Information About Cisco Cloud Services Platform
Cisco Cloud Services Platform is a software and hardware platform for data center network functions virtualization. This open kernel virtual machine (KVM) platform, with Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) as the base operating system, is designed to host networking virtual services. Cisco CSP provides REST APIs, a web interface, and a CLI for creating and managing the virtual machine (VM) lifecycle.
Setting Up Your CSP and Configuring Services
Summary Steps
Setting up your Cisco Cloud Services Platform (Cisco CSP) and creating services consists of the following high-level steps:
Procedure
| Step 1 |
Upgrade the Cisco CSP software or perform the initial setup. |
| Step 2 |
Log in to the Cisco CSP 2100. |
| Step 3 |
Generate and install an SSL certificate. |
| Step 4 |
Access Cisco CSP through the web interface. |
| Step 5 |
Upload the service image to the Cisco CSP. |
| Step 6 |
Create a service. |
| Step 7 |
Verify the service instance. |
Upgrading the Cisco CSP Software
You can upgrade the Cisco CSP software by installing an ISO image through any of the following methods:
-
Using the Cisco Integrated Management Controller (CIMC) KVM console: Map the ISO image to the Virtual CD/DVD by using the CIMC console and then install the image. The ISO image installation through CIMC console is useful for clean installations because the CIMC KVM or a direct console connected to the Cisco CSP system is required to perform the tasks described in Performing the Initial Setup.
-
Using the Cisco CSP 2100 CLI or REST APIs: Copy the update ISO image to the repository, specify the installation mode, and then install the image. The ISO image installation through CLI or REST APIs is more useful for software updates because the CIMC KVM or direct console support is not required to configure the system. After the installation is complete and the system reboots, the Cisco CSP 2100 system can be accessed through Secure Shell (SSH).
 Note |
Ensure that network connectivity is not lost while installation is in progress. Network issues might result in installation getting stuck in one of the various stages. In such a scenario, reinstall the ISO image, which means reattach the ISO image to the KVM console and reboot Cisco CSP. |
 Note |
Starting with Release 2.7.0, UEFI BIOS boot mode is supported in addition to the legacy boot mode. Once installed in legacy or UEFI boot mode, system can not be changed to boot in the other mode. Therefore systems installed with versions prior to 2.7.0 which can only use legacy boot mode can’t be upgraded to 2.7.0 if the UEFI boot mode is selected in 2.7.0. |
 Note |
Starting with Release 2.8.0, CSP supports secure boot. To enable secure boot in the BIOS mode, ensure that you upgrade CSP to 2.8.0 and the system requires the UEFI boot mode installation. |
Performing the Initial Setup
-
Filling out the questionaire through manual install.
-
Using PnP manager in NSO to load the Day-0 configuration file on CSP. This process is also known as zero touch provisioning.
Before you begin
-
Make sure that the Cisco CSP is set up correctly and is cabled for network access. For information about setting up the Cisco CSP, see the Cisco Cloud Services Platform Hardware Installation Guide.
-
Choose a hostname for your Cisco CSP.
-
Obtain the following information about the Cisco CSP from your network administrator:
-
Port channel or physical network interface card (pNIC) to be used as the management interface
-
VLAN values for the management port channel, the management interface, and the dedicated service management interface (optional)
-
Two pNIC members for the port channel to be used as the management interface (optional)
-
Password for the admin user
-
Management IP address
-
Netmask for the management interface
-
Default gateway IP address
-
Domain name server (DNS) (optional)
-
Domain name
-
Port channel or pNIC to be used as the dedicated service management interface (optional)
-
Two pNIC members for the port channel to be used as the dedicated service management interface (optional)
-
To perform zero touch provisioning, ensure that the following components are available:
-
Standard NSO (version 4.7) with PnP manager.
-
DHCP server (Windows or Linux) with option 43 (vendor-specific information) configuration.
-
CSP LOM Ports connected to upstream switch either as access port or in portchannel.
CSP-2K series: LOM ports should be used for management.
CSP-5K series: LOM/slot 1 (1G) ports should be used for management.
Procedure
| Step 1 |
Turn on the Cisco CSP. |
||
| Step 2 |
Enter admin as the username and admin as the password. You are prompted with whether CSP software installation should be carried out by the manual install or PnP manager modes. |
||
| Step 3 |
Enter yes or no depending on whether to exit PnP and continue with manual install or perform installation through zero touch provisioning. If you enter yes, continue from Step 4, else you are logged out of the CSP device. You can log in back with the box credentials mentioned in the Day-0 file. Meanwhile, the following action occurs for CSP software installation though PnP manager mode: Example:The following example shows the prompts described for the zero touch provisioning procedure. Example:Example: |
||
| Step 4 |
Enter yes or no depending upon whether you want to use a port channel for the management interface. Configuring a port channel as the management interface ensures that you always have connectivity with the Cisco CSP. You can connect to Cisco CSP even when one of the pNICs is down. Do one of the following:
|
||
| Step 5 |
Do the following to use a port channel as the management interface: |
||
| Step 6 |
Enter the pNIC interface number that you want to use as the management interface. |
||
| Step 7 |
Enter yes or no to specify the shared or dedicated mode for the management interface. Do one of the following:
|
||
| Step 8 |
Enter yes or no depending upon whether you want to specify a VLAN for the management interface. Do one of the following:
|
||
| Step 9 |
Enter yes to save the settings. |
||
| Step 10 |
Enter a new password for the admin user and then enter the password again for verification. |
||
| Step 11 |
Enter the hostname. |
||
| Step 12 |
Enter the IP address of the management interface. |
||
| Step 13 |
Enter the netmask of the management interface. |
||
| Step 14 |
Enter the IP address of the default gateway. |
||
| Step 15 |
Enter yes or no depending upon whether you want to specify the DNS. Do one of the following:
|
||
| Step 16 |
Enter the domain name; for example, cisco.com. |
||
| Step 17 |
Enter yes to save the settings. |
||
| Step 18 |
Enter yes or no to configure the dedicated service management interface. Do one of the following:
|
||
| Step 19 |
Do the following to configure a port channel as the dedicated service management interface: |
||
| Step 20 |
Enter the pNIC interface number that you want to use as the dedicated service management interface. |
||
| Step 21 |
Enter yes to save the settings. Your specified settings are saved and you are connected to the Cisco CSP console.
|
The following example shows the prompts described for the manual installation procedure.
localhost login: admin
Password:
**********************************************
**********************************************
**********************************************
**** ****
**** Cisco Cloud Services Platform ****
**** Version 2.5.0 ****
**** Built on 2018-10-8 ****
**** Cisco Systems Inc, copyright 2019 ****
**** ****
**********************************************
**********************************************
**********************************************
Verifying server information ...
System Information
Manufacturer: Cisco Systems Inc
Product Name: CSP
Version: 2.5.0
PNIC Remote Connectivity Information from LLDP
==================================================
PNIC Eth1-0 : system = No lldp detectd intf = No lldp detected state = down
PNIC Eth1-1 : system = sw-lab-n5k-3 intf = Ethernet100/1/46 state = up
PNIC Eth7-0 : system = sw-lab-n5k-3 intf = Ethernet100/1/48 state = up
PNIC Eth7-1 : system = No lldp detectd intf = No lldp detected state = down
PNIC Eth4-0 : system = sw-lab-n5k-3 intf = Ethernet100/1/45 state = up
PNIC Eth4-1 : system = sw-lab-n5k-3 intf = Ethernet100/1/47 state = up
PNIC Eth4-2 : system = No lldp detectd intf = No lldp detected state = down
PNIC Eth4-3 : system = No lldp detectd intf = No lldp detected state = down
Enable port channel for mgmt pnic (yes or no): no
Choose a PNIC for the management interface: Eth1-0, Eth1-1, Eth7-0, Eth7-1, Eth4-0, Eth4-1, Eth4-2, Eth4-3:
Eth4-0
Allow management interface to be shared with service VMs (yes or no)?: yes
Shared Management Interface Physical NIC : Eth4-0
Define a vlan for the mgmt interface(yes or no)?: yes
Choose a vlan for the management interface, valid values are between 1 and 4094: 180
Management vlan set to : 180
Do you want to save these settings (yes or no)?: yes
Please enter a password for the CSP admin user
The password must:
have at least 8 characters and at most 64 characters
have at least 1 digits
have at least 1 special character[allowed _-~#@=+^]
have at least 1 upper case character
have at least 1 lower case character
not have two or more same characters consecutively
not be an exact dictionary word match
Password:
Enter it again for verification:
Password:
Enter your hostname: csp1
Enter your management IP address: 1.2.3.4
Enter your netmask: 255.255.255.0
Enter your default gateway: 1.2.3.1
Do you want to configure a Domain Name Server (DNS) (yes or no)?: yes
Enter your Domain Name Server (DNS): 5.6.7.8
Enter your domain name: cisco.com
System Hostname : csp1
Management IP Address : 1.2.3.4
Management Netmask : 255.255.255.0
Management Gateway : 1.2.3.1
Domain Name Server (DNS) : 5.6.7.8
Domain Name : cisco.com
Do you want to save these settings (yes or no)?: yes
Saving configuration............
Do you wish to configure s Dedicated Service Management Port (yes or no)?: yes
Do you want to set the service mgmt port up as port channel (yes or no)?: yes
Port channel name: SRV-MGMT
Choose the first PNIC for the service mgmt port channel: Eth1-0, Eth1-1, Eth7-0, Eth7-1, Eth4-0, Eth4-1, Eth4-2,Eth4-3: Eth1-0
Service Mgmt Pnic member 1 set to : Eth1-0
Choose the second PNIC for the service mgmt port channel: Eth1-0, Eth1-1, Eth7-0, Eth7-1, Eth4-0, Eth4-1, Eth4-2, Eth4-3: Eth1-0
Service Mgmt Pnic member 2 set to : Eth1-0
Choose bond-mode for service mgmt port-channel(balance-slb or active-backup or balance-tcp)?: balance-slb
Choose lacp-type for service mgmt port-channel (active or passive or off)?: active
Choose vlan trunk for service mgmt port-channel: 72
Service Mgmt Port Channel: SRV-MGMT
Service Mgmt Member 1 : Eth1-0
Service Mgmt Member 2 : Eth1-1
Service Mgmt Bond Mode : balance-slb
Service Mgmt LACP type : active
Service Mgmt VLAN Trunk : 72
Do you want to save these settings (yes or no)?: yes
CSP expects HyperThreading to be disabled in BIOS
No Cavium card in the system
No Cavium card in the system
Welcome to the Cisco Cloud Services Platform CLI
TAC support: http://www.cisco.com/tac
Copyright (c) 2018-2019, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
The copyrights to certain works contained in this software are
owned by other third parties and used and distributed under
license. Certain components of this software are licensed under
the GNU General Public License (GPL) version 2.0 or the GNU
Lesser General Public License (LGPL) Version 2.1. A copy of each
such license is available at
http://www.opensource.org/licenses/gpl-2.0.php and
http://www.opensource.org/licenses/lgpl-2.1.php
admin connected from 127.0.0.1 using console on csp1
csp1#
Logging In to the Cisco CSP
You can log in to the Cisco CSP by using one of the following modes: web interface (accessible through a web browser), CLI, or REST APIs (accessible through cURL tool or Windows PowerShell). However, before logging in to the web interface or using the REST APIs, you must install an SSL certificate using the CLI. For detailed information about the CLI and available commands, see the Cisco Cloud Services Platform Command Reference Guide.
Generating and Installing an SSL Certificate
 Note |
For proof-of-concept (POC) or lab deployments, an SSL certificate is not required. You can skip this section and go to Accessing the Cisco CSP Web Interface. |
You must generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) to send to a Certification Authority (CA) to obtain an SSL certificate and use the CLI to install the SSL certificate on Cisco CSP. The default self-signed certificate installed on the Cisco CSP is only for temporary use.
Procedure
| Step 1 |
Log in to the Cisco CSP 2100 CLI in EXEC mode. |
||
| Step 2 |
On the command prompt, use the following command to create a CSR: After you enter the command, you are prompted for some information such as country name, state, city, email, common name, and so on. For detailed information about this command, see the Cisco Cloud Services Platform Command Reference Guide .
|
||
| Step 3 |
Provide the required information in the prompt. After you provide the required information, the following two files are generated in the /osp/certificates directory:
|
||
| Step 4 |
Send the myhost.csr file to a CA to obtain an SSL certificate. After you submit the CSR to a CA, the CA generates an SSL certificate and sends a certificate file to you. The CA may also send a certificate chain file. |
||
| Step 5 |
Copy the SSL certificate files that you received from the CA to the /osp/certificates directory using the scp command from an external server. |
||
| Step 6 |
On the Cisco CSP 2100 command prompt, enter the following command to install the certificate: After you enter the command, you are prompted for some information such as localhost (hostname including the domain name), key filename, certificate filename, and chain filename. For detailed information about this command, see the Cisco Cloud Services Platform Command Reference Guide. |
||
| Step 7 |
Provide the required information in the prompt. After you provide the required information, the SSL certificate is installed. To verify that the certificate is installed, follow the instructions in the next section to log in to the Cisco CSP web interface by using a web browser. After logging in, click the lock icon in the address bar to see information about the installed certificate. |
Accessing the Cisco CSP Web Interface
Procedure
| Step 1 |
Enter https://hostname or https://ip-address in a web browser.
|
||
| Step 2 |
Enter the username admin and the password. The Cisco CSP web interface is displayed. 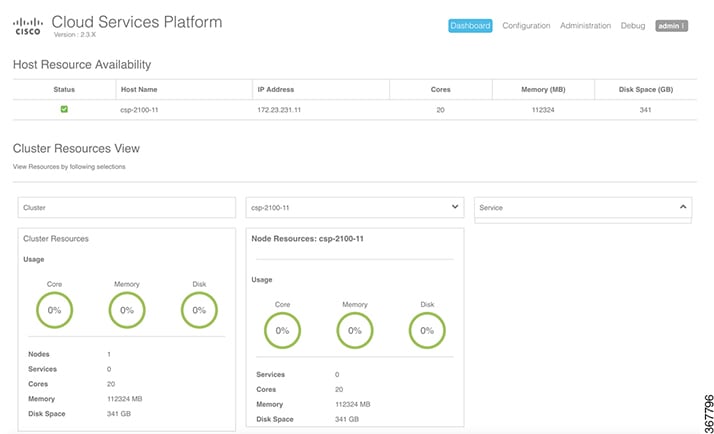 |
Overview of the Cisco CSP Web Interface
The Cisco CSP web interface consists of the following tabs and pages:
-
Dashboard: The Dashboard tab consists of the following pages:
-
Overview: Use the Overview page to view information about the host resources. You can filter resources by clusters, nodes, and services. You can also veiw the node level redundancy in a cluster.
-
System Information: You can view the following information from the various system information tabs:
-
Use the page to view information about core and memory.
-
Use the page to view information about all the core CPUs, which is represented in a table.
-
Use the page to view the graph of core CPUs and service CPUs. To view the graph of a specific core CPU, select a CPU from the CPUs drop-down list. To view a combined graph of all CPUs, select the CPU-All option from the CPUs drop-down list. Also, you can view the graph of service CPUs based on CPU selection from the CPUs drop-down list. The CPU-All option allows you to view the graph of all CPU of services.
-
Use the page to view information about the memory such as, used, free and total in a graphical and tabular format.
-
Use the page to view the CPU IO Statistics and Devices IO Statistics in a tabular format.
-
-
Services View: Use the Services View page to view information about the services traffic rate.
-
Network View: Use the Network View page to view information about statistics for a VNIC.
-
PNIC : Use the PNIC Statistic page to view information about statistics for a pNIC.
-
VNIC : Use the VNIC page to view information about statistics for a VNIC, Rx, and Tx.
-
Use the page to view information about VNIC received bytes and packets.
-
Use the page to view information about VNIC transmitted bytes and packets.
-
-
Resource Utilization: Use the Resource Utilization page to view statistical information about memory, disk, and CPU for a specific duration. You can choose a specific duration and get memory, disk, and CPU statistics for that time interval.
To view only the CPU graph, click the CPU tab. In the CPU screen, based on the services that has been selected, the associated CPU can be viewed in the CPU drop-down and the CPU graph updates accordingly.

Note
The CPU-ALL option in the CPU drop-down allows you to view graphs of all CPUs.
-
Cluster Redundancy: Use the Cluster Redundancy page to view the cluster migration report.
-
-
Configuration: The Configuration page consists of the following pages:
-
Repository: Use the Repository page to upload or remove an image and to view all available images.
-
Services: Use the Services page to create a new service or configure existing services, change the power mode of a service, and export a service. You can create a new service using a template or save a service as a template.

Note
You can view the CPU Map field for a specific CPU under Operational Data.
-
Service Template: Use the Services Templates page to view all available service templates and delete a service template.
-
pNICs: Use the pNICs page to view information about pNICs and port channels and to configure or unconfigure a pNIC as the management interface.
-
Port Channel: Use the Port Channel page to create a port channel, delete or edit a port channel, and to configure or unconfigure a port channel as the management interface.
-
SRIOV: Use the SRIOV page to enable, disable, configure, or unconfigure an SR-IOV interface.
-
System Settings: Use the System Settings page to enable or disable CPU pinning. You can enable or disable TPM configuration. When you change the status of TPM configuration, it shows a progress bar until the status gets completde from the REST API. After completion, the new configuration status appears as a selected value in the TPM configuration drop-down.
-
-
Administration: The Administration page consists of the following pages:
-
Password: Use the Password page to change the password for the admin user.
-
Host: Use the Host page to configure the host. You can configure the hostname, host domain name, DNS server, host IP, gateway IP, management MTU, management pNIC mode, and session idle timeout.
The host page includes the Hardware Configuration tab where you can only view all hardware information about the selected host. No operations such as add, delete, modify can be performed on the hardware configuration table.
-
NTP Server: Use the NTP Server page to configure an NTP server.
-
VNF Group: Use the VNF Group page to configure a VNF group name of a service.
-
User: Use the User page to create, modify, or delete a local user.
-
Cluster: Use the Cluster page to create, configure, and delete clusters.
-
NFS: Use the NFS page to create and configure NFS storage.
-
SNMP: Use the SNMP page to create and configure SNMP agent, communities, users, groups, and traps.
-
AAA: Use the AAA page to specify the AAA authentication mode and to create, modify, or delete a TACACS+ or RADIUS server.
-
IP Receive ACL: Use the IP Receive ACL page to configure the Access Control List (ACL) access for the management interface. You can specify the source network IP address, service type, priority, and action for the packets received from the specified source network.
-
Syslog: Use the Syslog page to configure multiple syslog servers. You can send internal log messages to multiple remote syslog server on TCP and UDP ports, or only on UDP port.
-
-
Debug: Use this page to view and download log files, core files, and TCP dump files.
Uploading Service Images Using the Cisco CSP Web Interface
Before you begin
Be sure to download the service image to your local machine or a location on your local network that is accessible to your Cisco CSP.
Procedure
| Step 1 |
Click the Configuration tab and then choose Repository. |
||
| Step 2 |
On the Repository Files page, click the add button (+). |
||
| Step 3 |
Click Browse. |
||
| Step 4 |
Navigate to the service image, select a service image, and click Open. |
||
| Step 5 |
Click Upload. After the service image is uploaded, the image name and other relevant information are displayed in the Repository Files table.
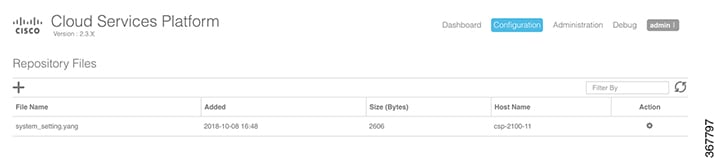 |
Creating a Service Instance
Procedure
| Step 1 |
Click the Configuration tab and then choose Services. |
||||
| Step 2 |
On the Service page, click the add (+) button. The Create Service page is displayed. |
||||
| Step 3 |
In the Name field, enter a name for the service. |
||||
| Step 4 |
From the Target Host Name drop-down list, choose the target host. |
||||
| Step 5 |
(Optional) In the VNF Management IP field, enter the VNF management IP address to be used in the service.
|
||||
| Step 6 |
From the Image Name drop-down list, choose an image file for the service. Starting with Release 2.7.0, you can export the service only in the zip file format (.zip). When you import the service through the zip file, the service page is automatically populated with the service configuration along with the UUID. You can choose to retain the existing UUID or click the trash icon to delete the existing UUID. A new UUID is generated if you delete the existing UUID.
Depending on the type of image selected, additional fields are displayed. If your service requires additional information, as is the case with Cisco VSM and Cisco VSG services, you must enter this information in the Additional Image Questionnaires section. For details about the additional information that your service requires, see the documentation for that service. |
||||
| Step 7 |
(Optional) Click Day Zero Config and in the Day Zero Config dialog box, do the following:
|
||||
| Step 8 |
(Optional) In the Number of Cores field, specify the number of cores. Make sure that the new value does not exceed the available resources. |
||||
| Step 9 |
(Optional) If you want to resize the disk, check the Do you want to resize disk? check box. This option is available only when a QCOW2 image is selected in the Image Name field. |
||||
| Step 10 |
(Optional) In the Disk Space (GB) field, specify the disk space. Make sure that the new value does not exceed the available resources. This field is not editable when a QCOW2 image is selected in the Image Name field and the Do you want to resize disk? check box is unchecked. |
||||
| Step 11 |
(Optional) In the RAM (MB) field, specify the RAM. Make sure that the new value does not exceed the available resources. |
||||
| Step 12 |
(Optional) To deploy the service on an NFS storage, check NFS Storage, and then select an NFS storage from the NFS drop-down list. |
||||
| Step 13 |
(Optional) To deploy the service on the distributed storage network, check Gluster. |
||||
| Step 14 |
(Optional) In the Disk Type field, specify the disk type. Valid choices are IDE or VIRTIO. |
||||
| Step 15 |
Click VNIC and in the VNIC Configuration dialog box, do the following: To add more vNICs, click VNIC and repeat all tasks described in this step. |
||||
| Step 16 |
(Optional) Click Storage and in the Storage Configuration dialog box, do the following: To add more storage, click Storage and repeat all tasks described this step. |
||||
| Step 17 |
(Optional) In the VNC Port field, enter a VNC port for the service. Valid range is from 8721 to 8784. |
||||
| Step 18 |
(Optional) In the VNC Password field, enter a password and then enter the same password in the Confirm VNC Password field.
|
||||
| Step 19 |
Click Serial Port and in the Serial Port dialog box, do the following:
To add more serial ports, click Serial Port and repeat all tasks described in this step. |
||||
| Step 20 |
(Optional) If you are configuring the services in redundancy, select the HA Service Configuration check box. The Cisco CSPs must be in the cluster mode. Do the following: |
||||
| Step 21 |
Click Deploy. The Service Test Creation dialog box is displayed indicating that the service is available. |
Verifying Your Service Instance
Make sure that your service instance is up and running.
Procedure
| Step 1 |
Click the Configuration tab and then choose Services. The Service table shows the current status of services. |
| Step 2 |
Find your service instance in the Service Name column, and check that the state is deployed and the power status is on. |
Configuring Multiple Syslog Servers
Ensure that CSP service instance is up and running.
Procedure
| Step 1 |
Click the Administration tab, and then select Syslog. |
| Step 2 |
On the Syslog page, you can perform either of the following:
|
| Step 3 |
If you select UDP as the mechanism to send log messages, in the UDP Port field, specify the UDP port values of the remote syslog server. |
| Step 4 |
If you do not select UDP as the mechanism to send log messages, specify both TCP and UDP port values of the remote syslog server. |
| Step 5 |
To add a remote syslog server, click the + button. |
| Step 6 |
In the Host field, specify the IPv4 IP address or host name of the remote syslog server, and then click Add. The newly added host is displayed in a table.
|
| Step 7 |
To add multiple syslog servers, repeat step 5 through step 6. You can add up to eight syslog servers. |
 Feedback
Feedback