Cisco Service Control Application for Broadband Reference Guide, Release 3.5.5
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- Updated:
- February 6, 2011
Chapter: SCA BB Proprietary MIB Reference
SCA BB Proprietary MIB Reference
Introduction
This chapter describes the proprietary CISCO-SCAS-BB Management Information Base (MIB) supported by the Service Control Engine (SCE) platform.
A MIB is a database of objects that can be monitored by a network management system (NMS). The SCE platform supports both the standard MIB-II and the proprietary Cisco Service Control Enterprise MIB. The CISCO-SCAS-BB MIB is the part of the Service Control Enterprise MIB that enables the external management system to monitor counters and metrics specific to the Cisco Service Control Application for Broadband (SCA BB).
•![]() Information About SNMP Configuration and Management
Information About SNMP Configuration and Management
•![]() Information About the Service Control Enterprise MIB
Information About the Service Control Enterprise MIB
•![]() Information About the CISCO-SCAS-BB MIB
Information About the CISCO-SCAS-BB MIB
•![]() Guidelines for Using the CISCO-SCAS-BB MIB
Guidelines for Using the CISCO-SCAS-BB MIB
Information About SNMP Configuration and Management
This section explains how to configure the SNMP interface, and how to load the MIB files.
•![]() Configuring the SNMP Interface on the SCE Platform
Configuring the SNMP Interface on the SCE Platform
•![]() The Order to Load the MIB Files
The Order to Load the MIB Files
Configuring the SNMP Interface on the SCE Platform
Before using the SNMP interface:
•![]() Enable SNMP access on the SCE platform (by default, SNMP access is disabled).
Enable SNMP access on the SCE platform (by default, SNMP access is disabled).
•![]() Set the values of SNMP parameters:
Set the values of SNMP parameters:
–![]() The community string to be used for client authentication.
The community string to be used for client authentication.
–![]() (Optional, recommended as a security measure) An access-list (ACL) of IP addresses. This limits access to SNMP information to a set of known locations. You can define a different community string for each ACL.
(Optional, recommended as a security measure) An access-list (ACL) of IP addresses. This limits access to SNMP information to a set of known locations. You can define a different community string for each ACL.
–![]() The destination IP address to which the SCE platform will send SNMP traps.
The destination IP address to which the SCE platform will send SNMP traps.

Note ![]() You can enable or disable specific traps.
You can enable or disable specific traps.
Related Info
For more information about SNMP configuration, refer to the following revalent document:
•![]() "Configuring and Managing the SNMP Interface" section in the "Configuring the Management Interface and Security" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide.
"Configuring and Managing the SNMP Interface" section in the "Configuring the Management Interface and Security" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide.
•![]() "Configuring and Managing the SNMP Interface" section in the "Configuring the Management Interface and Security" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 GBE Software Configuration Guide.
"Configuring and Managing the SNMP Interface" section in the "Configuring the Management Interface and Security" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 GBE Software Configuration Guide.
Required MIB Files
To access the SNMP variables on the SCE platform, you must load the SNMP browser with a standard MIB file (SNMPv2.mib) and proprietary Cisco MIB files (pcube.mib, pcubeSEMib.mib, and PCubeEngageMib.mib).

Note ![]() You can download the CISCO-SCAS-BB MIB file (PCubeEngageMib.mib) and other MIB files (pcube.mib and pcubeSEMib.mib) from ftp://ftp.cisco.com/pub/mibs/.
You can download the CISCO-SCAS-BB MIB file (PCubeEngageMib.mib) and other MIB files (pcube.mib and pcubeSEMib.mib) from ftp://ftp.cisco.com/pub/mibs/.
The Order to Load the MIB Files
The SCA BB proprietary MIB uses definitions that are defined in other MIBs, such as SNMPv2.mib and pcube.mib.
This means that the order in which the MIBs are loaded is important; to avoid errors, the MIBs must be loaded in the correct order.
Load the MIBs in the following order:
1. ![]() SNMPv2.mib
SNMPv2.mib
2. ![]() pcube.mib
pcube.mib
3. ![]() pcubeSEMib.mib
pcubeSEMib.mib
4. ![]() PCubeEngageMib.mib
PCubeEngageMib.mib
Information About the Service Control Enterprise MIB
The Service Control Enterprise MIB includes four main groups: Products, Modules, Management, and Workgroup. The Service Control enterprise tree structure is defined in a MIB file named pcube.mib.
•![]() The pcubeProducts subtree contains the sysObjectIDs of the Service Control products.
The pcubeProducts subtree contains the sysObjectIDs of the Service Control products.
Service Control product sysObjectIDs are defined in a MIB file named Pcube-Products-MIB.
•![]() The pcubeModules subtree provides a root object identifier from which MIB modules are defined.
The pcubeModules subtree provides a root object identifier from which MIB modules are defined.
•![]() The pcubeMgmt subtree contains the configuration copy MIB:
The pcubeMgmt subtree contains the configuration copy MIB:
–![]() pcubeConfigCopyMib enables saving the running configuration of Cisco products. This MIB is documented in the "Cisco Service Control MIBs" appendix of the Cisco SCE8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide or in the "Cisco Service Control MIBs" appendix of the Cisco SCE8000 GBE Software Configuration Guide.
pcubeConfigCopyMib enables saving the running configuration of Cisco products. This MIB is documented in the "Cisco Service Control MIBs" appendix of the Cisco SCE8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide or in the "Cisco Service Control MIBs" appendix of the Cisco SCE8000 GBE Software Configuration Guide.
•![]() The pcubeWorkgroup subtree contains:
The pcubeWorkgroup subtree contains:
–![]() pcubeSeEvents and pcubeSEObjs — pcubeSeMib, the SCE MIB, is the main MIB for the Service Control products and provides a wide variety of configuration and runtime statistics. This MIB is also documented in the "Cisco Service Control MIBs" appendix of the Cisco SCE8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide or in the "Cisco Service Control MIBs" appendix of the Cisco SCE8000 GBE Software Configuration Guide.
pcubeSeEvents and pcubeSEObjs — pcubeSeMib, the SCE MIB, is the main MIB for the Service Control products and provides a wide variety of configuration and runtime statistics. This MIB is also documented in the "Cisco Service Control MIBs" appendix of the Cisco SCE8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide or in the "Cisco Service Control MIBs" appendix of the Cisco SCE8000 GBE Software Configuration Guide.
–![]() pcubeEngageObjs — The CISCO-SCAS-BB MIB provides configuration and runtime status for SCA BB, and is described in the following section.
pcubeEngageObjs — The CISCO-SCAS-BB MIB provides configuration and runtime status for SCA BB, and is described in the following section.
Figure 6-1 illustrates the Service Control Enterprise MIB structure.
Figure 6-1 Service Control Enterprise MIB Structure
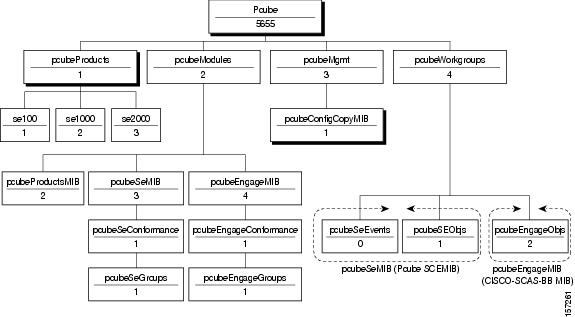

Note ![]() The following object identifier represents the Service Control Enterprise MIB: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5655 or so.org.dod.internet.private.enterprise.pcube.
The following object identifier represents the Service Control Enterprise MIB: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5655 or so.org.dod.internet.private.enterprise.pcube.
Information About the CISCO-SCAS-BB MIB
The CISCO-SCAS-BB MIB provides access to service usage counters through the SNMP interface. Using this MIB, a network administrator can collect usage information per service at link, package, or subscriber granularity.
The CISCO-SCAS-BB MIB is defined in the file PCubeEngageMib.mib.
The MIB is documented in the remainder of this chapter.
•![]() pcubeEngageObjs (pcubeWorkgroup 2)
pcubeEngageObjs (pcubeWorkgroup 2)
Using this Reference
This reference is divided into sections according to the MIB object groups. For each object, information is presented in the following format:
<Description of the object>
Access |
access control associated with the object |
Units |
unit of measurement used for the object |
Index
{Indexes used by the table}
Syntax
OBJECT DATA TYPE {
The general format of the object
}
pcubeEngageObjs (pcubeWorkgroup 2)
The pcubeEngageObjs objects provide current information about packages, service, and subscribers.
•![]() Service Group: serviceGrp (pcubeEngageObjs 1)
Service Group: serviceGrp (pcubeEngageObjs 1)
•![]() Link Group: linkGrp (pcubeEngageObjs 2)
Link Group: linkGrp (pcubeEngageObjs 2)
•![]() Package Group: packageGrp (pcubeEngageObjs 3)
Package Group: packageGrp (pcubeEngageObjs 3)
•![]() Subscriber Group: subscriberGrp (pcubeEngageObjs 4)
Subscriber Group: subscriberGrp (pcubeEngageObjs 4)
•![]() Service Counter Group: serviceCounterGrp (pcubeEngageObjs 5)
Service Counter Group: serviceCounterGrp (pcubeEngageObjs 5)
pcubeEngageObjs Objects
This table lists the pcubeEngageObjs objects. Each object consists of a number of subordinate object types, which are summarized in the following section.
serviceGrp |
{pcubeEngageObjs 1} |
linkGrp |
{pcubeEngageObjs 2} |
packageGrp |
{pcubeEngageObjs 3} |
subscriberGrp |
{pcubeEngageObjs 4} |
serviceCounterGrp |
{pcubeEngageObjs 5} |
pcubeEngageObjs Structure
This is a summary of the structure of pcubeEngageObjs. Note the table structure for objects that may have multiple entries.
serviceGrp
serviceTable-deprecated
linkGrp
linkServiceUsageTable
linkServiceUsageEntry
linkServiceUsageUpVolume
linkServiceUsageDownVolume
linkServiceUsageNumSessions
linkServiceUsageDuration
linkServiceUsageConcurrentSessions
linkServiceUsageActiveSubscribers
linkServiceUpDroppedPackets
linkServiceDownDroppedPackets
linkServiceUpDroppedBytes
linkServiceDownDroppedBytes
packageGrp
packageCounterTable
packageCounterEntry
packageCounterIndex
packageCounterStatus
packageCounterName
packageCounterActiveSubscribers
packageServiceUsageTable
packageServiceUsageEntry
packageServiceUsageUpVolume
packageServiceUsageDownVolume
packageServiceUsageNumSessions
packageServiceUsageDuration
packageServiceUsageConcurrentSessions
packageServiceUsageActiveSubscribers
packageServiceUpDroppedPackets
packageServiceDownDroppedPackets
packageServiceUpDroppedBytes
packageServiceDownDroppedBytes
subscriberGrp
subscribersTable
subscriberEntry
subscriberPackageIndex
subscriberServiceUsageTable
subscriberServiceUsageEntry
subscriberServiceUsageUpVolume
subscriberServiceUsageDownVolume
subscriberServiceUsageNumSessions
subscriberServiceUsageDuration
serviceCounterGrp
globalScopeServiceCounterTable
globalScopeServiceCounterEntry
globalScopeServiceCounterIndex
globalScopeServiceCounterStatus
globalScopeServiceCounterName
subscriberScopeServiceCounterTable
subscriberScopeServiceCounterEntry
subscriberScopeServiceCounterIndex
subscriberScopeServiceCounterStatus
subscriberScopeServiceCounterName
Service Group: serviceGrp (pcubeEngageObjs 1)
The Service group is deprecated. Use the Service Counter group.
serviceTable (serviceGrp 1)
Deprecated—Use the tables in the Service Counter group.
Access |
not-accessible |
Syntax
Counter32
Link Group: linkGrp (pcubeEngageObjs 2)
The Link Service group provides usage information per link for each global-scope service usage counter (for example, traffic statistics of a service for all subscribers using a particular link).
•![]() linkServiceUsageTable (linkGrp 1)
linkServiceUsageTable (linkGrp 1)
•![]() linkServiceUsageEntry (linkServiceUsageTable 1)
linkServiceUsageEntry (linkServiceUsageTable 1)
•![]() linkServiceUsageUpVolume (linkServiceUsageEntry 1)
linkServiceUsageUpVolume (linkServiceUsageEntry 1)
•![]() linkServiceUsageDownVolume (linkServiceUsageEntry 2)
linkServiceUsageDownVolume (linkServiceUsageEntry 2)
•![]() linkServiceUsageNumSessions (linkServiceUsageEntry 3)
linkServiceUsageNumSessions (linkServiceUsageEntry 3)
•![]() linkServiceUsageDuration (linkServiceUsageEntry 4)
linkServiceUsageDuration (linkServiceUsageEntry 4)
•![]() linkServiceUsageConcurrentSessions (linkServiceUsageEntry 5)
linkServiceUsageConcurrentSessions (linkServiceUsageEntry 5)
•![]() linkServiceUsageActiveSubscribers (linkServiceUsageEntry 6)
linkServiceUsageActiveSubscribers (linkServiceUsageEntry 6)
•![]() linkServiceUpDroppedPackets (linkServiceUsageEntry 7)
linkServiceUpDroppedPackets (linkServiceUsageEntry 7)
•![]() linkServiceDownDroppedPackets (linkServiceUsageEntry 8)
linkServiceDownDroppedPackets (linkServiceUsageEntry 8)
•![]() linkServiceUpDroppedBytes (linkServiceUsageEntry 9)
linkServiceUpDroppedBytes (linkServiceUsageEntry 9)
•![]() linkServiceDownDroppedBytes (linkServiceUsageEntry 10)
linkServiceDownDroppedBytes (linkServiceUsageEntry 10)
linkServiceUsageTable (linkGrp 1)
The Link Service Usage table provides usage information per link for each global-scope service usage counter.
Access |
not-accessible |
Syntax
SEQUENCE OF linkServiceUsageEntry
linkServiceUsageEntry (linkServiceUsageTable 1)
A Link Service Usage table entry containing parameters defining resource usage of one link for services included in one global-scope service usage counter.
Access |
not-accessible |
Index
{linkModuleIndex, linkIndex, globalScopeServiceCounterIndex}
Syntax
SEQUENCE{
linkServiceUsageUpVolume
linkServiceUsageDownVolume
linkServiceUsageNumSessions
linkServiceUsageDuration
linkServiceUsageConcurrentSessions
linkServiceUsageActiveSubscribers
linkServiceUpDroppedPackets
linkServiceDownDroppedPackets
linkServiceUpDroppedBytes
linkServiceDownDroppedBytes
}
linkServiceUsageUpVolume (linkServiceUsageEntry 1)
The upstream volume of services in this service usage counter carried over the link.
Access |
read-only |
Units |
kilobytes |
Syntax
Counter32

Note ![]() Although volume counters on the SCE platform hold 32-bit integers, CISCO-SCAS-BB MIB volume counters wraparound (turn back to zero) when the maximum 29-bit integer value (0x1FFFFFFF) is reached.
Although volume counters on the SCE platform hold 32-bit integers, CISCO-SCAS-BB MIB volume counters wraparound (turn back to zero) when the maximum 29-bit integer value (0x1FFFFFFF) is reached.
linkServiceUsageDownVolume (linkServiceUsageEntry 2)
The downstream volume of services in this service usage counter carried over the link.
Access |
read-only |
Units |
kilobytes |
Syntax
Counter32

Note ![]() Although volume counters on the SCE platform hold 32-bit integers, CISCO-SCAS-BB MIB volume counters wraparound (turn back to zero) when the maximum 29-bit integer value (0x1FFFFFFF) is reached.
Although volume counters on the SCE platform hold 32-bit integers, CISCO-SCAS-BB MIB volume counters wraparound (turn back to zero) when the maximum 29-bit integer value (0x1FFFFFFF) is reached.
linkServiceUsageNumSessions (linkServiceUsageEntry 3)
The number of sessions of services in this service usage counter carried over the link.
Access |
read-only |
Units |
Sessions |
Syntax
Counter32
linkServiceUsageDuration (linkServiceUsageEntry 4)
The aggregated session duration of services in this service usage counter carried over the link.
Access |
read-only |
Units |
seconds |
Syntax
Counter32
linkServiceUsageConcurrentSessions (linkServiceUsageEntry 5)
The number of concurrent sessions of services in this service usage counter carried over the link.
Access |
read-only |
Units |
sessions |
Syntax
Counter32
linkServiceUsageActiveSubscribers (linkServiceUsageEntry 6)
The number of active subscribers of services in this service usage counter carried over the link.
Access |
read-only |
Units |
subscribers |
Syntax
Counter32
linkServiceUpDroppedPackets (linkServiceUsageEntry 7)
The number of dropped upstream packets of services in this service usage counter carried over the link.
Access |
read-only |
Units |
packets |
Syntax
Counter32

Note ![]() To enable the SCE application to count dropped packets and dropped bytes, disable the accelerate-packet-drops feature on the SCE platform; if accelerate-packet-drops is enabled, the MIB dropped packets and dropped bytes counters constantly show the value 0xFFFFFFFF. For more information about the accelerate-packet-drops feature, see either the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide or the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 GBE Software Configuration Guide.
To enable the SCE application to count dropped packets and dropped bytes, disable the accelerate-packet-drops feature on the SCE platform; if accelerate-packet-drops is enabled, the MIB dropped packets and dropped bytes counters constantly show the value 0xFFFFFFFF. For more information about the accelerate-packet-drops feature, see either the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide or the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 GBE Software Configuration Guide.
linkServiceDownDroppedPackets (linkServiceUsageEntry 8)
The number of dropped downstream packets of services in this service usage counter carried over the link.
Access |
read-only |
Units |
packets |
Syntax
Counter32

Note ![]() To enable the SCE application to count dropped packets and dropped bytes, disable the accelerate-packet-drops feature on the SCE platform; if accelerate-packet-drops is enabled, the MIB dropped packets and dropped bytes counters constantly show the value 0xFFFFFFFF. For more information about the accelerate-packet-drops feature, see either the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide or the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 GBE Software Configuration Guide.
To enable the SCE application to count dropped packets and dropped bytes, disable the accelerate-packet-drops feature on the SCE platform; if accelerate-packet-drops is enabled, the MIB dropped packets and dropped bytes counters constantly show the value 0xFFFFFFFF. For more information about the accelerate-packet-drops feature, see either the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide or the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 GBE Software Configuration Guide.
linkServiceUpDroppedBytes (linkServiceUsageEntry 9)
The number of dropped upstream bytes of services in this service usage counter carried over the link.
Access |
read-only |
Units |
bytes |
Syntax
Counter32

Note ![]() To enable the SCE application to count dropped packets and dropped bytes, disable the accelerate-packet-drops feature on the SCE platform; if accelerate-packet-drops is enabled, the MIB dropped packets and dropped bytes counters constantly show the value 0xFFFFFFFF. For more information about the accelerate-packet-drops feature, see either the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide or the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 GBE Software Configuration Guide.
To enable the SCE application to count dropped packets and dropped bytes, disable the accelerate-packet-drops feature on the SCE platform; if accelerate-packet-drops is enabled, the MIB dropped packets and dropped bytes counters constantly show the value 0xFFFFFFFF. For more information about the accelerate-packet-drops feature, see either the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide or the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 GBE Software Configuration Guide.
linkServiceDownDroppedBytes (linkServiceUsageEntry 10)
The link service-counter number of dropped downstream bytes of services in this service usage counter carried over the link.
Access |
read-only |
Units |
bytes |
Syntax
Counter32

Note ![]() To enable the SCE application to count dropped packets and dropped bytes, disable the accelerate-packet-drops feature on the SCE platform; if accelerate-packet-drops is enabled, the MIB dropped packets and dropped bytes counters constantly show the value 0xFFFFFFFF. For more information about the accelerate-packet-drops feature, see either the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide or the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 GBE Software Configuration Guide.
To enable the SCE application to count dropped packets and dropped bytes, disable the accelerate-packet-drops feature on the SCE platform; if accelerate-packet-drops is enabled, the MIB dropped packets and dropped bytes counters constantly show the value 0xFFFFFFFF. For more information about the accelerate-packet-drops feature, see either the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide or the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 GBE Software Configuration Guide.
Package Group: packageGrp (pcubeEngageObjs 3)
The Package group provides general and usage information for each global-scope package usage counter (for example, traffic statistics of a service for all subscribers assigned to a particular package or group of packages).
•![]() packageCounterTable (packageGrp 1)
packageCounterTable (packageGrp 1)
•![]() packageCounterEntry (packageCounterTable 1)
packageCounterEntry (packageCounterTable 1)
•![]() packageCounterIndex (packageCounterEntry 1)
packageCounterIndex (packageCounterEntry 1)
•![]() packageCounterStatus (packageCounterEntry 2)
packageCounterStatus (packageCounterEntry 2)
•![]() packageCounterName (packageCounterEntry 3)
packageCounterName (packageCounterEntry 3)
•![]() packageCounterActiveSubscribers (packageCounterEntry 4)
packageCounterActiveSubscribers (packageCounterEntry 4)
•![]() packageServiceUsageTable (packageGrp 2)
packageServiceUsageTable (packageGrp 2)
•![]() packageServiceUsageEntry (packageServiceUsageTable 1)
packageServiceUsageEntry (packageServiceUsageTable 1)
•![]() packageServiceUsageUpVolume (packageServiceUsageEntry 1)
packageServiceUsageUpVolume (packageServiceUsageEntry 1)
•![]() packageServiceUsageDownVolume (packageServiceUsageEntry 2)
packageServiceUsageDownVolume (packageServiceUsageEntry 2)
•![]() packageServiceUsageNumSessions (packageServiceUsageEntry 3)
packageServiceUsageNumSessions (packageServiceUsageEntry 3)
•![]() packageServiceUsageDuration (packageServiceUsageEntry 4)
packageServiceUsageDuration (packageServiceUsageEntry 4)
•![]() packageServiceUsageConcurrentSessions (packageServiceUsageEntry 5)
packageServiceUsageConcurrentSessions (packageServiceUsageEntry 5)
•![]() packageServiceUsageActiveSubscribers (packageServiceUsageEntry 6)
packageServiceUsageActiveSubscribers (packageServiceUsageEntry 6)
•![]() packageServiceUpDroppedPackets (packageServiceUsageEntry 7)
packageServiceUpDroppedPackets (packageServiceUsageEntry 7)
•![]() packageServiceDownDroppedPackets (packageServiceUsageEntry 8)
packageServiceDownDroppedPackets (packageServiceUsageEntry 8)
•![]() packageServiceUpDroppedBytes (packageServiceUsageEntry 9)
packageServiceUpDroppedBytes (packageServiceUsageEntry 9)
•![]() packageServiceDownDroppedBytes (packageServiceUsageEntry 10)
packageServiceDownDroppedBytes (packageServiceUsageEntry 10)
packageCounterTable (packageGrp 1)
The Package Counter table provides information for each package usage counter.
Access |
non-accessible |
Syntax
SEQUENCE OF packageCounterEntry
packageCounterEntry (packageCounterTable 1)
A Package Counter table entry containing parameters defining one package usage counter.
Access |
non-accessible |
Index
{pmoduleIndex, packageCounterIndex}
Syntax
SEQUENCE {
packageCounterIndex
packageCounterStatus
packageCounterName
packageCounterActiveSubscribers
}
packageCounterIndex (packageCounterEntry 1)
The package usage counter index.
Access |
not-accessible |
Syntax
Integer32 (1...1023)
packageCounterStatus (packageCounterEntry 2)
The package usage counter status.
Access |
read-only |
Syntax
INTEGER {
0 (disabled)
1 (enabled)
}
packageCounterName (packageCounterEntry 3)
The name of the package usage counter.
Access |
read-only |
Syntax
SnmpAdminString
packageCounterActiveSubscribers (packageCounterEntry 4)
The total number of active subscribers of packages included in the package usage counter.
Access |
read-only |
Syntax
Counter32
packageServiceUsageTable (packageGrp 2)
The Package Service Usage table provides usage information for each global-scope package usage counter.
Access |
not-accessible |
Syntax
SEQUENCE OF packageServiceUsageEntry
packageServiceUsageEntry (packageServiceUsageTable 1)
A Package Service Usage table entry containing parameters defining resource usage of packages included in one global-scope package usage counter.
Access |
non-accessible |
Index
{pmoduleIndex, packageCounterIndex, globalScopeServiceCounterIndex}
Syntax
SEQUENCE {
packageServiceUsageUpVolume
packageServiceUsageDownVolume
packageServiceUsageNumSessions
packageServiceUsageDuration
packageServiceUsageConcurrentSessions
packageServiceUsageActiveSubscribers
packageServiceUpDroppedPackets
packageServiceDownDroppedPackets
packageServiceUpDroppedBytes
packageServiceDownDroppedBytes
}
packageServiceUsageUpVolume (packageServiceUsageEntry 1)
The upstream volume of packages in this package usage counter.
Access |
read-only |
Units |
kilobytes |
Syntax
Counter32

Note ![]() Although volume counters on the SCE platform hold 32-bit integers, CISCO-SCAS-BB MIB volume counters wraparound (turn back to zero) when the maximum 29-bit integer value (0x1FFFFFFF) is reached.
Although volume counters on the SCE platform hold 32-bit integers, CISCO-SCAS-BB MIB volume counters wraparound (turn back to zero) when the maximum 29-bit integer value (0x1FFFFFFF) is reached.
packageServiceUsageDownVolume (packageServiceUsageEntry 2)
The downstream volume of packages in this package usage counter.
Access |
read-only |
Units |
kilobytes |
Syntax
Counter32

Note ![]() Although volume counters on the SCE platform hold 32-bit integers, CISCO-SCAS-BB MIB volume counters wraparound (turn back to zero) when the maximum 29-bit integer value (0x1FFFFFFF) is reached.
Although volume counters on the SCE platform hold 32-bit integers, CISCO-SCAS-BB MIB volume counters wraparound (turn back to zero) when the maximum 29-bit integer value (0x1FFFFFFF) is reached.
packageServiceUsageNumSessions (packageServiceUsageEntry 3)
The number of sessions of packages in this package usage counter.
Access |
read-only |
Units |
sessions |
Syntax
Counter32
packageServiceUsageDuration (packageServiceUsageEntry 4)
The aggregated session duration seconds of packages in this package usage counter.
Access |
read-only |
Units |
seconds |
Syntax
Counter32
packageServiceUsageConcurrentSessions (packageServiceUsageEntry 5)
The number of concurrent sessions of packages in this package usage counter.
Access |
read-only |
Units |
sessions |
Syntax
Counter32
packageServiceUsageActiveSubscribers (packageServiceUsageEntry 6)
The number of active subscribers of packages in this package usage counter.
Access |
read-only |
Units |
subscribers |
Syntax
Counter32
packageServiceUpDroppedPackets (packageServiceUsageEntry 7)
The number of dropped upstream packets of packages in this package usage counter.
Access |
read-only |
Units |
packets |
Syntax
Counter32

Note ![]() To enable the SCE application to count dropped packets and dropped bytes, disable the accelerate-packet-drops feature on the SCE platform; if accelerate-packet-drops is enabled, the MIB dropped packets and dropped bytes counters constantly show the value 0xFFFFFFFF. For more information about the accelerate-packet-drops feature, see either the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide or the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 GBE Software Configuration Guide.
To enable the SCE application to count dropped packets and dropped bytes, disable the accelerate-packet-drops feature on the SCE platform; if accelerate-packet-drops is enabled, the MIB dropped packets and dropped bytes counters constantly show the value 0xFFFFFFFF. For more information about the accelerate-packet-drops feature, see either the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide or the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 GBE Software Configuration Guide.
packageServiceDownDroppedPackets (packageServiceUsageEntry 8)
The number of dropped downstream packets of packages in this package usagecounter.
Access |
read-only |
Units |
packets |
Syntax
Counter32

Note ![]() To enable the SCE application to count dropped packets and dropped bytes, disable the accelerate-packet-drops feature on the SCE platform; if accelerate-packet-drops is enabled, the MIB dropped packets and dropped bytes counters constantly show the value 0xFFFFFFFF. For more information about the accelerate-packet-drops feature, see either the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide or the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 GBE Software Configuration Guide.
To enable the SCE application to count dropped packets and dropped bytes, disable the accelerate-packet-drops feature on the SCE platform; if accelerate-packet-drops is enabled, the MIB dropped packets and dropped bytes counters constantly show the value 0xFFFFFFFF. For more information about the accelerate-packet-drops feature, see either the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide or the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 GBE Software Configuration Guide.
packageServiceUpDroppedBytes (packageServiceUsageEntry 9)
The number of dropped upstream bytes of packages in this package usage counter.
Access |
read-only |
Units |
bytes |
Syntax
Counter32

Note ![]() To enable the SCE application to count dropped packets and dropped bytes, disable the accelerate-packet-drops feature on the SCE platform; if accelerate-packet-drops is enabled, the MIB dropped packets and dropped bytes counters constantly show the value 0xFFFFFFFF. For more information about the accelerate-packet-drops feature, see either the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide or the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 GBE Software Configuration Guide.
To enable the SCE application to count dropped packets and dropped bytes, disable the accelerate-packet-drops feature on the SCE platform; if accelerate-packet-drops is enabled, the MIB dropped packets and dropped bytes counters constantly show the value 0xFFFFFFFF. For more information about the accelerate-packet-drops feature, see either the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide or the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 GBE Software Configuration Guide.
packageServiceDownDroppedBytes (packageServiceUsageEntry 10)
The number of dropped downstream bytes of packages in this package usage counter.
Access |
read-only |
Units |
bytes |
Syntax
Counter32

Note ![]() To enable the SCE application to count dropped packets and dropped bytes, disable the accelerate-packet-drops feature on the SCE platform; if accelerate-packet-drops is enabled, the MIB dropped packets and dropped bytes counters constantly show the value 0xFFFFFFFF. For more information about the accelerate-packet-drops feature, see either the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide or the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 GBE Software Configuration Guide.
To enable the SCE application to count dropped packets and dropped bytes, disable the accelerate-packet-drops feature on the SCE platform; if accelerate-packet-drops is enabled, the MIB dropped packets and dropped bytes counters constantly show the value 0xFFFFFFFF. For more information about the accelerate-packet-drops feature, see either the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide or the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 GBE Software Configuration Guide.
Subscriber Group: subscriberGrp (pcubeEngageObjs 4)
The Subscriber group provides general information for each subscriber and usage information per service usage counter for each subscriber (for example, traffic statistics of a service for a particular subscriber defined in the system).

Note ![]() For the SCE8000: To use the tables in this group, first create an entry to reference a particular subscriber in the cServiceControlSubscribersTable object of the CISCO-SERVICE-CONTROL-SUBSCRIBERS MIB (not the CISCO-SCAS-BB MIB). Using the index of this table (cServiceControlSubscribersIndex), information about the subscriber can be collected.
For the SCE8000: To use the tables in this group, first create an entry to reference a particular subscriber in the cServiceControlSubscribersTable object of the CISCO-SERVICE-CONTROL-SUBSCRIBERS MIB (not the CISCO-SCAS-BB MIB). Using the index of this table (cServiceControlSubscribersIndex), information about the subscriber can be collected.

Note ![]() For the SCE2000: To use the tables in this group, first create an entry to reference a particular subscriber in the subscribersPropertiesValueTable object of the subscriberGrp in the SCE MIB (not the CISCO-SCAS-BB MIB). Using the index of this table (spvIndex), information about the subscriber can be collected.
For the SCE2000: To use the tables in this group, first create an entry to reference a particular subscriber in the subscribersPropertiesValueTable object of the subscriberGrp in the SCE MIB (not the CISCO-SCAS-BB MIB). Using the index of this table (spvIndex), information about the subscriber can be collected.
•![]() subscribersTable (subscriberGrp 1)
subscribersTable (subscriberGrp 1)
•![]() subscribersEntry (subscribersTable 1)
subscribersEntry (subscribersTable 1)
•![]() subscriberPackageIndex (subscribersEntry 1)
subscriberPackageIndex (subscribersEntry 1)
•![]() subscriberServiceUsageTable (subscriberGrp 2)
subscriberServiceUsageTable (subscriberGrp 2)
•![]() subscriberServiceUsageEntry (subscriberServiceUsageTable 1)
subscriberServiceUsageEntry (subscriberServiceUsageTable 1)
•![]() subscriberServiceUsageEntry (subscriberServiceUsageTable 1)
subscriberServiceUsageEntry (subscriberServiceUsageTable 1)
•![]() subscriberServiceUsageDownVolume (subscriberServiceUsageEntry 2)
subscriberServiceUsageDownVolume (subscriberServiceUsageEntry 2)
•![]() subscriberServiceUsageNumSessions (subscriberServiceUsageEntry 3)
subscriberServiceUsageNumSessions (subscriberServiceUsageEntry 3)
•![]() subscriberServiceUsageDuration (subscriberServiceUsageEntry 4)
subscriberServiceUsageDuration (subscriberServiceUsageEntry 4)
Related Topics
•![]() Accessing Subscriber Information (the spvIndex)
Accessing Subscriber Information (the spvIndex)
subscribersTable (subscriberGrp 1)
The Subscribers Table provides information for each subscriber.
Access |
not-accessible |
Syntax
SEQUENCE OF subscribersEntry
subscribersEntry (subscribersTable 1)
A Subscribers Table entry containing the package index of each subscriber.
Access |
not-accessible |
Index
{pmoduleIndex, spvIndex}
Syntax
SEQUENCE {
subscriberPackageIndex
}
subscriberPackageIndex (subscribersEntry 1)
The package index of the subscriber's package.
Access |
read-only |
Syntax
Integer32 (1...255)
subscriberServiceUsageTable (subscriberGrp 2)
The Subscriber Service Usage table provides usage information per service usage counter for each subscriber.
Access |
not-accessible |
Syntax
Sequence of subscriberServiceUsageEntry
subscriberServiceUsageEntry (subscriberServiceUsageTable 1)
A Subscriber Service Usage table entry containing parameters defining resource usage by one subscriber of services included in one service usage counter.
Access |
not-accessible |
Index
{pmoduleIndex, spvIndex, subscriberScopeServiceCounterIndex}
Syntax
SEQUENCE {
subscriberServiceUsageUpVolume
subscriberServiceUsageDownVolume
subscriberServiceUsageNumSessions
subscriberServiceUsageDuration
subscriberServiceUsageEntry (subscriberServiceUsageTable 1)
A Subscriber Service Usage table entry containing parameters defining resource usage by one subscriber of services included in one service usage counter.
Access |
not-accessible |
Index
{pmoduleIndex, spvIndex, subscriberScopeServiceCounterIndex}
Syntax
SEQUENCE {
subscriberServiceUsageUpVolume
subscriberServiceUsageDownVolume
subscriberServiceUsageNumSessions
subscriberServiceUsageDuration
subscriberServiceUsageDownVolume (subscriberServiceUsageEntry 2)
The downstream volume of services in this service usage counter used by this subscriber.
Access |
read-only |
Units |
kilobytes |
Syntax
Counter32

Note ![]() Although volume counters on the SCE platform hold 32-bit integers, CISCO-SCAS-BB MIB volume counters wraparound (turn back to zero) when the maximum 29-bit integer value (0x1FFFFFFF) is reached.
Although volume counters on the SCE platform hold 32-bit integers, CISCO-SCAS-BB MIB volume counters wraparound (turn back to zero) when the maximum 29-bit integer value (0x1FFFFFFF) is reached.
subscriberServiceUsageNumSessions (subscriberServiceUsageEntry 3)
The number of sessions of services in this service usage counter used by this subscriber.
Access |
read-only |
Units |
sessions |
Syntax
Integer32 (1...65535)
subscriberServiceUsageDuration (subscriberServiceUsageEntry 4)
Aggregated session duration of services in this service usage counter used by this subscriber.
Access |
read-only |
Units |
seconds |
Syntax
Integer32 (1...65535)
Service Counter Group: serviceCounterGrp (pcubeEngageObjs 5)
The Service Counter group provides general information for each global-scope and subscriber-scope service usage counter. You can use it, for example, to read the names of the services as defined in a SCA BB service configuration.
•![]() globalScopeServiceCounterTable (serviceCounterGrp 1)
globalScopeServiceCounterTable (serviceCounterGrp 1)
•![]() globalScopeServiceCounterEntry (globalScopeServiceCounterTable 1)
globalScopeServiceCounterEntry (globalScopeServiceCounterTable 1)
•![]() globalScopeServiceCounterIndex (globalScopeServiceCounterEntry 1)
globalScopeServiceCounterIndex (globalScopeServiceCounterEntry 1)
•![]() globalScopeServiceCounterStatus (globalScopeServiceCounterEntry 2)
globalScopeServiceCounterStatus (globalScopeServiceCounterEntry 2)
•![]() globalScopeServiceCounterName (globalScopeServiceCounterEntry 3)
globalScopeServiceCounterName (globalScopeServiceCounterEntry 3)
•![]() subscriberScopeServiceCounterTable (serviceCounterGrp 2)
subscriberScopeServiceCounterTable (serviceCounterGrp 2)
•![]() subscriberScopeServiceCounterEntry (subscriberScopeServiceCounterTable 1)
subscriberScopeServiceCounterEntry (subscriberScopeServiceCounterTable 1)
•![]() subscriberScopeServiceCounterIndex (subscriberScopeServiceCounterEntry 1)
subscriberScopeServiceCounterIndex (subscriberScopeServiceCounterEntry 1)
•![]() subscriberScopeServiceCounterStatus (subscriberScopeServiceCounterEntry 2)
subscriberScopeServiceCounterStatus (subscriberScopeServiceCounterEntry 2)
•![]() subscriberScopeServiceCounterName (subscriberScopeServiceCounterEntry 3)
subscriberScopeServiceCounterName (subscriberScopeServiceCounterEntry 3)
globalScopeServiceCounterTable (serviceCounterGrp 1)
The Global-Scope Service Counter table consists of data about each service usage counter used by the link and by packages.
Access |
non-accesible |
Syntax
SEQUENCE OF globalScopeServiceCounterEntry
globalScopeServiceCounterEntry (globalScopeServiceCounterTable 1)
A Global-Scope Service Counter table entry containing parameters defining one global-scope service usage counter.
Access |
not-accessible |
Index
{pmoduleIndex, globalScopeServiceCounterIndex}
Syntax
SEQUENCE {
globalScopeServiceCounterIndex
globalScopeServiceCounterStatus
globalScopeServiceCounterName
}
globalScopeServiceCounterIndex (globalScopeServiceCounterEntry 1)
The global-scope service usage counter index.
Access |
not-accesible |
Syntax
Integer32 (1...255)
globalScopeServiceCounterStatus (globalScopeServiceCounterEntry 2)
The global-scope service usage counter status.
Access |
read-only |
Syntax
INTEGER {
0 (disabled)
1 (enabled)
}
globalScopeServiceCounterName (globalScopeServiceCounterEntry 3)
The name of the global-scope service usage counter.
Access |
read-only |
Syntax
SnmpAdminString
subscriberScopeServiceCounterTable (serviceCounterGrp 2)
The Subscriber-Scope Service Counter table consists of data about each service usage counter used by
subscribers.
Access |
not-accessible |
Syntax
SEQUENCE OF subscriberScopeServiceCounterEntry
subscriberScopeServiceCounterEntry (subscriberScopeServiceCounterTable 1)
A Subscriber-Scope Service Counter table entry containing parameters defining one subscriber-scope service usage counter.
Access |
not-accessible |
Index
{pmoduleIndex, subscriberScopeServiceCounterIndex}
Syntax
SEQUENCE {
subscriberScopeServiceCounterIndex
subscriberScopeServiceCounterStatus
subscriberScopeServiceCounterName
}
subscriberScopeServiceCounterIndex (subscriberScopeServiceCounterEntry 1)
The subscriber-scope service usage counter index.
Access |
not-accesible |
Syntax
Integer32 (1...255)
subscriberScopeServiceCounterStatus (subscriberScopeServiceCounterEntry 2)
The subscriber-scope service usage counter status.
Access |
read-only |
Syntax
INTEGER {
0 (disabled)
1 (enabled)
}
subscriberScopeServiceCounterName (subscriberScopeServiceCounterEntry 3)
The name of the subscriber-scope service usage counter.
Access |
read-only |
Syntax
SnmpAdminString
Guidelines for Using the CISCO-SCAS-BB MIB
This section provides guidelines to help access SNMP information about the SCE platform using the CISCO-SCAS-BB MIB.

Note ![]() Indices in SNMP start from 1; SCA BB indices start from 0. When accessing a counter in the SCA BB SNMP MIB by its index, add 1 to the index of the entity. For example, the global usage counter with index 0 will be located at globalScopeServiceCounter index 1.
Indices in SNMP start from 1; SCA BB indices start from 0. When accessing a counter in the SCA BB SNMP MIB by its index, add 1 to the index of the entity. For example, the global usage counter with index 0 will be located at globalScopeServiceCounter index 1.

Note ![]() Although volume counters on the SCE platform hold 32-bit integers, CISCO-SCAS-BB MIB volume counters wraparound (turn back to zero) when the maximum 29-bit integer value (0x1FFFFFFF) is reached.
Although volume counters on the SCE platform hold 32-bit integers, CISCO-SCAS-BB MIB volume counters wraparound (turn back to zero) when the maximum 29-bit integer value (0x1FFFFFFF) is reached.

Note ![]() To enable the SCE application to count dropped packets and dropped bytes, disable the accelerate-packet-drops feature on the SCE platform; if accelerate-packet-drops is enabled, the MIB dropped packets and dropped bytes counters constantly show the value 0xFFFFFFFF. For more information about the accelerate-packet-drops feature, see either the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide or the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 GBE Software Configuration Guide.
To enable the SCE application to count dropped packets and dropped bytes, disable the accelerate-packet-drops feature on the SCE platform; if accelerate-packet-drops is enabled, the MIB dropped packets and dropped bytes counters constantly show the value 0xFFFFFFFF. For more information about the accelerate-packet-drops feature, see either the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide or the "Counting Dropped Packets" section in the "Configuring the Line Interface" chapter of the Cisco SCE8000 GBE Software Configuration Guide.
•![]() globalScopeServiceCounterTable and subscriberScopeServiceCounterTable
globalScopeServiceCounterTable and subscriberScopeServiceCounterTable
•![]() Accessing Subscriber Information (the spvIndex)
Accessing Subscriber Information (the spvIndex)
globalScopeServiceCounterTable and subscriberScopeServiceCounterTable
The index of a service usage counter as defined in a SCA BB service configuration is used to reference services in the CISCO-SCAS-BB MIB. Since MIB index values count from 1, but SCA BB indices count from 0, the index used in the MIB must always be one greater than the index of the service it is referencing.
For example, to get the number of upstream bytes used by a service on a link, use LinkServiceTable.lnkServiceUpVolume (part of the linkGrp). The value assigned to serviceIndex for this table must be one greater than service index defined for this service in the service configuration.
To identify or change the index of a service, go to the Advanced tab of the Service Settings dialog box in the SCA BB Console (see the "Using the Service Configuration Editor: Traffic Classification" chapter of the Cisco Service Control Application for Broadband User Guide). For example, to reference the P2P service (which has a (default) service index of 9) in the MIB, a serviceIndex of 10 (= 9 + 1) must be used.
packageCounterTable
The package index, defined in a SCA BB service configuration, is used to reference entries in packageTable and packageServiceTable (part of the packageGrp). As with serviceIndex the value assigned to packageIndex must be one greater than the package index in the service configuration.
To identify or change the index of a package, go to the Advanced tab of the Package Settings dialog box in the SCA BB Console (see the "Using the Service Configuration Editor: Traffic Classification" chapter of the Cisco Service Control Application for Broadband User Guide). For example, to reference the default package (which has a package index of 0) in the MIB, a packageIndex of 1 (= 0 + 1) must be used.
Accessing Subscriber Information (the spvIndex)
In order to collect subscriber-level information using the SNMP interface, you must first create an entry in the proper subscriber MIB table and associate this entry with a subscriber name. Its index can be then be referred to in order to collect usage statistics for this subscriber.
The exact MIB objects vary, depending on the particular SCE platform, as described in the following sections.
Accessing Subscriber Information in the Cisco SCE 2000
Create an entry in the subscriberPropertiesValuesTable part of the subscriberGrp in pcubeSEMib (not PCubeEngageMib). After an entry in this table is created and associated with a subscriber name, its index (spvIndex) can be referred to in PCubeEngageMib to collect usage statistics for this subscriber.
An entry is created in the subscriberPropertiesValuesTable by setting the entry spvRowStatus object with CreateAndGo(4) then setting the name of the subscriber in the spvSubName property and the spvIndex variable to be used as an index to the subscriber.
For example, to poll the downstream volume of subscriber "sub123" for the P2P service using PCubeEngageMib, perform the following steps.
Step 1 ![]() Obtain the index of the P2P service from the SCA BB Console (this is a one-time operation that you should perform only if services are changed in the policy). In this example, assume that the P2P service index has its default value of 9.
Obtain the index of the P2P service from the SCA BB Console (this is a one-time operation that you should perform only if services are changed in the policy). In this example, assume that the P2P service index has its default value of 9.
Step 2 ![]() In order to create a subscriber entry, you must specify the index of the module and the desired spvIndex .
In order to create a subscriber entry, you must specify the index of the module and the desired spvIndex .
•![]() Set pmoduleIndex = 1.
Set pmoduleIndex = 1.
•![]() In SEMib:subscriberGrp:subscriberPropertiesValuesTable, choose an index for spvIndex (for this example we will arbitrarily choose index 7).
In SEMib:subscriberGrp:subscriberPropertiesValuesTable, choose an index for spvIndex (for this example we will arbitrarily choose index 7).
Step 3 ![]() Create an entry in SEMib:subscriberGrp:subscriberPropertiesValuesTable, at the index that you have chosen:
Create an entry in SEMib:subscriberGrp:subscriberPropertiesValuesTable, at the index that you have chosen:
•![]() Set spvRowStatus to 4 (using CreateAndGo).
Set spvRowStatus to 4 (using CreateAndGo).
•![]() Set spvSubName to "sub123".
Set spvSubName to "sub123".
Step 4 ![]() Read the subscriberServiceDownVolume property out of EngageMib:subscriberGrp:subscriberServiceTable Step 6 where spvIndex is set to 7 and serviceIndex is set to 10. (In general, you may walk the cServiceControlSubscribersTable in order to find out the various subscriber indexes, but in this case we have chosen it to be 7 so we can directly use the same index for accessing the data of this subscriber).
Read the subscriberServiceDownVolume property out of EngageMib:subscriberGrp:subscriberServiceTable Step 6 where spvIndex is set to 7 and serviceIndex is set to 10. (In general, you may walk the cServiceControlSubscribersTable in order to find out the various subscriber indexes, but in this case we have chosen it to be 7 so we can directly use the same index for accessing the data of this subscriber).
Accessing Subscriber Information in the Cisco SCE8000
Create an entry in the cServiceControlSubscribersTable of the CISCO-SERVICE-CONTROL-SUBSCRIBERS MIB. After an entry in this table is created and associated with a subscriber name, its index (cServiceControlSubscribersIndex) can be referred to in PCubeEngageMib (as spvIndex) to collect usage statistics for this subscriber.
An entry is created in the cServiceControlSubscribersTable table (at an index chosen by the user) by setting the entry cServiceControlSubscribersRowStatus object with CreateAndGo(4) then setting the name of the subscriber in the cServiceControlSubscribersName property.
For example, to poll the downstream volume of subscriber "sub123" for the P2P service using PCubeEngageMib, perform the following steps.
Step 1 ![]() Obtain the index of the P2P service from the SCA BB Console (this is a one-time operation that you should perform only if services are changed in the policy). In this example, assume that the P2P service index has its default value of 9.
Obtain the index of the P2P service from the SCA BB Console (this is a one-time operation that you should perform only if services are changed in the policy). In this example, assume that the P2P service index has its default value of 9.
Step 2 ![]() In order to create a subscriber entry, you must specify the indexes of the module and the desired cServiceControlSubscribersIndex.
In order to create a subscriber entry, you must specify the indexes of the module and the desired cServiceControlSubscribersIndex.
•![]() Set entPhyIndex according to the index of the Service Control Module (SCM) entry in the Entity MIB.
Set entPhyIndex according to the index of the Service Control Module (SCM) entry in the Entity MIB.
•![]() Choose an index for cServiceControlSubscribersIndex (for this example we will arbitrarily choose index 7).
Choose an index for cServiceControlSubscribersIndex (for this example we will arbitrarily choose index 7).
Step 3 ![]() Create an entry in ciscoServiceControlSubscribersMIB:cServiceControlSubscribersTable, at the index that you have chosen:
Create an entry in ciscoServiceControlSubscribersMIB:cServiceControlSubscribersTable, at the index that you have chosen:
•![]() Set cServiceControlSubscribersRowStatus to 4 (using CreateAndGo).
Set cServiceControlSubscribersRowStatus to 4 (using CreateAndGo).
•![]() Set cServiceControlSubscribersName to "sub123".
Set cServiceControlSubscribersName to "sub123".
Step 4 ![]() Read the subscriberServiceUsageDownVolume property out of EngageMib:subscriberGrp:subscriberServiceUsageTable where entPhyIndex is set as instructed, spvIndex is set to 7 and serviceIndex is set to 10. (In general, you may walk the cServiceControlSubscribersTable in order to find out the various subscriber indexes, but in this case we have chosen it to be 7 so we can directly use the same index for accessing the data of this subscriber).
Read the subscriberServiceUsageDownVolume property out of EngageMib:subscriberGrp:subscriberServiceUsageTable where entPhyIndex is set as instructed, spvIndex is set to 7 and serviceIndex is set to 10. (In general, you may walk the cServiceControlSubscribersTable in order to find out the various subscriber indexes, but in this case we have chosen it to be 7 so we can directly use the same index for accessing the data of this subscriber).
 Feedback
Feedback