSM VSB.
Reopen the control interface of the VSM VSB.
config t
interface vethernet slot/port
no shut
Example:
n1010-1# config t
n1010-1(config)# interface vethernet1/1
n1010-1(config-if)# no shut
The VSM control interface is again communicating with VEMs and vCenter.
Step 14 ![]() Verify that the control interface is up.
Verify that the control interface is up.
show virtual-service-blade name name
Example:
n1010-1(config)# show virtual-service-blade name VSM1
virtual-service-blade VSM1
. . .
VsbEthernet1/1/1: control vlan: 1306 state: up
VsbEthernet1/1/2: management vlan: 1304 state: up
VsbEthernet1/1/3: packet vlan: 1307 state: up
Interface: internal vlan: NA state: up
. . .
n1010-1(config)#
Step 15 ![]() Check the modules by entering the show module command at the VSM CLI.
Check the modules by entering the show module command at the VSM CLI.
Example:
n1000v(config)# show module
Mod Ports Module-Type Model Status
--- ----- -------------------------------- ------------------ ------------
1 0 Virtual Supervisor Module Nexus1000V active *
2 0 Virtual Supervisor Module Nexus1000V ha-standby
3 248 Virtual Ethernet Module NA ok
4 248 Virtual Ethernet Module NA ok
Mod Sw Hw
--- ---------------- ------------------------------------------------
1 4.2(1)SV1(4a) 0.0
2 4.2(1)SV1(4a) 0.0
3 4.2(1)SV1(4a) VMware ESXi 4.0.0 Releasebuild-208167 (1.9)
4 4.2(1)SV1(4a) VMware ESX 4.1.0 Releasebuild-260247 (2.0)
Mod MAC-Address(es) Serial-Num
--- -------------------------------------- ----------
1 00-19-07-6c-5a-a8 to 00-19-07-6c-62-a8 NA
2 00-19-07-6c-5a-a8 to 00-19-07-6c-62-a8 NA
3 02-00-0c-00-03-00 to 02-00-0c-00-03-80 NA
4 02-00-0c-00-04-00 to 02-00-0c-00-04-80 NA
Mod Server-IP Server-UUID Server-Name
--- --------------- ------------------------------------ --------------------
1 10.78.109.44 NA NA
2 10.78.109.44 NA NA
3 10.78.109.72 44454c4c-4300-1046-8043-b6c04f563153 10.78.109.72
4 10.78.109.71 44454c4c-3300-1056-8057-b3c04f583153 10.78.109.71
* this terminal session
n1000v(config)#
Step 16 ![]() Enable the HA peer.
Enable the HA peer.
enable [primary | secondary]
Example:
n1010-1(config)# enable secondary
The VSM is again operating in HA mode with a primary and secondary module.
Step 17 ![]() You have completed this procedure.
You have completed this procedure.
Verifying the Backup and Recovery
To verify the backup and recovery, use the following commands:
|
|
|
|---|---|
dir bootflash:export-import /folder-name |
Displays the contents of the export-import directory folder. |
show virtual-service-blade summary |
Displays the redundancy state (active or standby) and the redundancy role (primary or secondary) for each VSB. Note See Example 6-2 |
show virtual-service-blade [name name] |
Displays the configuration for a specific virtual service blade. See Example 6-3 |
Example 6-1 export-import directory
n1010-1(config-vsb-config)# dir bootflash:export-import/1
279955021 Sep 08 19:13:21 2011 Vdisk1.img.tar.00
Usage for bootflash://sup-local
310870016 bytes used
3680509952 bytes free
3991379968 bytes total
Example 6-2 Virtual Service Blade Summary
n1010-1(config-vsb-config)# show virtual-service-blade summary
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Name Role State Nexus1010-Module
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
VSM1 PRIMARY VSB POWERED OFF Nexus1010-PRIMARY
VSM1 SECONDARY VSB POWERED ON Nexus1010-SECONDARY
Example 6-3 Virtual Service Blade
n1010# show virtual-service-blade name VSM1
virtual-service-blade VSM1
Description:
Slot id: 1
Host Name:
Management IP:
VSB Type Name : VSM-1.1
vCPU: 1
Ramsize: 2048
Disksize: 3
Heartbeat: 0
HA Admin role: Primary
HA Oper role: NONE
Status: VSB POWERED OFF
Location: PRIMARY
SW version:
VsbEthernet1/1/1: control vlan: 1306 state: down
VsbEthernet1/1/2: management vlan: 1304 state: down
VsbEthernet1/1/3: packet vlan: 1307 state: up
Interface: internal vlan: NA state: up
HA Admin role: Secondary
HA Oper role: NONE
Status: VSB POWERED ON
Location: SECONDARY
SW version:
VSB Info:
n1010-1(config)#
Additional References
For additional information related to implementing system-level HA features, see the following sections:
•![]() MIBs
MIBs
•![]() RFCs
RFCs
Related Documents
Standards
|
|
|
|---|---|
No new or modified standards are supported by this feature, and support for existing standards has not been modified by this feature. |
— |
MIBs
|
|
|
|---|---|
No MIBs are supported by this feature |
RFCs
|
|
|
|---|---|
No RFCs are supported by this feature |
— |
Feature History for Export and Import
This section provides the export and import feature release history.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
VSB export and import |
4.2(1)SP1(3) |
This feature was introduced. |
 Feedback
Feedback