-
Cisco NAC Appliance - Clean Access Manager Configuration Guide, Release 4.9(2)
-
About This Guide
-
Introduction
-
Device Management: Adding Clean Access Servers, Adding Filters
-
Switch Management: Configuring Out-of-Band Deployment
-
Wireless LAN Controller Management: Configuring Wireless Out-of-Band Deployment
-
Configuring User Login Page and Guest Access
-
User Management: Configuring User Roles and Local Users
-
User Management: Configuring Authentication Servers
-
User Management: Traffic Control, Bandwidth, Schedule
-
Configuring Cisco NAC Appliance for Agent Login and Client Posture Assessment
-
Cisco NAC Appliance Agents
-
Monitoring and Troubleshooting Agent Sessions
-
Configuring Network Scanning
-
Monitoring Event Logs
-
Administering the CAM
-
Error and Event Log Messages
-
API Support
-
MIB Support
-
Open Source License Acknowledgements
-
Table Of Contents
Wireless LAN Controller Management: Configuring Wireless Out-of-Band Deployment
Wireless In-Band Versus Out-of-Band
Wireless Out-of-Band Requirements
Summary Steps to Configure Wireless Out-of-Band
Wireless Out-of-Band Virtual Gateway Deployment
Login and Authentication Flow in Wireless OOB Virtual Gateway Mode
Configure Your Network for Wireless Out-of-Band
Configure Your Wireless LAN Controllers
Wireless LAN Controllers Configuration Notes
Example Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Steps
Create the Dynamic Interface on the Wireless LAN Controller
Create the WLAN on the Wireless LAN Controller and Enable Cisco NAC Appliance Integration
Configure SNMP on the Wireless LAN Controller
Specify the CAM as the SNMP Trap Receiver
Wireless OOB Network Setup/Configuration Worksheet
Configure Wireless LAN Controller Connection on the CAM
Add a Wireless Out-of-Band Clean Access Server and Configure Environment
Configure Wireless LAN Controller Profiles
Add Wireless LAN Controller Profile
Add and Manage Wireless LAN Controllers
Add New Wireless LAN Controller
Search New Wireless LAN Controllers
View Wireless Out-of-Band Online Users
Wireless and Wired OOB User List Summary
Wireless LAN Controller Management: Configuring Wireless Out-of-Band Deployment
This chapter describes how to configure Cisco NAC Appliance for Wireless Out-of-Band (Wireless OOB) deployment. Topics include:
•
Wireless Out-of-Band Virtual Gateway Deployment
•
Configure Your Network for Wireless Out-of-Band
•
Configure Your Wireless LAN Controllers
•
Configure Wireless LAN Controller Connection on the CAM
See Cisco NAC Appliance - Clean Access Server Configuration Guide, Release 4.9(2) for additional information on OOB deployments.
Overview
In a traditional In-Band Cisco NAC Appliance wireless deployment, all network traffic to or from wireless client machines passes through the Clean Access Server (CAS). For high throughput or highly routed environments, a Cisco NAC Appliance Wireless Out-of-Band (Wireless OOB) deployment allows client traffic to pass through the network only in order to be authenticated and certified before being connected directly to the access network.
Wireless Out-of-Band can be configured in the following deployments:
•
Layer 2 Virtual Gateway
•
Layer 2 Real IP
•
Layer 3 Real IP
Note
Cisco NAC Appliance Release 4.8(1) and earlier versions support only Layer 2 Virtual Gateway deployment. All the above deployments are supported by Cisco NAC Appliance Release 4.8(2) and later.
Starting from NAC Appliance Release 4.9, the wireless OOB is supported for roaming as well. When the client machine roams, the connectivity is not lost.
Wireless Out-of-Band is supported in the following scenarios of roaming:
•
Bewteen Access Points: When client roams from one Access Point to another within the same Wireless controller (WLC).
•
Intra-subnet: When client roams from one WLC to another WLC, where Quarantine and Access VLANs are the same and have the same IP subnets. WLC-2 sends SNMP Trap to CAM notifying about the user mobility and CAM updates the database accordingly.
•
Inter-subnet: When client roams from one WLC to another within different subnets.
This section discusses the following topics:
•
Wireless In-Band Versus Out-of-Band
•
Wireless Out-of-Band Requirements
•
Summary Steps to Configure Wireless Out-of-Band
Wireless In-Band Versus Out-of-Band
Table 4-1 summarizes different characteristics of each type of deployment.
Wireless Out-of-Band Requirements
Wireless Out-of-band implementation of Cisco NAC Appliance requires the following to be in place:
•
Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers must be supported models that use at least the minimum supported version of IOS (supporting SNMP traps). See Table 4-2.
•
Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers must be Layer 2 adjacent to the Clean Access Server(s) with which they interoperate to support wireless client login for Cisco NAC Appliance Release 4.8(1) and earlier versions.
•
Clean Access Servers supporting wireless client login and authentication must be installed and configured in Virtual Gateway mode for Cisco NAC Appliance Release 4.8(1) and earlier versions.
•
For Cisco NAC Appliance Release 4.8(2) and later, Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers must be configured in bridging mode to interoperate with Layer 3 Out-of-Band wireless client login. Refer to DHCP Bridging Mode.
Note
Administrators can update the object IDs (OIDs) of supported WLCs through CAM updates (under Device Management > Clean Access > Updates > Summary | Settings). For example, if a new WLC of a supported model (Cisco 4400 Series) is released, administrators only need to perform Cisco Updates on the CAM to obtain support for the WLC OIDs, instead of performing a software upgrade of the CAM/CAS.
The update WLC OID feature only applies to existing models. If a new WLC series is introduced, administrators will still need to upgrade to ensure Wireless OOB support for the new WLCs. See Configure and Download Updates.
Note
The supported mode of HREAP in Cisco NAC Wireless Out-Of-Band is central authentication, central switching. In this state, the controller handles client authentication, and all client data is tunneled back to the controller. This state is valid only in connected mode.
Local Switching is not supported with Cisco NAC Wireless OOB.
Note
For the most current details on WLC model/IOS version support, refer to Switch Support for Cisco NAC Appliance.
DHCP Bridging Mode
To enable the DHCP bridging functionality on the controller, you must disable the DHCP proxy feature on the controller. By default, DHCP proxy is enabled.
In the 4.2.x.x codes this can be done using the CLI using the following commands:
(Cisco Controller) > config dhcp proxy disable(Cisco Controller) > show dhcp proxyDHCP Proxy Behavior: disabledThe DHCP bridging feature is a global setting, so it affects all DHCP transactions within the controller. You need to add ip helper statements in the wired infrastructure for all necessary VLANs on the controller.
You can disable the DHCP proxy through the User Interface as well. In the WLC graphical user interface, click Controller > Advanced > DHCP and uncheck the Enable DHCP Proxy check box as shown in Figure 4-1.
Figure 4-1
Disable DHCP Proxy
Note
Setting the DHCP Proxy using GUI is not available in all the versions. You can use the CLI command to disable the DHCP Proxy.
SNMP Control
In a Wireless OOB deployment, you can add WLCs to the Clean Access Manager's domain and communicate with the WLC using the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP). SNMP is an application layer protocol used by network management tools to exchange management information between network devices. Cisco NAC Appliance and Cisco WLCs support the following SNMP versions in a Wireless OOB environment:
•
SNMP V1
•
SNMP V2c (V2 with community string)
•
SNMP V3
•
SNMP V1
•
SNMP V2c
•
SNMP V3
•
SNMP V2c
You first need to configure the WLC to send and receive SNMP traffic to/from the Clean Access Manager, then configure matching settings on the Clean Access Manager to send and receive traffic to/from the WLC. This will enable the Clean Access Manager to get VLAN information from the WLC and coordinate with the WLC when wireless users log out (or are "kicked out") of the network and removed from the Online Users list.
Summary Steps to Configure Wireless Out-of-Band
To enable Wireless OOB in you access network, you need to perform the following tasks:
1.
Configure your Wireless LAN Controller:
a.
Enable SNMP read and write settings on the WLC.
b.
Enable SNMP trap transmission on the WLC using SNMP v2c (the SNMP v2c protocol is the only version of SNMP traps the CAM and WLCs have in common).
c.
Configure SSIDs/dynamic interfaces on the WLC with both an Authentication (Quarantine) VLAN and a standard Access VLAN.
2.
Ensure SNMP settings on the CAM match those assigned on the WLC using the guidelines in Configure SNMP Receiver.
3.
Create a new device profile on the CAM for the WLC using the guidelines in Add New Wireless LAN Controller.
Note
Unlike switch device profiles on the CAM, administrators do not configure or assign any Port Profiles for WLCs. VLAN assignments for Authentication (Quarantine) and Access VLANs originate form the WLC based on SNMP trap messages sent from the CAM following client posture assessment and remediation.
4.
Add the new WLC device profile to the Device List using the guidelines in Add and Manage Wireless LAN Controllers.
5.
Configure the CAS in your Cisco NAC Appliance network to support Wireless OOB network functions using the appropriate sections of the "Configuring the CAS Managed Network" chapter in the Cisco NAC Appliance - Clean Access Server Configuration Guide, Release 4.9(2):
–
Install the CAS according to the guidelines in the "Add New Server" section.
–
Ensure that the Cisco NAC Appliance system appropriately handles client traffic from the WLC's Authentication (Quarantine) VLAN by using the "Configuring Managed Subnets or Static Routes" section.
–
Since the CAS acts as a bridge in Virtual Gateway mode, be sure the CAS is configured to map the WLC's Access VLAN to the Cisco NAC Appliance Access VLAN (both on the Trusted VLAN) using the "Configure VLAN Mapping" section.
Wireless Out-of-Band Virtual Gateway Deployment
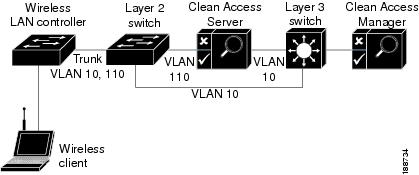
Figure 4-2 illustrates a typical Wireless OOB Virtual Gateway deployment. The WLC assigns two VLANs, AUthentication (Quarantine) VLAN 110 and Access VLAN 10, to one or more SSIDs/dynamic interfaces to support wireless client access. The WLC and the Layer 2 access switch have a VLAN trunk assignment for both VLANs so that client traffic automatically reaches the Layer 2 switch regardless of whether the wireless client machine has authenticated with Cisco NAC Appliance or not. The Layer 2 switch ensures that all unauthenticated traffic gets directed to the Clean Access Server via VLAN 110 and that authenticated clients remain Out-of-Band, thus bypasses the CAS and proceeding directly to the internal network via Access VLAN 10.
Figure 4-2 Wireless Out-of-Band Layer 2 VGW Mode
Login and Authentication Flow in Wireless OOB Virtual Gateway Mode
1.
The unauthenticated wireless user connects to a Wireless LAN Controller through an associated wireless access point.
2.
The WLC sends an association trap informing the CAM that a wireless user is logging in with Cisco NAC Appliance network access credentials.
Note
For Layer 3 Wireless OOB network, the MAC address of the device is added to the discovered clients list, when the WLC sends an association trap. When the user is logging in with the browser, the MAC address is detected. The MAC address detection is done using Java applet or ActiveX control.
If the device cannot run Java applet or ActiveX, then the MAC address is not detected and this leads to error.3.
When the wireless client first logs into the Wireless OOB network, the user profile is assigned to Authentication (Quarantine) VLAN 110.
4.
The CAS assigns the client machine an IP address from the access VLAN 10 and the WLC authenticates the client.
Note
If Single-Sign On (SSO) is configured for the Wireless OOB network, the WLC also sends the appropriate RADIUS accounting packets to the CAS.
Cisco WLCs do not support IPSec communication with the Cisco NAC Appliance network, so you cannot provide RADIUS SSO capability to users in your FIPS 140-2 compliant environment.5.
Cisco NAC Appliance performs posture assessment and remediation on the client machine and, if the client machine meets security requirements, authenticates the client and sends an SNMP SET command to the WLC granting access to the internal network.
6.
The WLC switches the client IP address from the Authentication (Quarantine) VLAN 110 to the Access VLAN 10 and (now that the client machine has authenticated with Cisco NAC Appliance) traffic between the wireless client machine and the internal network moves Out-of-Band, bypassing the CAS.
When the user logs out of the wireless OOB network, the WLC sends another SNMP update to the CAM to ensure the CAM removes the user profile from the wireless Online Users list. Likewise, if the Cisco NAC Appliance administrator is forced to "kick" a user out of the network, the CAM sends an SNMP trap to the WLC and the WLC, in return, automatically moves the user back to the Authentication (Quarantine) VLAN, thus directing the now unauthenticated client traffic to the CAS.
Configure Your Network for Wireless Out-of-Band
The CAM communicates with associated WLCs using SNMP and manages Wireless OOB CASs through the admin network. The trusted interface of the CAS connects to the admin/management network, and the untrusted interface of the CAS connects to the managed client network.
When a wireless client connects to a WLC, the WLC automatically assigns the client to an Authentication (Quarantine) VLAN and the traffic to/from the client goes through the CAS. After the client is authenticated and certified through the Clean Access Server, the WLC receives an SNMP message from the CAM allowing the client access to the network via the Access VLAN. Once on the access VLAN, traffic to and from certified clients moves Out-of-Band, bypassing the Clean Access Server.
The next sections describe the configuration steps needed to set up your Wireless OOB deployment:
•
Configure Your Wireless LAN Controllers
•
Configure Wireless LAN Controller Connection on the CAM
Configure Your Wireless LAN Controllers
This section describes the steps needed to set up Wireless LAN Controllers (WLCs) to be used with Cisco NAC Appliance for Wireless Out-of-Band.
•
Wireless LAN Controllers Configuration Notes
•
Example Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Steps
•
Wireless OOB Network Setup/Configuration Worksheet
Wireless LAN Controllers Configuration Notes
The following considerations should be taken into account when configuring Wireless LAN Controllers for OOB:
•
Cisco NAC Appliance only supports Wireless OOB deployments with Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers.
•
WLCs must be configured to interact with the CAM using SNMP read, write, and trap functions.
•
Each service set identifier (SSID)/dynamic interface on the WLC must have both an Authentication (Quarantine) VLAN and Access VLAN configured.
•
When SSID is setup to perform Wireless SSO and there is a overlapping of IP subnets over multiple SSIDs, even after roaming from one SSID to another, the user is still listed under Online Users in the CAM. To avoid this, create separate IP ranges for each SSID.
•
Ensure that any access/aggregation switches in the network between the WLCs and the Clean Access Server have the same Authentication (Quarantine) and Access VLANs trunked.
•
Authentication and Access VLANs are defined on the WLC and changes between the two are transmitted to the CAM using SNMP traps—administrators do not assign VLANs from the CAM via user role assignments or otherwise.
•
When a wireless user logs off, the WLC also sends SNMP information to the CAM to ensure the user ID is removed from the Online Users list. Likewise, if the administrator must kick any users out of the Online Users list, the CAM informs the WLC via SNMP and the WLC automatically assigns the wireless client to the Authentication (Quarantine) VLAN.
•
If Single Sign-On (SSO) is required for wireless users, the WLC must also be configured to transmit RADIUS accounting packets to the CAS. Cisco WLCs do not support IPSec communication with the Cisco NAC Appliance network, so you cannot provide RADIUS SSO capability to users in your FIPS 140-2 compliant environment.
Note
The VPN Auto Logout feature does not work in a Wireless OOB deployment. If VPN Auto Logout signs a user out of the system, the CAM will not learn of the disconnection from the WLC.
•
If your wireless access network provides services for Wireless IP Phones, ensure you configure a separate SSID for such devices so that they do not encounter the Cisco NAC Appliance authentication process.
Example Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Steps
This section provides a configuration example for a Cisco 4400 series Wireless LAN Controller.
•
Create the Dynamic Interface on the Wireless LAN Controller
•
Create the WLAN on the Wireless LAN Controller and Enable Cisco NAC Appliance Integration
•
Configure SNMP on the Wireless LAN Controller
•
Specify the CAM as the SNMP Trap Receiver
Create the Dynamic Interface on the Wireless LAN Controller
To create and specify settings for a new Dynamic Interface on the Wireless LAN Controller:
Step 1
In the WLC graphical user interface, click Controller > Interfaces to open the Interfaces page.
Step 2
Click New and enter an Interface Name and VLAN ID in the Interfaces > New page that appears.
Step 3
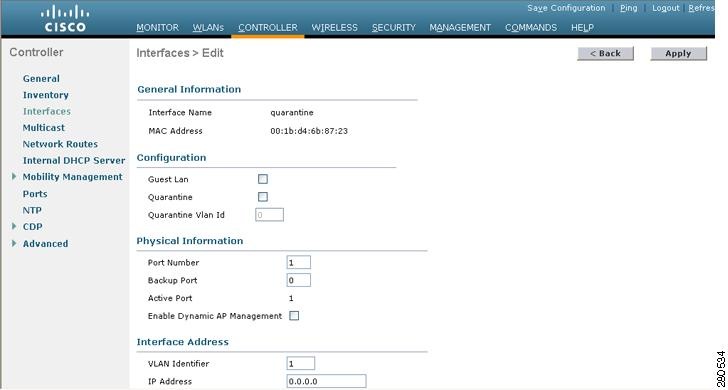
Click Apply to commit your changes. The Interfaces > Edit page appears (Figure 4-3).
Figure 4-3 WLC 4400 Interfaces > Edit Page
Step 4
Configure the following parameters:
•
Guest LAN
•
Enable the Quarantine option and specify a quarantine Quarantine VLAN ID.
Note
Check the Quarantine check box if you want to configure this VLAN as unhealthy or you want to configure network access control (NAC) Out-of-Band integration. Doing so causes the data traffic of any client that is assigned to this VLAN to pass through the controller.
•
Physical port assignment
•
VLAN identifier
•
Fixed IP address, IP netmask, and default gateway
•
Primary and secondary DHCP servers
•
Access control list (ACL) name, if required
Note
To ensure proper operation, you must set the Port Number and Primary DHCP Server parameters.
Step 5
Click Save Configuration to save your changes.
Step 6
Repeat this procedure for each dynamic interface that you want to create or edit.
For more information, refer to the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide, Release 5.1.
Create the WLAN on the Wireless LAN Controller and Enable Cisco NAC Appliance Integration
To create a new WLAN on the Wireless LAN Controller and enable integration with Cisco NAC Appliance:
Step 1
In the WLC graphical user interface, click WLANs > New. The WLANs > New page appears.
Step 2
Choose WLAN from the Type dropdown menu.
Step 3
Enter up to 32 alphanumeric characters for the profile name to be assigned to this WLAN in the Profile Name field. The profile name must be unique.
Step 4
Enter up to 32 alphanumeric characters for the SSID to be assigned to this WLAN in the WLAN SSID field.
Step 5
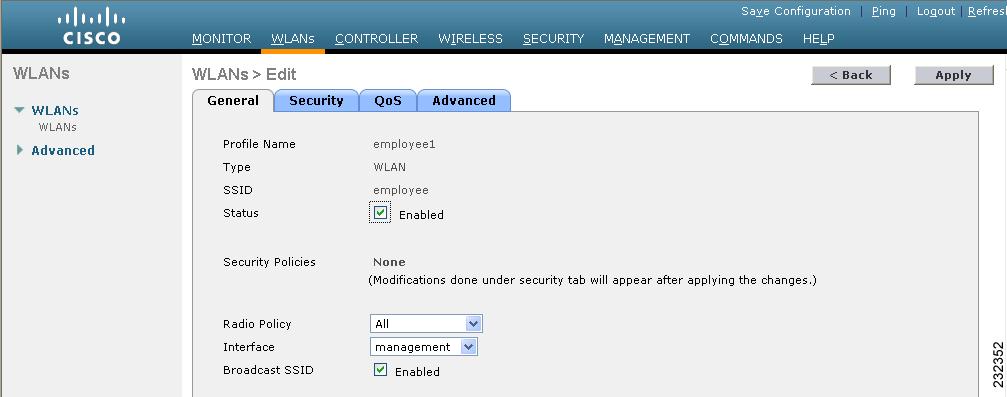
Click Apply to commit your changes. The WLANs > Edit page appears (Figure 4-4).
Figure 4-4 WLC 4400 WLANs > Edit Page
Step 6
On the General tab, check the Status checkbox to enable this WLAN.
CautionLeave this option unchecked (disabled) until you have finished making configuration changes to the WLAN.
Step 7
On the Advanced tab, check the State checkbox under the "NAC" heading to enable WLC integration with Cisco NAC Appliance.
Step 8
Specify a Quarantine VLAN ID for wireless user sessions when authenticating with Cisco NAC Appliance.
Step 9
Click Apply to commit your changes.
Step 10
Click Save Configuration to save your changes.
For more information, refer to the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide, Release 5.1.
Configure SNMP on the Wireless LAN Controller
To ensure the Wireless LAN Controller is able to receive and process SNMP transmissions from the CAM regarding OOB client machine status in the Cisco NAC Appliance system, you must enable and configure SNMP behavior on the WLC.
To create a new SNMP community and enable SNMP on the WLC:
Step 1
Click Management and then Communities under SNMP. The SNMP v1 / v2c Community page appears.
Step 2
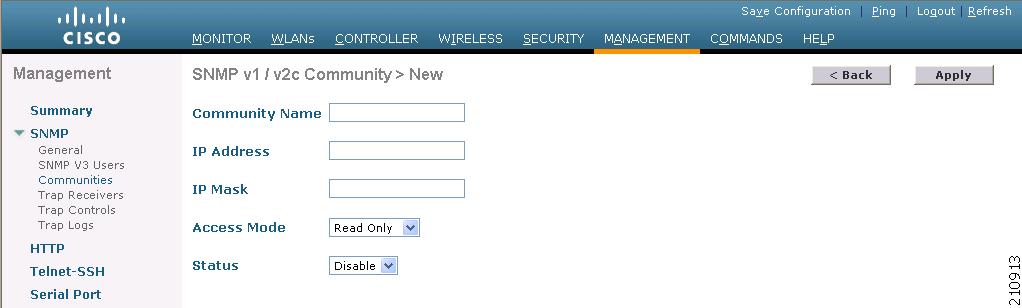
Click New to create a new community. The SNMP v1 / v2c Community > New page appears (Figure 4-5).
Figure 4-5 SNMP v1 / v2c Community > New Page
Step 3
In the Community Name field, enter a unique name containing up to 16 alphanumeric characters. (Do not enter "public" or "private.")
Step 4
Enter the IP Address of the CAM from which this device accepts SNMP packets with the associated community and the respective IP Mask.
Step 5
Choose Read/Write from the Access Mode dropdown menu to specify the access level for this community.
Step 6
Choose Enable from the Status dropdown menu to activate this community.
Step 7
Click Apply to commit your changes.
Step 8
Click Save Configuration to save your settings.
Step 9
Repeat this procedure if a "public" or "private" community still appears on the SNMP v1 / v2c Community page.
For more information, refer to the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide, Release 5.1.
Specify the CAM as the SNMP Trap Receiver
Once you enable and configure SNMP on the Wireless LAN Controller, you must also ensure the WLC knows which CAM is receiving SNMP trap messages.
To specify the host name and IP address of the SNMP trap receiver CAM:
Step 1
Click Management and then Trap Receivers under SNMP. The SNMP Trap Receivers > New page appears (Figure 4-6).
Figure 4-6 SNMP Trap Receivers > New Page
Step 2
Specify the host name of the CAM to receive SNMP traps from the WLC in the Trap Receiver Name field.
Step 3
Enter the CAM's IP address in the IP Address field.
Step 4
Choose Enable from the Status dropdown menu.
Step 5
Click Apply to commit your changes.
Step 6
Click Save Configuration to save your settings.
Wireless OOB Network Setup/Configuration Worksheet
Table 4-3 summarizes information needed to configure WLCs and the Clean Access Manager.
Configure Wireless LAN Controller Connection on the CAM
This section describes the web admin console configuration steps to implement Wireless OOB. In general, you first configure Group and Wireless LAN Controller profiles, and the CAM's SNMP Receiver settings under OOB Management > Profiles. After the WLC profile is configured, add the new WLC you want to communicate with to the Clean Access Manager's domain under OOB Management > Devices, and ensure the new profile appears in the Devices list.
The configuration sequence is as follows:
1.
Plan your settings and configure the switches to be managed, as described in previous section, Configure Your Wireless LAN Controllers
2.
Add a Wireless Out-of-Band Clean Access Server and Configure Environment
4.
Configure Wireless LAN Controller Profiles
6.
Add and Manage Wireless LAN Controllers
Add a Wireless Out-of-Band Clean Access Server and Configure Environment
Almost all the CAM/CAS configuration for Wireless Out-of-Band deployment is done directly in the OOB Management module of the CAM web console. If your Wireless LAN Controller installation features great enough throughput/bandwidth, you can (and may need to) configure more than one Clean Access Server to handle all of the authentication traffic between wireless client machines and the Cisco NAC Appliance system.
To add a Wireless OOB Clean Access Server to the CAM:
Step 1
Choose the Out-of-Band Virtual Gateway option from the Server Type dropdown menu (Figure 4-7).
Figure 4-7 Add New OOB Server
The Clean Access Server itself must be either In-Band or Out-of-Band. The Clean Access Manager can control both In-Band and Out-of-Band CASs in its domain.
Note
You can only deploy CASs supporting wireless client machine authentication in Virtual Gateway mode.
Step 2
Enter the IP address of the Clean Access Server's eth0 (trusted) interface in the Server IP Address field.
Step 3
(Optional) Enter the Clean Access Server location/description/purpose in the Server Location field.
Step 4
Click Add Clean Access Server.
Configure Group Profiles
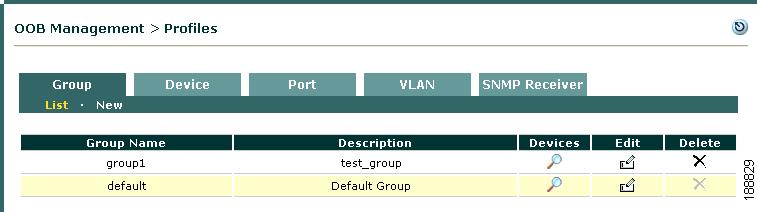
When you first add a WLC to the Clean Access Manager's domain (under OOB Management > Devices), a Group profile must be applied to add the new WLC. There is a predefined Group profile called default, shown in Figure 4-8. All WLCs are automatically put in the default group when you add them. You can leave this default Group profile setting, or you can create additional Group profiles as needed. If you are adding and managing a large number of WLCs, creating multiple Group profiles allows you to filter which sets of devices to display from the list of WLCs (under OOB Management > Devices > Devices > List).
Figure 4-8 Group Profiles List
Add Group Profile
Step 1
Go to OOB Management > Profiles > Group > New (Figure 4-9).
Figure 4-9 New Group
Step 2
Enter a single word for the Group Name. You can use digits and underscores, but no spaces.
Step 3
Enter an optional Description.
Step 4
Click Add. The new Group profile appears under OOB Management > Profiles > Group > List.
Edit Group Profile
Step 1
To edit the profile later, after actual WLCs are added, go to OOB Management > Profiles > Group > List and click the Edit icon for the new Group profile.
Step 2
The Edit page appears (Figure 4-10).
Figure 4-10 Edit Group
Step 3
You can toggle the WLCs that belong in the Group profile by selecting the IP address of the WLC from the Member Devices or Available Devices columns and clicking the Join or Remove buttons as applicable.
Step 4
Click the Update button when done to save your changes.
Note
To delete a group profile, you must first remove the joined switches and/or WLCs from the profile.
Configure Wireless LAN Controller Profiles
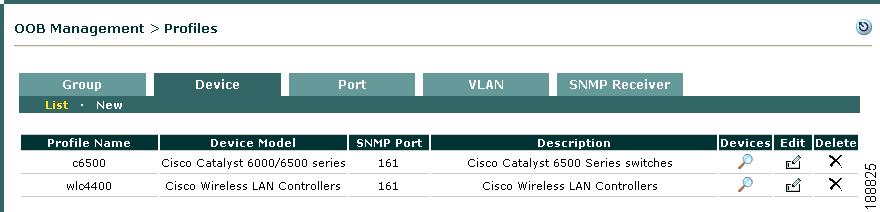
A WLC profile must first be created under OOB Management > Profiles > Device > New, then applied when a new WLC is added. A WLC profile classifies WLCs of the same model and SNMP settings, as shown in Figure 4-11. The WLC profile configures how the CAM learns client Authentication/Access VLAN assignments from the WLC and when to remove Wireless OOB clients from the Online Users list for a WLC of that type.
Figure 4-11 Device Profiles List
The Device profiles list under OOB Management > Profiles > Device > List provides three icons:
•
Devices—Clicking this icon brings up the list of added devices under OOB Management > Devices > Devices > List (see Figure 4-15).
•
Edit—Clicking this icon brings up the Edit Device profile form (see Figure 4-13).
•
Delete—Clicking this icon deletes the Device profile (a confirmation dialog appears first).
Add Wireless LAN Controller Profile
Use the following steps to add a Wireless LAN Controller profile.
Step 1
Go to OOB Management > Profiles > Device > New (Figure 4-12).
Figure 4-12 New Wireless LAN Controller Profile
Step 2
Enter a single word for the Profile Name. You can use digits and underscores but no spaces.
Note
It is a good idea to enter a WLC name that identifies the model and SNMP read and write versions, for example "WLC4400v2v3."
Step 3
Enter the SNMP Port configured on the WLC to receive read/write requests. The default port is 161 for SNMP GET/SET and the default port is 162 for Traps.
Step 4
Enter an optional Description.
Note
You can click the link available at the top of this tab to view the list of supported device models.
Step 5
Configure SNMP Read Settings to match those on the WLC.
•
Choose the SNMP Version: SNMP V1, SNMP V2C, or SNMP V3.
•
Type the Community String for SNMP V1 or SNMP V2C configured for the WLC.
Step 6
If SNMP V3 is used for SNMP Read Settings on the WLC, configure the following settings to match those on the switch:
•
Choose a Security Method from the dropdown menu: NoAuthNoPriv, AuthNoPriv(MD5), AuthNoPriv(SHA), AuthPriv(MD5+DES), or AuthPriv(SHA+DES).
•
Type the User Name.
•
Type the User Auth.
•
Type the User Priv.
Step 7
Configure SNMP Write Settings to match those on the WLC.
•
Choose the SNMP Version: SNMP V1, SNMP V2C, or SNMP V3.
•
Type the Community String for SNMP V1 or SNMP V2C configured for the WLC.
Step 8
If SNMP v3 is used for SNMP write settings on the WLC, configure the following settings to match those on the WLC:
•
Choose a Security Method from the dropdown menu: NoAuthNoPriv, AuthNoPriv(MD5), AuthNoPriv(SHA), AuthPriv(MD5+DES-CBC), or AuthPriv(SHA+DES-CBC).
•
Type the User Name.
•
Type the User Auth.
•
Type the User Priv.
Note
When WLC is rebooted, the SNMP V3 write may fail as the WLC SNMP engineboots value is not synced with CAM engineboots value. Each time you reboot WLC, update the switch profile. It is recommended to upgrade WLC to the latest version. For more details, refer to the caveat CSCtb78072 in Release Notes for Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers and Lightweight Access Points for Release 7.0.116.0.
Step 9
Click Add to add the Wireless LAN Controller profile to OOB Management > Profiles > Device > List (Figure 4-15).
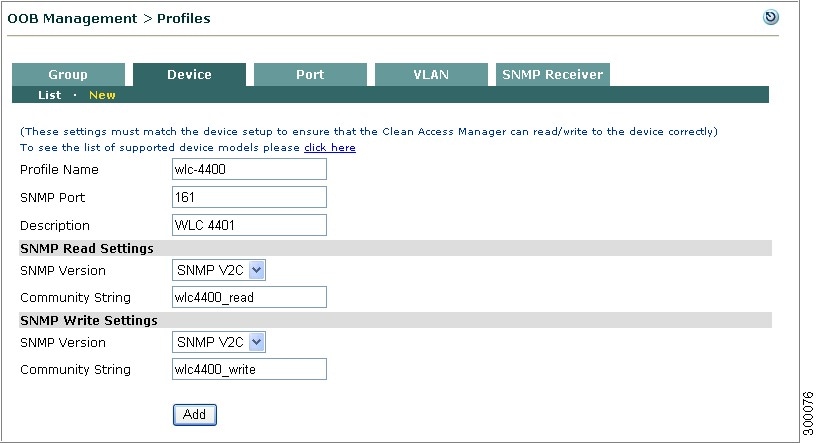
Figure 4-13 illustrates a WLC profile defining a Cisco 440 Wireless LAN Controller with the same SNMP settings: SNMP V2c with read community string "wlc4400_read" and write community string "wlc4400_write."
Figure 4-13 Example Wireless LAN Controller Profile
Configure SNMP Receiver
The SNMP Receiver form configures how the SNMP Receiver running on the Clean Access Manager receives and responds to SNMP trap notifications from WLCs when user events occur (such as when a user first logs on to or logs off of the network). The SNMP Receiver configuration on the CAM must match the WLC configuration in order for the WLC to send SNMP traps to the CAM.
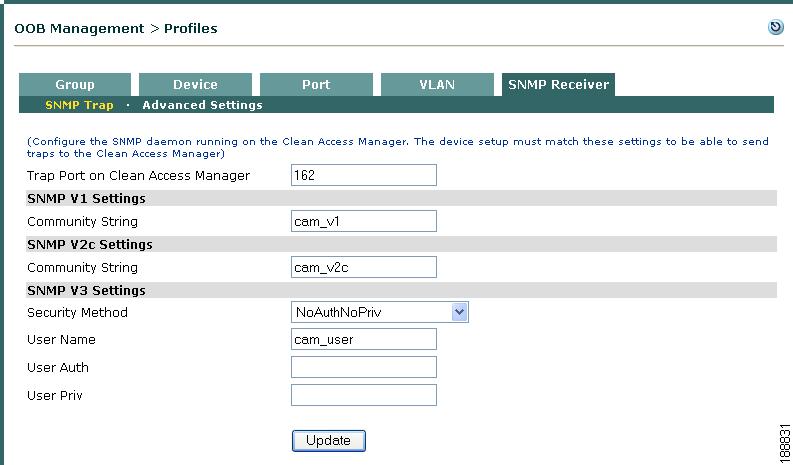
SNMP Trap
This page configures settings for the SNMP traps the CAM receives from switches and WLCs. The Clean Access Manager SNMP Receiver can simultaneously support different versions of SNMP (V1, V2c, V3) when controlling groups of switches and/or WLCs in which individual devices may be using different versions of SNMP.
Step 1
Go to OOB Management > Profiles > SNMP Receiver > SNMP Trap (Figure 4-14).
Figure 4-14 CAM SNMP Receiver
Step 2
Use the default Trap Port on Clean Access Manager (162) or enter a new port number here.
Step 3
For SNMP V1 Settings, type the Community String used on switches using SNMP V1.
Step 4
For SNMP V2c Settings, type the Community String used on switches using SNMP V2c.
Step 5
For SNMP V3 Settings, configure the following fields used on switches using SNMP V3:
•
Choose the Security Method from the dropdown menu: NoAuthNoPriv, AuthNoPriv(MD5), AuthNoPriv(SHA), AuthPriv(MD5+DES-CBC), or AuthPriv(SHA+DES-CBC)
•
Type the User Name.
•
Type the User Auth.
•
Type the User Priv
Step 6
Click Update to save settings.
Add and Manage Wireless LAN Controllers
The pages under the OOB Management > Devices > Devices tab are used to discover and add new switches and WLCs within an IP range, add new switches or WLCs by exact IP address, and manage the list of associated devices. There are two methods to add new managed WLCs:
•
Add New Wireless LAN Controller
•
Search New Wireless LAN Controllers
Figure 4-15 List of Devices
The list of devices under OOB Management > Devices > Devices > List displays all switches added from the New or Search forms. Wireless LAN Controller entries in the list include the WLC's IP address, MAC address, Description, and WLC Profile. You can sort the entries on the list by Device Group or Device Profile dropdowns, or you can simply type a Device IP and hit Enter to search for a switch by its address. Additionally the List provides one control and two icons:
•
Config—Clicking the Config icon brings up the Config Tab for the WLC.
•
Delete—Clicking the Delete icon deletes the WLC from the list (a confirmation dialog appears before the WLC entry is removed).
Note
The Port Profile dropdown is only used for adding switches to the Devices list and does not pertain to WLCs.
Profile links do not apply to WLCs and are "grayed out" in the Devices list for WLC entries.
Add New Wireless LAN Controller
The New page allows you to add WLCs when exact IP addresses are already known.
Step 1
Go to OOB Management > Devices > Devices > New (Figure 4-16).
Figure 4-16 Add New Wireless LAN Controller
Step 2
Choose the Device Profile from the dropdown menu to apply to the WLC to be added.
Step 3
Choose the Device Group for the WLC from the dropdown menu.
Step 4
Type the IP Addresses of the WLC(s) you want to add. Separate each IP address by line.
Step 5
Enter an optional Description of the new switch.
Step 6
Click the Add button to add the WLC(s).
Step 7
Click the Reset button to reset the form.
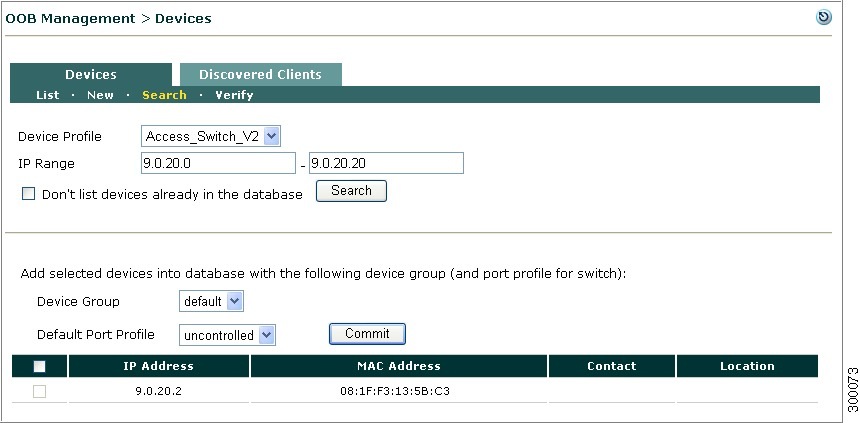
Search New Wireless LAN Controllers
The Search page allows you to discover and add unmanaged switches within an IP range.
Step 1
Go to OOB Management > Devices > Devices > Search (Figure 4-17).
Figure 4-17 Search Devices
Step 2
Select a Device Profile from the dropdown list. The read community string of the selected WLC profile is used to find WLCs with matching read settings.
Step 3
Type an IP Range in the text box. (The maximum range for a search is 256 addresses.)
Step 4
By default, the Don't list devices already in the database checkbox is already checked. If you uncheck this box, the resulting search will include devices you have already added.
Step 5
Choose a Device Group from the dropdown to apply to the WLCs found in the search.
Step 6
Click the checkbox to the left of each WLC you want to connect with the CAM. Alternatively, click the checkbox at the top of the column to add all WLCs found from the search.
Note
While all WLCs matching the read community string of the WLC profile used for the search are listed, only those WLCs matching the read SNMP version and community string can be added using the Commit button. The CAM cannot communicate with a WLC unless its write SNMP settings match those configured for its WLC profile.
Step 7
Click the Commit button to add the new devices. These devices are listed under OOB Management > Devices > Devices > List.
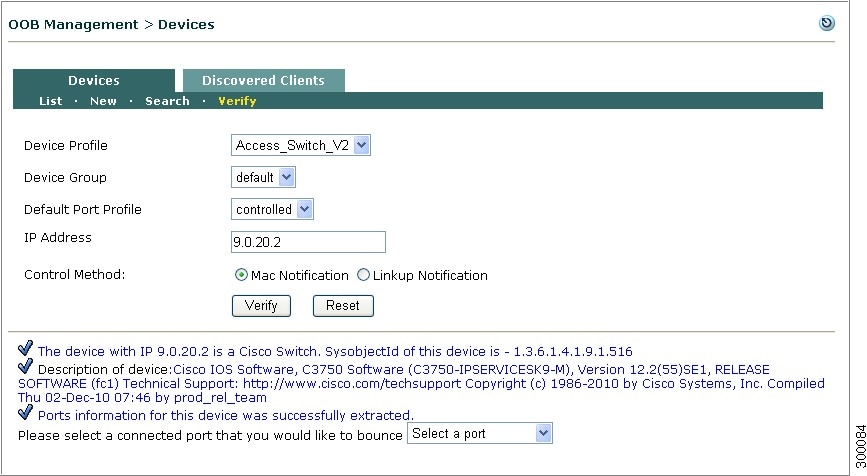
Verify Devices
The Verify page allows you to verify the devices. This utility verifies a device already added to CAM or a new device that is yet to be added to CAM. The device may be a switch or WLC.
Note
Before verifying a device, ensure that you have setup the device profile and port profile, and configured the SNMP receiver for the device.
Step 1
Go to OOB Management > Devices > Devices > Verify.
Figure 4-18 Verify Devices
Step 2
Choose a Device Profile from the dropdown.
Step 3
Choose a Device Group from the dropdown.
Step 4
Choose a Default Port Profile from the dropdown.
Step 5
Type a valid IP Address in the text box.
Step 6
Choose the Control Method to configure the SNMP trap notification type that the CAM SNMP Receiver will use for a particular switch.
Note
The Control Method is applicable only for the switches.
•
MAC Notification—If a switch supports MAC Notification, choose this option.
Note
To support a variety of switch configurations, Cisco NAC Appliance supports switches using both MAC Change Notification and MAC Move Notification traps.
•
Linkup Notification—If a switch does not support MAC Notification, then choose this option.
Step 7
Click Verify.
The device is verified and the results are displayed at the bottom of the page as shown in Figure 4-19.
Figure 4-19 Verify Devices
- Result
The device status is displayed and you can select a connected port that you would like to bounce from the dropdown.
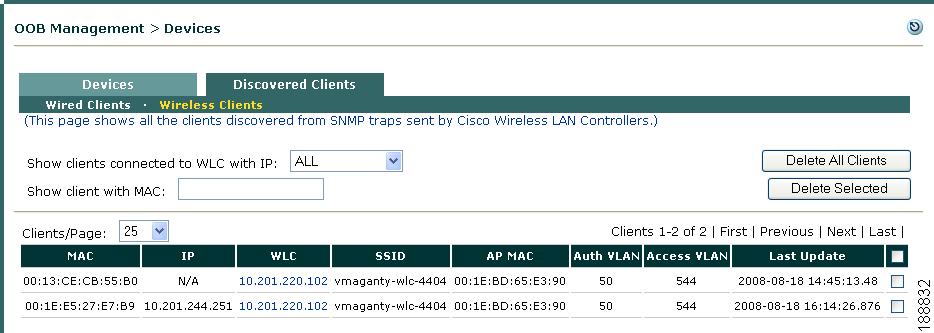
Discovered Wireless Clients
Figure 4-20 shows the OOB Management > Devices > Discovered Clients > Wireless Clients page. The Wireless Clients page lists all clients discovered by the Clean Access Manager via SNMP traps between the CAM and the WLC. The page records the activities of Out-of-Band clients (regardless of VLAN), based on the SNMP trap information that the Clean Access Manager receives.
When a client connects to a WLC and is assigned to the Authentication (Quarantine) VLAN, a trap is sent and the Clean Access Manager creates an entry on the Wireless Clients page. The Clean Access Manager adds a client's MAC address, IP address, associated WLC, Access Point MAC address, and Authentication (Quarantine) and Access VLAN assignments to the Wireless Clients list. Thereafter, the CAM updates the entry as it receives new SNMP trap information for the client.
Removing an entry from the Wireless Clients list clears this status information for the Wireless OOB client from the CAM.
Figure 4-20 Wireless Clients
Elements of the page are as follows:
•
Show clients connected to WLC with IP—Leave the default of ALL WLCs displayed, or choose a specific WLC from the dropdown menu. The dropdown menu displays all managed WLCs configured on the CAM.
•
Show client with MAC—Type a specific MAC address and press Enter to display a particular client.
•
Clients/Page—Leave the default of 25 entries displayed per page, or choose from the dropdown menu to displays 50, 100, 200, or ALL entries on the page.
•
Delete All Clients—This button removes all clients on the list.
•
Delete Selected—This button only removes the clients selected in the check column to the far right of the page.
•
Note that you can click any of the following column headings to sort results by that column:
–
MAC—MAC address of discovered wireless client
–
IP—IP address of the wireless client
–
WLC—IP address of the originating Wireless LAN Controller. Clicking the WLC IP address brings up the OOB Management > Devices > WLC [IP address] > Config > Basic page for the WLC. (For more information, see Config Tab.)
–
SSID—The service set identifier to which the wireless client has been associated for network access.
–
AP MAC—The MAC address of the WLC Access Point through which the client is accessing the network
–
Auth VLAN—Authentication (Quarantine) VLAN
A value of "N/A" in this column indicates that the VLAN ID for this MAC address is unavailable from the WLC.–
Access VLAN—Access VLAN of the client
A value of "N/A" in this column indicates the Access VLAN ID is unavailable for the client. For example, if the user is switched to the Authentication VLAN but has never successfully logged into Cisco NAC Appliance (due to wrong user credentials), this machine will never have been assigned to the Access VLAN.–
Last Update—The last time the CAM updated the information of the entry.
See Wireless Out-of-Band Users for additional details on monitoring Out-of-Band users.
Config Tab
The Config tab allows you to modify Basic and Group profile settings for a particular Wireless LAN Controller:
Basic
The Basic tab (Figure 4-21) shows the following values configured for the WLC.
Figure 4-21 Config > Basic
•
The first values come from the initial configuration done on the WLC itself:
–
IP Address
–
MAC Address
–
Location
–
Contact
–
System Info (translated from the MIB for the WLC)
•
Device Profile—Shows the Device Profile you are using for this WLC configured under OOB Management > Profiles > Device. The WLC Device Profile sets the model type, the SNMP port on which to send SNMP traps, SNMP version for read and write and corresponding community strings, or authentication parameters (SNMP V3 Write).
•
Description—Optional description of the WLC. To change this field, type a new description and click Update.
Group
This page displays all the Group Profiles configured in the Clean Access Manager, and the Group Profiles to which the WLC currently belongs. You can add the WLC to other Groups, or you can remove the WLC from a Group Joined. To change the Group membership for all switches, go to OOB Management > Profiles > Group (see Configure Group Profiles).
Figure 4-22 Config > Group
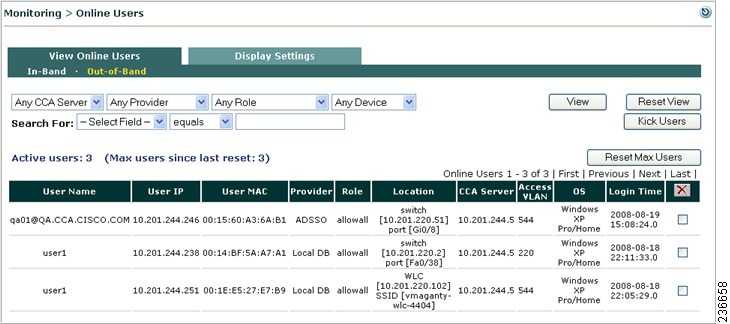
View Wireless Out-of-Band Online Users
When Out-of-Band is enabled, the Monitoring > View Online Users page displays links for both In-Band and Out-of-Band users and display settings (Figure 4-23). See Out-of-Band Users for details.
Figure 4-23 View Out-of-Band Online Users
Wireless Out-of-Band Users
Wireless OOB User Sessions
The following events trigger Wireless OOB users' disconnection from the Cisco NAC Appliance system:
•
SNMP trap messages from the WLC
•
Certified Timer expiration
•
Session Timer expiration
•
Manual removal from CAM
Following log-off, users must undergo authentication again before they are allowed back into the internal network. For additional details, see also Interpreting Event Logs and Manage Certified Devices.
Wireless and Wired OOB User List Summary
Table 3-4 describes the lists used to track Out-of-Band users.

 Feedback
Feedback