Feedback Feedback
|
Table Of Contents
Configuration Checklist for Packet Capturing
Adding an End User to the Standard Packet Sniffer Users Group
Configuring Packet-Capturing Service Parameters
Configuring Packet Capturing in the Phone Configuration Window
Configuring Packet Capturing in Gateway and Trunk Configuration Windows
Packet Capturing Configuration Settings
Cisco CallManager Troubleshooting Tools
Troubleshooting Perfmon Data Logging
Configuring Troubleshooting Perfmon Data Logging
Viewing the Perfmon Log Files with the Microsoft Performance Tool
Cisco Discovery Protocol Support
Simple Network Management Protocol Support
Troubleshooting the Server Without Root Access
Serviceability GUI and CLI Commands for Commonly-used Linux Commands
How to Collect Logs and Trace Files
How to Schedule Collection of Logs and Trace Files
How to Free Up Space on the Hard Disk
How to Reboot the Cisco CallManager Server
How to Change Debug Levels for Traces
Verify Cisco CallManager Services Are Running
Where to Find More Information
Troubleshooting Tools
This section addresses the tools and utilities that you use to configure, monitor, and troubleshoot Cisco CallManager 5.0(1) and provides general guidelines for collecting information to avoid repetitive testing and recollection of identical data.
Note
To access some of the URL sites listed this document, you must be a registered user and you must be logged in.
This section contains the following topics:
•
Cisco CallManager Troubleshooting Tools
•
Troubleshooting Perfmon Data Logging
•
Troubleshooting the Server Without Root Access
•
Where to Find More Information
Sniffer Traces
Typically, you collect sniffer traces by connecting a laptop or other sniffer-equipped device on a Catalyst port that is configured to span the VLAN or port(s) (CatOS, Cat6K-IOS, XL-IOS) that contains the trouble information. If no free port is available, connect the sniffer-equipped device on a hub that is inserted between the switch and the device.
Tip
To help facilitate reading and interpreting of the traces by the TAC engineer, Cisco recommends using Sniffer Pro software because it is widely used within the TAC.
Have available the IP/MAC addresses of all equipment that is involved, such as IP phones, gateways, Cisco CallManagers, and so on.
Collecting Traces
The video described below will show you how to gather basic Call Connection Manager (CCM) and Signal Distribution Layer (SDL) traces from your CallManager cluster. You can then use this information in your TAC Service Request.
After watching this video, you will be able to:
•
Document the problem
•
Reproduce the problem and gather the necessary information
•
Get this information to your TAC Engineer
You can view this informative Flash video at:
www.cisco.com/warp/public/788/video_64826/callmanager-tool.html
(available to non-registered users)www.cisco.com/warp/customer/788/video_64826/callmanager-tool.html
(available to registered users)Debugs
The output from debug privileged EXEC commands provides diagnostic information about a variety of internetworking events relating to protocol status and network activity in general.
Set up your terminal emulator software (such as HyperTerminal), so it can capture the debug output to a file. In HyperTerminal, click Transfer; then, click Capture Text and choose the appropriate options.
Before running any IOS voice gateway debugs, make sure that
service timestamps debug datetime msecis globally configured on the gateway.
Note
Avoid collecting debugs in a live environment during operation hours.
Preferably, collect debugs during non-working hours. If debugs must be collected in a live environment, configure
no logging consoleandlogging buffered. To collect the debugs, use show log.Some debugs can be lengthy, so collect them directly on the console port (default logging console) or on the buffer (logging buffer). Collecting debugs over a Telnet session may have an impact on the device performance, and the result could be incomplete debugs, which requires that you re-collect them.
To stop a debug, use the no debug all or undebug all commands. Verify that the debugs have been turned off by using the command show debug.
Packet Capture
This section contains information on the following topics:
•
Configuration Checklist for Packet Capturing
•
Adding an End User to the Standard Packet Sniffer Users Group
•
Configuring Packet-Capturing Service Parameters
•
Configuring Packet Capturing in the Phone Configuration Window
•
Configuring Packet Capturing in Gateway and Trunk Configuration Windows
•
Packet Capturing Configuration Settings
Packet Capturing Overview
Because third-party troubleshooting tools that sniff media and TCP packets do not work after you enable encryption, you must use Cisco CallManager Administration to perform the following tasks if a problem occurs:
•
Analyze packets for messages that are exchanged between Cisco CallManager and the device (Cisco IP Phone, Cisco SIP IP Phone, Cisco IOS MGCP gateway, H.323 gateway, H.323/H.245/H.225 trunk, or SIP trunk).
•
Capture the Secure RealTime Protocol (SRTP) packets between the devices.
•
Extract the media encryption key material from messages and decrypt the media between the devices.
Tip
Performing this task for several devices at the same time may cause high CPU usage and call-processing interruptions. Cisco strongly recommends that you perform this task when you can minimize call-processing interruptions.
For more information, see the Cisco CallManager Security Guide.
Configuration Checklist for Packet Capturing
Extracting and analyzing pertinent data includes performing the following tasks in Table 2-1:
Table 2-1 Configuration Checklist for Packet Capturing
Step 1
Add end users to the Standard Packet Sniffer Users group.
Adding an End User to the Standard Packet Sniffer Users Group
Step 2
Configure packet capturing service parameters in the Service Parameter Configuration window in Cisco CallManager Administration; for example, configure the Packet Capture Enable service parameter.
Step 3
Configure packet capturing settings on a per-device basis in the Phone or Gateway or Trunk Configuration window.
Note
Cisco strongly recommends that you do not enable packet capturing for many devices at the same time because this task may cause high CPU usage in your network.
•
Configuring Packet Capturing in the Phone Configuration Window
•
Configuring Packet Capturing in Gateway and Trunk Configuration Windows
Step 4
Capture SRTP packets by using a sniffer trace between the affected devices.
Refer to the documentation that supports your sniffer trace tool.
Step 5
After you capture the packets, set the Packet Capture Enable service parameter to False.
•
Configuring Packet-Capturing Service Parameters
Step 6
Gather the files that you need to analyze the packets.
Step 7
Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC) analyzes the packets. Contact TAC directly to perform this task.
Adding an End User to the Standard Packet Sniffer Users Group
End users that belong to the Standard Packet Sniffer Users group can configure the Packet Capture Mode and Packet Capture Duration settings for devices that support packet capturing. If the user does not exist in the Standard Packet Sniffer Users group, the user cannot initiate packet capturing.
The following procedure, which describes how to add an end user to the Standard Packet Sniffer Users group, assumes that you configured the end user in Cisco CallManager Administration, as described in the Cisco CallManager Administration Guide.
Procedure
Step 1
Find the user group, as described in the Cisco CallManager Administration Guide.
Step 2
After the Find/List window displays, click the Standard Packet Sniffer Users link.
Step 3
Click the Add Users to Group button.
Step 4
Add the end user, as described in the Cisco CallManager Administration Guide.
Step 5
After you add the user, click Save.
Configuring Packet-Capturing Service Parameters
To configure parameters for packet capturing, perform the following procedure:
Procedure
Step 1
In Cisco CallManager Administration, choose System > Service Parameters.
Step 2
From the Server drop-down list box, choose an Active server where you activated the Cisco CallManager service.
Step 3
From the Service drop-down list box, choose the Cisco CallManager (Active) service.
Step 4
Scroll to the TLS Packet Capturing Configuration pane and configure the packet capturing settings.
Tip
For information on the service parameters, click the name of the parameter or the question mark that displays in the window.
Note
For packet capturing to occur, you must set the Packet Capture Enable service parameter to True.
Step 5
For the changes to take effect, click Save.
Step 6
To continue packet-capturing configuration, see one of the following sections:
•
Configuring Packet Capturing in the Phone Configuration Window
•
Configuring Packet Capturing in Gateway and Trunk Configuration Windows
Configuring Packet Capturing in the Phone Configuration Window
After you enable packet capturing in the Service Parameter window, you can configure packet capturing on a per-device basis in the Phone Configuration window of Cisco CallManager Administration.
You enable or disable packet capturing on a per-phone basis. The default setting for packet capturing equals None.
Tip
Cisco strongly recommends that you do not enable packet capturing for many phones at the same time because this task may cause high CPU usage in your network.
If you do not want to capture packets or if you completed the task, set the Packet Capture Enable service parameter to False.To configure packet capturing for phones, perform the following procedure:
Procedure
Step 1
Before you configure the packet-capturing settings, see the "Configuration Checklist for Packet Capturing" section.
Step 2
Find the SIP or SCCP phone, as described in the Cisco CallManager Administration Guide.
Step 3
After the Phone Configuration window displays, configure the troubleshooting settings, as described in Table 2-2.
Step 4
After you complete the configuration, click Save.
Step 5
In the Reset dialog box, click OK.
Tip
Although Cisco CallManager Administration prompts you to reset the device, you do not need to reset the device to capture packets.
Additional Steps
Capture SRTP packets by using a sniffer trace between the affected devices.
After you capture the packets, set the Packet Capture Enable service parameter to False.
See the "Analyzing Captured Packets" section.
Configuring Packet Capturing in Gateway and Trunk Configuration Windows
The following gateways and trunks support packet capturing in Cisco CallManager Administration:
•
Cisco IOS MGCP gateways
•
H.323 gateways
•
H.323/H.245/H.225 trunks
•
SIP trunks
Tip
Cisco strongly recommends that you do not enable packet capturing for many devices at the same time because this task may cause high CPU usage in your network.
If you do not want to capture packets or if you completed the task, set the Packet Capture Enable service parameter to False.To configure packet capturing settings in the Gateway or Trunk Configuration window, perform the following procedure:
Procedure
Step 1
Before you configure the packet capturing settings, see the "Configuration Checklist for Packet Capturing" section.
Step 2
Perform one of the following tasks:
•
Find the Cisco IOS MGCP gateway, as described in the Cisco CallManager Administration Guide.
•
Find the H.323 gateway, as described in the Cisco CallManager Administration Guide.
•
Find the H.323/H.245/H.225 trunk, as described in the Cisco CallManager Administration Guide.
•
Find the SIP trunk, as described in the Cisco CallManager Administration Guide.
Step 3
After the configuration window displays, locate the Packet Capture Mode and Packet Capture Duration settings.
Tip
If you located a Cisco IOS MGCP gateway, ensure that you configured the ports for the Cisco IOS MGCP gateway, as described in the Cisco CallManager Administration Guide. The packet-capturing settings for the Cisco IOS MGCP gateway display in the Gateway Configuration window for endpoint identifiers. To access this window, click the endpoint identifier for the voice interface card.
Step 4
Configure the troubleshooting settings, as described in Table 2-2.
Step 5
After you configure the packet-capturing settings, click Save.
Step 6
In the Reset dialog box, click OK.
Tip
Although Cisco CallManager Administration prompts you to reset the device, you do not need to reset the device to capture packets.
Additional Steps
Capture SRTP packets by using a sniffer trace between the affected devices.
After you capture the packets, set the Packet Capture Enable service parameter to False.
See the "Analyzing Captured Packets" section.
Packet Capturing Configuration Settings
Use Table 2-2, which describes the Packet Capture Mode and Packet Capture Duration settings, with the following sections:
•
Configuring Packet Capturing in the Phone Configuration Window
•
Configuring Packet Capturing in Gateway and Trunk Configuration Windows
Analyzing Captured Packets
Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC) analyzes the packets by using a debugging tool. Before you contact TAC, capture SRTP packets by using a sniffer trace between the affected devices. Contact TAC directly after you gather the following information:
•
Packet Capture File—https://<IP address or server name>/pktCap/pktCap.jsp?file=mm-dd-yyyy.pkt, where you browse into the server and locate the packet-capture file by month, date, and year (mm-dd-yyyy)
•
Key for the file—https://<IP address or server name>/pktCap/pktCap.jsp?key=mm-dd-yyyy.pkt, where you browse into the server and locate the key by month, date, and year (mm-dd-yyyy)
•
User name and password of end user that belongs to the Standard Packet Sniffer Users group
For more information, see the Cisco CallManager Security Guide.
Cisco CallManager Troubleshooting Tools
Refer to the Cisco CallManager Serviceability Administration Guide and the Cisco CallManager Serviceability System Guide for detailed information of the following different types of tools that Cisco CallManager Serviceability provides to monitor and analyze the various Cisco CallManager systems.
Cisco Secure Telnet
Cisco Secure Telnet allows Cisco Service Engineers (CSE) transparent firewall access to the Cisco CallManager node on your site. Using strong encryption, Cisco Secure Telnet enables a special Telnet client from Cisco Systems to connect to a Telnet daemon behind your firewall. This secure connection allows remote monitoring and troubleshooting of your Cisco CallManager nodes, without requiring firewall modifications.
Note
Cisco provides this service only with your permission. You must ensure that a network administrator is available at your site to help initiate the process.
Command Line Interface
The command line interface (CLI) is used to access the Cisco CallManager system for basic maintenance and failure recovery. Access to the system can be obtained by either a hard-wired terminal (a system monitor and keyboard) or by performing a SSH session.
The account name and password are created at install time. The password can be changed after install, but the account name can never be changed.
A command is a text instruction that caused the system to perform some function. Commands may be stand alone or they can have mandatory or optional arguments or options.
A level is a collection of commands; for example, show is a level, whereas show status is a command. Each level and command also has an associated privilege level. You will be allowed to execute a command only if you have a sufficient privilege level.
For complete information on the Cisco CallManager CLI command set, see Appendix A in the Cisco IP Telephony Platform Administration Guide, Release 5.0(1).
Troubleshooting Perfmon Data Logging
CautionEnabling the troubleshooting perfmon data logging feature impacts system performance on the selected node. Do not enable this parameter unless Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC) directs you to do so.
The troubleshooting perfmon data logging feature assists Cisco TAC in identifying system problems. When you enable troubleshooting perfmon data logging, you initiate the collection of a set of Cisco CallManager and operating system performance statistics on the selected node. The statistics that are collected include comprehensive information that can be used for system diagnosis and information from a set of counters that is not a part of the current set of preconfigured counters.
Because an extensive amount of information is collected in a short time, Cisco recommends that you do not enable the enable troubleshooting perfmon data logging for any extended time and that you enable the Log Partitioning Monitor to monitor disk usage while troubleshooting perfmon data logging is enabled.
When you enable the troubleshooting perfmon data feature on a system with no active phone calls and you use the default setting for the troubleshooting perfmon data logging parameters, Cisco estimates that the system experiences a less than 5 percent increase in CPU utilization, and an insignificant increase in the amount of memory being used, and it write approximately 50 MB of information to the log files daily.
You can perform the following administrative tasks with the troubleshooting perfmon data logging feature:
•
Enable and disable the trace filter for Troubleshooting perfmon data logging.
•
Monitor a set of predefined System and Cisco CallManager performance objects and counters on each server.
•
Logs the monitored performance data in CSV file format on the local server in the active log partition and the cm/log/ris/csv directory. The log file uses the following naming convention: PerfMon_<node>_<month>_<day>_<year>_<hour>_<minute>.csv; for example PerfMon_172.19.240.80_06_15_2005_11_25.csv.
•
Specify the polling rate. This rate specifies the rate at which performance data is gathered and logged. You can configure the polling rate down to 5 seconds. Default polling rate equals 15 seconds.
•
Specifiy the maximum number of log files that will be stored on disk. Log files exceeding this limit are purged automatically by removing the oldest log file.
•
Specify the rollover criteria of the log file based on the maximum size of the file in Megabytes. The default value specifies 2 MB.
•
Collect the log file by using TCT/SOAP TCT (trace collection tool) or Command Line Interface.
•
View the log file in graphical format by using the Microsoft Windows performance tool.
The troubleshooting perfmon data logging feature collects information from the following counters within the following perfmon objects. Refer to the "Performance Objects and Counters" chapter in Cisco CallManager Serviceability System Guide for a description on the counters:
•
Cisco CallManager Object:
–
CallManagerHeartBeat
–
CallsActive
–
CallsAttempted
–
CallsCompleted
–
InitializationState
–
RegisteredHardwarePhones
–
RegisteredMGCPGateway
•
Cisco CallManager System Performance Object:
–
QueueSignalsPresent 1-High
–
QueueSignalsPresent 2-Normal
–
QueueSignalsPresent 3-Low
–
QueueSignalsPresent 4-Lowest
–
QueueSignalsProcessed 1-High
–
QueueSignalsProcessed 2-Normal
–
QueueSignalsProcessed 3-Low
–
QueueSignalsProcessed 4-Lowest
–
QueueSignalsProcessed Total
•
Cisco TFTP
–
BuildAbortCount
–
BuildCount
–
BuildDeviceCount
–
BuildDialruleCount
–
BuildDuration
–
BuildSignCount
–
BuildSoftkeyCount
–
BuildUnitCount
–
ChangeNotifications
–
DeviceChangeNotifications
–
DialruleChangeNotifications
–
EncryptCount
–
GKFoundCount
–
GKNotFoundCount
–
HeartBeat
–
HttpConnectRequests
–
HttpRequests
–
HttpRequestsAborted
–
HttpRequestsNotFound
–
HttpRequestsOverflow
–
HttpRequestsProcessed
–
HttpServedFromDisk
–
LDFoundCount
–
LDNotFoundCount
–
MaxServingCount
–
Requests
–
RequestsAborted
–
RequestsInProgress
–
RequestsNotFound
–
RequestsOverflow
–
RequestsProcessed
–
SegmentsAcknowledged
–
SegmentsFromDisk
–
SegmentsSent
–
SEPFoundCount
–
SEPNotFoundCount
–
SIPFoundCount
–
SIPNotFoundCount
–
SoftkeyChangeNotifications
–
UnitChangeNotifications
•
Process Object:
–
PID
–
STime
–
% CPU Time
–
Page Fault Count
–
VmData
–
VmSize
–
Thread Count
•
Memory Object:
–
Used Kbytes
–
Free Kbytes
–
Total Kbytes
–
Shared Kbytes
–
Buffers Kbytes
–
Cached Kbytes
–
Free Swap Kbytes
–
Total Swap Kbytes
–
Used Swap Kbytes
–
Pages Input
–
Pages Output
–
Pages
–
% Page Usage
–
% VM Used
–
% Mem Used
•
Processor Object:
–
Irq Percentage
–
Softirq Percentage
–
IOwait Percentage
–
User Percentage
–
Nice Percentage
–
System Percentage
–
Idle Percentage
–
%CPU Time
•
Thread Object—Troubleshooting Perfmon Data Logger only logs CCM threads:
–
PID
–
%CPU Time
•
Partition Object:
–
Used Mbytes
–
Total Mbytes
–
%Used
–
% Wait in Read Time
–
% Wait in Write Time
–
% CPU Time
–
Read Bytes Per Sec
–
Write Bytes Per Sec
–
Queue Length
•
IP Object:
–
In Receives
–
InHdr Errors
–
In Unknown Protos
–
In Discards
–
In Delivers
–
Out Requests
–
Out Discards
–
Reasm Reqds
–
Reasm Oks
–
Reasm Fails
–
Frag OKs
–
Frag Fails
–
Frag Creates
–
InOut Requests
•
TCP Object:
–
Active Opens
–
Passive Opens
–
Attempt Fails
–
Estab Resets
–
Curr Estab
–
In Segs
–
Out Segs
–
Retrans Segs
–
InOut Segs
•
Network Interface Object:
–
Rx Bytes
–
Rx Packets
–
Rx Errors
–
Rx Dropped
–
Rx Multicast
–
Tx Bytes
–
Tx Packets
–
Tx Errors
–
Tx Dropped
–
Total Bytes
–
Total Packets
–
Tx QueueLen
•
System Object:
–
Allocated FDs
–
Freed FDs
–
Being Used FDs
–
Max FDs
–
Total Processes
–
Total Threads
–
Total CPU Time
The procedure below provides the steps for using the troubleshooting perfmon data logging feature.
Procedure
Step 1
Configure the Troubleshooting Perfmon Data Logging parameters in the Cisco RIS Data Collector service.
See the"Configuring Troubleshooting Perfmon Data Logging" section
Step 2
Verify that log partition monitoring is enabled.
See the Cisco CallManager Administration Guide.
Step 3
Collect the log files for the Cisco RIS Data Collector service on the server that has troubleshooting perfmon data logging enabled
•
If you want to download the log files by using RTMT, refer to Cisco CallManager CallManager Administration Guide.
•
If you want to download the log files by using the CLI, refer to Cisco IP Telephony Platform Administration Guide.
Step 4
View the log files by using Microsoft Windows Performance tool.
See the "Viewing the Perfmon Log Files with the Microsoft Performance Tool" section
Step 5
When you have collected all the necessary files, disable troubleshooting perfmon data logging by setting the Enable Logging parameter to False.
Configuring Troubleshooting Perfmon Data Logging
The following procedure describes how to configure the troubleshooting perfmon data logging feature.
Procedure
Step 1
In Cisco CallManager Administration, choose System > Service Parameters.
The Service Parameter Configuration window displays.
Step 2
From the Server drop-down list box, choose the server.
Step 3
From the Service drop-down list box, choose Cisco RIS Data Collector.
Step 4
Enter the appropriate settings as described in Table 2-4.
Step 5
Click Save.
Viewing the Perfmon Log Files with the Microsoft Performance Tool
To view the log files by using the Microsoft Performance tool, follow these steps:
Procedure
Step 1
Choose Start > Settings > Control Panel > Administrative Tools > Performance.
Step 2
In the application window, click the right mouse button and choose Properties.
Step 3
Click the Source tab in the System Monitor Properties dialog box.
Step 4
Browse to the directory where you downloaded the perfmon log file and choose the perfmon csv file. The log file has the following naming convention: PerfMon_<node>_<month>_<day>_<year>_<hour>_<minute>.csv; for example, PerfMon_172.19.240.80_06_15_2005_11_25.csv.
Step 5
Click Apply.
Step 6
Click the Time Range button. To specify the time range in the perfmon log file that you want to view, drag the bar to the appropriate starting and ending times.
Step 7
To open the Add Counters dialog box, click the Data tab and click Add t.
Step 8
From the Performance Object drop-down box, choose the perfmon object. If an object has multiple instances, you may choose All instances or select only the instances that you are interested in viewing.
Step 9
You can choose All Counters or select only the counters that you are interested in viewing.
Step 10
To add the selected counters, click Add
Step 11
When you finish selecting counters, click Close.
CiscoWorks2000
CiscoWorks2000 serves as the network management system of choice for all Cisco devices including Cisco CallManager. Because CiscoWorks2000 is not bundled with Cisco CallManager, you must purchase it separately. Use the following tools with CiscoWorks2000 for remote serviceability:
•
Cisco Discovery Protocol Support
•
Simple Network Management Protocol Support
Refer to the Cisco CallManager Serviceability Administration Guide and the CiscoWorks2000 documentation for more information on CiscoWorks2000 at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/cw2000/index.htm
System Log Management
Although it can be adapted to other network management systems, Cisco Syslog Analysis, which is packaged with CiscoWorks2000 Resource Manager Essentials, provides the best method to manage Syslog messages from Cisco devices.
Cisco Syslog Analyzer serves as the component of Cisco Syslog Analysis that provides a common storage and analysis of the system log for multiple applications. The other major component, Syslog Analyzer Collector, gathers log messages from Cisco CallManager servers.
These two Cisco applications work together to provide a centralized system logging service for Cisco IP Telephony Solutions.
Refer to the Cisco CallManager Serviceability Administration Guide for more information.
Cisco Discovery Protocol Support
The Cisco Discovery Protocol Support enables discovery of Cisco CallManager servers and management of those servers by CiscoWorks2000.
Refer to the Cisco CallManager Serviceability Administration Guide and the CiscoWorks2000 documentation for more information on CiscoWorks2000 at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/cw2000/index.htm
Simple Network Management Protocol Support
Network management systems (NMS) use SNMP, an industry-standard interface, to exchange management information between network devices. A part of the TCP/IP protocol suite, SNMP enables administrators to remotely manage network performance, find and solve network problems, and plan for network growth.
An SNMP-managed network comprises three key components: managed devices, agents, and network management systems.
•
A managed device designates a network node that contains an SNMP agent and resides on a managed network. Managed devices collect and store management information and make it available by using SNMP.
•
An agent, as network management software, resides on a managed device. An agent contains local knowledge of management information and translates it into a form that is compatible with SNMP.
•
A network management system comprises an SNMP management application together with the computer on which it runs. An NMS executes applications that monitor and control managed devices. An NMS provides the bulk of the processing and memory resources that are required for network management. The following NMSs share compatibility with Cisco CallManager:
–
CiscoWorks2000
–
HP OpenView
–
Third-party applications that support SNMP and Cisco CallManager SNMP interfaces
For detailed information, refer to the Cisco CallManager Serviceability Administration Guide and the Cisco CallManager Serviceability System Guide.
Troubleshooting the Server Without Root Access
This section is a quick reference for commands and utilities to help you troubleshoot a Cisco CallManager server with root access disabled. It includes the following topics:
•
Serviceability GUI and CLI Commands for Commonly-used Linux Commands
–
How to Collect Logs and Trace Files
–
How to Schedule Collection of Logs and Trace Files
–
How to Free Up Space on the Hard Disk
–
How to Reboot the Cisco CallManager Server
–
How to Change Debug Levels for Traces
Serviceability GUI and CLI Commands for Commonly-used Linux Commands
Real Time Monitoring Tool (RTMT) is a client application you can install on your PC by downloading the RTMT client from your server at this URL:
https://<server_ipaddress>:8443/ccmadmin/pluginsFindList.do
Procedure
Step 1
Log in to Cisco CallManager.
Step 2
Choose Applications > Plugins.
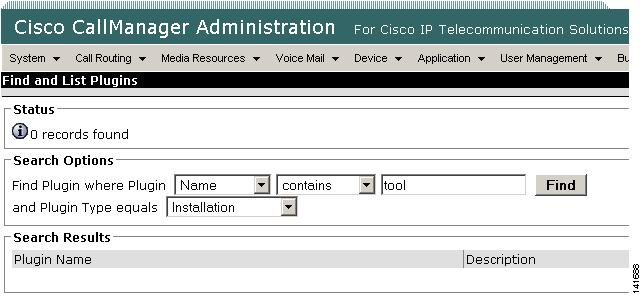
The Find and List Plugins screen screen is displayed as shown in Figure 2-1
Figure 2-1 Cisco CallManager Find and List Plugins Screen
Step 3
Set the selection boxes to Name contains and enter tool.
Step 4
Set the Plugin Type selection box to Installation.
Step 5
Click Find.
The Search Results box will display links to both the Windows and Linux versions of the Cisco CallManager Real-Time Monitoring Tool.
Step 6
Download the appropriate RTMT installation plugin (Windows or Linux version).
Step 7
Install the RMT client application on your PC or workstation.
Table 2-5 provides a summary of the CLI commands and GUI selections detailed in following sections.
Common Troubleshooting Tasks
How to Collect Logs and Trace Files
GUI
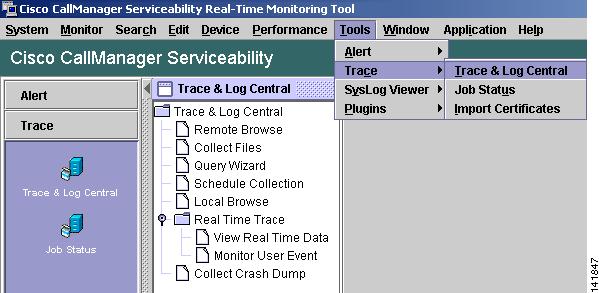
Using the RTMT client application, go to the Tools menu and select Trace > Trace & Log Central to see the different trace utilities.
Figure 2-2 Cisco CallManager RTMT Trace & Log Central
CLI
•
file list
•
file get
•
file view
How to Schedule Collection of Logs and Trace Files
GUI
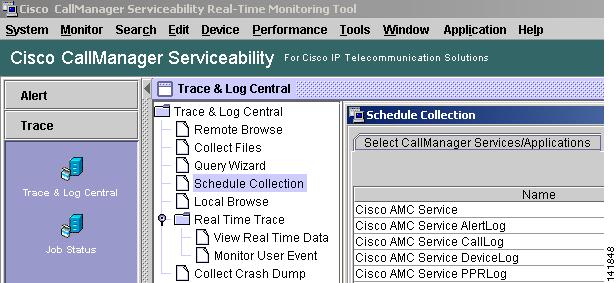
Using the RTMT client application go to the Tools menu and select Trace & Log Central > Schedule Collection.
Figure 2-3 Cisco CallManager RTMT Schedule Collection
How to Access the Database
CLI
Log in as admin and use any of the following show commands:
•
show tech database
•
show tech dbinuse
•
show tech dbschema
•
show tech devdefaults
•
show tech gateway
•
show tech locales
•
show tech notify
•
show tech procedures
•
show tech routepatterns
•
show tech routeplan
•
show tech systables
•
show tech table
•
show tech triggers
•
show tech version
•
show tech params*
To run a SQL command use the run command:
•
run <sql command>
How to Free Up Space on the Hard Disk
You can only delete files from the Log partition.
GUI
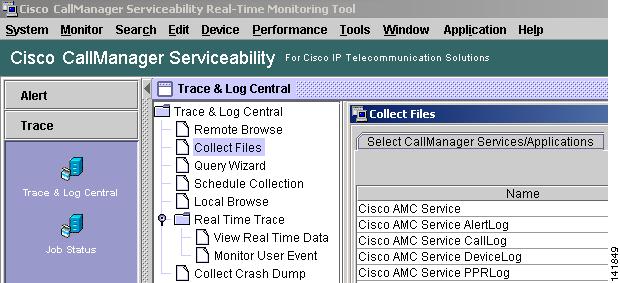
Using the RTMT client, go to the Tools menu and select Trace & Log Central > Collect Files.
Figure 2-4 Cisco CallManager RTMT Collect Files
Choose the criteria to select the files you want to collect, then check the option Delete Files. This will delete the files on the Cisco CallManager server after downloading the files to your PC.
CLI:
•
file delete
How to Look at Core Files
GUI
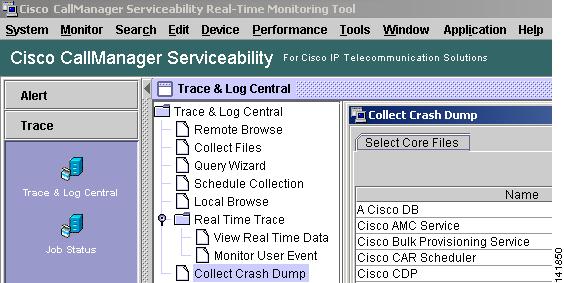
It is not possible to view the core files; however, you can download the Core files by using the RTMT application and selecting Tools > Trace & Log Central > Collect Crash Dump.
Figure 2-5 Cisco CallManager RTMT Collect Crash Dump
CLI
•
Core [options..]
How to Reboot the Cisco CallManager Server
GUI
Login to the Platform Web page on the server and go to Restart > Current Version.
CLI
•
utils system restart
How to Change Debug Levels for Traces
GUI
Login to the Serviceability web page at https://<server_ipaddress>:8443/ccmservice/ and go to Trace > Configuration
CLI
•
set trace enable [Detailed, Significant, Error, Arbitrary, Entry_exit, State_Transition, Special] [syslogmib, cdpmib, dbl, dbnotify]
How to Look at Netstats
GUI
none
CLI
•
show network status
Troubleshooting Tips
The following tips may help you when troubleshooting the Cisco CallManager.
Tip
Check the release notes for Cisco CallManager for known problems. The release notes provide descriptions and workaround solutions for known problems.
Tip
Know where your devices are registered.
Each Cisco CallManager log traces files locally. If a phone or gateway is registered to a particular Cisco CallManager, then the call processing gets done on that Cisco CallManager if the call is initiated there. You will need to capture traces on that Cisco CallManager to debug a problem.
A common mistake involves having devices registered on a subscriber server, but capturing traces on the publisher server. These trace files will be nearly empty (and definitely will not have the call in them).
Another common problem involves having Device 1 registered to CM1 and Device 2 registered to CM2. If Device 1 calls Device 2, the call trace occurs in CM1 and if Device 2 calls Device 1 the trace occurs in CM2. If you are troubleshooting a two-way calling issue, you need both traces from both Cisco CallManagers to obtain all the information needed to troubleshoot.
Tip
Know the approximate time of the problem.
Multiple calls may have been made, so knowing the approximate time of the call helps TAC quickly locate the trouble.
You can obtain statistics on a Cisco IP Phone 79xx by pressing the i button twice during an active call.
When you are running a test to reproduce the issue and produce information, know the following data that is crucial to understanding the issue:
•
Calling number/called number
•
Any other number that is involved in the specific scenario
•
Time of the call
Note
Remember that time synchronization of all equipment is important for troubleshooting.
If you are reproducing a problem, make sure to choose the file for the timeframe by looking at the modification date and the timestamps in the file. The best way to collect the right trace is to reproduce a problem and then quickly locate the most recent file and copy it from the Cisco CallManager server.
Tip
Save the log files to prevent them from being overwritten.
Files will get overwritten after some time. The only way to know which file is being logged to is to choose View >Refresh on the menu bar and look at the dates and times on the files.
Verify Cisco CallManager Services Are Running
Use the following procedure to verify which Cisco CallManager services are active on a server.
Procedure
Step 1
From Cisco CallManager Administration, choose Navigation > Cisco CallManager Serviceability.
The Cisco CallManager Serviceability window displays.
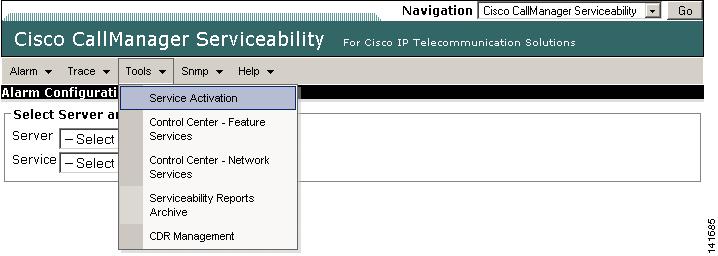
Step 2
Choose Tools > Service Activation as shown in Figure 2-6.
Figure 2-6 Cisco CallManager Serviceability Window Tools Menu
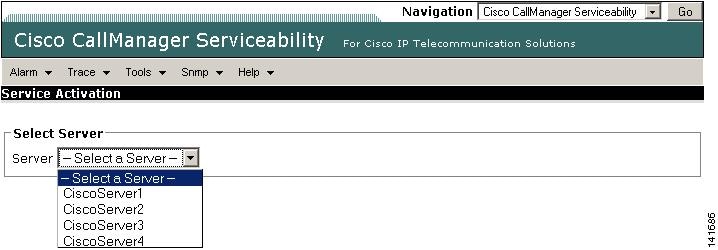
Step 3
From the Servers column, choose the desired server as shown in Figure 2-7.
Figure 2-7 Cisco CallManager Serviceability Window Service Activation
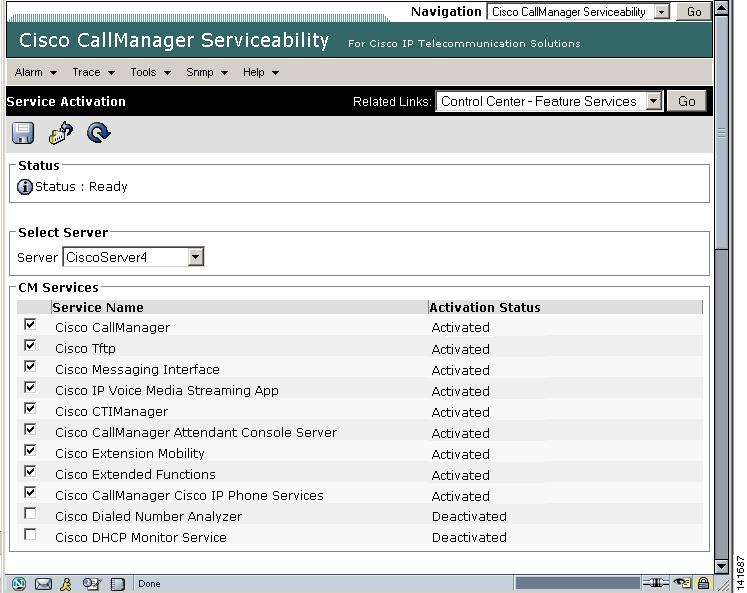
The server that you choose displays next to the Current Server title, and a series of boxes with configured services displays.
Activation Status column displays either Activated or Deactivated in the Cisco CallManager line as shown in Figure 2-8.
Figure 2-8 Service Activation Window
If the Activated status displays, the specified Cisco CallManager service is active on the chosen server.
If the Deactivated status displays, continue with the following steps.
Step 4
Check the check box for thedesired Cisco CallManager service.
Step 5
Click the Update button.
The Activation Status column displays Activated in the specifed Cisco CallManager service line.
The sepcified Cisco CallManager service is now active for the chosen server.
Perform the following procedure if the Cisco CallManager has been in service and you want to verify if it is currently running.
Procedure
Step 1
From Cisco CallManager Administration, choose Navigation > Cisco CallManager Serviceability.
The Cisco CallManager Serviceability window displays.
Step 2
Choose Tools > Control Center - Feature Services.
Step 3
From the Servers column, choose the server.
The server that you chose displays next to the Current Server title, and a box with configured services displays.
The Status column displays which services are running for the chosen server.
Where to Find More Information
Additional Cisco Documentation
•
Cisco CallManager Serviceability Administration Guide
•
Cisco CallManager Serviceability System Guide
•
Cisco CallManager Administration Guide
•
Cisco CallManager Security Guide
•
Installation Guide for Cisco CallManager