- Preface
- Overview
- Overview of the VNMC GUI
- Configuring Primary Authentication
- Configuring RBAC
- Configuring Trusted Points
- Configuring VNMC Profiles
- Configuring VM Managers
- Configuring Tenants
- Configuring Service Policies and Profiles
- Configuring Device Policies and Profiles
- Configuring Managed Resources
- Configuring Administrative Operations
- Index
Cisco Virtual Network Management Center GUI Configuration Guide, Release 2.0
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
Chapter: Configuring Managed Resources
Configuring Managed Resources
This section includes the following topics:
- Resource Management
- Resource Manager
- Virtual Machines
- Virtual Security Gateways
- ASA 1000V Cloud Firewalls
- Managing Compute Firewalls
- Managing Edge Firewalls
- Verifying ASA 1000V, VSG, and VSM Registration
- Examining Fault Details
- Launching ASDM from VNMC
- Managing Pools
Resource Management
You manage VMs by discovering those VMs that have at least one network interface configured with a Nexus 1000V port profile.
Resource Manager
Resource Manager manages logical edge and compute firewalls and their association with ASA 1000Vs and VSGs, respectively. When an edge firewall is associated with an ASA 1000V, the device configuration profile information (defined by the edge firewall) is pushed to the ASA 1000V which, in turn, triggers the ASA 1000V to download the security profiles and policies from Policy Manager.
- Maintaining an inventory of ASA 1000Vs, VSGs, and VSMs.
- With user input, defining compute firewalls and associating them with VSGs for provisioning.
- With user input, defining edge firewalls and associating them with ASA 1000Vs for provisioning.
- Integrating with VMware vCenter instances to retrieve VM attributes.
Virtual Machines
Virtualization allows you to create multiple VMs that run in isolation, side by side on the same physical machine. Each VM has virtual RAM, a virtual CPU and NIC, and an operating system and applications. Because of virtualization, the operating system sees a consistent set of hardware regardless of the actual physical hardware components.
VMs are encapsulated in files for rapid saving, copying, and provisioning, which means that you can move full systems, configured applications, operating systems, BIOS, and virtual hardware within seconds, from one physical server to another. Encapsulated files allow for zero-downtime maintenance and continuous workload consolidation.
Instances of Cisco VNMC are installed on VMs.
Virtual Security Gateways
- Receive traffic from Virtual Network Service Data Path (vPath). For every new flow, the vPath component encapsulates the first packet and sends it to a VSG as specified in the Nexus 1000V port profiles. It assumes that the VSG is Layer 2 adjacent to vPath. The mechanism used for communication between vPath and the VSG is similar to VEM and Nexus 1000V VSM communication on a packet VLAN.
- Perform application fix-up processing such as FTP, TFTP, and RSH.
- Evaluate policies by inspecting the packets sent by vPath using network, VM, and custom attributes.
- Transmit the policy evaluation results to vPath.
Each vPath component maintains a flow table for caching VSG policy evaluation results.
ASA 1000V Cloud Firewalls
In VNMC, edge firewall objects are associated to an ASA 1000V instance. After association, all applicable profile types for the ASA 1000V device type are pushed to the ASA 1000V instance. All edge profile objects that are created at the same organization level as the edge firewall object are pushed to the device.
Managing Compute Firewalls
VNMC enables you to add, edit, and delete compute firewalls. In addition, you can assign a VSG to compute firewall, thereby placing the VSG in service. The following topics describe these activities in more detail.
- Adding a Compute Firewall
- Editing a Compute Firewall
- Deleting a Compute Firewall
- Assigning a VSG
- Unassigning a VSG
Adding a Compute Firewall
This procedure describes how to add a compute firewall to VNMC so that you can assign it to a VSG, and thereby place the VSG in service.
When you add a new compute firewall, the firewall data IP address can be the same as the data IP address of an existing compute firewall in VNMC as long as the firewalls have different organizational paths. That is, as long as the firewalls do not reside in the same organization, including parent and child organizations.
 Note |
We recommend that you add the compute firewall at the tenant level or below, and not at the root level. |
Editing a Compute Firewall
You can edit existing compute firewalls as needed.
| Step 1 | In the Resource Management tab, choose Managed Resources > root > tenant > Compute Firewalls > where tenant is the required tenant. |
| Step 2 | In the General tab, select the compute firewall you want to edit, then click Edit. |
| Step 3 | In the Edit dialog box, modify the following fields as appropriate, using the information in the following tables, then click OK. |
General Tab
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Compute firewall name (read-only). |
Description |
Brief firewall description. |
Pool Name |
The pool assigned to the compute firewall, if any. Only one pool can be assigned to a compute firewall at a time. To change the pool, click Assign Pool. |
States |
|
Config State |
One of the following compute firewall configuration states: not-applied, applying, failed-to-apply, or applied. |
Association State |
One of the following compute firewall association states: unassociated, associating, associated, disassociating, or failed. |
Faults Associated with Firewall |
Displays faults associated with the firewall. This information is available only if the compute firewall has been associated with a VSG. |
View Device Faults |
Displays faults associated with the device. This information is available only if the compute firewall has been associated with a VSG. |
Firewall Settings |
|
Device Profile |
Device profile associated with the firewall. To change the device profile, click Select, then choose the desired profile. |
Management Hostname |
Management hostname for the compute firewall. |
Data IP Address |
Compute firewall data IP address. The vPath component running on each VEM uses the data IP address to determine the MAC address of the VSG (via ARP). Once the VSG MAC address has been resolved, vPath can communicate with the VSG using MAC in MAC encapsulation. Subsequently for each new flow initiated by a VM, vPath sends the first packet of the flow to the VSG for policy evaluation. vPath caches the VSG policy decision in a flow table. This is the same IP address which is configured in the vservice CLI command on the Nexus 1000v port profile. |
Data IP Subnet |
Firewall data IP subnet mask. |
VSG Details This information is available only if the compute firewall has been associated with a VSG. |
|
Task |
Click to open the Edit VSG dialog box. |
VSG Service ID |
Internal identification number of the VSG. |
VSG Mgmt IP |
VSG management IP address. |
HA Role |
High availability (HA) role of the VSG: HA or standalone mode. |
Association |
Association state of the VSG: unassociated, associating, associated, disassociating, or failed. |
Reachable |
Whether or not the VSG can be reached. |
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Show Resolved Policies |
Click to view and optionally modify the security policies applied to the compute firewall. This option is available only if the selected profile has been configured in the corresponding VSM port profile. |
Properties |
Displays the properties of the port profile associated with the compute firewall. |
Compute Security Profile |
Name of the compute firewall security profile. |
Port Profile |
Name of the associated port profile. |
Org |
Distinguished name (DN) of the organization. |
VSG Data IP |
VSG data IP address. |
Config State |
VSG configuration state. |
Deleting a Compute Firewall
| Step 1 | Choose Resource Management > Managed Resources > root > tenant > Compute Firewalls. |
| Step 2 | In the General tab, select the compute firewall you want to delete, then click Delete. |
| Step 3 | When prompted, confirm the deletion. |
Assigning a VSG
- Register the VSG with VNMC. For information on registering a VSG with VNMC, see the Cisco Virtual Security Gateway, Release 4.2(1)VSG1(4.1) and Cisco Virtual Network Management Center, Release 2.0 Installation and Upgrade Guide.
- Add a compute firewall toVNMC. For more information, see Adding a Compute Firewall.
| Step 1 | Choose Resource Management > Managed Resources > root > tenant > Compute Firewalls. |
| Step 2 | In the General tab, select the compute firewall to which you want to assign a VSG, then click Assign VSG. |
| Step 3 | In the Assign VSG dialog box, select the desired IP address from the VSG Management IP drop-down list, then click OK. |
Unassigning a VSG
| Step 1 | Choose Resource Management > Managed Resources > root > tenant > Compute Firewalls. |
| Step 2 | In the Compute Firewalls table, select the firewall with the VSG you want to unassign. |
| Step 3 | Click Unassign VSG/Pool. |
| Step 4 | In the Confirm dialog box, click Yes. |
Managing Edge Firewalls
Managing edge firewalls involves adding edge firewalls to VNMC, configuring the edge firewall data interfaces, and then assigning an ASA 1000V to the edge firewall to place the ASA 1000V in service. The following topics describe these activities in more detail.
Adding an Edge Firewall
This procedure describes how to add an edge firewall to VNMC so that you can assign it to an ASA 1000V instance, and thereby place the ASA 1000V in service.
When you add a new edge firewall, the firewall data IP address identified as the primary IP address of the inside data interface can be the same as the IP address of an inside data interface for an existing edge firewall in VNMC long as the firewalls have different organizational paths. That is, as long as the edge firewalls do not reside in the same organization, including parent and child organizations.
 Note |
We recommend that you add edge firewalls at the tenant level or lower, and not at the root level. |
| Step 1 | Choose Resource Management > Managed Resources > root > tenant > Edge Firewalls. |
| Step 2 | Click Add Edge Firewall. |
| Step 3 | In the Add Edge Firewall dialog box, specify the information as described in Add Edge Firewall Dialog Box, then click OK. |
What to Do Next
After you add the edge firewall, assign an ASA 1000V to it so that you can manage the ASA 1000V using VNMC. For more information, see Assigning an ASA 1000V.
Add Edge Firewall Dialog Box
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Edge firewall name. |
Description |
Brief description of the edge firewall. |
HA Mode |
High Availability (HA) role of the edge firewall: HA or standalone. |
Device Profile |
|
Edge Device Profile |
|
Adding a Data Interface
When you add an edge firewall, you also need to specify inside and outside interfaces for data communications.
| Step 1 | Choose Resource Management > Managed Resources > root > tenant > Edge Firewalls. |
| Step 2 | In the Edge Firewalls pane, select the edge firewall to add or modify data interfaces, then click Edit. |
| Step 3 | In the Edit Edge Firewall dialog box, click Add Data Interface. |
| Step 4 | For each interface you add, enter the information as described in Fields in the Add Data Interface Dialog Box, then click OK. |
Add Data Interface Dialog Box
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Interface name. |
Description |
Brief interface description. |
Role |
Whether the interface is for inside or outside communications. |
DHCP |
Available for outside interfaces only. Check the Enable DHCP check box to enable DHCP on the interface. |
Primary IP Address |
IP address for this interface. |
Secondary IP Address |
Available if the edge firewall is in High Availability (HA) Mode. Secondary IP address for this interface. |
Subnet Mask |
Mask to apply to the IP address. |
Edge Security Profile |
Available for outside interfaces only. To apply an edge security profile: |
Assigning an ASA 1000V
- Register the ASA 1000V to VNMC. For more information, see the Cisco Virtual Network Management Center 2.0 Quick Start Guide.
- Add an edge firewall to VNMC. For more information, see Adding an Edge Firewall.
| Step 1 | Choose Resource Management > Managed Resources > root > tenant > Edge Firewalls > edge-firewall. |
| Step 2 | Click Assign ASA 1000V. |
| Step 3 | In the Assign ASA 1000V dialog box, choose the required ASA 1000V from the drop-down list, then click OK. |
Unassigning an ASA 1000V
If required you can unassign an ASA 1000V from an edge firewall.
| Step 1 | Choose Resource Management > Managed Resources > root > tenant > Edge Firewalls > edge-firewall. |
| Step 2 | Click Unassign ASA 1000V/Pool. |
| Step 3 | In the confirmation dialog box, click OK. |
Verifying ASA 1000V, VSG, and VSM Registration
VNMC enables you to verify that ASA 1000Vs, VSGs, and VSMs are successfully registered.
| Step 1 | Choose Administration > Service Registry > Clients. |
| Step 2 | In the Clients table, confirm that the Oper State column contains registered for the ASA 1000V, VSG, and VSM entries. |
Examining Fault Details
VNMC enables you to examine the policy and configuration errors that prevent the successful application of a policy. For example, if you apply a policy to an edge firewall and the Config State field displays the Failed-to-Apply state, you can examine the configuration errors to identify the issue and resolve the problem.
The following topics describe these features in more detail.
Examining Faults and Configuration Errors for Edge Firewalls
VNMC enables you to view the faults and events associated with edge firewalls, and their policies and configurations.
| Step 1 | Choose Resource Management > Managed Resources > root > tenant > Edge Firewalls > edge-firewall. |
| Step 2 | In the General tab, review the configuration, association, and fault information in the States area. |
| Step 3 |
If faults are indicated, view fault details as follows:
|
| Step 4 |
To view more information, double-click an entry in any of the tables. In the Faults table in the new browser window, you can click Refresh Now to view updated information. |
Examining Faults for Compute Firewalls
VNMC enables you to examine faults and events for compute firewalls.
| Step 1 | Choose Resource Management > Managed Resources > root > tenant > Compute Firewalls > compute-firewall. |
| Step 2 | In the General tab, review the configuration, association, and fault information in the States area. |
| Step 3 |
If faults are indicated, view fault details as follows:
|
| Step 4 | To view more information, double-click an entry in any of the tables. |
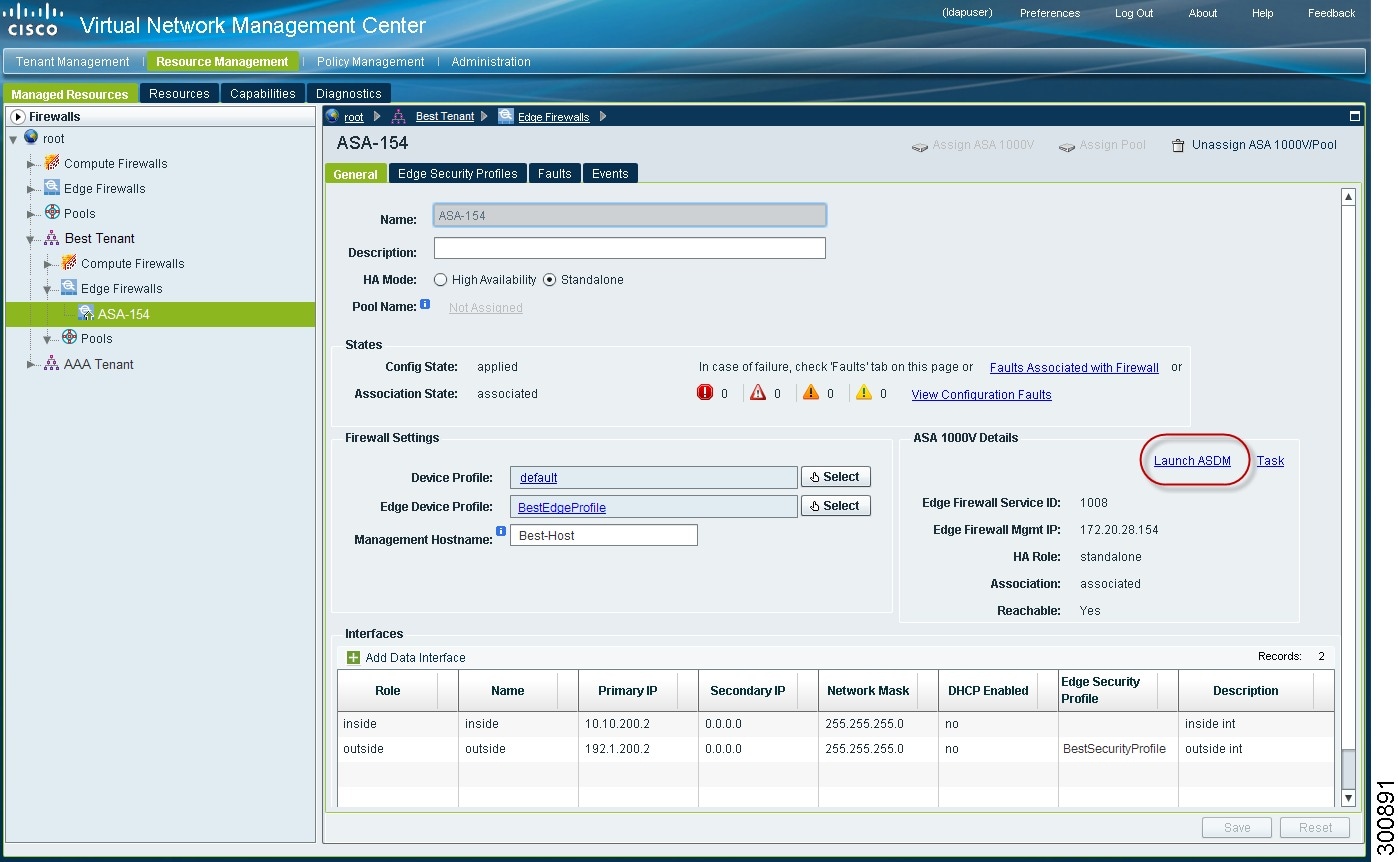
Launching ASDM from VNMC
VNMC enables you to launch Cisco Adaptive Security Device Manager (ASDM) as a Web Start application on your desktop.
You can set up ASDM to be used by the ASA 1000V when it is configured for either VNMC management mode or ASDM management mode. When the ASA 1000V is configured to use VNMC management mode, you can use ASDM to monitor the status of the ASA 1000V, but you cannot use it to manage configurations.
Before You Begin
-
Do one of the following: - If you have not already deployed the ASA 1000V OVA, do so now; during the deployment, provide the ASDM client IP address.
-
If you have already deployed the ASA 1000V OVA, apply the following configuration by using the VM console in the vSphere client: -
Add a route on the management interface to the ASDM client subnet by issuing the following command: where interface is the management interface to the ASDM client subnet, ip is the IP address of the host that accesses ASDM, subnet is the ASDM client subnet, and next-hop-ip is the IP address of the gateway.ASA1000V(config)# route interface ip subnet next-hop-ip

Note
Perform this step only if the next hop gateway IP address was not specified when deploying the ASA 1000V. -
Allow HTTP access via the management interface for the ASDM client subnet by entering the following command: where ip is the IP address of the host that accesses ASDM, and interface is the ASDM client interface.ASA1000V(config)# http ip subnet interface

Note
Perform this step only if the ASDM client IP address was not specified when deploying the ASA 1000V.
-
-
Confirm the following: - Assign the edge firewall to an ASA 1000V instance. If the edge firewall is not assigned to an ASA 1000V instance, the ASDM options are not displayed in the UI.
- Confirm that your system is configured to run downloaded Java Web Start applications.
For more information about configuring ASDM, see the Cisco ASA 1000V Cloud Firewall Getting Started Guide.
| Step 1 | Choose Resource Management > Managed Resources > root > tenant > Edge Firewalls > edge-firewall where edge-firewall is the edge firewall for which you want to launch ASDM. | ||
| Step 2 |
In the General tab, click Launch ASDM in the ASA 1000V Details area. See Example Screens for ASDM. The ASDM Launch screen opens in a new browser window. |
||
| Step 3 |
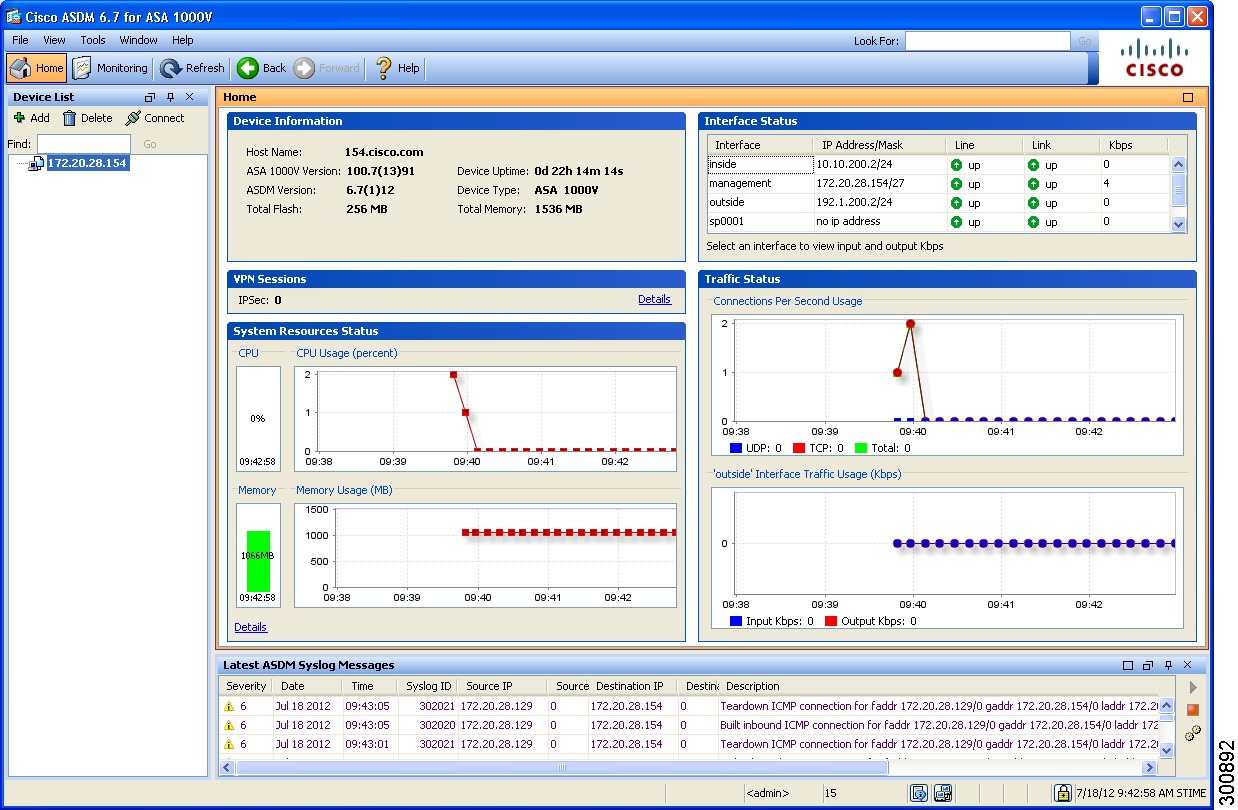
In the ASDM Launch screen, click Run ASDM.
ASDM opens in a new window on your desktop as shown in Example Screens for ASDM. |
Example Screens for ASDM
Managing Pools
Adding a Pool
| Step 1 | Choose Resource Management > Managed Resources > root > tenant > Pools. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Step 2 | In the General tab, click Add Pool. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Step 3 |
In the Add Pool dialog box, enter the information as described in the following table, then click OK:
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Step 4 | (Optional) Assign pool members to the pool by performing the following tasks: | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Step 5 | Click OK. | ||||||||||||||||||||
Assigning a Pool
After you have created a pool, you can assign it to a compute or edge firewall.
| Step 1 | Choose Resource Management > Managed Resources > root > Compute Firewalls or Edge Firewalls. |
| Step 2 | In the list of firewalls, select the required firewall, then click Assign Pool. |
| Step 3 | In the Assign Pool dialog box, either choose a pool from the Name drop-down list or click Add Pool to add a new pool. |
| Step 4 | Click OK. |
Editing a Pool
| Step 1 | Choose Resource Management > Managed Resources > root > tenant > Pools. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Step 2 | In the General tab, select the pool that you want to edit, then click Edit. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Step 3 |
In the Edit Pool dialog box, edit the information as required by using the information in the following table, then click OK.
|
||||||||||||||||||||
Unassigning a Pool
If required, you can unassign a pool from a compute or edge firewall.
| Step 1 | Choose Resource Management > Managed Resources > root > Compute Firewalls or Edge Firewalls. |
| Step 2 | In the list of firewalls, select the required firewall, then click Unassign object/Pool where object is either ASA 1000V or VSG, depending on whether you selected an edge or compute firewall. |
| Step 3 | When prompted, confirm the deletion. |
Deleting a Pool
| Step 1 | Choose Resource Management > Managed Resources > root > tenant > Pools. |
| Step 2 | In the General tab, select the pool you want to delete, then click Delete. |
| Step 3 | When prompted, confirm the deletion. |
 Feedback
Feedback