area
—A physically connected portion of a routing domain in which all devices are assigned a common area address. Also known as
the Level-1 subdomain. A routing domain may consist of multiple areas that are reachable by traversing the Level-2 subdomain.
area
address
—The high-order octets of the Network Entity Title (NET) assigned to an IS. All ISs in the same Level-1 area are assigned
the same area address.
CLNP
—ISO Connectionless Network Protocol as defined in ISO 8473.
DIS
—Designated Intermediate System. An IS elected by all the ISs operating on a multiaccess circuit at a given level to represent
the multiaccess circuit. The DIS sends pseudonode LSPs on behalf of the circuit advertising adjacencies to all the ISs operating
on that circuit.
domain
—The portion of a network on which the IS-IS protocol is configured to operate. The routing domain consists of all Level-1
areas and the Level-2 subdomain.
ES
—end system. An ES is any nonrouting host or node.
Integrated
IS-IS
—Extended form of IS-IS that supports multiple network protocols. Extensions have been defined in IETF documents, especially
RFC 1195.
IS
—intermediate system. OSI term for a device.
IP
—Internet Protocol Version 4, also known as IPv4.
IPv6
—Internet Protocol Version 6.
IS-IS
—Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System. Routing protocol as defined in ISO/IEC 10589.
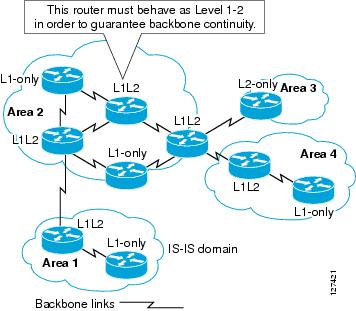
Level-1
router
—An IS that supports Level-1 routing for its assigned area.
Level-2
router
—An IS that supports Level-2 routing.
Level-2
subdomain
—All Level-2 capable devices in a domain and the links that interconnect them. Level-1 areas are interconnected via the Level-2
subdomain. For routing in a domain to work properly, the Level-2 subdomain must not be partitioned.
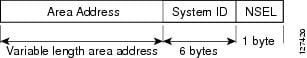
NET
—Network Entity Title. An address assigned to an instance of the IS-IS protocol. The NET includes an area address, a system
ID, and an N-selector. When multiple NETs are assigned to an IS-IS instance, only the area address portion of the NET may
differ.
NSEL
—N-selector. The least significant octet of a Network Entity Title. It is always assigned the value 00.
system
ID
—The part of the NET that immediately follows the area address. The field is 6 octets long.

 Feedback
Feedback