- Preface
- Chapter 1 Overview
- Chapter 2 Using the aregcmd Commands
- Chapter 3 Using the Graphical User Interface
- Chapter 4 Cisco Prime Access Registrar Server Objects
- Chapter 5 Using the radclient Command
- Chapter 6 Configuring Local Authentication and Authorization
- Chapter 7 RADIUS Accounting
- Chapter 8 Diameter
- Chapter 9 Extensible Authentication Protocols
- Chapter 10 Using WiMAX in Cisco Prime Access Registrar
- Chapter 11 Using Extension Points
- Chapter 12 Using Replication
- Chapter 13 Using On-Demand Address Pools
- Chapter 14 Using Identity Caching
- Chapter 15 Using Trusted ID Authorization with SESM
- Chapter 16 Using Prepaid Billing
- Chapter 17 Using Cisco Prime Access Registrar Server Features
- Chapter 18 Directing RADIUS Requests
- Chapter 19 Wireless Support
- Chapter 20 Using LDAP
- Chapter 21 Using Open Database Connectivity
- Chapter 22 SIGTRAN-M3UA
- Chapter 23 Using SNMP
- Chapter 24 Enforcement of Licensing Models
- Chapter 25 Backing Up the Database
- Chapter 26 Using the REX Accounting Script
- Chapter 27 Logging Syslog Messages
- Chapter 28 Troubleshooting Cisco Prime Access Registrar
- Appendix A: Cisco Prime Access Registrar Tcl, REX and Java Dictionaries
- Appendix B: Environment Dictionary
- Appendix C: RADIUS Attributes
- Glossary
- Index
Using Prepaid Billing
Cisco Prime Access Registrar (Cisco Prime AR) supports two types of prepaid billing, IS835C and Cisco Real-time Billing (CRB), a Cisco proprietary solution. The IS835C version adheres to industry standards and is the preferred version.
Three components are required to support a prepaid billing service, such as the following:
•![]() AAA client
AAA client
•![]() Cisco Prime AR server
Cisco Prime AR server
•![]() External prepaid billing server
External prepaid billing server
The most important factor for an effective prepaid billing service is in developing a shared library to be configured under the prepaid RemoteServer object. The shared library should be developed to implement all specified API functions. You will have to provide a shared library that meets the needs of your environment. The shared library must implement the API functions to perform the various tasks required for your specific implementation of the prepaid billing service.

Note ![]() Cisco works with you to develop the prepaid billing service and implement the API. For more information, contact your Cisco systems engineer.
Cisco works with you to develop the prepaid billing service and implement the API. For more information, contact your Cisco systems engineer.
The chapter contains the following sections:
•![]() Implementing the Prepaid Billing API
Implementing the Prepaid Billing API
Overview
When a subscriber uses a prepaid billing service, each call requires a set of data about the subscriber. However, the AAA network has no previous knowledge of the subscriber's usage behavior. Cisco Prime AR uses an iterative authorization paradigm over multiple sessions to support the prepaid billing solution.
Each time an authorization request is made, the billing server apportions a fraction of the subscriber's balance into a quota. When a subscriber uses multiple sessions, each session must obtain its own quota. When a previously allocated quota is depleted, a session must be reauthorized to obtain a new quota.

Note ![]() The granularity and the magnitude of the quota is in the design and implementation of the prepaid billing server and is beyond the scope of this document. In general, a smaller quota generates more network traffic, but allows more sessions per subscriber. When the quota is equal to a subscriber's total account balance, there is minimal network traffic, but only one session can be supported.
The granularity and the magnitude of the quota is in the design and implementation of the prepaid billing server and is beyond the scope of this document. In general, a smaller quota generates more network traffic, but allows more sessions per subscriber. When the quota is equal to a subscriber's total account balance, there is minimal network traffic, but only one session can be supported.
When a subscriber's current quota is depleted, the AAA client initiates a reauthorization request sending Access-Request packets. After the Cisco Prime AR server receives the request, it forwards the request to the billing server. The billing server then returns the next quota to use. The new quota might not be the same as the previous, and the billing server might adjust the quota dynamically.
IS835C Prepaid Billing
Cisco Prime AR acts as a RADIUS protocol head for all the requirements specified in the cdma2000 Wireless IP Network Standard: PrePaid Packet Data Service specification:
http://www.3gpp2.org/Public_html/specs/X.S0011-006-C-v1.0.pdf
As long as the prepaid client understands or accepts what the external billing server sends, the service should work. The Cisco Prime AR server neither imposes nor is affected by the values of attributes returned from the external billing server.
For additional information, see cdma2000 Wireless IP Network Standard: Accounting Services and 3GPP2 RADIUS VSAs at the following URL:
http://www.3gpp2.org/Public_html/specs/X.S0011-005-C-v1.0.pdf
The IS835C specification requires that the Cisco Prime AR server be able to determine that a particular user is a prepaid billing user. A user is accepted as a valid prepaid user when the response dictionary of the incoming packet contains the Cisco Prime AR internal subattribute named prepaid.
The IS835C specification requires prepaid users to first be authenticated by the RADIUS server. This requires the configuration of a group service with an authentication service first, followed by the prepaid service that adds prepaid attributes as shown in Setting Up an Authentication Group Service. The group service configuration enables the AA service to add the prepaid subattribute to the response dictionary upon successful authentication, before the prepaid service is invoked.
Configuring IS835C Prepaid Billing
To configure an IS835C prepaid billing service, use the following sections to configure the required Cisco Prime AR objects:
•![]() Setting Up a Prepaid Billing RemoteServer
Setting Up a Prepaid Billing RemoteServer
•![]() Setting Up an IS835C Prepaid Service
Setting Up an IS835C Prepaid Service
•![]() Setting Up Local Authentication
Setting Up Local Authentication
•![]() Setting Up an Authentication Group Service
Setting Up an Authentication Group Service
Setting Up a Prepaid Billing RemoteServer
Cisco Prime AR loads the library dynamically and registers the API functions, then calls out the library initialization API once at startup. The call to initialize functions initializes various data structures and connections with the billing server, as required.
Table 16-1 lists and describes the properties required for an IS835C RemoteServer object.
Setting up a Prepaid Billing Remote Server
To set up a prepaid billing remote server:
Step 1 ![]() Use aregcmd to add a RemoteServer under /Radius/RemoteServers.
Use aregcmd to add a RemoteServer under /Radius/RemoteServers.
cd /radius/remoteserver
add prepaid-is835c
Step 2 ![]() Set remoteserver protocol to prepaid-is835c.
Set remoteserver protocol to prepaid-is835c.
cd prepaid-is835c
set protocol prepaid-is835c
Set Protocol prepaid-is835c
The following is the default configuration of a prepaid-is835c RemoteServer.
[ //localhost/Radius/RemoteServers/prepaid-is835c ]
Name = prepaid-is835c
Description =
Protocol =
IPAddress =
Port = 0
Filename =
Connections = 8
Setting Up an IS835C Prepaid Service
Cisco Prime AR uses a service type prepaid to support the prepaid billing solution. The prepaid service mediates between the client NAS and the external prepaid billing server.
Setting up an IS835C Prepaid Service
To set up an IS835C prepaid service:
Step 1 ![]() Use aregcmd to add a prepaid service under /Radius/Services:
Use aregcmd to add a prepaid service under /Radius/Services:
cd /radius/services
add prepaid
Added prepaid
Step 2 ![]() Set the service type to prepaid.
Set the service type to prepaid.
cd prepaid
set type prepaid
Set Type prepaid
A prepaid service has the following default properties:
[ //localhost/Radius/Services/prepaid ]
Name = prepaid
Description =
Type = prepaid
IncomingScript~ =
OutgoingScript~ =
OutagePolicy~ = RejectAll
OutageScript~ =
MultipleServersPolicy = Failover
RemoteServers/
Step 3 ![]() Add a reference to the is835c-prepaid RemoteServer.
Add a reference to the is835c-prepaid RemoteServer.
cd RemoteServer
add 1 prepaid-is835c
Added 1
Setting Up Local Authentication
If you use the Cisco Prime AR server for authentication and authorization in your prepaid billing solution, you should configure an AA service. For example, you might configure a service similar to local-users (in the example configuration) for authentication and authorization of local users.
If some of the users are non-prepaid users or if the prepaid users need to have RADIUS authorization attributes returned, you should configure an AA service to perform that authentication and authorization.
Setting up a Local Authentication
To set up a local authentication:
Step 1 ![]() Use aregcmd to set up a local authentication service.
Use aregcmd to set up a local authentication service.
cd /radius/services
add Prepaid-LocalAuthentication
Added prepaid-LocalAuthentication
cd prepaid-LocalAuthentication
[ //localhost/Radius/Services/prepaid-LocalAuthentication ]
Name = prepaid-LocalAuthentication
Description =
Type =
Step 2 ![]() Set the service type to local.
Set the service type to local.
set type local
Set Type local
Step 3 ![]() Set the UserList property to the userlist that contains IS835C prepaid users.
Set the UserList property to the userlist that contains IS835C prepaid users.
set UserList userlist_name
Set UserList userlist_name

Note ![]() You can use an LDAP or ODBC service in place of the local authentication service.
You can use an LDAP or ODBC service in place of the local authentication service.
The authentication service must add the Cisco Prime AR internal attribute prepaid (subattribute 22) to the response upon successful authentication.
Setting Up an Authentication Group Service
Your prepaid billing solution usually requires a group service to tie together an AA service with a prepaid service, a group service to tie together an accounting service with a prepaid service, or both.
If you are using an AA service with your prepaid billing solution, you must configure a group service, for example prepaid-users, that ties the requests to the AA service (local-users in our example) with the prepaid service.
If you are using Cisco Prime AR for an accounting service with your prepaid billing solution, you must configure a group service, for example prepaid-file, that ties accounting requests to both the regular accounting service (local-file in our example) and the prepaid service.
Setting up an Authentication Group Service
To set up an authentication group service:
Step 1 ![]() Use aregcmd to add a prepaid authentication group service under /Radius/Services.
Use aregcmd to add a prepaid authentication group service under /Radius/Services.
cd /radius/services
add prepaid-groupAuthentication
Added prepaid-groupAuthentication
cd prepaid-groupAuthentication
[ //localhost/Radius/Services/prepaid-groupAuthentication ]
Name = group-prepaidAuthentication
Description =
Type =
Step 2 ![]() Set the service type to group.
Set the service type to group.
set type group
Set Type group
The group service requires the ResultRule to be set to AND, the default setting for a group service.
ls
[ //localhost/Radius/Services/group-prepaidAuthentication ]
Name = group-prepaidAuthentication
Description =
Type = group
IncomingScript~ =
OutgoingScript~ =
ResultRule = AND
GroupServices/
Step 3 ![]() Change directory to GroupServices and add references to the prepaid service and the authentication service.
Change directory to GroupServices and add references to the prepaid service and the authentication service.
cd GroupServices
[ //localhost/Radius/Services/group-prepaidAuthentication/GroupServices ]
add 1 Prepaid-LocalAuthentication
Added 1
add 2 prepaid
Added 2
CRB Prepaid Billing
Cisco Real-Time Billing (CRB) is a Cisco proprietary method of providing prepaid billing service. Cisco Prime AR uses vendor-specific attributes (VSA) to extend the standard RADIUS protocol to carry information not usually present in the standard RADIUS packet. Cisco Prime AR uses a set of VSAs allocated to the Cisco VSA pool [26,9].
Cisco Prime AR required several different types of measurements to support a prepaid billing solution. These measurements require the use of metering variables to perform usage accounting. Table 16-2 lists the different measurements and what the AAA client, Cisco Prime AR server, and billing server do with them.
Cisco Prime AR provides maximum flexibility to billing servers by allowing the metering variable to be modified as the service is used. This requires network nodes to measure all parameters all the time, but to report values only after receiving a reauthorization request.

Note ![]() If you have been using an earlier implementation of CRB prepaid billing (Cisco Access Registrar 3.5.2 or earlier), you must recompile the API implementation with the newer API due to the addition of the parameter ebs_context as the first parameter to all API methods. Contact your Cisco systems engineer for assistance with the new API.
If you have been using an earlier implementation of CRB prepaid billing (Cisco Access Registrar 3.5.2 or earlier), you must recompile the API implementation with the newer API due to the addition of the parameter ebs_context as the first parameter to all API methods. Contact your Cisco systems engineer for assistance with the new API.
This section contains the following topics:
•![]() Configuring CRB Prepaid Billing
Configuring CRB Prepaid Billing
•![]() Configuring CRB Prepaid Billing for SSG
Configuring CRB Prepaid Billing for SSG
Configuring CRB Prepaid Billing
To configure an CRB prepaid billing service, use the following sections to configure the required Cisco Prime AR objects:
•![]() Setting Up a Prepaid Billing RemoteServer
Setting Up a Prepaid Billing RemoteServer
•![]() Setting Up a CRB Prepaid Service
Setting Up a CRB Prepaid Service
•![]() Setting Up a Local Accounting Service
Setting Up a Local Accounting Service
•![]() Setting Up a Local Authentication Service
Setting Up a Local Authentication Service
•![]() Setting Up a Prepaid Accounting Group Service
Setting Up a Prepaid Accounting Group Service
•![]() Setting Up an Authentication Group Service
Setting Up an Authentication Group Service
If you are using CRB prepaid billing with Service Selection Gateway (SSG), you must also configure extension point scripts and prepaid clients. See Configuring CRB Prepaid Billing for SSG.
Setting Up a Prepaid Billing RemoteServer
Table 16-3 lists and describes the properties required for an CRB RemoteServer object.
Setting up a Prepaid Billing Remote Server
To set up a prepaid billing remote server:
Step 1 ![]() Use aregcmd to add a RemoteServer under /Radius/RemoteServers.
Use aregcmd to add a RemoteServer under /Radius/RemoteServers.
cd /radius/remoteservers
add prepaid-crb
Added prepaid-crb
Step 2 ![]() Set the RemoteServer protocol to prepaid-crb.
Set the RemoteServer protocol to prepaid-crb.
cd prepaid-crb
set protocol prepaid-crb
Set Protocol prepaid-crb
The following is the default configuration of a prepaid-crb RemoteServer.
[ //localhost/Radius/RemoteServers/prepaid-crb ]
Name = prepaid-crb
Description =
Protocol =
IPAddress =
Port = 0
Filename =
Connections = 8
Setting Up a CRB Prepaid Service
Cisco Prime AR uses a service type prepaid to support the prepaid billing solution. The prepaid service mediates between the client NAS and the external prepaid billing server.
The prepaid service must receive accounting requests to accurately charge the prepaid billing user. You can also set the prepaid service in a group service to log accounting requests locally or to proxy the accounting requests to another service or to both locations.
Setting up a CRB Prepaid Service
To set up a CRB prepaid service:
Step 1 ![]() Use aregcmd to add a prepaid service under /Radius/Services:
Use aregcmd to add a prepaid service under /Radius/Services:
cd /radius/services
add prepaid
Added prepaid
Step 2 ![]() Set the service type to prepaid.
Set the service type to prepaid.
cd prepaid
set type prepaid
Set Type prepaid
A prepaid service has the following default properties:
[ //localhost/Radius/Services/prepaid ]
Name = prepaid
Description =
Type = prepaid
IncomingScript~ =
OutgoingScript~ =
OutagePolicy~ = RejectAll
OutageScript~ =
MultipleServersPolicy = Failover
RemoteServers/
Step 3 ![]() Add a reference to the prepaid-crb RemoteServer.
Add a reference to the prepaid-crb RemoteServer.
cd RemoteServers
add 1 prepaid-crb
Added 1

Note ![]() The following steps are required only when using Prepaid-CRB with SSG.
The following steps are required only when using Prepaid-CRB with SSG.
Step 4 ![]() Set the IncomingScript to IncomingScript PPI-Parse-Prepaid-Incoming.
Set the IncomingScript to IncomingScript PPI-Parse-Prepaid-Incoming.
set IncomingScript PPI-Parse-Prepaid-Incoming
Set IncomingScript PPI-Parse-Prepaid-Incoming
Step 5 ![]() Set the OutgoingScript to OutgoingScript PPO-Parse-Prepaid-Outgoing.
Set the OutgoingScript to OutgoingScript PPO-Parse-Prepaid-Outgoing.
set OutgoingScript PPO-Parse-Prepaid-Outgoing
Set OutgoingScript PPO-Parse-Prepaid-Outgoing
Setting Up a Local Accounting Service
If you want to use the Cisco Prime AR server to record the accounting records locally or to forward the accounting records to another RADIUS server, you must configure an accounting service. You might configure a service similar to local-file (in the example configuration) for accounting requests. Accounting requests can be logged locally (with an accounting service) or remotely (with a RADIUS service).
If you use the prepaid billing server to generate the accounting records, an accounting service is not necessary.
Setting up a Local Accounting Service
To set up a local accounting service:
Step 1 ![]() Use aregcmd to add a local accounting service under /Radius/Services.
Use aregcmd to add a local accounting service under /Radius/Services.
cd /radius/services
add prepaid-LocalFileAccounting
add prepaid-LocalFileAccounting
Step 2 ![]() Set the service type to file.
Set the service type to file.
cd prepaid-LocalFileAccounting
set type file
Set Type file
The file type service has the following properties:
[ //localhost/Radius/Services/prepaid-LocalFileAccounting ]
Name = prepaid-LocalFileAccounting
Description =
Type = file
IncomingScript~ =
OutgoingScript~ =
OutagePolicy~ = RejectAll
OutageScript~ =
FilenamePrefix = accounting
MaxFileSize = "10 Megabytes"
MaxFileAge = "1 Day"
RolloverSchedule =
UseLocalTimeZone = FALSE
Step 3 ![]() Set the FilenamePrefix to Prepaid-Accounting.
Set the FilenamePrefix to Prepaid-Accounting.
set FilenamePrefix Prepaid-Accounting
Set FilenamePrefix Prepaid-Accounting
Step 4 ![]() Set the MaxFileAge to one hour.
Set the MaxFileAge to one hour.
set MaxFileAge "1 Hour"
Set MaxFileAge "1 Hour"
The MaxFileSize should remain at the default value of 10 megabytes.
Step 5 ![]() Set UseLocalTimeZone to TRUE.
Set UseLocalTimeZone to TRUE.
set UseLocalTimeZone TRUE
Set UseLocalTimeZone TRUE
Setting Up a Local Authentication Service
If you use the Cisco Prime AR server for authentication and authorization in your prepaid billing solution, you should configure an AA service. For example, you might configure a service similar to local-users (in the example configuration) for authentication and authorization of local users.
If some of the users are non-prepaid users or if the prepaid users need to have RADIUS authorization attributes returned, you should configure an AA service to perform that authentication and authorization.
If all of the users in a realm are prepaid users and the prepaid billing client does not require normal RADIUS authorization attributes, an AA service is not necessary.
Setting up a Local Authentication Service
To set up a local authentication service:
Step 1 ![]() Use aregcmd to set up a local authentication service.
Use aregcmd to set up a local authentication service.
cd /radius/services
add Prepaid-LocalAuthentication
Added prepaid-LocalAuthentication
cd prepaid-LocalAuthentication
[ //localhost/Radius/Services/prepaid-LocalAuthentication ]
Name = prepaid-LocalAuthentication
Description =
Type =
Step 2 ![]() Set the service type to local.
Set the service type to local.
set type local
Set Type local
Step 3 ![]() Set the UserList property to the userlist that contains IS835C prepaid users.
Set the UserList property to the userlist that contains IS835C prepaid users.
set UserList userlist_name
Set UserList userlist_name

Note ![]() You can use an LDAP or ODBC service in place of the local authentication service.
You can use an LDAP or ODBC service in place of the local authentication service.
Setting Up a Prepaid Accounting Group Service
A prepaid billing solution usually requires a group service to tie together an AA service with a prepaid service, a group service to tie together an accounting service with a prepaid service, or both.
If you are using an AA service with your prepaid billing solution, you must configure a group service, for example prepaid-users, that ties the requests to the AA service (local-users in our example) with the prepaid service.
If you are using Cisco Prime AR for an accounting service with your prepaid billing solution, you must configure a group service, for example prepaid-file, that ties accounting requests to both the regular accounting service (local-file in our example) and the prepaid service.
Setting up a Prepaid Accounting Group Service
To set up a prepaid accounting group service:
Step 1 ![]() Use aregcmd to create an accounting group service under /Radius/Services.
Use aregcmd to create an accounting group service under /Radius/Services.
cd /radius/services
add Prepaid-Accounting
Added prepaid-accounting
Step 2 ![]() Set the service type to group.
Set the service type to group.
cd prepaid-accounting
[ //localhost/Radius/Services/prepaid-accounting ]
Name = prepaid-accounting
Description =
Type =
set type group
Set Type group
The group service has the following properties:
[ //localhost/Radius/Services/prepaid-accounting ]
Name = prepaid-accounting
Description =
Type = group
IncomingScript~ =
OutgoingScript~ =
ResultRule = AND
GroupServices/
Step 3 ![]() Reference the Prepaid and Prepaid-LocalAccounting services under GroupServices.
Reference the Prepaid and Prepaid-LocalAccounting services under GroupServices.
cd GroupServices
[ //localhost/Radius/Services/prepaid-accounting/GroupServices ]
add 1 prepaid
Added 1
add 2 prepaid-LocalFileAccounting
Added 2
Setting Up an Authentication Group Service
A prepaid billing solution usually requires a group service to tie together an AA service with a prepaid service, a group service to tie together an accounting service with a prepaid service, or both.
If you are using an AA service with your prepaid billing solution, you must configure a group service, for example prepaid-users, that ties the requests to the AA service with the prepaid service.
If you are using Cisco Prime AR for an accounting service with your prepaid billing solution, you must configure a group service, for example prepaid-file, that ties accounting requests to both the regular accounting service and the prepaid service.
Setting up an Authentication Group Service
To set up an authentication group service:
Step 1 ![]() Use aregcmd to add a prepaid authentication group service under /Radius/Services.
Use aregcmd to add a prepaid authentication group service under /Radius/Services.
cd /radius/services
add prepaid-groupAuthentication
Added group-prepaidAuthentication
cd group-prepaidAuthentication
[ //localhost/Radius/Services/group-prepaidAuthentication ]
Name = group-prepaidAuthentication
Description =
Type =
Step 2 ![]() Set the service type to group.
Set the service type to group.
set type group
Set Type group
The group service requires the ResultRule to be set to AND, the default setting for a group service.
ls
[ //localhost/Radius/Services/group-prepaidAuthentication ]
Name = group-prepaidAuthentication
Description =
Type = group
IncomingScript~ =
OutgoingScript~ =
ResultRule = AND
GroupServices/
Step 3 ![]() Change directory to GroupServices and add references to the prepaid service and the authentication service.
Change directory to GroupServices and add references to the prepaid service and the authentication service.
cd GroupServices
[ //localhost/Radius/Services/group-prepaidAuthentication/GroupServices ]
add 1 Prepaid-LocalAuthentication
Added 1
add 2 prepaid
Added 2
Configuring CRB Prepaid Billing for SSG
In addition to the configuration described in CRB Prepaid Billing, when using CRB-Prepaid billing with SSG, you must also perform the following:
•![]() Setting Up an Outgoing Script
Setting Up an Outgoing Script
•![]() Setting Up an Incoming Script
Setting Up an Incoming Script
•![]() Setting Up a Prepaid Outgoing Script
Setting Up a Prepaid Outgoing Script
Setting Up an Outgoing Script
To set up an outgoing script:
Step 1 ![]() Use aregcmd to add the PCO-Parse-Client-Outgoing outgoing script under /Radius/Scripts:
Use aregcmd to add the PCO-Parse-Client-Outgoing outgoing script under /Radius/Scripts:
cd /radius/scripts
add PCO-Parse-Client-Outgoing
Added PCO-Parse-Client-Outgoing
cd PCO-Parse-Client-Outgoing
[ //localhost/Radius/Scripts/PCO-Parse-Client-Outgoing ]
Name = PCO-Parse-Client-Outgoing
Description =
Language =
Step 2 ![]() Set the language to tcl.
Set the language to tcl.
set language tcl
Set Language tcl
Step 3 ![]() Set the filename to PCO-parse.client-outgoing.tcl.
Set the filename to PCO-parse.client-outgoing.tcl.
set filename PCO-parse.client-outgoing.tcl
Set Filename PCO-parse.client-outgoing.tcl
Step 4 ![]() Set the EntryPoint to PCO-parse-client-outgoing.
Set the EntryPoint to PCO-parse-client-outgoing.
set EntryPoint PCO-parse-client-outgoing
Set EntryPoint PCO-parse-client-outgoing
Setting Up an Incoming Script
To set up an incoming script:
Step 1 ![]() Use aregcmd to add the PPI-Parse-Prepaid-Incoming script under /Radius/Scripts.
Use aregcmd to add the PPI-Parse-Prepaid-Incoming script under /Radius/Scripts.
cd /radius/scripts
add PPI-Parse-Prepaid-Incoming
Step 2 ![]() Set the language to tcl.
Set the language to tcl.
cd PPI-Parse-Prepaid-Incoming
set language tcl
Set Language tcl
Step 3 ![]() Set the filename to PPI-Parse-Prepaid-Incoming.tcl.
Set the filename to PPI-Parse-Prepaid-Incoming.tcl.
set filename PPI-Parse-Prepaid-Incoming.tcl
Set Filename PPI-Parse-Prepaid-Incoming.tcl
Step 4 ![]() Set the EntryPoint to PPO-Parse-Prepaid-Outgoing.
Set the EntryPoint to PPO-Parse-Prepaid-Outgoing.
set EntryPoint PPO-Parse-Prepaid-Outgoing
Set EntryPoint PPO-Parse-Prepaid-Outgoing
Setting Up a Prepaid Outgoing Script
To set up a prepaid outgoing script:
Step 1 ![]() Use aregcmd to add the PPO-Parse-Prepaid-Outgoing outgoing script under /Radius/Scripts:
Use aregcmd to add the PPO-Parse-Prepaid-Outgoing outgoing script under /Radius/Scripts:
cd /radius/scripts
Step 2 ![]() Add the PPO-Parse-Prepaid-Outgoing outgoing script under /Radius/Scripts.
Add the PPO-Parse-Prepaid-Outgoing outgoing script under /Radius/Scripts.
cd /radius/scripts
add PPO-Parse-Prepaid-Outgoing
Added PPO-Parse-Prepaid-Outgoing
Step 3 ![]() Set the language to tcl.
Set the language to tcl.
cd PPO-Parse-Prepaid-Outgoing
set language tcl
Set Language tcl
Step 4 ![]() Set the filename to PPO-Parse-Prepaid-Outgoing.tcl.
Set the filename to PPO-Parse-Prepaid-Outgoing.tcl.
set filename PPO-Parse-Prepaid-Outgoing.tcl
Set Filename PPO-Parse-Prepaid-Outgoing.tcl
Step 5 ![]() Set the EntryPoint to PPO-Parse-Prepaid-Outgoing.
Set the EntryPoint to PPO-Parse-Prepaid-Outgoing.
set EntryPoint PPO-Parse-Prepaid-Outgoing
Set EntryPoint PPO-Parse-Prepaid-Outgoing
Adding Prepaid Clients
To add prepaid clients:
Step 1 ![]() Use aregcmd to add the prepaid clients under /Radius/Clients.
Use aregcmd to add the prepaid clients under /Radius/Clients.
cd /radius/clients
add SSG
A RADIUS client has the following properties:
[ //localhost/Radius/Clients/ssg ]
Name = ssg
Description =
IPAddress =
SharedSecret =
Type = NAS
Vendor =
IncomingScript~ =
OutgoingScript~ =
EnableDynamicAuthorization = FALSE
NetMask =
Step 2 ![]() Set the IPAddress property to the client IP address.
Set the IPAddress property to the client IP address.
set IPAddress aaa.bbb.ccc.ddd
Set IPAddress aaa.bbb.ccc.ddd
Step 3 ![]() Set the SharedSecret.
Set the SharedSecret.
set sharedsecret cisco
Set SharedSecret cisco
Step 4 ![]() Set the OutgoingScript to PCO-Parse-Client-Outgoing.
Set the OutgoingScript to PCO-Parse-Client-Outgoing.
set out PCO-Parse-Client-Outgoing
Set OutgoingScript PCO-Parse-Client-Outgoing
Generic Call Flow
This section describes the generic call flow for the Cisco Prime AR CRB prepaid billing. The call flow is controlled by the AAA client. The Cisco Prime AR server converts VSAs into calls to the billing server.

Note ![]() For information about call flows and attributes for IS835C, see IS835C Prepaid Billing.
For information about call flows and attributes for IS835C, see IS835C Prepaid Billing.
The packet flows presented in Figure 16-1 are specific to the Cisco Prime AR CRB prepaid billing only. The headlines in the packet flows are general and do represent all data transferred. The letters c, s, and b in Figure 16-1 designate the packet's source of client, server, or billing server, respectively.
Figure 16-1 Generic Call Flow Diagram
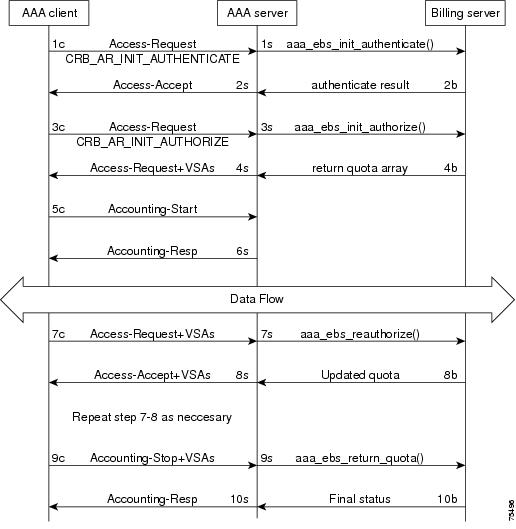
This section contains the following topics:
•![]() Access-Request (Authentication)
Access-Request (Authentication)
•![]() Access-Accept (Authentication)
Access-Accept (Authentication)
•![]() Access-Request (Authorization)
Access-Request (Authorization)
•![]() Access-Accept (Authorization)
Access-Accept (Authorization)
•![]() Access-Request (Quota Depleted)
Access-Request (Quota Depleted)
•![]() Accept-Accept (Quota Depleted)
Accept-Accept (Quota Depleted)
•![]() Accounting Stop (Session End)
Accounting Stop (Session End)
•![]() Accounting Response (Final Status)
Accounting Response (Final Status)
Access-Request (Authentication)
Flow 1c shows the client sending the Access-Request to AAA Server, part of a normal authentication request. The exact nature of the message contents is dictated by the access technology, be it be CDMA1X-RTT, GPRS, or another. The Access-Request might involve other messages such as PAP/CHAP or another form of authentication.
The Flow 1c Access-Request might contain a prepaid specific VSA, CRB_AUTH_REASON. Table 16-4 lists the attributes included in the authentication Access-Request. This tells the Cisco Prime AR server to authenticate the subscriber with the Prepaid server as well. If the value is CRB_AR_INIT_AUTHENTICATE, the initial quota must be obtained for a single service prepaid solution. If this VSA is not present, the Cisco Prime AR server will not authenticate with the Prepaid billing server.
In Flow 1s, the Cisco Prime AR server sends a call to the billing server to authenticate the prepaid user and possibly determine more information about the subscriber's account. The Cisco Prime AR server can be configured to generate this packet flow, using a subscriber profile parameter, if the request is from a prepaid subscriber.
Access-Accept (Authentication)
Flow 2b shows the billing server returning the authentication result. The billing server returns a failure if the prepaid subscriber has an inadequate balance.
Flow 2s shows the Cisco Prime AR server sending the Access-Accept to the AAA client. This message flow contains at least one prepaid billing-specific VSA (listed in Table 16-5) and might contain other access technology-specific attributes.
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
26, 9 |
CRB__USER_TYPE CRB_AR_INIT_AUTHENTICATE |
Optional |
Access-Request (Authorization)
In Flow 3c, the AAA client sends another Access-Request, this time to authorize the subscriber. Table 16-6 lists the attributes required by the Cisco Prime AR server to authorize the subscriber. The session key ID used must be specified using a prepaid VSA pointing to the RADIUS attribute (standard or VSA).
.In Flow 3s, the Cisco Prime AR server sends the Prepaid billing server to obtain a quota. The quota might contain several values depending on the number of measurement parameters chosen.
Access-Accept (Authorization)
Flow 4b shows the billing server returning the quota array for the subscriber.
In Flow 4s, the Cisco Prime AR server converts the quota array received into VSAs and sends an Access-Accept with the assembled VSAs to the AAA client. Table 16-7 lists the prepaid-specific VSAs that might be included in the Access-Accept response message sent to the AAA client. For more detailed information about the VSAs, see Vendor-Specific Attributes.
Flows 3c through 4s are repeated for every service started or restarted by the AAA client.
However, if the return parameters indicate that the authorization is rejected, an Access-Accept message is generated and sent to the client as shown in Table 16-8. When this type of error condition occurs, no other VSA is included in the Access-Accept message.
Accounting-Start
In Flow 5c, the AAA client sends the Accounting-Start. In Flow 6s, the Cisco Prime AR server replies with the Accounting-Response.
Data Flow
At this point, the data transfer begins. The AAA client monitors the subscriber's allocated quotas for metering parameters. A subscriber's Reauthorization request is generated when a quota for at least one of the metering parameters, is depleted.
Access-Request (Quota Depleted)
Flow 7c shows the client sending an Access-Request to the Cisco Prime AR server because at least one quota has been depleted. The Access-Request includes different measurements of how much of the quotas were used in VSA format. This enables the billing server to account for the usage and manage the subscriber's balance before assigning a new quota. Table 16-9 lists the attributes returned to the Cisco Prime AR server:
Accept-Accept (Quota Depleted)
Flow 7s shows the Cisco Prime AR server returning the used quota array to the billing server. The call includes aaa_ebs_reauthoriz(). The billing server sends an updated quota array for the next period to the Cisco Prime AR server.
In Flow 8s, the Cisco Prime AR server converts the quota array into VSAs and sends them to the AAA client.
Accounting Stop (Session End)
In Flow 9c, the client sends an Accounting-Stop to the Cisco Prime AR server to end the session. The Accounting-Stop message includes an updated quota array with the usage adjustments since the previous authorization in the VSA form.
Table 16-11 lists the attributes included in the Accounting-Stop message set to the Cisco Prime AR server and forwarded to the billing server.
Accounting Response (Final Status)
In Flow 9s, the Cisco Prime AR server sends the used quota array to the billing server in an Accounting-Stop message. Any values returned by the billing server in Flow 10b are discarded.
Flow 10s shows the Cisco Prime AR server sending final Accounting-Response message to the AAA client.
Vendor-Specific Attributes
Vendor-specific attributes are included in specific RADIUS packets to communicate prepaid user balance information from the Cisco Prime AR server to the AAA client, and actual usage, either interim or total, between the NAS and the Cisco Prime AR Server.
Table 16-12 lists the VSAs that will be defined in the API. Table 16-12 also lists the string to be used with Cisco-AVPair below the VSA.

Note ![]() VSAs that start with CRB are used for Cisco Radius Billing prepaid service.
VSAs that start with CRB are used for Cisco Radius Billing prepaid service.
Implementing the Prepaid Billing API
A shared library must implement the API functions to perform the various tasks given in the description of each of the function. This needs to be compiled as a shared library and then specified as part of the remote server configuration at the Filename property. See Setting Up a Prepaid Billing RemoteServer or Setting Up a Prepaid Billing RemoteServer.
At startup, Cisco Prime AR loads the library dynamically and registers the API functions, then calls out the library initialization API once at startup. The call to initialize functions initializes various data structures and connections with the billing server, as required.

Note ![]() Cisco works with you to develop the prepaid billing service and implement the API. For more information, contact your Cisco systems engineer.
Cisco works with you to develop the prepaid billing service and implement the API. For more information, contact your Cisco systems engineer.
At various times, according to the call flow described in the Prepaid Call Flow Specification (CRB or IS835C), Cisco Prime AR calls out appropriate API functions present in the shared library. The values for the arguments passed to these API calls are purely derived from the incoming RADIUS packet and Cisco Prime AR does not maintain any dynamic information related to the call flow. It is up to the API function to make use of the information passed to it as C structures to contact the Billing server, get appropriate data, and return the same to Cisco Prime AR using the designated arguments.

Note ![]() See the API specifications for more details pertaining to the arguments and return values of the API.
See the API specifications for more details pertaining to the arguments and return values of the API.
 Feedback
Feedback