-
Cisco Unity Troubleshooting Guide (With IBM Lotus Domino), Release 4.0(5)
-
Index
-
Preface
-
Introduction
-
Diagnostic Trace Utilities and Logs
-
Internal and External Calls
-
Call Transfers
-
Messages
-
AMIS Networking
-
Audio Quality
-
Message Waiting Indicators (MWIs)
-
Message Notification
-
Hardware
-
Error Messages
-
Third-Party Fax Integration
-
Utilities
-
Subscriber and Administrator Access
-
Reports
-
Failover
-
Cisco Personal Communications Assistant
-
Media Master Control Bar
-
Appendix: Cisco Unity Services and Their Functions
-
Table Of Contents
AMIS Messages Are Not Delivered Promptly
AMIS Messages Are Not Delivered at All
Double-Checking Newly Configured Systems
Troubleshooting AMIS Message Delivery
Following the Outbound AMIS Message Flow
Messages Are Not Delivered to the Interop Gateway Mail File
Messages Are Not Delivered to the UAmis Mail File
Messages Are Stuck in the UAmis Mail File
Messages Leave the UAmis Mail File But Are Not Delivered
Following the Inbound AMIS Message Flow
Gathering Logs and Resetting Traces to Default Values
AMIS Troubleshooting Procedures
"C" and "D" DTMF Hang-Up Tones Cause AMIS Calls to Fail
Advanced Troubleshooting: Viewing the Frames and Digits in an AMIS Call
AMIS Networking
Cisco Unity supports the Audio Messaging Interchange Specification analog (AMIS-a) protocol, which provides a mechanism for transferring voice messages between different voice messaging systems. The following sections provide information on troubleshooting AMIS Networking problems:
•
AMIS Messages Are Not Delivered Promptly
•
AMIS Messages Are Not Delivered at All
AMIS Messages Are Not Delivered Promptly
There are a number of reasons that AMIS messages may not be delivered promptly (or why subscribers may perceive that they are not being delivered promptly):
•
Outbound AMIS messages can be restricted to use only certain voice messaging ports. If the ports designated to handle AMIS messages are busy with other calls, outbound AMIS messages can be delayed. You can use either the Port Usage Analyzer in Tools Depot or the AMIS Out Traffic report in the Cisco Unity Administrator to obtain information on AMIS outbound transmissions. If the total AMIS transmission time approaches the limit of the ports dedicated to AMIS deliveries, review the AMIS schedule and port assignments to determine whether additional resources (time and/or ports) should be dedicated to AMIS message traffic.
•
AMIS delivery of non-urgent messages can be restricted to occur only at scheduled delivery times. Be sure to let subscribers know if your organization uses a schedule to restrict the delivery of non-urgent AMIS messages; subscribers can then mark AMIS messages as urgent, or use an alternative form of communication, as appropriate.
•
Some AMIS messages may be undeliverable. An undeliverable message is returned to the sender with a nondelivery receipt (NDR) status; the sender or the administrator can make corrections and resend the message. This may also appear to the recipient as a delayed delivery.
AMIS Messages Are Not Delivered at All
The following sections provide information on how to troubleshoot AMIS message delivery problems:
•
Double-Checking Newly Configured Systems
•
Troubleshooting AMIS Message Delivery
•
Following the Outbound AMIS Message Flow
•
Following the Inbound AMIS Message Flow
•
Gathering Logs and Resetting Traces to Default Values
•
"C" and "D" DTMF Hang-Up Tones Cause AMIS Calls to Fail
•
Advanced Troubleshooting: Viewing the Frames and Digits in an AMIS Call
Double-Checking Newly Configured Systems
If you have just configured Cisco Unity for AMIS Networking, and AMIS messages are not being delivered, review the following list to verify that your configuration follows these basic guidelines.
1.
Confirm that the other voice messaging system is supported by Cisco Unity for AMIS messaging. Refer to the "Supported AMIS-Compliant Voice Messaging Systems" section of the Cisco Unity System Requirements, and Supported Hardware and Software, available at http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/voice/c_unity/sysreq/40_sysrq.htm.
2.
If Cisco Unity is integrated with Cisco CallManager, verify that the Cisco gateway version is supported for use with AMIS as described in the "Supported Cisco Gateways for Use with AMIS" section of the Cisco Unity System Requirements, and Supported Hardware and Software.
3.
Refer back to the "Setting Up Cisco Unity to Use AMIS" section in the "AMIS Networking" chapter of the Networking in Cisco Unity Guide to double-check the configuration. (The guide is available at http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/voice/c_unity/unity40/net/net405/dom/index.htm.)In particular:
–
Confirm that the settings on each AMIS delivery location are correct.
–
If your installation includes multiple Cisco Unity servers, confirm that the search scopes include the AMIS bridgehead server. The Subscriber and Blind Addressing search scopes (which are set on the Network > Primary Location > Addressing Options page in the Cisco Unity Administrator) must be set to either the dialing domain or global level. This must be done for each Cisco Unity server in the network. The search scopes for the auto-attendant and directory handlers (which are configured separately) must also include the AMIS bridgehead server.
Troubleshooting AMIS Message Delivery
For either new or existing AMIS Networking configurations, use the following list as a starting point:
1.
Check to see whether there are AMIS-related errors or warnings in the Windows Event Viewer Application Log on the AMIS bridgehead server. Most of the AMIS-related errors and warnings that are logged to the Event Viewer provide sufficient detail about the problem and how to resolve it.
2.
Use the Domino Administrator to confirm that the UAmis Person document has not been inadvertently deleted. Also verify that the UAmis mail file itself exists on the Domino server and directory specified in the Person document.
Unless you have moved the UAmis mail file, it should be located on the Domino server that was chosen in the Message Store Configuration wizard when the Cisco Unity AMIS bridgehead server was set up. If the UAmis mail file has been moved, and there are errors in the Event Viewer indicating that Cisco Unity cannot locate the UAmis mail file, refer to the "UAmis Mail File" section in the "Cisco Unity Data and Log Files" chapter in the Cisco Unity Maintenance Guide for information on how to move the UAmis mail file such that Cisco Unity is aware of the change. (The Cisco Unity Maintenance Guide is available at http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/voice/c_unity/unity40/maint/maint405/dom/index.htm.)
3.
Use the Domino Administrator to confirm that the Interop Gateway Foreign domain document exists. Also verify that the Interop Gateway mail file itself exists on the Domino server and directory specified in the Foreign domain document. See the "To Confirm That the Interop Gateway Foreign Domain Document and Mail File Exist" procedure. Note that if Cisco Unity cannot find the Interop Gateway mail file, you should see errors in Event Viewer. In this case:
–
If the Interop Gateway Foreign domain document and/or mail file has been inadvertently deleted, reconfigure the Interop Gateway, as described in the "Configuring the Interop Gateway" section in the "AMIS Networking" of the Networking in Cisco Unity Guide. Be sure to use the same Foreign domain name that you used previously.
–
If you suspect that the Interop Gateway mail file may have been inadvertently moved to another Domino server, refer to the "Moving the Interop Gateway Mail File" section in the "AMIS Networking" chapter of the Networking in Cisco Unity Guide for information on how to move the mail file such that Cisco Unity is aware of the change.
4.
Use the Domino Administrator to confirm that Interop Gateway Foreign domain name is correct. See the "To Confirm That the Foreign Domain Name Settings Are Correct" procedure.
If you determine that the Foreign domain name has been changed in some but not all of the places where the name is stored, refer to the "Changing the Interop Gateway Foreign Domain Name" section in the "AMIS Networking" chapter of the Networking in Cisco Unity Guide for information on how to move the mail file such that Cisco Unity is aware of the change.
The Networking in Cisco Unity Guide is available at http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/voice/c_unity/unity40/net/net405/dom/index.htm.
If you have not determined what is causing the problem, continue with the next section, "Enabling Traces."
Enabling Traces
Before you continue troubleshooting the AMIS message delivery problem, do the following procedures to enable the applicable traces. The logs will be needed by Cisco TAC if you are unable to resolve the problem.
•
To Set AMIS Diagnostic Traces
•
To Set Interop Gateway Diagnostic Traces
To Set AMIS Diagnostic Traces
Step 1
On the Windows Start menu on the Cisco Unity AMIS bridgehead server, click Programs > Cisco Unity > Unity Diagnostic Tool.
Step 2
On the Cisco Unity Diagnostic Tasks screen, click Configure Macro Traces. The Welcome to the Configure Macro Traces wizard is displayed.
Step 3
Click Next. The Configure Macro Traces page is displayed.
Step 4
Expand AMIS Message Traces. As applicable, click either the Extensive Outgoing AMIS Message Traces check box or the Extensive Incoming AMIS Message Traces check box. (See the "AMIS Diagnostic Traces" section for a list of the micro traces that are included in the macro traces.)
Step 5
Click Next and then click Finish.
Step 6
On the Cisco Unity Diagnostic Tasks screen, click Start New Log Files.
To Set Interop Gateway Diagnostic Traces
Step 1
On the Windows Start menu on the Cisco Unity server on which the Interop Gateway service is running (this may or may not be the bridgehead server), click Programs > Cisco Unity > Unity Diagnostic Tool.
Step 2
On the Cisco Unity Diagnostic Tasks screen, click Configure Micros Traces. The Welcome to the Configure Micro Traces wizard is displayed.
Step 3
Click Next. The Configure Micro Traces page is displayed.
Step 4
Scroll down and click the DGateway check box to select all the DGateway micro traces.
Step 5
Click Next and then click Finish.
Step 6
On the Cisco Unity Diagnostic Tasks screen, click Start New Log Files.
Following the Outbound AMIS Message Flow
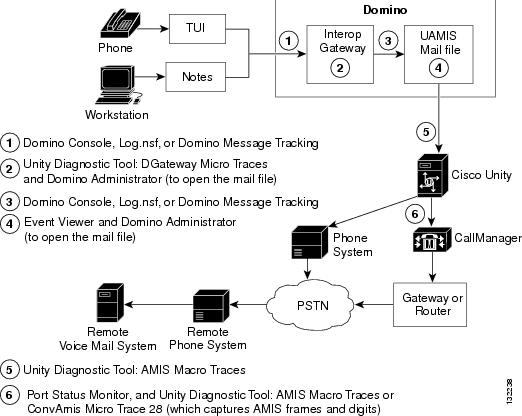
Figure 6-1 shows at a high level the flow of outbound AMIS messages through Cisco Unity to the remote voice messaging system, and the logs and other tools that you can use to troubleshoot problems along the path.
Figure 6-1 Outbound AMIS Message Flow and Troubleshooting Tools
In the above illustration, the Cisco Unity server that is used by Cisco Unity subscribers to send messages may or may not be the same as the Cisco Unity AMIS bridgehead server, so it was left out for the sake of simplicity. Additionally, the path from the Cisco Unity bridgehead server to the PSTN depends on the phone system integration. Two paths are shown in the illustration because transmission problems can occur at the gateway or router used with Cisco CallManager integrations. If you do not have a Cisco CallManager integration, ignore that path. Note also that the Interop Gateway service actually runs on a Cisco Unity server, and the Interop Gateway mail file is on a Domino server.
Use Figure 6-1 in conjunction with the following task list to trace the path that outbound AMIS messages take, which will help you locate the problem. The links take you to procedures in the "AMIS Troubleshooting Procedures" section.
1.
Send a test AMIS message.
2.
Determine whether the message made it to the Interop Gateway mail file. Do the "To Confirm That Messages Arrive at the Interop Gateway Mail File" procedure.
If you determine that the messages are not being delivered to the Interop Gateway mail file, see the "Messages Are Not Delivered to the Interop Gateway Mail File" section for information on how to troubleshoot this problem.
3.
Determine whether the message was delivered to the UAmis mail file. Do the "To Confirm That Messages Are Being Delivered to the UAmis Mail File" procedure.
If you determine that messages are not being delivered to the UAmis mail file, see the "Messages Are Not Delivered to the UAmis Mail File" procedure for information on how to troubleshoot the problem.
4.
If messages are being delivered to the UAmis mail file, but are not being sent on from there, see the "Messages Are Stuck in the UAmis Mail File" procedure for information on how to troubleshoot this problem.
5.
If messages are leaving the UAmis mail file, but are not delivered to users on the other voice messaging system, see the "Messages Leave the UAmis Mail File But Are Not Delivered" section for information on how to troubleshoot this problem.
Messages Are Not Delivered to the Interop Gateway Mail File
Each Cisco Unity server has a corresponding Person document and mail file in Domino. When subscribers send messages, Cisco Unity hands off the messages to the Domino server on which the corresponding Cisco Unity server mail file was created. For AMIS recipients, Domino then routes the message to the Interop Gateway mail file. The route the message takes depends on your Domino configuration. When Cisco Unity hands off an AMIS message to Domino for delivery to the Interop Gateway mail file, you should see an entry in the Domino console or in log.nsf from the Domino router about routing the message (look for the Foreign domain name).
If you have determined that messages are not being delivered to the Interop Gateway mail file, use the following list to troubleshoot the problem.
To Troubleshoot Why Messages Are Not Delivered to the Interop Gateway Mail File
1.
Confirm that the following Domino servers are running:
–
The Domino server used by Cisco Unity for message delivery
–
The Domino server on which the Interop Gateway mail file is located
–
All Domino servers used in message routing to the Domino server on which the Interop Gateway mail file is located
Also confirm that the Domino router is running on all of those servers.
2.
Scroll back through the Domino console or look in log.nsf for a message similar to "No route point found to <Foreign Domain Name>." If you see this message, review your Connection documents to see whether you can determine what is preventing Domino from routing the message to the Domino server on which the Interop Gateway mail file is located. Refer to your Domino Administrator documentation for more information.
The "No route point found" message may also indicate that the Interop Gateway Foreign domain name may have been changed in some but not all of the places where the name is stored. If you suspect that the Interop Gateway Foreign domain name may have been inadvertently changed, refer to the "Changing the Interop Gateway Foreign Domain Name" section in the "AMIS Networking" chapter of the Networking in Cisco Unity Guide for information on how to change the Foreign domain name such that Cisco Unity is aware of the change. The Networking in Cisco Unity Guide is available at http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/voice/c_unity/unity40/net/net405/dom/index.htm.
3.
Check to see if the message is stuck in MAIL.BOX on the Domino server used by the sending Cisco Unity for message delivery, or if the message is stuck in MAIL.BOX on any of the Domino servers that are involved in routing messages to the Domino server on which the Interop Gateway mail file is located. Refer to your Domino documentation for more information.
4.
If you are unable to determine why messages are not delivered to the Interop Gateway mail file, see the "Gathering Logs and Resetting Traces to Default Values" section for details on how to gather the necessary logs to provide to Cisco TAC.
Messages Are Not Delivered to the UAmis Mail File
After processing an outbound AMIS message, the Interop Gateway gives the message back to Domino for delivery to the UAmis mail file. After sending an outbound AMIS message as a test, you should see an entry in the Domino console or in log.nsf from the Domino router about routing the message to UAmis_<Server Name>. If you have determined that outbound AMIS messages are not being delivered to the UAmis mail file, use the following list to troubleshoot the problem.
To Troubleshoot Why Messages Are Not Delivered to the UAmis Mail File
1.
On the Cisco Unity server on which the Interop Gateway Configuration wizard was run, confirm that the Interop Gateway service, CsDomInteropGty, is running. If the service is not running, start it. See the "To Confirm That the Interop Gateway Service Is Running" procedure.
2.
Confirm that the following Domino servers are running:
–
The Domino server on which the Interop Gateway mail file is located
–
The Domino server on which the UAmis mail file is located
–
All Domino servers used in message routing to the Domino server on which the UAmis mail file is located
Also confirm that the Domino router is running on all of those servers.
3.
Review your Connection documents to make sure that there is nothing preventing Domino from routing messages to the Domino server on which the UAmis mail file is located. Refer to your Domino Administrator documentation for more information.
4.
Check to see if the message is stuck in MAIL.BOX on any of the Domino servers that are involved in routing messages from the Domino server on which the Interop Gateway mail file is located to the Domino server on which the UAmis mail file is located. Refer to your Domino documentation for more information.
5.
If you are unable to determine why messages are not delivered to the UAmis mail file, see the "Gathering Logs and Resetting Traces to Default Values" section for details on how to gather the necessary logs to provide to Cisco TAC.
Messages Are Stuck in the UAmis Mail File
When outbound AMIS messages are delivered to the UAmis mail file, the AMIS schedule and the AMIS restriction table determine when Cisco Unity will make the phone call to transmit the message to the remote voice messaging system. When an AMIS delivery number is allowed by the restriction table, messages to the number are sent immediately from the UAmis mail file—the schedule settings do not matter. On the other hand, when the delivery number is disallowed by the restriction table, messages to the number are queued in the UAmis mail file until the active hours of the AMIS schedule.
An error is logged in the Windows Event Viewer Application Log when messages remain in the UAmis mail file for more than 24 hours. Only one error is logged in the Event log, no matter how many messages remain in the UAmis mail file. An additional error is logged daily until the messages are either sent or deleted from the UAmis mail file.
If you have determined that messages are stuck in the UAmis mail file, use the following list to troubleshoot the problem.
To Determine Why Messages Are Stuck in the UAmis Mail File
1.
Check the Event Viewer for AMIS-related errors.
2.
In the Cisco Unity Administrator, review the settings for the AMIS restriction table. If any delivery numbers are disallowed, messages addressed to these numbers will be queued in the UAmis mail file. This may not be what you intended. To send the messages immediately, change the AMIS schedule so that it is active during the time that you are troubleshooting. After the messages are sent from the UAmis mail file, reset the AMIS schedule and adjust the AMIS restriction table as needed.
3.
Review the AMIS schedule. Confirm that the schedule has sufficient Active hours set for sending all the messages.
4.
Go to the System > Ports page, and confirm that there is at least one port configured for outbound AMIS messages.
If messages were piling up in the UAmis mail file because of insufficient resources (time on the schedule and/or ports), use either the Port Usage Analyzer in Tools Depot or the AMIS Out Traffic report in the Cisco Unity Administrator to obtain information on AMIS outbound transmissions. Then review the AMIS schedule and port assignments to determine whether additional resources (time and/or ports) should be dedicated to AMIS message traffic.
5.
Confirm that the delivery phone numbers on all AMIS delivery locations are valid. To confirm that the delivery phone numbers are valid, in the Cisco Unity Administrator, go to the Network > Delivery Locations > Profile page of each AMIS delivery location to confirm the delivery phone number.
6.
In the Domino Administrator or Notes, open the UAmis mail file to confirm that the messages are marked as Unread. Messages that have been manually marked as Read will not be sent from the UAmis mail file. For example, if someone has been monitoring the UAmis mail file and has opened a message, that message will not be sent. Check the message properties of an AMIS message as described in the "To View Properties of a Message in the UAmis Mail File" procedure.
7.
If you are unable to determine why messages are stuck in the UAmis mail file, see the "Gathering Logs and Resetting Traces to Default Values" section for details on how to gather the necessary logs to provide to Cisco TAC.
Messages Leave the UAmis Mail File But Are Not Delivered
Use the following steps to troubleshoot problems with messages that leave the UAmis mail file but are not delivered to users of the remote voice messaging system.
To Troubleshoot Undelivered Messages
1.
Check the Event Viewer for AMIS-related errors.
2.
Double-check the AMIS configuration in Cisco Unity, as follows:
a.
In the Cisco Unity Administrator, go to the Network > AMIS Options > Delivery Options page. Review the settings for If the Remote System Does Not Answer and If the Remote System Is Busy. These settings should be set to at least the default values (Hang Up After 4 Rings; Try Calling 4 Times; Retry Every 5 Minutes). Otherwise, the remote voice messaging system may not be given enough time to answer.
b.
Go to the Network > Delivery Options > Profile page of each of the AMIS delivery location. If the Disable Outbound Messages to this AMIS Location check box is checked, change the Delivery Phone Number as needed, and uncheck the check box.
c.
Go to the Network > Primary Location > Profile page. Confirm that the Node ID is accepted by the remote voice messaging system.
3.
Determine whether the calls to an AMIS location are actually being made or whether there is something unexpected happening during the AMIS transmission. You can use the Port Status Monitor in Tools Depot to observe call progress. Do the "To Use the Port Status Monitor to Watch Details of an AMIS Transmission" procedure.
4.
If the outgoing AMIS calls are to a long-distance number, check the phone system to see if there are restrictions on placing long distance calls.
5.
Determine whether the hang-up tones could be the source of the problem. See the ""C" and "D" DTMF Hang-Up Tones Cause AMIS Calls to Fail" section.
6.
If you are unable to determine why messages are not delivered, see the "Gathering Logs and Resetting Traces to Default Values" section for details on how to gather the necessary logs to provide to Cisco TAC.
7.
Optionally, if you are interested in learning more about the AMIS protocol and would like to attempt deciphering a log file of the transmitted frames and digits, see the "Advanced Troubleshooting: Viewing the Frames and Digits in an AMIS Call" section.
Following the Inbound AMIS Message Flow
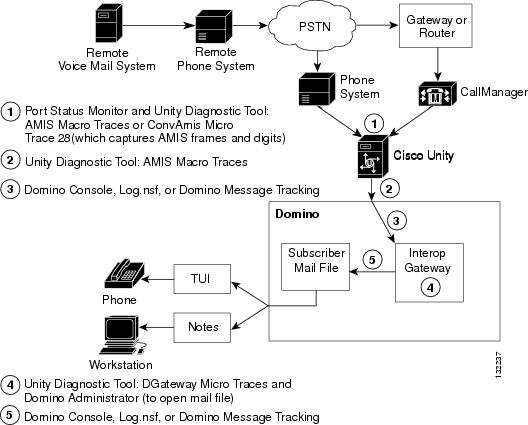
Figure 6-2 shows at a high level the flow of inbound AMIS messages from the remote voice messaging system to Cisco Unity, and the logs and other tools that you can use to troubleshoot problems along the path.
Figure 6-2 Inbound AMIS Message Flow and Troubleshooting Tools
In the above illustration, the Cisco Unity server used by Cisco Unity subscribers to listen to messages may or may not be the same as the Cisco Unity AMIS bridgehead server, so it was left out for the sake of simplicity. Additionally, the path from the PSTN to the Cisco Unity bridgehead server depends on the phone system integration. Two paths are shown in the illustration because transmission problems can occur at the gateway or router used with Cisco CallManager integrations. If you do not have a Cisco CallManager integration, ignore that path. Note also that the Interop Gateway service actually runs on a Cisco Unity server, and the Interop Gateway mail file is on a Domino server.
Use the following task list to troubleshoot problems with inbound AMIS messages:
1.
Go to the Network > Delivery Options > Profile page of each of the AMIS delivery locations. Confirm that the Node ID entered on the page exactly matches the node ID that the remote voice messaging system transmits.
2.
Determine whether the hang-up tones could be the source of the problem. See the ""C" and "D" DTMF Hang-Up Tones Cause AMIS Calls to Fail" section.
3.
Verify that the Cisco Unity call routing rules route calls to a call handler such as the Opening Greeting (this is the default behavior when Cisco Unity is initially installed).
4.
Determine whether the message made it to the Interop Gateway mail file. Do the "To Confirm That Messages Arrive at the Interop Gateway Mail File" procedure.
5.
If the message was not delivered to the Interop Gateway mail file, something may have gone wrong during the AMIS transmission. Use the Port Status Monitor to observe incoming AMIS call progress to see if that provides a clue. See the "To Use the Port Status Monitor to Watch Details of an AMIS Transmission" procedure.
6.
If you have been unable to fix the problem and will be contacting Cisco TAC, see the "Gathering Logs and Resetting Traces to Default Values" section to gather the necessary log files.
7.
Optionally, if you are interested in learning more about the AMIS protocol and would like to attempt deciphering a log file of the transmitted frames and digits, see the "Advanced Troubleshooting: Viewing the Frames and Digits in an AMIS Call" section.
Gathering Logs and Resetting Traces to Default Values
If you have been unable to determine why messages are not being delivered, gather the diagnostic log files from the Unity Diagnostic tool to provide to Cisco TAC. Be sure to set the traces back to their default values, as extensive logging takes up a great deal of disk space. See the following instructions:
•
To Retrieve Unity Diagnostic Tool Log Files
•
To Retrieve the Unity Diagnostic Tool Log File for the Interop Gateway
To Retrieve Unity Diagnostic Tool Log Files
Step 1
On the Windows Start menu on the Cisco Unity AMIS bridgehead server, click Programs > Cisco Unity > Unity Diagnostic Tool.
Step 2
On the Cisco Unity Diagnostic Tasks screen, click Gather Log Files. The Welcome to the Gather Log Files wizard is displayed.
Step 3
Click Select Logs.
Step 4
If desired, click Browse to change the directory for the log files.
Step 5
Click Next. The Select Logs to Gather page is displayed.
Step 6
Expand AvCsMgr, and click to select the check box for the last diagnostic file.
Step 7
Expand AvMsgStoreMonitor, and click to select the check box for the last diagnostic file.
Step 8
If the Interop Gateway service is running on this server, expand CsDomInteropGty, and click to select the check box for the last diagnostic file.
Otherwise, you will need to run the Unity Diagnostic tool on the Cisco Unity server on which the Interop Gateway service is running to gather the log file for the Interop Gateway, as detailed in the next "To Retrieve the Unity Diagnostic Tool Log File for the Interop Gateway" procedure.
Step 9
Click Next. When the processing of the files is finished, the Completing the Gather Logs wizard page is displayed.
Step 10
Click View Directory to open a window of the directory.
Step 11
On the Completing the Gather Logs wizard page, click Finish.
Step 12
On the Cisco Unity Diagnostic Task page, click Reset to Default Traces.
Step 13
Click Start New Log Files.
Step 14
Exit the Cisco Unity Diagnostic tool.
To Retrieve the Unity Diagnostic Tool Log File for the Interop Gateway
Step 1
On the Windows Start menu on the Cisco Unity server on which the Interop Gateway service is running, click Programs > Cisco Unity > Unity Diagnostic Tool.
Step 2
On the Cisco Unity Diagnostic Tasks screen, click Gather Log Files. The Welcome to the Gather Log Files wizard is displayed.
Step 3
Click Select Logs.
Step 4
If desired, click Browse to change the directory for the log files.
Step 5
Click Next. The Select Logs to Gather page is displayed.
Step 6
Expand CsDomInteropGty, and click to select the check box for the last diagnostic file.
Step 7
Click Next. When the processing of the files is finished, the Completing the Gather Logs wizard page is displayed.
Step 8
Click View Directory to open a window of the directory.
Step 9
On the Completing the Gather Logs wizard page, click Finish.
Step 10
On the Cisco Unity Diagnostic Task page, click Reset to Default Traces.
Step 11
Click Start New Log Files.
Step 12
Exit the Cisco Unity Diagnostic tool.
AMIS Troubleshooting Procedures
Use the following procedures as needed to troubleshoot problems with AMIS message delivery. Note that the procedures in this section are not necessarily in the order in which you need to do them. For information on when to use the procedures, and the correct order in which to do them, see the preceding topics:
•
Troubleshooting AMIS Message Delivery
•
Following the Outbound AMIS Message Flow
•
Following the Inbound AMIS Message Flow
To Confirm That the Interop Gateway Foreign Domain Document and Mail File Exist
Step 1
In the Domino Administrator, click the Configuration tab.
Step 2
In the left pane, expand Messaging > Domains. You should see the Foreign domain document used by the Interop Gateway in the list in the right pane. (You may need to expand the list in the right pane.)
Step 3
Open the Foreign domain document.
Step 4
Confirm that the Foreign domain name is correct.
Step 5
Click the Mail Information tab, and write down the server name and mail file name.
Step 6
Close the Foreign domain document.
Step 7
Browse to the directory on the Domino server specified in the Foreign domain document, and confirm that the Interop Gateway mail file itself exists.
To Confirm That Messages Arrive at the Interop Gateway Mail File
Step 1
On the Cisco Unity server on which the Interop Gateway service is running, open the Services MMC. (On the Windows Start menu, click Programs > Administrative Tools > Services.)
Step 2
Right-click CsDomInteropGty, and click Stop.
Step 3
Send a test AMIS message. Because the Interop Gateway service has been stopped, if the message arrives at the Interop Gateway mail file, the message will remain there until the service is started.
Step 4
Use the Domino Administrator or Notes to open the Interop Gateway mail file to see if the message is there.
In order to use the Domino Administrator or Notes to access the Interop Gateway mail file, you will need to make sure that you have permission to do so. How you do this depends on the Domino version and security policies for your organization. Use the following as a guide, and consult your Domino documentation for more information:
If the Domino server on which the Interop Gateway mail file is located is running Domino 6.0 or later:
•
If you have Full Access Administration rights, you will be able to open the mail file.
•
If someone who has Full Access Administration rights is available, have the administrator add you to the Interop Gateway mail file Access Control List (ACL) with at least Editor permissions.
If the Domino server on which the Interop Gateway mail file is located is running Domino 5.x, or if someone with Full Access Administration rights is unavailable:
•
Log on to the Domino Administrator by using the name and password of the Person document that was created for the Cisco Unity server on which the Interop Gateway service was configured to run. This account should have Editor plus Delete Documents permissions in the ACL of the Interop Gateway mail file.
You can either use this account whenever you open the Interop Gateway mail file, or you can add yourself to the Interop Gateway mail file ACL with at least Editor permissions.
Step 5
After seeing whether the message is in the mail file, close it.
Step 6
On the Cisco Unity server, restart the Interop Gateway service, CsDomInteropGty, and close the Services MMC.
To Confirm That Messages Are Being Delivered to the UAmis Mail File
Step 1
In the Cisco Unity Administrator, change the AMIS restriction table to disallow all numbers. This will result in all AMIS messages remaining queued in the UAmis mail file until the AMIS schedule becomes active.
For detailed instructions on changing the restriction table, see the "To Change the AMIS Restriction Table to Disallow All Delivery Numbers" procedure, and then continue with Step 2.
Step 2
Change the AMIS schedule so that it is inactive during the time that you are troubleshooting. This will result in messages remaining in the UAmis mail file long enough for you to see them.
For detailed instructions on changing the schedule, see the "To Change the AMIS Schedule so That It Is Inactive While Troubleshooting" procedure, and then continue with Step 3.
Step 3
Use the Domino Administrator or Notes to open the UAmis mail file to see if the message is there.
In order to use the Domino Administrator or Notes to access the UAmis mail file, you will need to make sure that you have permission to do so. How you do this depends on the Domino version and the security policies for your organization. Use the following as a guide, and consult your Domino documentation for more information:
If the Domino server on which the UAmis mail file is located is running Domino 6.0 or later:
•
If you have Full Access Administration rights, you will be able to open the mail file.
•
If someone who has Full Access Administration rights is available, have the administrator add you to the UAmis mail file Access Control List (ACL) with at least Editor permissions.
If the Domino server on which the UAmis mail file is located is running Domino 5.x, or if someone with Full Access Administration rights is unavailable:
•
Log on to the Domino Administrator by using the name and password of the Person document that was created for the Cisco Unity AMIS bridgehead server. This account should have Editor plus Delete Documents permissions in the ACL of the UAmis mail file.
You can either use this account whenever you open the UAmis mail file, or you can add yourself to the UAmis mail file ACL with at least Editor permissions.
Step 4
Send a test message to see whether it is delivered to the UAmis mail file. If you are using blind addressing, be sure to verify that you are using a valid Dial ID number from a Delivery Location.
Step 5
After testing, reset the AMIS restriction table and schedule back to the desired settings for normal operations.
To Confirm That the Foreign Domain Name Settings Are Correct
The Foreign domain name used by the Interop Gateway is stored in several places, and the name must be exactly the same in each place. The following procedure describes how to check the Foreign domain name in each of the places in which it is stored.
Step 1
In the Domino Administrator, click the Configuration tab.
Step 2
In the left pane, expand Messaging > Domains. You should see the Foreign domain document used by the Interop Gateway in the list in the right pane (you may need to expand the list).
Step 3
Write down the name displayed in the list and then close the Foreign domain document.
Step 4
If the recipient of the AMIS message(s) that you are tracing is an AMIS subscriber, do the following sub-steps. Otherwise, skip to Step 5.
a.
In the Domino Administrator, click the People and Groups tab.
b.
In the left pane, expand People such that you see the Person document for the AMIS subscriber when you scroll through the list in the right pane.
c.
Double-click the Person document for the AMIS subscriber.
d.
On the Basics tab in the Forwarding Address field, write down the Foreign domain name. This is the name to the right of the @ symbol.
e.
Close the Person document.
Step 5
On a Cisco Unity server desktop, double-click the Cisco Unity Tools Depot icon.
Step 6
In the left pane of the Tools Depot window, expand Administration Tools and double-click Advanced Settings Tool.
Step 7
In the Unity Settings list, click Networking—Change Interop Gateway Foreign Domain Name (Domino Only).
Step 8
Write down the name in the Current Value field.
Step 9
Close the Advanced Settings tool.
Step 10
In the left pane of the Tools Depot window, expand Diagnostic Tools.
Step 11
Double-click Data Link Explorer.
Step 12
In the Table Name list, scroll down and click Configuration.
Step 13
In the Column Name list, click NodeName.
Step 14
In the list in the bottom pane, scroll down towards the end of the list, and click the row where the name in the NodeName column is ForeignDomain.
Step 15
Write down the name in the NodeValue column.
Step 16
Close the Data Link Explorer window and exit Tools Depot.
Step 17
Compare the names you wrote down in Step 3, Step 4, Step 8, and Step 15. If the names are not exactly the same, change the Foreign domain name according to the instructions in the "Changing the Interop Gateway Foreign Domain Name" section in the "AMIS Networking" chapter of the Networking in Cisco Unity Guide, available at http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/voice/c_unity/unity40/net/net405/dom/index.htm.
If the names are exactly the same, and your installation consists of multiple Cisco Unity servers, repeat Step 5 through Step 17 on another Cisco Unity server until you have checked the settings on all of the Cisco Unity servers. If you discover a mismatch at any point and change the Foreign domain name according to the instructions in the "Changing the Interop Gateway Foreign Domain Name" section, the name will be changed on every AMIS subscriber Person document and every Cisco Unity server.
To Change the AMIS Restriction Table to Disallow All Delivery Numbers
Step 1
In the Cisco Unity Administrator, go to the Network > AMIS Options > Delivery Options page.
Step 2
Click View next to Local Dial Restriction Table to display the AMIS restriction table.
Step 3
On the AMIS restriction table page, click Add Dial String.
Step 4
In the Call Pattern box, enter *.
Step 5
In the Allow This String box, click No.
Step 6
Click the Save icon.
To Change the AMIS Schedule so That It Is Inactive While Troubleshooting
Step 1
In the Cisco Unity Administrator, go to the Network > AMIS Options > Schedule page.
Step 2
Click the applicable blocks so that the schedule is inactive while you are troubleshooting.
Step 3
Click the Save icon.
To Confirm That the Interop Gateway Service Is Running
Step 1
On the Windows Start menu on the Cisco Unity server on which the Interop Gateway Configuration wizard was run, click Programs > Administrative Tools > Services.
Step 2
Locate the CsDomInteropGateway service in the Name column.
Step 3
If the Status column indicates that the Interop Gateway service is not running, right-click the service and click Start.
To View Properties of a Message in the UAmis Mail File
Step 1
Open the UAmis mail file by using Notes or the Domino Administrator.
Step 2
Right-click an AMIS message and click Document Properties.
Step 3
Click the Fields tab (the second tab from the left), and check the following message properties:
•
AVP_AMIS_DESTINATION_NODE—The AMIS delivery location Dial ID.
•
AVP_AMIS_RECIPIENT—The remote mailbox number of the recipient.
•
AVP_AMIS_SENDER_ADDRESS—The message sender.
•
AVP_SUBMIT_TIME—The time that the message was submitted. Note that the timestamp is in GMT.
Step 4
Close the Document Properties window.
To Use the Port Status Monitor to Watch Details of an AMIS Transmission
Step 1
In the Cisco Unity Administrator, go to the System > Ports page, and change the settings as needed so that only one port is enabled for outbound AMIS calls, and that all other functions (such as Message Notification and Dialout MWIs) on that port are disabled. This makes it easier to observe the call progress information in the Port Status Monitor.
Note
For any outgoing call troubleshooting—AMIS, MWI, message notification, or TRAP—it is best to use one of the last ports because the higher-numbered ports are most likely being used for outgoing tasks. Cisco Unity searches for available ports for outgoing tasks starting with the last port.
Step 2
On a Cisco Unity server, double-click the Cisco Unity Tools Depot icon on the desktop.
Step 3
In the left pane of the Tools Depot window, expand Switch Integration Tools.
Step 4
Double-click Port Status Monitor.
Step 5
In the list of ports in the left pane, click the port configured for outbound AMIS outbound calls.
Step 6
Click Ports > Start Selected. A window is displayed in the right pane, which will contain call progress information.
Step 7
Use the phone to dial in to Cisco Unity on a port other than the one configured for outbound AMIS calls, and send a test message to someone on the remote voice messaging system.
Step 8
Observe the information in the Port Status Monitor window.
You should see the dialout information and the states that the AMIS call goes through. An AMIS call goes through a finite number of states during an AMIS transmission, and as the call progresses, you should see the descriptive name of each state in the Port Status Monitor window. For detailed information about the AMIS transmission states, refer to the White Paper: AMIS Analog Networking Definitions, available at http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/voice/c_unity/whitpapr/amis.htm.
"C" and "D" DTMF Hang-Up Tones Cause AMIS Calls to Fail
"C" and "D" DTMF tones, also known as fourth-column tones, are just like the twelve other DTMF tones ("0-9," "*," and "#") found on a regular analog phone. They are commonly used for in-band analog integrations and other "non-human" tasks.
The first action of an AMIS call is the handshake between the originating and receiving voice messaging systems. The originating system dials the number of the destination system. When the originating system detects that the destination system has answered the call, the originating system transmits a "C" tone to the destination. If the destination system answers the call and detects the "C" tone, it should respond with a "D" tone within 10 seconds. After transmitting the "D" tone, the destination system expects a Start Session frame.
Note
For more information on the details of an AMIS call, refer to the White Paper: AMIS Analog Networking Definitions, available at http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/voice/c_unity/whitpapr/amis.htm.
Many Toshiba phone systems use the "D" tone to indicate to voice messaging systems that a disconnect has occurred. Other phone systems may also use the "C" or "D" tones to indicate that a disconnect has occurred. When this is the case, a parameter of "HangUpTone=C" or "HangUpTone=D" will be defined in the active switch configuration file on the Cisco Unity server.
If "HangUpTone=C" is defined, the AMIS feature cannot be used on that system. When a remote voice messaging system dials Cisco Unity and sends the "C" tone to initiate the AMIS handshake, Cisco Unity interprets it as a disconnect signal from the phone system and hangs up on the call.
Similarly, if "HangUpTone=D" is defined, the AMIS feature cannot be used on that system. When Cisco Unity dials the remote voice messaging system and sends the "C" tone to initiate the AMIS handshake, and the remote system responds with the "D" tone, Cisco Unity interprets it as a disconnect signal from the phone system and hangs up on the call.
To fix this problem, configure the phone system to use another type of disconnect indication (such as the reorder tone, dial tone, or loop current reversal), then remove the HangUpTone parameter from the active switch file. However, if this recommended action is not possible, configure the phone system to use "A" or "B" as a hang-up tone, and then modify the HangUpTone parameter in the active switch file to match this new value.
The default values for the hang-up packets expected by Cisco Unity (defined in avanaglog.avd) have been chosen to work with AMIS. Changing these values may cause AMIS calls to fail.
To Obtain the Name(s) of the Active Switch File(s)
Step 1
On the Cisco Unity server, start Regedit.
CautionChanging the wrong registry key or entering an incorrect value can cause the server to malfunction. Before you edit the registry, confirm that you know how to restore it if a problem occurs. (Refer to the "Restoring" topics in Registry Editor Help.) Note that for Cisco Unity failover, registry changes on one Cisco Unity server must be made manually on the other Cisco Unity server, because registry changes are not replicated. If you have any questions about changing registry key settings, contact Cisco TAC.
Step 2
If you do not have a current backup of the registry, click Registry > Export Registry File, and save the registry settings to a file.
Step 3
Expand the key
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Active Voice\Miu\1.0\Initialization\Switch 0.
For dual-switch integrations, also expand the key
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Active Voice\Miu\1.0\Initialization\Switch 1.
Step 4
View the Switch Configuration File value under the ...\Switch 0 key to obtain the name of the active switch file, and then click Cancel. For dual-switch integrations, also view the Switch Configuration File value under the ...\Switch 1 key to obtain the name of the second active switch file, and then click Cancel.
Step 5
Close Regedit.
To Edit the Active Switch File(s)
Step 1
On the Cisco Unity server, browse to the \CommServer\IntLib directory. (C:\CommServer is the default directory in which Cisco Unity is installed. If Cisco Unity is installed in another directory, use that path instead.)
Step 2
Open the active switch file with a text editor.
Step 3
In the [Configuration] section, if "HangUpTone=" does not exist, or if it is set to any value other than "C" or "D," do not change anything in the file, because the parameter does not conflict with AMIS. Close the file, and skip to Step 5.
Step 4
If "HangUpTone=" is set to either the "C" or "D" DTMF tone, the action you take depends on the new disconnect indication that you configured on the phone system, as follows:
•
If the phone system uses some other type of disconnect indication, such as the reorder tone, dial tone, or loop current reversal, remove the HangUpTone parameter from the active switch file. Save and close the file.
•
If the phone system uses either the "A" or "B" DTMF tone as a hang-up tone, modify the "HangUpTone=" to match this new value. Save and close the file.
Step 5
For dual-switch integrations, repeat Step 1 through Step 4 to edit the second active switch file.
Step 6
Stop and restart Cisco Unity to activate the changes to the active switch file.
Advanced Troubleshooting: Viewing the Frames and Digits in an AMIS Call
If you have determined that AMIS calls (either outbound or inbound) are being made, but the call is failing for some reason, you may want to obtain a trace of the frames and digits sent during an AMIS call to see if you can determine what the problem is and resolve it. To obtain such a trace, you enable the Conv Amis 28 micro trace in the Unity Diagnostic tool, disable all other traces, and place another test call. Although the available macro traces—Extensive Incoming AMIS Message Traces, and Extensive Outgoing AMIS Message Traces—both include the Conv Amis 28 micro trace, they also include many other micro traces, which makes it more difficult to follow the call progress. (Note however that when you are asked to provide log files to Cisco TAC, you will need to provide the log file from the applicable macro trace.)
When using the Unity Diagnostic tool to gather the log file for the Conv Amis 28 micro trace, select the diagnostic log file within the AvCsMgr process. After obtaining a trace of the frames and digits, refer to the White Paper: AMIS Analog Networking Definitions for detailed information about the AMIS protocol. (The white paper is available at http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/voice/c_unity/whitpapr/amis.htm.)

 Feedback
Feedback