Table Of Contents
Requirements and Prerequisites
Product Overview
Cisco Secure Erase is a SAN-based product that erases existing data on a specific Logical Unit Number (LUN) on a storage array. The data erased using Secure Erase cannot be reconstructed.
Cisco Secure Erase runs on the Storage Service Module (SSM). The SSM must be installed on the Cisco MDS switch on which you want to run Cisco Secure Erase.
This chapter includes the following sections:
•
Requirements and Prerequisites
About Secure Erase
Cisco Secure Erase for the Cisco MDS 9500 or 9200 family of switches provides significant advantages over traditional data erase mechanisms. These advantages include platform independence, higher speed, lower cost, and easier deployment.
Cisco Secure Erase uses special algorithms to erase data. These algorithms erase data by specifying pattern sequences that are repeatedly written to the target media. This process overcomes the traditional problem of data remanance.
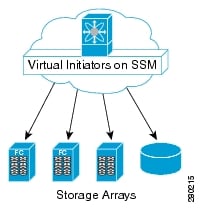
Figure 1-1 Cisco Secure Erase Topology
The Secure Erase feature runs on the SSM intelligent linecard, which is responsible for managing the data erasing process. This process is executed by virtual initiators (VIs) created on the SSM. The host or servers connected to SAN have no role in the data erasing process. The storage ports can be connected anywhere in the SAN provided they are accessible from the switch where Cisco Secure Erase is running.
Secure Erase Job
A Secure Erase job contains information about the following:
•
Target Enclosures where Secure Erase functions are performed. A single target enclosure can be made up of multiple ports spanning multiple VSANs.
•
Storage port(s) coming out of the Storage Enclosure. These storage ports can belong to separate VSANs.
•
VIs that will execute Secure Erase operations. Like target ports, a job also contains VIs that are part of different VSANs.
•
Secure Erase sessions.
All actions such as start, stop, abort, and validate are performed at the job level. These actions impact all sessions in a job.
Secure Erase Session
A Secure Erase session is a unit of erase that is defined by the following parameters:
•
Target LUN(s) where Secure Erase needs to be performed.
•
Storage port with which you would access the above mentioned LUN.
•
Secure Erase algorithm to be used for the erase procedure.
•
Virtual Initiator is selected out of the VIs available in the job automatically. The selection is based on a load balancing algorithm.
Concepts and Terminology
Cisco Secure Erase uses the following concepts and terminologies:
Secure Erase
Cisco Secure Erase is a SAN-based feature that erases existing data on a specific target. The data erased through Secure Erase cannot be reconstructed.
Secure Erase Job
Secure Erase job is an enclosure where multiple target ports and VIs that belong to different VSANs can be added.
Secure Erase Session
Secure Erase session is a unit of Secure Erase operation that contains the target and algorithms to be used.
Secure Erase Algorithm
Secure Erase is based on erase algorithms recommended by the United States Department of Defense, the Royal Canadian Police and NIST-800-88 algorithm recommended by the National Institute of Standards and Technology, agency of US Department of Commerce.
Secure Erase algorithms specify a sequence of patterns to be written on physical media with the objective of erasing the data and overcoming the problem of data remanence.
SSM
An SSM is an MDS switch module that provides intelligent services. The Secure Erase feature is executed on the SSM.
VI
A VI is a Virtual Initiator residing on the SSM.
LUN
A Logical Unit Number (LUN) is a unit of storage that you can specify for Secure Erase. The LUN is only a unique number in the content of a storage port.
FUA
A FUA is a Force Unit Access bit. Secure Erase turns the bit on in all the writes.
Features and Capabilities
Cisco Secure Erase has the following features and capabilities:
Configuration Using CLI
Secure Erase provides a set of CLI commands. The CLI runs on the supervisor and the requests are directly sent to the Secure Erase process running on the SSM.
Support Function
Secure Erase supports multiple storage ports and multiple storage arrays.
Data Erase
Secure Erase supports data erase using different algorithms.
Secure Erase Algorithms
Secure Erase provides algorithm recommended by the United States Department of Defense, the Royal Canadian Police, and the NIST-800-88 algorithm recommended by the National Institute of Standards and Technology, an agency of the US Department of Commerce. There is a provision to create and use your own proprietary algorithms.
Synchronize Cache
Synchronize cache is a SCSI command to request the storage controller to synchronize the data present in the cache to the physical media. This command can specify an LBA range for which the cache needs to be synchronized. Secure Erase executes this command at every step of the algorithm to instruct the storage controller to write each pattern to the physical media before next pattern is written.
Please check with the array vendor to find out whether synchronize cache is supported.
Requirements and Prerequisites
The following prerequisites are required to set up Secure Erase:
Software Requirements
Cisco Secure Erase has the following software requirements:
•
MDS switches hosting the SSM must be running SAN-OS release 3.3(1a) or later.
•
The Fabric Manager server version must be SAN-OS 3.3(1a) or later.
Hardware Requirements
Cisco Secure Erase has the following hardware requirements:
•
SSM
The following switches support the SSM:
•
All MDS 9200 family switches
•
All MDS 9500 family switches
Software Licenses
Cisco Secure Erase uses the Storage Services Enabler (SSE) Package for the licensing. The SSE license package is not included with the SSM.

 Feedback
Feedback