Feedback Feedback
|
Table Of Contents
Configuring RADIUS Support: Learning Who the Subscriber Is
Configuring RADIUS Inspection: Endpoint
Configuring RADIUS Inspection: Proxy
Configuring RADIUS Inspection: Monitor
Configuring RADIUS Inspection: Packet of Disconnect
Extracting the Billing Plan ID Using RADIUS
Reporting Arbitrary RADIUS Attributes
RADIUS Attributes Required for CSG User Table
Configuring RADIUS Support: Learning Who the Subscriber Is
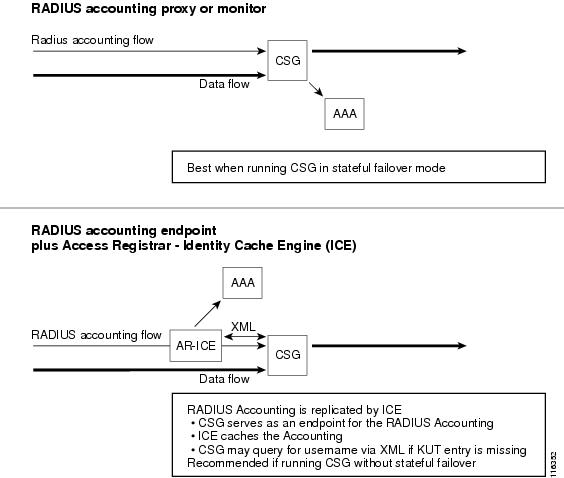
Figure 5-1 illustrates the placement of the CSG in the RADIUS accounting and data flows.
Figure 5-1 RADIUS Accounting and Data Flows
This chapter contains the following information:
•
Configuring RADIUS Inspection: Endpoint
•
Configuring RADIUS Inspection: Proxy
•
Configuring RADIUS Inspection: Monitor
•
Configuring RADIUS Inspection: Packet of Disconnect
•
Extracting the Billing Plan ID Using RADIUS
•
Reporting Arbitrary RADIUS Attributes
•
RADIUS Attributes Required for CSG User Table
Configuring RADIUS Inspection: Endpoint
This configuration specifies the port number for the RADIUS accounting endpoint.
The CSG RADIUS features require that you configure the NAS to direct RADIUS messages to the CSG IP address (or to the alias address if this is a redundant configuration). You must also configure your NAS to the specific CSG port number.
Here is a sample configuration for the RADIUS endpoint:
module csg 3radius endpoint 1.2.3.4 key secret
Note
You can still use the existing radius key and radius acct-port commands in CSG user group configuration mode to configure the CSG as a RADIUS Accounting endpoint, but we recommend that you use the radius endpoint command in module CSG configuration mode. The CSG 3.1(3)C5(5) supports both endpoint configuration methods. However, if you plan to use RADIUS PoD with RADIUS endpoint, then you must use the radius endpoint command in module CSG configuration mode.
We do not recommend using both configuration methods in the same environment.
Configuring RADIUS Inspection: Proxy
The CSG enhances the proxy function to allow operation with clients that use large numbers of port numbers. RADIUS Proxy provides a way to remove the chance of routing errors (RADIUS is targeted at the CSG addresses directly), and must be used in place of Monitor when the CSGs are being load-balanced.
RADIUS Proxy supports both RADIUS Access and RADIUS Accounting.
Note
The old proxy function is still supported, and operates as before if you configure it in the old way. However, we strongly recommend that you use the new proxy support.
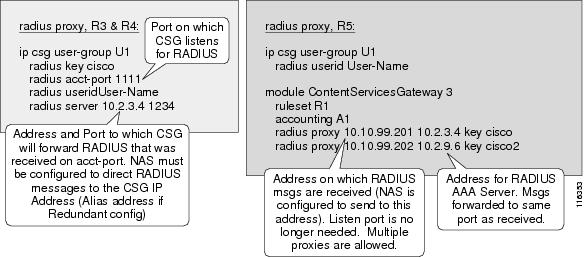
Figure 5-2 illustrates the differences between configurations.
Figure 5-2 RADIUS Proxy Configuration Changes
Using a CSG 3.1(3)C4(1) RADIUS configuration on the CSG 3.1(3)C5(1) or later results in the CSG 3.1(3)C4(1) behavior.
Configuring RADIUS Inspection: Monitor
RADIUS Monitor provides a way to insert the CSG without changing the AAA or NAS addresses in the network. The CSG monitors the traffic between the RADIUS client and the RADIUS server, looking for RADIUS messages flowing through it that match the configured rule. The address of the server must be configured.
Optionally, a RADIUS key is configured. If the key is configured, the CSG parses and acts on the message only if the RADIUS Authenticator is correct. If the key is not configured, the CSG always parses the message. The message is forwarded regardless of the key being configured or correct. Here is a sample configuration:
ip csg user-group U1radius userid User-Nameradius monitor 10.2.3.4 1234 key cisco --> Address, Port, and Key for RADIUS AAA Server.radius monitor 10.2.3.9 1234 key cisco2radius monitor 10.2.7.4 3901 key cisco --> Multiple AAA destinations can be monitored.All RADIUS messages, including access messages, are forwarded, except when the IP or UDP headers specify a length larger than the physical packet size.
Configuring RADIUS Inspection: Packet of Disconnect
This configuration specifies the following Packet of Disconnect (PoD) characteristics:
•
The RADIUS attributes to be copied from the RADIUS Start message and sent to the NAS in the PoD message.
•
The NAS port to which the CSG should send the PoD message, and the key to use in calculating the Authenticator.
•
The number of times to retry the RADIUS PoD message if it is not acknowledged, and the interval between retries.
Here is a sample configuration for RADIUS PoD:
ip csg user-group G1radius userid User-Nameradius pod attribute 44radius pod nas 1.1.1.0 1.1.1.255 1700 key secretradius pod nas 1701 key passwordradius pod timeout 30 retransmits 5mod csg 3radius proxy 1.2.3.4 5.6.7.8 key secretExtracting the Billing Plan ID Using RADIUS
Prior to the CSG 3.1(3)C5(1), the CSG required that the quota server provide the Billing Plan ID. The information had to be provisioned to the quota server, or the quota server had to act as a surrogate (retrieving from the authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) server in order to send to the CSG). It was not possible to distinguish between prepaid and postpaid users if the quota server was unavailable.
The CSG now adds the ability to extract the Billing Plan ID from RADIUS Access Accept using a CSG VSA. The following information is included:
•
Attribute number: 26 (=vendor specific)
•
Vendor ID: 9 (=Cisco)
•
Subattribute: 1 (=Cisco generic)
•
Format: csg:billing_plan= where the billing plan name appears after the equal sign (=). If the attribute is present, but no billing plan is specified, the user is postpaid.
The new user-profile command enables the billing plan function. If the CSG is configured to get the billing plan from RADIUS, and the billing plan sub-attribute is included in the RADIUS messages, the CSG does not query the quota server (that is, no User Profile Request). If the billing plan attribute is not present in the RADIUS messages by the time the CSG receives the Accounting Start with the user ID, the CSG queries the quota server.
Reporting Arbitrary RADIUS Attributes
The operator can specify a set of attributes to be extracted from RADIUS Accounting Start messages for each subscriber and reported with each transaction record.
Note
VSAs (attribute 26) are not separable (all are sent).
The CSG saves these attributes for each subscriber and replaces them when a new Accounting Start is received.
For example, in a GPRS environment you can use this capability as follows:
•
NAS-IP-Address (4) identifies the GGSN to which the subscriber is tunneled.
•
SGSN IP (26/10415/6) identifies the SGSN the subscriber is accessing.
•
Acct-session-ID (44) uniquely identifies the session on this NAS and can be used for correlation to GGSN accounting records.
RADIUS Attributes Required for CSG User Table
The User Table identifies all users known to the CSG. The table is populated based on the contents of RADIUS Accounting Start messages, or from the user database, if either feature is enabled in your configuration. The CSG requires the following RADIUS attributes in the RADIUS Accounting Start in order to build an entry for a user in the CSG User Table table:
•
8 (Framed-IP-Address)
•
Either 4 (NAS-IP-Address) or 32 (NAS-Identifier)
•
Either 1 (User-Name) or 31 (Calling-Station-Id), as configured
When the CSG receives the RADIUS Access Accept with Billing Plan ID included, it caches the information. The cached information is identified by user ID (either RADIUS Attribute 1 or RADIUS Attribute 31, as configured). When the CSG receives the RADIUS Accounting Start message with the user ID, it builds a User Table entry using the cached information.
Note
Cached information is not displayed in the output of the show module csg accounting users command.