Feedback Feedback
|
Table Of Contents
Release Notes for Cisco MGX Route Processor Module (RPM-XF) for MGX 8850 Release 3.0.00 (PXM45)
Features Not Supported in This Release
RPM-XF Limitations and Restrictions
RPM-XF auto_config File Management
Known Anomalies for RPM-XF Platform Software and Service Module Firmware
RPM-XF Boot File and Firmware File Names and Sizes
Cisco IOS Release Compatibility Information
Using XModem to Download Flash to RPM-XF Cards
Obtaining Technical Assistance
Release Notes for Cisco MGX Route Processor Module (RPM-XF) for MGX 8850 Release 3.0.00 (PXM45)
Contents
About These Release Notes
Cisco documentation and additional literature are available in a CD-ROM package, which ships with your product. The Documentation CD-ROM, a member of the Cisco Connection Family, is updated monthly. Therefore, it might be more current than printed documentation. To order additional copies of the Documentation CD-ROM, contact your local sales representative or call customer service. The CD-ROM package is available as a single package or as an annual subscription.
Note that for Release 3, the user documentation (command reference, overview, and installation and configuration guides) use the MGX Release 3 and Cisco IOS documents in addition to this release note.
Product documentation for MGX 8850 is available at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/wanbu/8850r30/index.htm
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/wanbu/8850r30/rpm/index.htmFeatures
The MGX RPM-XF is a next-generation, high performance model of the RPM for the MGX 8850 platform, using PXM45 processor modules. It is a router module based on an RM7000A MIPS processing engine that fits into slots 1-6 and slots 9-14 in MGX 8850.
The RPM-XF hardware provides forwarding technology for packet switching capabilities in excess of 2-million pps. The forwarding engine is packet based and is interfaced to the midplane of the system through a combination of switch interface technologies. For more information on the RPM-XF, refer to the Cisco MGX Route Processor Module (RPM-XF) Installation and Configuration Guide, Release 3.
RPM-XF Redundancy Support
RPM-XF 1:N redundancy is used to switch configuration and traffic from one RPM-XF module to another module. Route processing continues with minimal traffic loss even if an RPM-XF fails and there is no operator or direct access to swap the failed card or fix the problem. Currently we support RPM-XF warm redundancy, which ensures Layer 2 state restoration. Layer 3 state is restored via convergence.
The main benefits are:
•
An RPM-XF card with hardware problems can be fixed while the redundant standby card takes over its functionality.
•
Software upgrades are easier and can be done with less downtime.
•
LAN interface redundancy supported with MAC addresses of primary RPM-XF copied to standby RPM-XF.
•
1:N Redundancy support for Gigabit Ethernet interface backcards during front card switchover.
•
Y cable redundancy support for POS backcards during front card switchover. (With Y cable, 1:N redundancy is restricted to N = 1).
The following are the general guidelines for redundancy on the RPM--XF:
•
Addred is not allowed between RPM-PR and RPM-XF.
•
To configure redundancy, the Primary RPM-XF should be in Active state and Secondary RPM-XF card must be in Active/Standby state.
•
Removal of the Active RPM-XF back card does not cause switchover to the standby RPM-XF.
•
User has to make sure that E:RPM/auto_config_slot# is created before adding redundancy. This may require a login to primary card through the command line and manually adding boot config e:auto_config_slot# followed by a write mem.
•
Executing switchcc back-to-back with switchredcd can cause problems. We recommend giving a gap of at least 5 seconds between switchredcd and a switchcc.
•
IOS software on a standby card should be the same or higher version than the Active RPM-XF card.
•
Booting the card from an image on tftp server is not recommended when the card is in redundancy group. The card should be booted from image in bootflash or PXM disk only.
•
Configuring the standby RPM-XF is not recommended.
Features Not Supported in This Release
The following features are not supported in this release.
•
LSC Redundancy
•
MPLS TE tunnels on ATM Interfaces
•
VC Merge
•
RPM-PR to RPM-XF upgrade
•
OIR of backcards without interfaces in shutdown mode
•
Per packet load balancing
•
Modem connectivity on Auxiliary port
•
EIBGP Multipath load-balancing
Network Management Features
Network management features are detailed in the CWM Release 11.0 Release Notes at: http://cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/wanbu/svplus/index.htm
SNMP MIB
SNMP MGX Release 3 MIB are provided with the delivery of this release. The MIB is in standard ASN.1 format and is located in the same directory within the release bundle on CCO. These files may be compiled with most standards-based MIB compilers. The tar file for MIB contains the file that contains the MIB release notes. This contains only MGX MIBS.
Cisco IOS MIBS are not part of this bundle. They are part of 12.2(8)T4 CCO release.
RPM-XF Limitations and Restrictions
The RPM-XF limitations and restrictions that apply to this release are as follows:
•
E: RPM/auto_config_slot# must be created before adding redundancy. This may require a login through the CLI and manually adding the boot config command followed by a write mem.
•
There is a traffic parameter mismatch between allowed PCR and actual PCR. When a UBR or VBR VC is configured, the CLI allows the value of up to 1198080 kbps, but the actual maximum value is 1197656 kbps. So any value greater than 1197656 kbps would be reset to 1197656kbps.
•
PVPs can not operate at a rate greater than 599039 kbps.
•
For VBR VCs, if the PCR is not equal to the SCR, the PCR can not be greater than half of the line rate.
•
High speed VC (SCR greater than or equal to 500,000 kbps) would not get full-configured rate for single flow (unique source and destination IP address). This happens because for high speed VCs, the PXF creates two queues and these queues can't be shared for same stream. Sharing two queues for same stream would cause out of sequence packets.
•
PXF queue selection algorithm may cause traffic drop for multiple stream going to same destination via multiple paths. When the PXF gets a packet, it selects the output queue based on source and destination IP address. These addresses hash into one of the queues for the selected destination. So if there are multiple paths for the same destination, there is a possibility that multiple streams would hash to one queue, causing some queues to overflow, while others might be under-utilized.
•
PXF buffer depletion may occur if packets of the same size (especially packets greater than 640 bytes) are sent to a congested interface.
•
Currently VBR-nrt and VBR-rt are treated with same priority system wide.
•
RPM-XF PVP only supports UBR.
•
PVP in RPM-XF is not OAM managed.
•
If out-of-sync SPVC or SPVP exist on RPM-XF, shrinking of PNNI partition would not be permitted.
•
A single RPM-XF can only function as either an Edge LSR or as an LSC, but not as both.
•
Because RPM-XF only supports UBR, VBR-rt and VBR-nrt, on the PXM, dsppnportrsrc for RPM-XF port will show 0 available resource for CBR, ABR and signaling service types. Also, cnfpnportcac for CBR and ABR will be rejected.
•
If RPM-XF is configured as an eLSR, RPM-XF does not support incoming VC-merge lvcs. There is a problem logged against LSC module that it cannot support both VC-merge/non-VC-merge supporting VSI slaves at the same time. So for now, if RPM-XF eLSR is part of a cell based MPLS network (with RPM-PRs or AXSMs in the same node), disable the VC-merge feature on LSC. (Note that VC-merge is enabled on LSC by default).
•
RPM-XF eLSR only supports at most two MPLS sub-interfaces. Attempting to configure over the limit will result in an error message.
•
Although RPM-XF VSI slave supports connections statistics Get command, only packets and bytes counts are available. Therefore, show xtag cross-connect traffic int xtagatm connection statistic display on LSC are actually packet counts from RPM-XF eLSR.
•
There are known performance issues with LVCs cleanup/re-establishment in the case of TDP/LDP/VSI sessions flapping. TDP/LDP/VSI sessions flapping can be caused by shut/no shut of mpls/xtagatm interfaces or resetting any of the eLSRs. These performance issues are more noticeable when the number of LVCs exceeds the recommended limits of 4000.
•
OIR of MGX-1GE and MGX-1OC12POS-IR back cards are supported only with interfaces in shutdown state.
•
MGX-1GE back card does not have the capability to provide line loopback.
•
Flow Control Option is not configurable with MGX-1GE back card.
•
MGX-1GE back card does not support SFP security.
•
Line loopback and internal loopback cannot be set at the same time for the MGX-1OC12POS-IR back card with AMCC Mux.
•
pos ais-shut command is not supported on MGX-1OC12POS-IR back card.
•
Net booting from the MGX-UI-XF fast ethernet ports does not work.
The performance limits supported in this release are the following:
•
2K ATM SPVC Connection endpoints
•
2K IDBs
•
4K LVCs
•
100 VPCs
•
256 Policymap
•
100 OSPF neighbors
•
6 IOS-based cards in MGX shelf
•
500 VRFs: 500
•
500 BGP CE Peers
•
100 RIP CE sessions
•
500 Static CEs
•
100,000 VPN Routes per PE
•
250K non-VPN Routes per RPM-XF
•
50 Xtag interfaces per RPM-XF
•
300 OAM enabled connections
For more RPM-XF performance details, contact your sales representative.
Notes and Cautions
The following notes and cautions should be reviewed before using this release.
•
Attempting to initiate RPM-XF switchover when write mem is in progress on the active RPM-XF card may lead to the card coming up with a partial configuration. When an addred is executed, an automatic write mem is triggered on the primary RPM-XF. If the primary card fails when the write mem is in progress, the card may come up with a partial configuration. The duration of write mem depends on the configuration size and can take up to 4 minutes to complete.
•
There is a new stable "Boot-Hold" state displayed on the PXM45 when dspcds is executed. This state indicates that the RPM-XF is running only boot image. This state is reached when config register is set to 0x1 or when the bootldr cannot find the run-time image, but found the boot image. Enter cc to access the RPM-XF from the PXM45.
•
Valid boot image need not be the first file in the boot flash. The RPM-XF will load from any valid boot image from the bootflash:. The run-time image can be the first file in the boot flash and RPM-XF will come up with that image.
•
Trying to change PCR value of VP tunnel or changing MTU of switch interface with more than 4K VCs may cause CPU hog.
•
If there is a large number of VCs (PVCs or LVCs or both) on RPM-XF card, executing disruptive operations on the main switch interface (int switch1) may cause flapping of protocols that run on these VCs. Examples of disruptive operations are clear int switch1 and modification of PVP parameters. These operations cause deactivation and re-activation of all VCs under the main switch interface. Depending on the number of VCs, the time required to complete such operations may exceed certain protocol timeout limit. Examples of protocols that may be affected are OSPF and TDP/LDP.
•
RPM-XF VSI slave tends to output informational warning/trace back messages caused by misconfigurations and CAC failures (onto console/IOS log file). These messages are mostly for information/debugging purpose. When these messages are observed, confirm that connection status is still intact and traffic is still passing successfully.
•
Due to PXF scr granularity, the configured scr on IOS pvc CLI may not be the same as the actual scr programmed in the PXF. PXF bandwidth chunk size is 18 kbps; all PXF VC scr will be programmed as multiples of 18 kbps. For instance, if the PVCs were configured with 50 kbps as pcr, 54 kbps would be programmed in PXF. show atm pvc display will show 50 kbps, and VSI Slave will account 50 kbps during CAC. However, 54 kbps is actually being used. So as a result, when bandwidth usage is reaching the maximum value, both VSI Slave and PNNI will continue to allow connection provisioning, because VSI Slave and PNNI available bandwidth shows more than PXF actually has left.
•
Saveallcnf (issued on the PXM45/B card) captures configuration data saved by the RPM-XF card (as well as AXSM and PXM45 cards), and saves it on the active PXM45/B card's hard disk. Configure the RPM-XF to store its configuration on the PXM45/B hard disk (E:/RPM) by entering boot config e:auto_config_slot# in the running configuration of the RPM-XF. To ensure that the saved file contains the latest RPM-XF configuration, execute the write mem command on each RPM-XF card prior to the entering saveallcnf command. This also ensures that the RPM-XF files on the active PXM45 hard disk will contain the latest configuration to be saved.
•
For ELSR to LSC connectivity, the default control VC used is 32. If PNNI partition exists with VCI 32 as part of its partition range, when an MPLS partition is added, there are two options to handle the situation:
–
Add the MPLS controller and define its partition with available range. On eLSR, define control VC from any VCI value within the range defined in partition. The same VC should be defined on LSC on xTag interface.
–
Reconfigure PNNI partition to spare the control VC usage both on RPM-XF and AXSM, AXSM/B or AXSM-E APS Management Information.
•
Whenever the RPM-XF configuration is changed, enter the write mem command on the RPM-XF to save the configuration. If this is not done, the changed configuration will be lost on an RPM-XF card reboot or RPM-XF switchover, in the case of redundancy.
RPM-XF auto_config File Management
The RPM-XF auto_config_slot# file stores the configuration for the RPM-XF card. The slot# portion of the name should be set to the logical slot number that corresponds to the RPM-XF card. This file can be stored in bootflash or in the E:RPM directory on the PXM45 hard disk. The configuration is also stored in NVRAM using the name startup-config.
When the RPM-XF card is inserted or rebooted, it searches for the configuration file in the following sequence:
1.
If there is an auto_config file corresponding to its logical slot on the PXM45 hard disk, the RPM-XF card uses the configuration stored on the hard disk.
2.
If boot variable points to configuration stored in the PXM45 hard disk or Bootflash and if the file is not found, the card comes up as Active-F with the default configuration.
3.
If there is no auto_config file on the hard disk, then the NVRAM version is used.
Note
In case of RPM-XF redundancy, the configuration should always be stored in auto_config_slot# file in the E:RPM directory of the PXM45 hard disk. Failure to find the auto_config file will lead to aborting of a user-initiated switchover (switchredcd) and a fatal error will be flagged.
Card Management
The following card management notes and cautions should be reviewed before using this release.
•
There is a new stable state displayed on the PXM dspcds command—Boot-Hold, which signifies that the RPM-XF is running the boot image only. On the RPM-XF, the prompt will display as boot>
•
The run-time IOS image cannot be used as a bootloader to load a different IOS image.
•
Change of console speed on the terminal server may cause the card to end up in the ROMMON state. To avoid this, set the config register to 0x2102.
Another workaround is to enter cont on the ROMMON within 2 minutes of going into ROMMON state. This will bring the card to its original stable state.
Note
It is recommended to always use 9600 baud as the console speed.
•
The IOS version of the runtime as well as the boot image will be displayed in the dspcd, dsprevs, and dsprevs -s output. The version will be displayed under the heading of IOS version. Revision Control is not available for RPM-XF (like RPM-PR).
Note
The commands loadrev and setrev do not apply for RPM-XF.
RPM-XF Bootflash Precautions
The RPM-XF bootflash is used to store boot image, configuration and run- time files. Erasing the boot image from the Flash will cause the card to not boot.
The RPM-XF boot image, which comes loaded on the Flash, will work for all RPM-XF IOS images. Therefore, there is no reason to delete or move the factory installed boot image.
In order to avoid any unnecessary failures that would require card servicing, do the following:
•
Never erase the boot file from the RPM Flash
•
Never change the position of the boot file on the RPM Flash
•
Use care when "squeezing" the Flash to clean it up.
As long as the boot file remains intact in the first position on the flash, the RPM-XF will boot successfully.
If the bootflash is corrupted, use the tftpdnld procedure described in the Cisco MGX Route Processor Module (RPM-XF) Installation and Configuration Guide or xmodem procedure described in "Using XModem to Download Flash to RPM-XF Cards" later is this document to download a new boot image.
Known Anomalies for RPM-XF Platform Software and Service Module Firmware
The following is the list of known anomalies in the RPM service module firmware and software for this release. Included with each is a brief discussion of the problem. A more in-depth discussion is available in the Release Note enclosure of the problem record in Bug Navigator.
Compatibility Notes
RPM-XF Boot File and Firmware File Names and Sizes
The following table displays the RPM-XF boot and firmware file names and sizes for this release.
Table 1 RPM Boot and Firmware File Names and Sizes
rpmxf-boot-mz.122-8.YP
2650352
rpmxf-p12-mz.122-8.YP
7445884
RPM-XF Compatibility Matrix
MGX RPM-XF Hardware
Table 2 shows the front card and back card compatibility for the RPM-XF hardware supported in this release. The table lists the card model/ name, part numbers, the minimum version and the minimum revisions of each card supported. Note that there may be more than one 800 level part numbers for the same front cards. The minimum version is identified by the last 2 digits of the 800 level numbers.
Table 3 SFP Compatibility Matrix for MGX-1GE
Min. VersionMGX-GE-SX
MGX-GE-LHLX
MGX-GE-ZX
30-1301-01
30-1299-01
10-1439-01
A0
A0
A0
Cisco IOS Release Compatibility Information
All IOS firmware can be downloaded from CCO from the following location:
http://www.cisco.com/kobayashi/sw-center/sw-ios.shtml
Using XModem to Download Flash to RPM-XF Cards
Use the xmodem feature to download the flash to an RPM-XF card. During this process, the card should be connected to a target machine through HyperTerminal with settings of 9600, n, 8, and 1.
Step 1
Put the node in monitor mode by entering the priv command to gain access to the privileged commands as follows:
rommon 1> privYou now have access to the full set of monitor commands. Warning: some commands will allow you to destroy your configuration and/or system images and could render the machine unbootable.Step 2
The xmodem command becomes available and the general syntax of this command and availability of this can be checked by giving xmodem command without any parameters on the CLI, as follows:
rommon 2 > xmodemusage: xmodem [-cys]-c CRC-16-y ymodem-batch protocol-s<speed> Set speed of download, where speed may be1200|2400|4800|9600|19200|38400rommon 3 >The command line options for xmodem are as follows:
Note
If you do not find the xmodem commands, then the xmodem feature is not available on this rommom version. In that case, you must return the card to Cisco.
Note
The rommon "xmodem/ymodem" transfer only works on the console port. You can only download files to the router. You cannot use "xmodem/ymodem" to get files from the router.
For example:
rommon 4> xmodem -cys 38400Do not start sending the image yet...Invoke this application for disaster recovery. Do you wish tocontinue? y/n [n]: yNote, if the console port is attached to a modem, both theconsole port and the modem must be operating at the same baudrate. Use console speed 38400 bps for download [confirm]Step 3
At this point, change the preferences in HyperTerminal and adjust the speed from 9600 to 38400.
Note
You can continue at the speed of 9600 as well by either not specifying the -s option in the command, or by specifying 9600 explicitly, but it will take longer.
The console will display the following message:
Download will be performed at 38400. Make sure your terminalemulator is set to this speed before sending file. Ready toreceive file ...Step 4
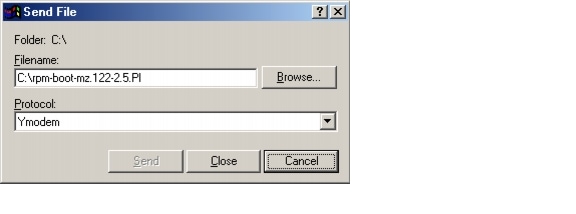
Use the Transfer-->Send File option in HyperTerminal to start the image transfer.
In the Filename box, browse and choose the image file to be downloaded. Also since we used the "y" option while invoking the xmodem, set the transfer protocol to ymodem or use Xmodem protocol by not specifying the -y option on the command line.
The transfer screen comes up and transfer starts. (The transfer may not start immediately; wait for some time and it should start.)
After the transfer is completed (it should typically take about 10-15 minutes), the following messages are displayed on HyperTerminal console:
Returning console speed to 9600.Please reset your terminal emulator to this speed...Step 5
Return the console speed back to 9600 through HyperTerminal's Preferences menu option.
Usually, due to time lag between changing HyperTerminal speed back to 9600, you might see a bunch of garbage. To avoid this, disconnect and reconnect the HyperTerminal to get the console back again.
The system will reset itself from here and will boot with new software image.
Related Documentation
Cisco documentation and additional literature are available in a CD-ROM package, which ships with your product. The Documentation CD-ROM, a member of the Cisco Connection Family, is updated monthly. Therefore, it might be more current than printed documentation. To order additional copies of the Documentation CD-ROM, contact your local sales representative or call customer service. The CD-ROM package is available as a single package or as an annual subscription.
Note that for Release 3, the user documentation (command reference, overview, and installation and configuration guides) use the MGX Release 3 and Cisco IOS documents in addition to this release note.
Product documentation for MGX 8850 is available at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/wanbu/8850r30/index.htm
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/wanbu/8850r30/rpm/index.htmObtaining Documentation
The following sections explain how to obtain documentation from Cisco Systems.
World Wide Web
You can access the most current Cisco documentation on the World Wide Web at the following URL:
Translated documentation is available at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/public/countries_languages.shtml
Documentation CD-ROM
Cisco documentation and additional literature are available in a Cisco Documentation CD-ROM package, which is shipped with your product. The Documentation CD-ROM is updated monthly and may be more current than printed documentation. The CD-ROM package is available as a single unit or through an annual subscription.
Ordering Documentation
Cisco documentation is available in the following ways:
•
Registered Cisco Direct Customers can order Cisco product documentation from the Networking Products MarketPlace:
http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/order/order_root.pl
•
Registered Cisco.com users can order the Documentation CD-ROM through the online Subscription Store:
http://www.cisco.com/go/subscription
•
Nonregistered Cisco.com users can order documentation through a local account representative by calling Cisco corporate headquarters (California, USA) at 408 526-7208 or, elsewhere in North America, by calling 800 553-NETS (6387).
Documentation Feedback
If you are reading Cisco product documentation on Cisco.com, you can submit technical comments electronically. Click Leave Feedback at the bottom of the Cisco Documentation home page. After you complete the form, print it out and fax it to Cisco at 408 527-0730.
You can e-mail your comments to bug-doc@cisco.com.
To submit your comments by mail, use the response card behind the front cover of your document, or write to the following address:
Cisco Systems
Attn: Document Resource Connection
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-9883We appreciate your comments.
Obtaining Technical Assistance
Cisco provides Cisco.com as a starting point for all technical assistance. Customers and partners can obtain documentation, troubleshooting tips, and sample configurations from online tools by using the Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC) Web Site. Cisco.com registered users have complete access to the technical support resources on the Cisco TAC Web Site.
Cisco.com
Cisco.com is the foundation of a suite of interactive, networked services that provides immediate, open access to Cisco information, networking solutions, services, programs, and resources at any time, from anywhere in the world.
Cisco.com is a highly integrated Internet application and a powerful, easy-to-use tool that provides a broad range of features and services to help you to
•
Streamline business processes and improve productivity
•
Resolve technical issues with online support
•
Download and test software packages
•
Order Cisco learning materials and merchandise
•
Register for online skill assessment, training, and certification programs
You can self-register on Cisco.com to obtain customized information and service. To access Cisco.com, go to the following URL:
Technical Assistance Center
The Cisco TAC is available to all customers who need technical assistance with a Cisco product, technology, or solution. Two types of support are available through the Cisco TAC: the Cisco TAC Web Site and the Cisco TAC Escalation Center.
Inquiries to Cisco TAC are categorized according to the urgency of the issue:
•
Priority level 4 (P4)—You need information or assistance concerning Cisco product capabilities, product installation, or basic product configuration.
•
Priority level 3 (P3)—Your network performance is degraded. Network functionality is noticeably impaired, but most business operations continue.
•
Priority level 2 (P2)—Your production network is severely degraded, affecting significant aspects of business operations. No workaround is available.
•
Priority level 1 (P1)—Your production network is down, and a critical impact to business operations will occur if service is not restored quickly. No workaround is available.
Which Cisco TAC resource you choose is based on the priority of the problem and the conditions of service contracts, when applicable.
Cisco TAC Web Site
The Cisco TAC Web Site allows you to resolve P3 and P4 issues yourself, saving both cost and time. The site provides around-the-clock access to online tools, knowledge bases, and software. To access the Cisco TAC Web Site, go to the following URL:
All customers, partners, and resellers who have a valid Cisco services contract have complete access to the technical support resources on the Cisco TAC Web Site. The Cisco TAC Web Site requires a Cisco.com login ID and password. If you have a valid service contract but do not have a login ID or password, go to the following URL to register:
http://www.cisco.com/register/
If you cannot resolve your technical issues by using the Cisco TAC Web Site, and you are a Cisco.com registered user, you can open a case online by using the TAC Case Open tool at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/tac/caseopen
If you have Internet access, it is recommended that you open P3 and P4 cases through the Cisco TAC Web Site.
Cisco TAC Escalation Center
The Cisco TAC Escalation Center addresses issues that are classified as priority level 1 or priority level 2; these classifications are assigned when severe network degradation significantly impacts business operations. When you contact the TAC Escalation Center with a P1 or P2 problem, a Cisco TAC engineer will automatically open a case.
To obtain a directory of toll-free Cisco TAC telephone numbers for your country, go to the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/687/Directory/DirTAC.shtml
Before calling, please check with your network operations center to determine the level of Cisco support services to which your company is entitled; for example, SMARTnet, SMARTnet Onsite, or Network Supported Accounts (NSA). In addition, please have available your service agreement number and your product serial number.
This document is to be used in conjunction with the Cisco WAN Switching MGX 8850 Release 3 publications.
CCIP, the Cisco Powered Network mark, the Cisco Systems Verified logo, Cisco Unity, Follow Me Browsing, FormShare, Internet Quotient, iQ Breakthrough, iQ Expertise, iQ FastTrack, the iQ Logo, iQ Net Readiness Scorecard, Networking Academy, ScriptShare, SMARTnet, TransPath, and Voice LAN are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc.; Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn, Discover All That's Possible, The Fastest Way to Increase Your Internet Quotient, and iQuick Study are service marks of Cisco Systems, Inc.; and Aironet, ASIST, BPX, Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP, CCIE, CCNA, CCNP, Cisco, the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, the Cisco IOS logo, Cisco Press, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo, Empowering the Internet Generation, Enterprise/Solver, EtherChannel, EtherSwitch, Fast Step, GigaStack, IOS, IP/TV, LightStream, MGX, MICA, the Networkers logo, Network Registrar, Packet, PIX, Post-Routing, Pre-Routing, RateMUX, Registrar, SlideCast, StrataView Plus, Stratm, SwitchProbe, TeleRouter, and VCO are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and certain other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned in this document or Web site are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (0203R)
Copyright © 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc.
All rights reserved.