Configure DNS Doctoring for Three NAT Interfaces on ASA Release 9.x
Available Languages
Contents
Introduction
This document provides a sample configuration to perform Domain Name System (DNS) doctoring on the ASA 5500-X Series Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) that uses Object/Auto Network Address Translation (NAT) statements. DNS doctoring allows the security appliance to rewrite DNS A-records.
DNS rewrite performs two functions:
- Translates a public address (the routable or mapped address) in a DNS reply to a private address (the real address) when the DNS client is on a private interface.
- Translates a private address to a public address when the DNS client is on the public interface.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco states that DNS inspection must be enabled in order to perform DNS doctoring on the security appliance. DNS inspection is on by default.
When DNS inspection is enabled, the security appliance performs these tasks:
- Translates the DNS record based on the configuration completed with the use of object/auto NAT commands (DNS rewrite). Translation only applies to the A-record in the DNS reply. Therefore reverse lookups, which request the Pointer (PTR) record, are not affected by DNS rewrite. In Version ASA 9.0(1) and later, translation of the DNS PTR record for reverse DNS lookups when using IPv4 NAT, IPv6 NAT, and NAT64 with DNS inspection enabled for the NAT rule.
- Enforces the maximum DNS message length (the default is 512 bytes and the maximum length is 65535 bytes). Reassembly is performed as necessary in order to verify that the packet length is less than the maximum length configured. The packet is dropped if it exceeds the maximum length.
- Enforces a domain-name length of 255 bytes and a label length of 63 bytes.
Verifies the integrity of the domain-name referred to by the pointer if compression pointers are encountered in the DNS message.
Checks to see if a compression pointer loop exists.
Components Used
The information in this document is based on the ASA 5500-X Series Security Appliance, Version 9.x.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Related Products
This configuration can also be used with the Cisco ASA 5500 Series Security Appliance, Version 8.4 or later.
Background Information
In a typical DNS exchange, a client sends a URL or hostname to a DNS server in order to determine the IP address of that host. The DNS server receives the request, looks up the name-to-IP-address mapping for that host, and then provides the A-record with the IP address to the client. While this procedure works well in many situations, problems can occur. These problems can occur when the client and the host that the client tries to reach are both on the same private network behind NAT, but the DNS server used by the client is on another public network.
Scenario: Three NAT Interfaces - Inside, Outside, DMZ
Topology
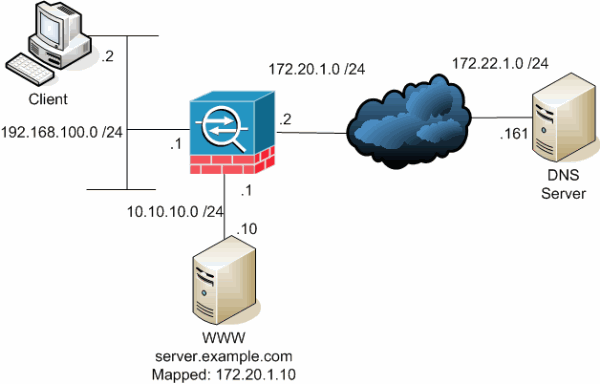
This diagram is an example of this situation. In this case, the client at 192.168.100.2 wants to use the server.example.com URL in order to access the WWW server at 10.10.10.10. DNS services for the client are provided by the external DNS server at 172.22.1.161. Because the DNS server is located on another public network, it does not know the private IP address of the WWW server. Instead, it knows the WWW server mapped address of 172.20.1.10. Thus, the DNS server contains the IP-address-to-name mapping of server.example.com to 172.20.1.10.
Problem: Client Cannot Access the WWW Server
Without DNS doctoring or another solution enabled in this situation, if the client sends a DNS request for the IP address of server.example.com, it is unable to access the WWW server. This is because the client receives an A-record that contains the mapped public address of 172.20.1.10 for the WWW server. When the client tries to access this IP address, the security appliance drops the packets because it does not allow packet redirection on the same interface. Here is what the NAT portion of the configuration looks like when DNS doctoring is not enabled:
ASA Version 9.x
!
hostname ciscoasa
!--- Output suppressed.
access-list OUTSIDE extended permit tcp any host 10.10.10.10 eq www
!--- Output suppressed.
object network obj-192.168.100.0
network 192.168.100.0 255.255.255.0
nat (inside,outside) dynamic interface
object network obj-10.10.10.10
host 10.10.10.10
nat (dmz,outside) static 172.20.1.10
!--- Static translation to allow hosts on the outside access
!--- to the WWW server.
access-group OUTSIDE in interface outside
!--- Output suppressed.
This is what the configuration looks like in the ASDM when DNS doctoring is not enabled:
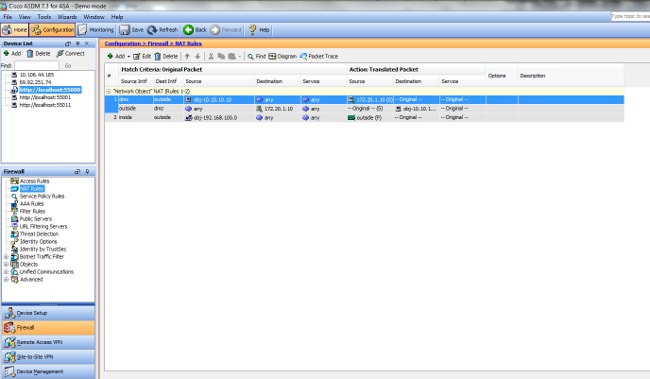
Here is a packet capture of the events when DNS doctoring is not enabled:
- The client sends the DNS query.
No. Time Source Destination Protocol Info
1 0.000000 192.168.100.2 172.22.1.161 DNS Standard query
A server.example.com
Frame 1 (78 bytes on wire, 78 bytes captured)
Ethernet II, Src: Cisco_c8:e4:00 (00:04:c0:c8:e4:00), Dst: Cisco_9c:c6:1f
(00:0a:b8:9c:c6:1f)
Internet Protocol, Src: 192.168.100.2 (192.168.100.2), Dst: 172.22.1.161
(172.22.1.161)
User Datagram Protocol, Src Port: 50879 (50879), Dst Port: domain (53)
Domain Name System (query)
[Response In: 2]
Transaction ID: 0x0004
Flags: 0x0100 (Standard query)
Questions: 1
Answer RRs: 0
Authority RRs: 0
Additional RRs: 0
Queries
server.example.com: type A, class IN
Name: server.example.com
Type: A (Host address)
Class: IN (0x0001) - PAT is performed on the DNS query by the ASA and the query is forwarded. Note that the source address of the packet has changed to the outside interface of the ASA.
No. Time Source Destination Protocol Info
1 0.000000 172.20.1.2 172.22.1.161 DNS Standard query
A server.example.com
Frame 1 (78 bytes on wire, 78 bytes captured)
Ethernet II, Src: Cisco_9c:c6:1e (00:0a:b8:9c:c6:1e), Dst: Cisco_01:f1:22
(00:30:94:01:f1:22)
Internet Protocol, Src: 172.20.1.2 (172.20.1.2), Dst: 172.22.1.161
(172.22.1.161)
User Datagram Protocol, Src Port: 1044 (1044), Dst Port: domain (53)
Domain Name System (query)
[Response In: 2]
Transaction ID: 0x0004
Flags: 0x0100 (Standard query)
Questions: 1
Answer RRs: 0
Authority RRs: 0
Additional RRs: 0
Queries
server.example.com: type A, class IN
Name: server.example.com
Type: A (Host address)
Class: IN (0x0001) - The DNS server replies with the mapped address of the WWW server.
No. Time Source Destination Protocol Info
2 0.005005 172.22.1.161 172.20.1.2 DNS Standard query response
A 172.20.1.10
Frame 2 (94 bytes on wire, 94 bytes captured)
Ethernet II, Src: Cisco_01:f1:22 (00:30:94:01:f1:22), Dst: Cisco_9c:c6:1e
(00:0a:b8:9c:c6:1e)
Internet Protocol, Src: 172.22.1.161 (172.22.1.161), Dst: 172.20.1.2
(172.20.1.2)
User Datagram Protocol, Src Port: domain (53), Dst Port: 1044 (1044)
Domain Name System (response)
[Request In: 1]
[Time: 0.005005000 seconds]
Transaction ID: 0x0004
Flags: 0x8580 (Standard query response, No error)
Questions: 1
Answer RRs: 1
Authority RRs: 0
Additional RRs: 0
Queries
server.example.com: type A, class IN
Name: server.example.com
Type: A (Host address)
Class: IN (0x0001)
Answers
server.example.com: type A, class IN, addr 172.20.1.10
Name: server.example.com
Type: A (Host address)
Class: IN (0x0001)
Time to live: 1 hour
Data length: 4
Addr: 172.20.1.10 - The ASA undoes the translation of the destination address of the DNS response and forwards the packet to the client. Note that without DNS doctoring enabled, the Addr in the answer is still the mapped address of the WWW server.
No. Time Source Destination Protocol Info
2 0.005264 172.22.1.161 192.168.100.2 DNS Standard query response
A 172.20.1.10
Frame 2 (94 bytes on wire, 94 bytes captured)
Ethernet II, Src: Cisco_9c:c6:1f (00:0a:b8:9c:c6:1f), Dst: Cisco_c8:e4:00
(00:04:c0:c8:e4:00)
Internet Protocol, Src: 172.22.1.161 (172.22.1.161), Dst: 192.168.100.2
(192.168.100.2)
User Datagram Protocol, Src Port: domain (53), Dst Port: 50879 (50879)
Domain Name System (response)
[Request In: 1]
[Time: 0.005264000 seconds]
Transaction ID: 0x0004
Flags: 0x8580 (Standard query response, No error)
Questions: 1
Answer RRs: 1
Authority RRs: 0
Additional RRs: 0
Queries
server.example.com: type A, class IN
Name: server.example.com
Type: A (Host address)
Class: IN (0x0001)
Answers
server.example.com: type A, class IN, addr 172.20.1.10
Name: server.example.com
Type: A (Host address)
Class: IN (0x0001)
Time to live: 1 hour
Data length: 4
Addr: 172.20.1.10 - At this point the client tries to access the WWW server at 172.20.1.10. The ASA creates a connection entry for this communication. However, because it does not allow traffic to flow from inside to outside to DMZ, the connection times out. The ASA logs show this:
%ASA-6-302013: Built outbound TCP connection 54175 for
outside:172.20.1.10/80 (172.20.1.10/80) to inside:192.168.100.2/11001
(172.20.1.2/1024)
%ASA-6-302014: Teardown TCP connection 54175 for outside:172.20.1.10/80
to inside:192.168.100.2/11001 duration 0:00:30 bytes 0 SYN Timeout
Solution: "dns" Keyword
DNS Doctoring with the "dns" Keyword
DNS doctoring with the dns keyword gives the security appliance the ability to intercept and rewrite the contents of the DNS server replies to the client. When properly configured, the security appliance can alter the A-record in order to allow the client in such a scenario as discussed in the " Problem: Client Cannot Access WWW Server" section to connect. In this situation with DNS doctoring enabled, the security appliance rewrites the A-record to direct the client to 10.10.10.10 instead of 172.20.1.10. DNS doctoring is enabled when you add the dns keyword to a static NAT statement (Version 8.2 and earlier) or object/auto NAT statement (Version 8.3 and later) .
Version 8.2 and Earlier
This is the final configuration of the ASA to perform DNS doctoring with the dns keyword and three NAT interfaces for versions 8.2 and earlier.
ciscoasa#show running-config
: Saved
:
ASA Version 8.2.x
!
hostname ciscoasa
enable password 9jNfZuG3TC5tCVH0 encrypted
names
dns-guard
!
interface Ethernet0/0
nameif outside
security-level 0
ip address 172.20.1.2 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/1
nameif inside
security-level 100
ip address 192.168.100.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/2
nameif dmz
security-level 50
ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Management0/0
shutdown
no nameif
no security-level
no ip address
management-only
!
passwd 2KFQnbNIdI.2KYOU encrypted
ftp mode passive
access-list OUTSIDE extended permit tcp any host 172.20.1.10 eq www
pager lines 24
logging enable
logging buffered debugging
mtu outside 1500
mtu inside 1500
mtu dmz 1500
asdm image disk0:/asdm512-k8.bin
no asdm history enable
arp timeout 14400
global (outside) 1 interface
nat (inside) 1 192.168.100.0 255.255.255.0
static (inside,dmz) 192.168.100.0 192.168.100.0 netmask 255.255.255.0
static (dmz,outside) 172.20.1.10 10.10.10.10 netmask 255.255.255.255 dns
access-group OUTSIDE in interface outside
route outside 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.20.1.1 1
timeout xlate 3:00:00
timeout conn 1:00:00 half-closed 0:10:00 udp 0:02:00 icmp 0:00:02
timeout sunrpc 0:10:00 h323 0:05:00 h225 1:00:00 mgcp 0:05:00 mgcp-pat 0:05:00
timeout sip 0:30:00 sip_media 0:02:00 sip-invite 0:03:00 sip-disconnect 0:02:00
timeout uauth 0:05:00 absolute
username cisco password ffIRPGpDSOJh9YLq encrypted
http server enable
no snmp-server location
no snmp-server contact
snmp-server enable traps snmp authentication linkup linkdown coldstart
telnet timeout 5
ssh timeout 5
console timeout 0
!
class-map inspection_default
match default-inspection-traffic
!
!
policy-map type inspect dns MY_DNS_INSPECT_MAP
parameters
message-length maximum 512
policy-map global_policy
class inspection_default
inspect ftp
inspect h323 h225
inspect h323 ras
inspect rsh
inspect rtsp
inspect esmtp
inspect sqlnet
inspect skinny
inspect sunrpc
inspect xdmcp
inspect sip
inspect netbios
inspect tftp
inspect dns MY_DNS_INSPECT_MAP
inspect icmp
policy-map type inspect dns migrated_dns_map_1
parameters
message-length maximum 512
!
service-policy global_policy global
prompt hostname context
Cryptochecksum:d6637819c6ea981daf20d8c7aa8ca256
: end
Version 8.3 and Later
ASA Version 9.x
!
hostname ciscoasa
!--- Output suppressed.
access-list OUTSIDE extended permit tcp any host 10.10.10.10 eq www
!--- Output suppressed.
object network obj-192.168.100.0
network 192.168.100.0 255.255.255.0
nat (inside,outside) dynamic interface
object network obj-10.10.10.10
host 10.10.10.10
nat (dmz,outside) static 172.20.1.10 dns
!--- Static translation to allow hosts on the outside access
!--- to the WWW server.
access-group OUTSIDE in interface outside
!--- Output suppressed.
ASDM Configuration
Complete these steps in order to configure DNS doctoring in the ASDM:
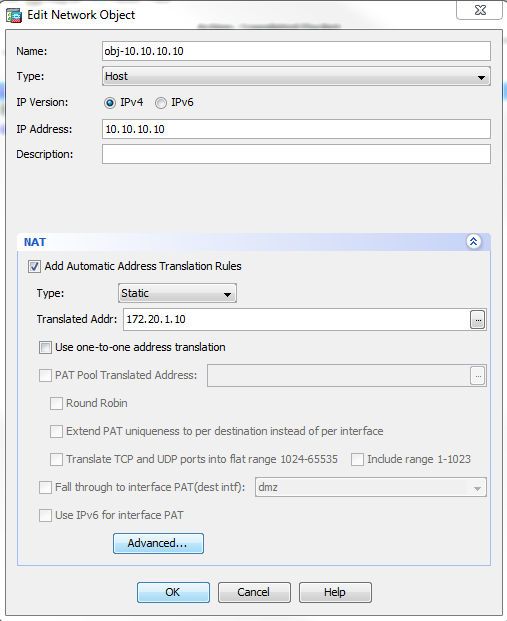
- Choose Configuration > NAT Rules and choose the Object/Auto rule to be modified. Click Edit.
- Click Advanced...
- Check the Translate DNS replies for rule check box.
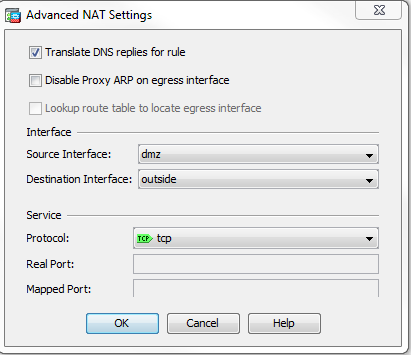
- Click OK in order to leave the NAT Options window.
- Click OK in order to leave the Edit Object/Auto NAT Rule window.
- Click Apply in order to send your configuration to the security appliance.
Verify
Here is a packet capture of the events when DNS doctoring is enabled:
- The client sends the DNS query.
No. Time Source Destination Protocol Info
1 0.000000 192.168.100.2 172.22.1.161 DNS Standard query
A server.example.com
Frame 1 (78 bytes on wire, 78 bytes captured)
Ethernet II, Src: Cisco_c8:e4:00 (00:04:c0:c8:e4:00), Dst: Cisco_9c:c6:1f
(00:0a:b8:9c:c6:1f)
Internet Protocol, Src: 192.168.100.2 (192.168.100.2), Dst: 172.22.1.161
(172.22.1.161)
User Datagram Protocol, Src Port: 52985 (52985), Dst Port: domain (53)
Domain Name System (query)
[Response In: 2]
Transaction ID: 0x000c
Flags: 0x0100 (Standard query)
Questions: 1
Answer RRs: 0
Authority RRs: 0
Additional RRs: 0
Queries
server.example.com: type A, class IN
Name: server.example.com
Type: A (Host address)
Class: IN (0x0001) - PAT is performed on the DNS query by the ASA and the query is forwarded. Note that the source address of the packet has changed to the outside interface of the ASA.
No. Time Source Destination Protocol Info
1 0.000000 172.20.1.2 172.22.1.161 DNS Standard query
A server.example.com
Frame 1 (78 bytes on wire, 78 bytes captured)
Ethernet II, Src: Cisco_9c:c6:1e (00:0a:b8:9c:c6:1e), Dst: Cisco_01:f1:22
(00:30:94:01:f1:22)
Internet Protocol, Src: 172.20.1.2 (172.20.1.2), Dst: 172.22.1.161
(172.22.1.161)
User Datagram Protocol, Src Port: 1035 (1035), Dst Port: domain (53)
Domain Name System (query)
[Response In: 2]
Transaction ID: 0x000c
Flags: 0x0100 (Standard query)
Questions: 1
Answer RRs: 0
Authority RRs: 0
Additional RRs: 0
Queries
server.example.com: type A, class IN
Name: server.example.com
Type: A (Host address)
Class: IN (0x0001) The DNS server replies with the mapped address of the WWW server.
No. Time Source Destination Protocol Info
2 0.000992 172.22.1.161 172.20.1.2 DNS Standard query response
A 172.20.1.10
Frame 2 (94 bytes on wire, 94 bytes captured)
Ethernet II, Src: Cisco_01:f1:22 (00:30:94:01:f1:22), Dst: Cisco_9c:c6:1e
(00:0a:b8:9c:c6:1e)
Internet Protocol, Src: 172.22.1.161 (172.22.1.161), Dst: 172.20.1.2
(172.20.1.2)
User Datagram Protocol, Src Port: domain (53), Dst Port: 1035 (1035)
Domain Name System (response)
[Request In: 1]
[Time: 0.000992000 seconds]
Transaction ID: 0x000c
Flags: 0x8580 (Standard query response, No error)
Questions: 1
Answer RRs: 1
Authority RRs: 0
Additional RRs: 0
Queries
server.example.com: type A, class IN
Name: server.example.com
Type: A (Host address)
Class: IN (0x0001)
Answers
server.example.com: type A, class IN, addr 172.20.1.10
Name: server.example.com
Type: A (Host address)
Class: IN (0x0001)
Time to live: 1 hour
Data length: 4
Addr: 172.20.1.10- The ASA undoes the translation of the destination address of the DNS response and forwards the packet to the client. Note that with DNS doctoring enabled, the Addr in the answer is rewritten to be the real address of the WWW server.
No. Time Source Destination Protocol Info
6 2.507191 172.22.1.161 192.168.100.2 DNS Standard query response
A 10.10.10.10
Frame 6 (94 bytes on wire, 94 bytes captured)
Ethernet II, Src: Cisco_9c:c6:1f (00:0a:b8:9c:c6:1f), Dst: Cisco_c8:e4:00
(00:04:c0:c8:e4:00)
Internet Protocol, Src: 172.22.1.161 (172.22.1.161), Dst: 192.168.100.2
(192.168.100.2)
User Datagram Protocol, Src Port: domain (53), Dst Port: 50752 (50752)
Domain Name System (response)
[Request In: 5]
[Time: 0.002182000 seconds]
Transaction ID: 0x0004
Flags: 0x8580 (Standard query response, No error)
Questions: 1
Answer RRs: 1
Authority RRs: 0
Additional RRs: 0
Queries
server.example.com: type A, class IN
Name: server.example.com
Type: A (Host address)
Class: IN (0x0001)
Answers
server.example.com: type A, class IN, addr 10.10.10.10
Name: server.example.com
Type: A (Host address)
Class: IN (0x0001)
Time to live: 1 hour
Data length: 4
Addr: 10.10.10.10 At this point, the client tries to access the WWW server at 10.10.10.10. The connection succeeds.
Final Configuration with the "dns" Keyword
This is the final configuration of the ASA to perform DNS doctoring with the dns keyword and three NAT interfaces.
ciscoasa# sh running-config
: Saved
:
: Serial Number: JMX1425L48B
: Hardware: ASA5510, 1024 MB RAM, CPU Pentium 4 Celeron 1600 MHz
:
ASA Version 9.1(5)4
!
hostname ciscoasa
enable password 9jNfZuG3TC5tCVH0 encrypted
passwd 2KFQnbNIdI.2KYOU encrypted
names
dns-guard
!
interface Ethernet0/0
shutdown
nameif outside
security-level 0
ip address 172.20.1.2 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/1
shutdown
nameif inside
security-level 100
ip address 192.168.100.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/2
shutdown
nameif dmz
security-level 50
ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/3
shutdown
no nameif
no security-level
no ip address
!
interface Management0/0
management-only
shutdown
no nameif
no security-level
no ip address
!
ftp mode passive
object network obj-192.168.100.0
subnet 192.168.100.0 255.255.255.0
object network obj-10.10.10.10
host 10.10.10.10
access-list OUTSIDE extended permit tcp any host 10.10.10.10 eq www
pager lines 24
logging enable
logging buffered debugging
mtu outside 1500
mtu inside 1500
mtu dmz 1500
no failover
icmp unreachable rate-limit 1 burst-size 1
asdm image disk0:/asdm512-k8.bin
no asdm history enable
arp timeout 14400
no arp permit-nonconnected
!
object network obj-192.168.100.0
nat (inside,outside) dynamic interface
object network obj-10.10.10.10
nat (dmz,outside) static 172.20.1.10 dns
access-group OUTSIDE in interface outside
route outside 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.20.1.1 1
timeout xlate 3:00:00
timeout pat-xlate 0:00:30
timeout conn 1:00:00 half-closed 0:10:00 udp 0:02:00 icmp 0:00:02
timeout sunrpc 0:10:00 h323 0:05:00 h225 1:00:00 mgcp 0:05:00 mgcp-pat 0:05:00
timeout sip 0:30:00 sip_media 0:02:00 sip-invite 0:03:00 sip-disconnect 0:02:00
timeout sip-provisional-media 0:02:00 uauth 0:05:00 absolute
timeout tcp-proxy-reassembly 0:01:00
timeout floating-conn 0:00:00
dynamic-access-policy-record DfltAccessPolicy
user-identity default-domain LOCAL
http server enable
no snmp-server location
no snmp-server contact
snmp-server enable traps snmp authentication linkup linkdown coldstart warmstart
crypto ipsec security-association pmtu-aging infinite
crypto ca trustpool policy
telnet timeout 5
no ssh stricthostkeycheck
ssh timeout 5
ssh key-exchange group dh-group1-sha1
console timeout 0
threat-detection basic-threat
threat-detection statistics access-list
no threat-detection statistics tcp-intercept
webvpn
anyconnect-essentials
username cisco password ffIRPGpDSOJh9YLq encrypted
!
class-map inspection_default
match default-inspection-traffic
!
!
policy-map type inspect dns preset_dns_map
parameters
message-length maximum client auto
message-length maximum 512
policy-map global_policy
class inspection_default
inspect dns preset_dns_map
inspect ftp
inspect h323 h225
inspect h323 ras
inspect rsh
inspect rtsp
inspect esmtp
inspect sqlnet
inspect skinny
inspect sunrpc
inspect xdmcp
inspect sip
inspect netbios
inspect tftp
inspect ip-options
inspect icmp
policy-map type inspect dns MY_DNS_INSPECT_MAP
parameters
message-length maximum 512
policy-map type inspect dns migrated_dns_map_1
parameters
message-length maximum 512
!
service-policy global_policy global
prompt hostname context
Cryptochecksum:3a8e3009aa3db1d6dba143abf25ee408
: end
Alternative Solution: Destination NAT
Destination NAT can provide an alternative to DNS doctoring. The use of destination NAT in this situation requires that a static object/auto NAT translation is created between the WWW server public address on the inside and real address on the DMZ. Destination NAT does not change the contents of the DNS A-record that is returned from the DNS server to the client. Instead, when you use destination NAT in a scenario such as discussed in this document, the client can use the public IP address 172.20.1.10 that is returned by the DNS server in order to connect to the WWW server. The static object/auto translation allows the security appliance to translate the destination address from 172.20.1.10 to 10.10.10.10. Here is the relevant portion of the configuration when destination NAT is used:
ASA Version 9.x
!
hostname ciscoasa
!--- Output suppressed.
access-list OUTSIDE extended permit tcp any host 10.10.10.10 eq www
!--- Output suppressed.
object network obj-192.168.100.0
network 192.168.100.0 255.255.255.0
nat (inside,outside) dynamic interface
!--- The nat and global commands allow
!--- clients access to the Internet.
object network obj-10.10.10.10
host 10.10.10.10
nat (dmz,outside) static 172.20.1.10
!--- Static translation to allow hosts on the outside access
!--- to the WWW server.
object network obj-10.10.10.10-1
host 10.10.10.10
nat (dmz,inside) static 172.20.1.10
Destination NAT Achieved with Manual/Twice NAT Statement
ASA Version 9.x
!
hostname ciscoasa
!--- Output suppressed.
access-list OUTSIDE extended permit tcp any host 10.10.10.10 eq www
!--- Output suppressed.
object network obj-192.168.100.0
network 192.168.100.0 255.255.255.0
nat (inside,outside) dynamic interface
object network obj-10.10.10.10
host 10.10.10.10
object network obj-172.20.1.10
host 172.20.1.10
nat (inside,dmz) source dynamic obj-192.168.100.0 interface
destination static obj-172.20.1.10 obj-10.10.10.10
!--- Static translation to allow hosts on the inside access
!--- to the WWW server via its outside address.
access-group OUTSIDE in interface outside
!--- Output suppressed.
Complete these steps in order to configure destination NAT in the ASDM:
- Choose Configuration > NAT Rules and choose Add > Add "Network Object" NAT Rule....
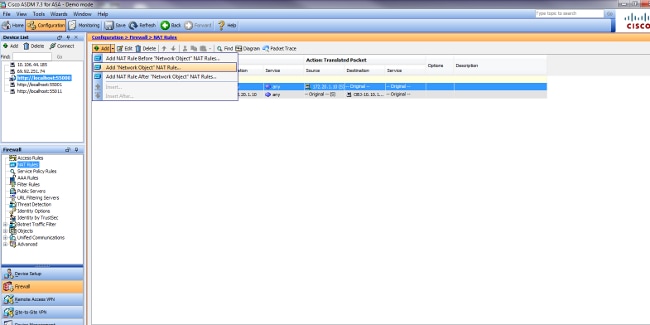
- Fill in the configuration for the new static translation.
- In the Name field, enter obj-10.10.10.10.
- In the IP Address field, enter the address of the WWW server IP address.
- From the Type drop-down list, choose Static.
- In the Translated Addr field, enter the address and interface that you want to map the WWW server to.
- Click Advanced.
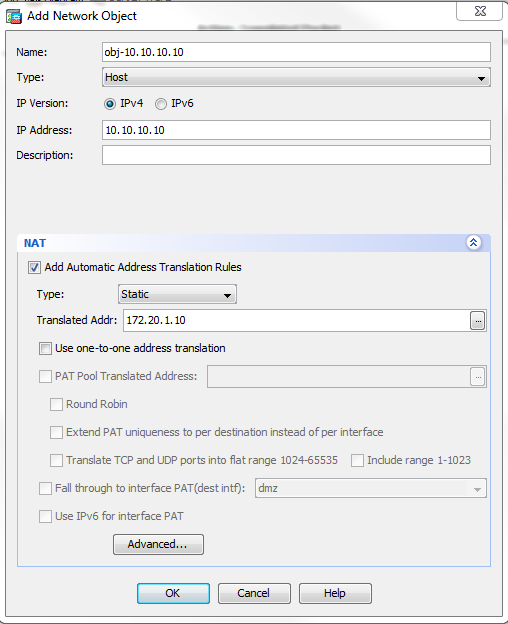
- In the Source Interface drop-down list, choose dmz.
- In the Destination Interface drop-down list, choose inside.
In this case, the inside interface is chosen to allow hosts on the inside interface to access the WWW server via the mapped address 172.20.1.10.
- Click OK in order to leave the Add Object/Auto NAT Rule window.
- Click Apply in order to send the configuration to the security appliance.
Alternative Method with Manual/Twice NAT and the ASDM
- Choose Configuration > NAT Rules and choose Add > Add Nat rule before "Network Object" NAT Rule....
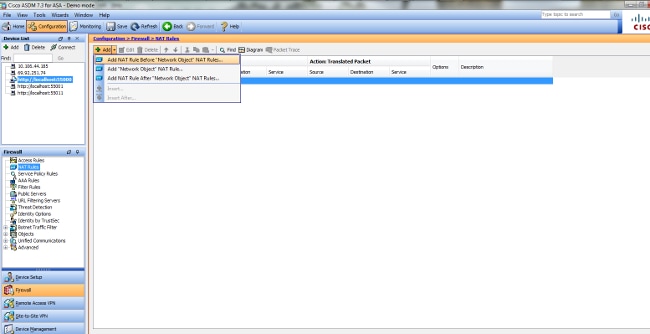
- Fill in the configuration for the Manual/Twice Nat translation.
- In the Source Interface drop-down list, choose inside.
- In the Destination Interface drop-down list, choose dmz.
- In the Source Address field, enter the inside network object (obj-192.168.100.0).
- In the Destination Address field, enter the translated DMZ server IP object (172.20.1.10).
- In the Source NAT Type drop-down list, choose Dynamic PAT (Hide).
- In the Source Address [Action: Translated Packet section] field, enter dmz.
- In the Destination Address [Action: Translated Packet section] field, enter the DMZ server real IP object (obj-10.10.10.10).
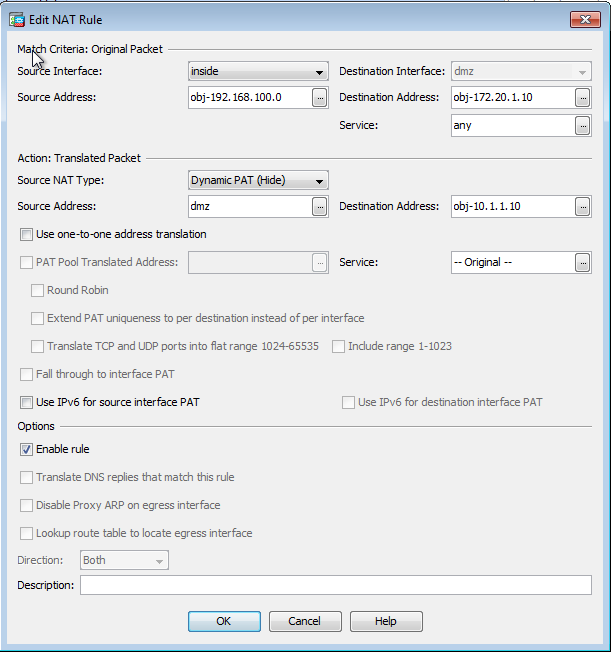
- Click OK in order to leave the Add Manual/Twice NAT Rule window.
- Click Apply in order to send the configuration to the security appliance.
Here is the sequence of events that take place when destination NAT is configured. Assume that the client has already queried the DNS server and received a reply of 172.20.1.10 for the WWW server address:
- The client attempts to contact the WWW server at 172.20.1.10.
%ASA-7-609001: Built local-host inside:192.168.100.2
- The security appliance sees the request and recognizes that the WWW server is 10.10.10.10.
%ASA-7-609001: Built local-host dmz:10.10.10.10
- The security appliance creates a TCP connection between the client and the WWW server. Note the mapped addresses of each host in parentheses.
%ASA-6-302013: Built outbound TCP connection 67956 for dmz:10.10.10.10/80
(172.20.1.10/80) to inside:192.168.100.2/11001 (192.168.100.2/11001) - The show xlate command on the security appliance verifies that the client traffic translates through the security appliance. In this case, the first static translation is in use.
ciscoasa#show xlate
3 in use, 9 most used
Global 192.168.100.0 Local 192.168.100.0
Global 172.20.1.10 Local 10.10.10.10
Global 172.20.1.10 Local 10.10.10.10 - The show conn command on the security appliance verifies that the connection has succeeded between the client and the WWW server through the security appliance. Note the real address of the WWW server in parentheses.
ciscoasa#show conn
TCP out 172.20.1.10(10.10.10.10):80 in 192.168.100.2:11001
idle 0:01:38 bytes 1486 flags UIO
Final Configuration with Destination NAT
This is the final configuration of the ASA to perform DNS doctoring with destination NAT and three NAT interfaces.
ASA Version 9.x
!
hostname ciscoasa
enable password 9jNfZuG3TC5tCVH0 encrypted
passwd 2KFQnbNIdI.2KYOU encrypted
names
dns-guard
!
interface Ethernet0/0
shutdown
nameif outside
security-level 0
ip address 172.20.1.2 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/1
shutdown
nameif inside
security-level 100
ip address 192.168.100.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/2
shutdown
nameif dmz
security-level 50
ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/3
shutdown
no nameif
no security-level
no ip address
!
interface Management0/0
management-only
shutdown
no nameif
no security-level
no ip address
!
ftp mode passive
object network obj-192.168.100.0
subnet 192.168.100.0 255.255.255.0
object network obj-10.10.10.10
host 10.10.10.10
object network obj-10.10.10.10-1
host 10.10.10.10
object network obj-172.20.1.10
host 172.20.1.10
access-list OUTSIDE extended permit tcp any host 10.10.10.10 eq www
pager lines 24
logging enable
logging buffered debugging
mtu outside 1500
mtu inside 1500
mtu dmz 1500
no failover
icmp unreachable rate-limit 1 burst-size 1
asdm image disk0:/asdm512-k8.bin
no asdm history enable
arp timeout 14400
no arp permit-nonconnected
!
object network obj-192.168.100.0
nat (inside,outside) dynamic interface
object network obj-10.10.10.10
nat (dmz,outside) static 172.20.1.10
object network obj-10.10.10.10-1
nat (dmz,inside) static 172.20.1.10
access-group OUTSIDE in interface outside
route outside 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.20.1.1 1
timeout xlate 3:00:00
timeout pat-xlate 0:00:30
timeout conn 1:00:00 half-closed 0:10:00 udp 0:02:00 icmp 0:00:02
timeout sunrpc 0:10:00 h323 0:05:00 h225 1:00:00 mgcp 0:05:00 mgcp-pat 0:05:00
timeout sip 0:30:00 sip_media 0:02:00 sip-invite 0:03:00 sip-disconnect 0:02:00
timeout sip-provisional-media 0:02:00 uauth 0:05:00 absolute
timeout tcp-proxy-reassembly 0:01:00
timeout floating-conn 0:00:00
dynamic-access-policy-record DfltAccessPolicy
user-identity default-domain LOCAL
http server enable
no snmp-server location
no snmp-server contact
snmp-server enable traps snmp authentication linkup linkdown coldstart warmstart
crypto ipsec security-association pmtu-aging infinite
crypto ca trustpool policy
telnet timeout 5
no ssh stricthostkeycheck
ssh timeout 5
ssh key-exchange group dh-group1-sha1
console timeout 0
threat-detection basic-threat
threat-detection statistics access-list
no threat-detection statistics tcp-intercept
webvpn
anyconnect-essentials
username cisco password ffIRPGpDSOJh9YLq encrypted
!
class-map inspection_default
match default-inspection-traffic
!
!
policy-map type inspect dns preset_dns_map
parameters
message-length maximum client auto
message-length maximum 512
policy-map global_policy
class inspection_default
inspect dns preset_dns_map
inspect ftp
inspect h323 h225
inspect h323 ras
inspect rsh
inspect rtsp
inspect esmtp
inspect sqlnet
inspect skinny
inspect sunrpc
inspect xdmcp
inspect sip
inspect netbios
inspect tftp
inspect ip-options
inspect icmp
policy-map type inspect dns MY_DNS_INSPECT_MAP
parameters
message-length maximum 512
policy-map type inspect dns migrated_dns_map_1
parameters
message-length maximum 512
!
service-policy global_policy global
prompt hostname context
Cryptochecksum:2cdcc45bfc13f9e231f3934b558f1fd4
: end
Configure
Complete these steps in order to enable DNS inspection (if it has been previously disabled). In this example, DNS inspection is added to the default global inspection policy, which is applied globally by a service-policy command as though the ASA began with a default configuration.
- Create an inspection policy map for DNS.
ciscoasa(config)#policy-map type inspect dns MY_DNS_INSPECT_MAP
- From the policy-map configuration mode, enter parameter configuration mode in order to specify parameters for the inspection engine.
ciscoasa(config-pmap)#parameters
- In policy-map parameter configuration mode, specify the maximum message length for DNS messages to be 512.
ciscoasa(config-pmap-p)#message-length maximum 512
- Exit out of policy-map parameter configuration mode and policy-map configuration mode.
ciscoasa(config-pmap-p)#exit
ciscoasa(config-pmap)#exit - Confirm that the inspection policy-map was created as desired.
ciscoasa(config)#show run policy-map type inspect dns
!
policy-map type inspect dns MY_DNS_INSPECT_MAP
parameters
message-length maximum 512
! - Enter policy-map configuration mode for the global_policy.
ciscoasa(config)#policy-map global_policy
ciscoasa(config-pmap)# - In policy-map configuration mode, specify the default layer 3/4 class map, inspection_default.
ciscoasa(config-pmap)#class inspection_default
ciscoasa(config-pmap-c)# - In policy-map class configuration mode, use the inspection policy map created in steps 1-3 in order to specify that DNS should be inspected.
ciscoasa(config-pmap-c)#inspect dns MY_DNS_INSPECT_MAP
- Exit out of policy-map class configuration mode and policy-map configuration mode.
ciscoasa(config-pmap-c)#exit
ciscoasa(config-pmap)#exit - Verify that the global_policy policy-map is configured as desired.
ciscoasa(config)#show run policy-map
!
!--- The configured DNS inspection policy map.
policy-map type inspect dns MY_DNS_INSPECT_MAP
parameters
message-length maximum 512
policy-map global_policy
class inspection_default
inspect ftp
inspect h323 h225
inspect h323 ras
inspect rsh
inspect rtsp
inspect esmtp
inspect sqlnet
inspect skinny
inspect sunrpc
inspect xdmcp
inspect sip
inspect netbios
inspect tftp
inspect dns MY_DNS_INSPECT_MAP
!--- DNS application inspection enabled. - Verify that the global_policy is applied globally by a service-policy.
ciscoasa(config)#show run service-policy
service-policy global_policy global
Verify
Use this section to confirm that your configuration works properly.
The Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) (OIT) supports certain show commands. Use the OIT to view an analysis of show command output.
Capture DNS Traffic
One method to verify that the security appliance rewrites DNS records correctly is to capture the packets in question, as discussed in the previous example. Complete these steps in order to capture traffic on the ASA:
- Create an access list for each capture instance you want to create.The ACL should specify the traffic that you want to capture. In this example, two ACLs have been created.
- The ACL for traffic on the outside interface:
access-list DNSOUTCAP extended permit ip host 172.22.1.161 host
172.20.1.2
!--- All traffic between the DNS server and the ASA.
access-list DNSOUTCAP extended permit ip host 172.20.1.2 host
172.22.1.161
!--- All traffic between the ASA and the DNS server. - The ACL for traffic on the inside interface:
access-list DNSINCAP extended permit ip host 192.168.100.2 host
172.22.1.161
!--- All traffic between the client and the DNS server.
access-list DNSINCAP extended permit ip host 172.22.1.161 host
192.168.100.2
!--- All traffic between the DNS server and the client.
- The ACL for traffic on the outside interface:
- Create the capture instance(s):
ciscoasa#capture DNSOUTSIDE access-list DNSOUTCAP interface outside
!--- This capture collects traffic on the outside interface that matches
!--- the ACL DNSOUTCAP.
ciscoasa# capture DNSINSIDE access-list DNSINCAP interface inside
!--- This capture collects traffic on the inside interface that matches
!--- the ACL DNSINCAP. - View the capture(s).
Here is what the example captures look like after some DNS traffic has been passed:
ciscoasa#show capture DNSOUTSIDE
2 packets captured
1: 14:07:21.347195 172.20.1.2.1025 > 172.22.1.161.53: udp 36
2: 14:07:21.352093 172.22.1.161.53 > 172.20.1.2.1025: udp 93
2 packets shown
ciscoasa#show capture DNSINSIDE
2 packets captured
1: 14:07:21.346951 192.168.100.2.57225 > 172.22.1.161.53: udp 36
2: 14:07:21.352124 172.22.1.161.53 > 192.168.100.2.57225: udp 93
2 packets shown - (Optional) Copy the capture(s) to a TFTP server in PCAP format for analysis in another application.
Applications that can parse the PCAP format can show additional details such as the name and IP address in DNS A records.
ciscoasa#copy /pcap capture:DNSINSIDE tftp
...
ciscoasa#copy /pcap capture:DNSOUTSIDE tftp
Troubleshoot
This section provides information you can use to troubleshoot your configuration.
DNS Rewrite Is Not Performed
Make sure that you have DNS inspection configured on the security appliance.
Translation Creation Failed
If a connection cannot be created between the client and the WWW server, it might be due to a NAT misconfiguration. Check the security appliance logs for messages which indicate that a protocol failed to create a translation through the security appliance. If such messages appear, verify that NAT has been configured for the desired traffic and that no addresses are incorrect.
%ASA-3-305006: portmap translation creation failed for tcp src
inside:192.168.100.2/11000 dst inside:192.168.100.10/80
Clear the xlate entries, and then remove and reapply the NAT statements in order to resolve this error.
Related Information
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)








 Feedback
Feedback