Table Of Contents
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Components and Process
Supported Cisco MeetingPlace System Configurations
About the Cisco MeetingPlace Video-Conferencing Process
How Video Conferences Are Scheduled
About the Minimum Number of Video Ports Scheduled
How the Link Between the Cisco IPVC MCU and the Cisco MeetingPlace Audio Server Is Established
How Video Conference Participants Join Meetings
About Displaying the Status and Options of Video Participants in the Meeting Room
How Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Tracks Port Availability
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Components and Process
This chapter describes the components that are required for the Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration solution:
•
Supported Cisco MeetingPlace System Configurations
•
About the Cisco MeetingPlace Video-Conferencing Process
Overview of Components
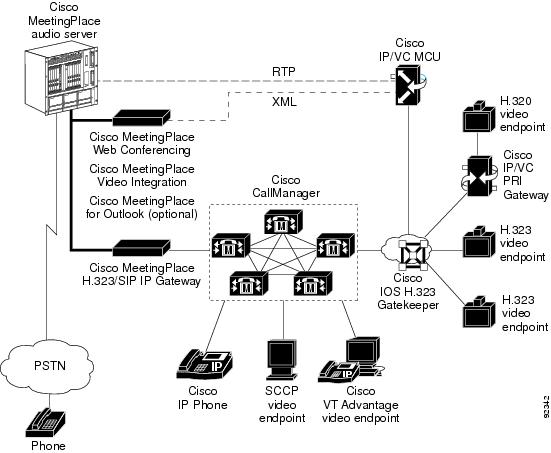
The components shown in Figure 2-1 and described in Table 2-1 work together to provide video conferences that are integrated with Cisco MeetingPlace voice and web conferences.
In the Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration solution, Cisco MeetingPlace components provide audio conferencing and web conferencing data collaboration, and the Cisco IPVC MCU and its associated components provide video conferencing. Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration integrates the two solutions to provide integrated voice, data, and video conferencing.
Figure 2-1
Supported Cisco MeetingPlace System Configurations
Supported Cisco MeetingPlace system configurations include the following. Complete system requirements and a Cisco MeetingPlace version compatibility matrix are in the Release Note for Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Release 5.3:
•
One Cisco MeetingPlace 8100 series server.
•
One or more Cisco MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway servers.
•
Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing servers in any configuration that is supported in Release 5.3. However, Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration can be installed only on a single Cisco MeetingPlace web-conferencing server.
•
Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration installed on a Cisco MeetingPlace web-conferencing server. If your system has a DMZ configuration, see Preparing to Install the Video Integration with DMZ Configurations, page 3-17 for important considerations before installing Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration. A DMZ configuration includes one or more servers in a DMZ outside the corporate firewall.
•
(Optional) Cisco MeetingPlace for Outlook.
•
(Optional) Cisco MeetingPlace for Lotus Notes.
•
(Optional) Cisco MeetingPlace SMTP E-Mail Gateway.
The following additional components are also supported:
•
One Cisco IPVC MCU with all components including an H.323 gatekeeper.
•
(Optional) Cisco CallManager.
About the Cisco MeetingPlace Video-Conferencing Process
The process of creating, running, and terminating an integrated video, audio, and web conference is described in this section.
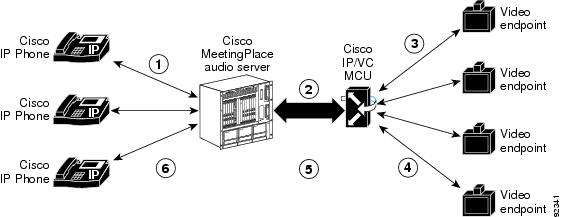
Participants who are using audio-only devices connect to the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server. Participants with video equipment connect to the Cisco IPVC MCU, which processes both the video and the audio channel of the video endpoints. Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration mixes the audio streams from both systems to allow all participants to hear and speak to each other. Figure 2-2 shows this process.
Figure 2-2
How Video Conferences Are Scheduled
A user fills in a standard Cisco MeetingPlace conference scheduling form in Microsoft Outlook, Lotus Notes, Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing, or MeetingTime; then the user submits that form to Cisco MeetingPlace audio server. If the user has indicated that the conference will include video participants, the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server verifies that resources are available, and if so, schedules the requested number of video ports and (depending on system configuration) notifies invitees.
About the Minimum Number of Video Ports Scheduled
In order to prevent more video conferences from being scheduled than the Cisco IPVC MCU can support at one time, Cisco MeetingPlace may schedule more video ports than the meeting scheduler specifies for a conference. The minimum number of ports that Cisco MeetingPlace schedules for each conference is determined by the formula [(Total number of video conference ports - Number of video floater ports + Number of video overbook ports)/ Total number of video conferences available]. If a user does not schedule fewer ports than the number of ports resulting from this calculation, Cisco MeetingPlace schedules the number of ports that the scheduler specifies. Floater and overbook ports are defined in About Configuring Port Parameters, page 4-7.
How Video Conferences Start
The Cisco IPVC MCU is configured to allow Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration to control all H.323 video-conferencing resources and meeting operations on the Cisco IPVC MCU, including initiating meetings. Cisco MeetingPlace does not control SCCP resources on the Cisco IPVC MCU.
Before a video conference can be started on the Cisco IPVC MCU, a Cisco MeetingPlace meeting must exist on the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server. However, the meeting does not need to be scheduled in advance; it can be scheduled as an immediate or reservationless meeting, as long as video ports and video conferences are available at the time of the request.
The first Cisco MeetingPlace conference participant who joins the video conference initiates the creation of the video conference on the Cisco IPVC MCU. Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration verifies that the conference is currently in session or within the guard times of the existing meeting, then tells the Cisco IPVC MCU to immediately create a video conference with the Meeting ID.
The Meeting ID for the video conference includes the MeetingPlace service prefix that identifies Cisco MeetingPlace conferences on the Cisco IPVC MCU, plus the standard Cisco MeetingPlace Meeting ID for that conference. This Meeting ID is used by the gatekeeper or Cisco CallManager to route incoming calls for this conference over the network to the Cisco IPVC MCU.
Conferences cannot be created by dialing in to the Cisco IPVC MCU unless the meeting has been scheduled on Cisco MeetingPlace audio server. If a participant dials in to the Cisco IPVC MCU to start a conference, the Cisco IPVC MCU sends information about the new video conference to Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration. If the conference has not been scheduled in Cisco MeetingPlace, is not currently in session, or is outside the guard times of a scheduled meeting, Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration tells the Cisco IPVC MCU not to create the conference.
How the Link Between the Cisco IPVC MCU and the Cisco MeetingPlace Audio Server Is Established
When the first video participant joins an authorized video conference, either by outdialing from the Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing meeting room or by dialing in to the Cisco IPVC MCU, Cisco MeetingPlace creates the link that connects the audio channel of the video conference and the audio channel of the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server.
To initiate this link, Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration tells the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server to outdial to the Cisco IPVC MCU; the call is routed through the Cisco MeetingPlace H.323/SIP IP Gateway to Cisco CallManager or to the H.323 gatekeeper, either of which has been configured to route the call to the Cisco IPVC MCU. Either the gatekeeper or the Cisco IPVC MCU can route the call to the correct conference. The routing pattern (outdialed number) for this transaction is composed of the service prefix that identifies Cisco MeetingPlace conferences on the Cisco IPVC MCU (and also is unique among the routing patterns configured on the gatekeeper and CallManager) plus the Cisco MeetingPlace Meeting ID of the conference. Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration tries three times to establish this link.
After the link is established, the entire audio channel of the video conference on the Cisco IPVC MCU becomes a participant in the Cisco MeetingPlace audio conference and vice versa.
Note
The video link appears as a named participant in the in-session tab in MeetingTime, but not in the Cisco MeetingPlace web-conferencing meeting room. It also is included in some reports, but not all. See About Video-Conferencing Statistics, page 4-13.
After the link is established, all further communication between the Cisco IPVC MCU and the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server is handled through the Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration component, which communicates with the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server through MPAgent. MPAgent is a component of Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing, which is a prerequisite to installation of Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration. Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration communicates with the Cisco IPVC MCU using proprietary XML messaging.
If the link between Cisco MeetingPlace and the Cisco IPVC MCU is disconnected, Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration attempts to reestablish it three times, checking every minute, or when another participant joins the conference.
How Video Conference Participants Join Meetings
There are several ways additional participants can join the video conference. The process of adding participants to the conference depends on how they enter the meeting.
If a Participant Joins a Scheduled Video Conference by Outdialing From the Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing Meeting Room
When a participant clicks Connect from within Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing, or in a calendar entry in Cisco MeetingPlace for Lotus Notes, or in the MeetingPlace tab of a meeting notification in Cisco MeetingPlace for Outlook, Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration sends a message to the Cisco IPVC MCU to outdial to the endpoint of the participant. When the participant has successfully joined the video conference, the Cisco IPVC MCU notifies Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration, and the status of the participant is recorded in the participant list that is displayed in the meeting room of Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing.
If a Participant Joins a Scheduled Video Conference by Dialing in to the Cisco IPVC MCU
Participants dial in to the conference from their video endpoint by using the number provided in the Connect dialog box in the Cisco MeetingPlace web-conferencing meeting room. This number is the service prefix on the Cisco IPVC MCU that identifies Cisco MeetingPlace conferences, plus the Cisco MeetingPlace Meeting ID. Cisco CallManager or the gatekeeper routes all incoming H.323 calls that begin with the specified service prefix to the Cisco IPVC MCU, which routes each call to the correct video conference based on the Cisco MeetingPlace meeting ID number portion of the number that was dialed.
When participants attempt to join the video conference by dialing in from their video endpoint, the Cisco IPVC MCU accepts the call only if the conference is not restricted to profiled or invited users and does not require a password. (This is because the Cisco IPVC MCU cannot authenticate dial-in participants.) If the participant is granted access, the Cisco IPVC MCU checks with Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration to see if the meeting is in session and within the guard times. If so, the Cisco IPVC MCU admits the participant to the video conference and notifies Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration that the participant has joined the conference. Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration notifies Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing and the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server of the status of the participant.
If a Participant Joins a Video Conference on an Ad-Hoc Basis
If all scheduled video-conferencing ports for a meeting that is already in progress are already in use and an additional participant attempts to join the video conference, the user may be able to join on an ad-hoc basis. In this case, the Cisco IPVC MCU polls Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration to see if video-conferencing ports are available, and if they are, the Cisco IPVC MCU allows the participant to join the conference.
How Video Conferences Run
About the Video Images
The visual stream to and from the video endpoints is entirely processed by the Cisco IPVC MCU. After the call is connected, the media stream is routed from the video endpoint, through the Cisco IPVC MCU for processing into a unified video stream, and back to the video endpoints for display to the users. However, users control the status of the transmission (for example, started, paused, or terminated) from within the Cisco MeetingPlace web-conferencing meeting room. See About Displaying the Status and Options of Video Participants in the Meeting Room.
About the Audio Channel
The audio streams of the Cisco IPVC MCU and Cisco MeetingPlace are mixed to allow audio and video-conferencing participants to hear and speak to each other. The audio channel from each video endpoint is routed to the Cisco IPVC MCU, then passed through the video link to the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server, where it is mixed with the audio from audio-only endpoints and sent back to all users, to form a seamless audio experience for participants on both video and audio-only endpoints.
About Displaying the Status and Options of Video Participants in the Meeting Room
When the Cisco IPVC MCU admits a participant to a video conference, the Cisco IPVC MCU notifies Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration, which notifies Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing. Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing identifies the participant as a video participant in the participant list in the Cisco MeetingPlace web-conferencing meeting room. The participant name displayed comes from the participant's profile or guest information if they outdialed from Cisco MeetingPlace, and from the gatekeeper if they dialed in to the video conference. When a participant mutes, pauses, changes the view of, or terminates their video connection, Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing registers this change in the meeting room user interface and passes the request to Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration, which passes the request to the Cisco IPVC MCU where it is performed. If the user terminates the connection by hanging up the video endpoint, the Cisco IPVC MCU notifies Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration, which then notifies Cisco MeetingPlace Web Conferencing so that the status of that participant can be updated.
When a video participant speaks, the Now Speaking display shows "Video Participant."
How Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration Tracks Port Availability
The number of available ports and conferences is determined by the Cisco IPVC MCU. Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration polls the Cisco IPVC MCU every 30 minutes for this information and passes it to the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server, which displays it in MeetingTime. Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration uses this information to regulate the creation of and entry to video conferences.
How Video Conferences End
The video conference on the Cisco IPVC MCU ends when the Cisco MeetingPlace conference ends, according to the standard rules for ending conferences on the Cisco MeetingPlace audio server. At this time, Cisco MeetingPlace Video Integration tells the Cisco IPVC MCU to terminate the video conference.

 Feedback
Feedback