-
Cisco Guard Configuration Guide (Software Version 6.0)
-
Index
-
Preface
-
Product Overview
-
Initializing the Guard
-
Configuring the Guard
-
Configuring Traffic Diversion
-
Configuring Zones
-
Configuring Zone Filters
-
Configuring Policy Templates and Policies
-
Learning the Zone Traffic Characteristics
-
Protecting Zones
-
Using Interactive Protect Mode
-
Using Attack Reports
-
Using Guard Diagnostics Tools
-
Performing Maintenance Tasks
-
Analyzing Guard Mitigation
-
Understanding Zone Traffic Diversion
-
Troubleshooting Diversion
-
Table Of Contents
Configuring Policy Templates and Policies
Understanding and Configuring Policy Templates
Configuring the Maximum Number of Services
Configuring the Minimum Threshold
Configuring Policy Template States
Configuring All Policy Template Parameters Simultaneously
Understanding and Managing the Policy Services
Understanding the Guard Protection Levels
Understanding the Packet Types that the Guard Monitors
Understanding the Traffic Characteristics that the Guard Monitors
Configuring the Policy Threshold
Setting the Threshold as Fixed
Configuring a Threshold Multiplier
Multiplying a Threshold by a Factor
Configuring Specific IP Thresholds
Configuring the Proxy Threshold
Configuring the Policy Timeout
Configuring the Policy Interactive Status
Backing Up the Policy Configuration
Configuring Policy Templates and Policies
This chapter describes the Cisco Guard (Guard) zone policies, policy structure, and policy templates, and it describes how to configure the zone policy and the policy template parameters.
This chapter contains the following sections:
•
Understanding and Configuring Policy Templates
•
Understanding the Policy Path
•
Configuring Policy Parameters
•
Backing Up the Policy Configuration
Understanding Zone Policies
The zone policies enable the Guard to perform a statistical analysis of the zone traffic flow. The zone policies are configured to take action against a particular traffic flow if they identify that flow as malicious or abnormal, which occurs when the flow exceeds the policy threshold, and configure filters (dynamic filters) dynamically to protect the traffic flow according to the severity of the attack.
Every zone configuration contains a set of policies. When you create a new zone using a policy template, the Guard configures the new zone with policies associated with the template. When you create a new zone by copying an existing zone, the Guard configures the new zone with the policies of the existing zone.
To create zone-specific policies and tune their thresholds to recognize normal zone traffic, the Guard learns the zone traffic in a two-phase learning process (see "Understanding the Learning Process" section on page 1-4). The Guard uses predefined policy templates to construct the policies and then learns the policy thresholds as determined by the zone traffic. The Guard uses each policy template to create policies that the Guard requires to protect the zone against a specific Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) threat. After the Guard creates and tunes the zone policies, you can add and delete policies or change policy parameters.
Policies have cross dependencies and priorities. If two different policies define the same traffic flow, the Guard analyzes the flow using the policy that is more specific. For example, policies relating to TCP services exclude the HTTP services that are handled by the HTTP-related policies.
You can configure the policy operational aspects, which define the policy triggers and the action that the policy takes once it is activated.
Understanding and Configuring Policy Templates
A policy template is a collection of policy construction rules that the Guard uses during the policy construction phase to create the zone policies. At the end of the policy construction phase, the Guard has a set of zone-specific policies that it created using the policy templates. The name of the policy template is derived from the characteristics that are common to all the policies that it creates and can be a protocol (such as DNS), an application (such as HTTP), or the objective (such as ip_scan). For example, the policy template tcp_connections produces policies that relate to connections, such as the number of concurrent connections. When you create a new zone, the Guard includes a set of policy templates in the zone configuration.
Table 7-1 describes the Guard policy templates. The Guard includes these policy templates when you create a new zone using the GUARD_DEFAULT zone template.
Table 7-1 Policy Templates
dns_tcp
DNS-TCP protocol traffic.
dns_udp
DNS-UDP protocol traffic.
fragments
Fragmented traffic.
http
HTTP traffic that flows, by default, through port 80 (or other user-configured ports).
ip_scan
IP scanning. A situation in which a client from a specific source IP address tries to access many destination IP addresses in the zone. This policy template is designed primarily for zones in which the IP address definition is a subnet.
By default, this policy template is disabled. The default action for this policy template is notify.
Note
The policies that are produced from this policy template consume system resources and can affect the performance of the Guard.
other_protocols
Non-TCP and non-UDP protocols.
port_scan
Port scanning. A situation in which a client from a specific source IP address tries to access many ports in the zone.
By default, this policy template is disabled. The default action for this policy template is notify.
Note
The policies that are produced from this policy template consume system resources and can affect the performance of the Guard.
tcp_connections
TCP connection characteristics.
tcp_not_auth
TCP connections that have not been authenticated by the Guard anti-spoofing functions.
tcp_outgoing
TCP connections initiated by the zone.
tcp_ratio
Ratios between different types of TCP packets, for example, the number of SYN packets compared to the number of FIN/RST packets.
tcp_services
TCP services on ports other than HTTP related, such as ports 80 and 8080.
tcp_services_ns
TCP services. By default, the policies created from this policy template monitor IRC ports (666X), SSH, and Telnet. This policy template does not create policies with actions that require the Guard to apply the strong protection level to the traffic flow. See the "Understanding the Protection Cycle" section on page 1-6 for more information about the strong protection level.
udp_services
UDP services.
The Guard includes additional policy templates for zones that were created from zone templates that are designed for specific types of attacks or specific services. Table 7-2 details the policy templates that the Guard adds to a zone configuration based on a specific zone template.
Table 7-2 Additional Policy Templates
GUARD_VOIP
sip_udp—Constructs a group of policies that monitor VoIP1 applications that use SIP2 over UDP to establish the VoIP sessions and RTP/RTCP3 to transmit voice data between the SIP end points after sessions are established.
1 VoIP = Voice over IP
2 SIP = Session Initiation Protocol
3 RTP/RTCP = Real-Time Transport Protocol/Real-Time Control Protocol
Note
The Guard looks for indicators of TCP traffic first on dedicated ports 6660 to 6670 and 21 to 23 as follows:
•
If traffic is traced on these ports, the tcp_services_ns policy template constructs a group of policies, and the tcp_services policy template monitors TCP services on other ports.
•
If no traffic is traced on these ports, the tcp_services_ns policy template is not used.
You can add services to policies that were created from the tcp_services_ns policy template.
The Guard includes additional policy templates that protect zones for which you do not want to use the TCP proxy anti-spoofing functions in which the Guard serves as a proxy. You can use these policy templates if the zone is controlled based on the IP addresses, such as an Internet Relay Chat (IRC) server-type zone, or if you do not know the type of services that are running on the zone.
If you define a zone with the GUARD_TCP_NO_PROXY zone template, the Guard uses the policy templates described in Table 7-3. The Guard replaces the policy templates http, tcp_connections, and tcp_outgoing with the policy templates http_ns, tcp_connections_ns, and tcp_outgoing_ns policies. The http_ns, tcp_connections_ns, and tcp_outgoing_ns policy templates do not create policies with actions that require the Guard to apply the strong protection level to the traffic flow.
Table 7-3 details the Guard policy templates for GUARD_TCP_NO_PROXY.
To view a list of all policy templates, use the policy-template command in zone configuration mode and press Tab twice.
During the learning process, zone traffic flows transparently through the Guard. Each active policy template produces a group of policies based on the policy definitions and the zone traffic characteristics. The Guard ranks the services (protocol and port numbers) that the policy template monitors by the level of traffic volume. The Guard then selects the services that have the highest traffic volume and that have exceeded the defined minimum threshold, and it creates a policy for each service. Some policy templates create an additional policy to handle all traffic flows for which a specific policy was not added with a service of any.
You can configure the following policy template parameters:
•
Maximum Number of Services—Defines the maximum number of services that the Guard picks up for the policy template to create specific policies.
•
Minimum Threshold—Defines the minimum threshold that must be exceeded for the Guard to rank the service.
•
Policy Template State—Defines whether or not the Guard produces policies from the policy template.
To configure the policy template parameters, enter the policy template configuration mode by entering the following command in zone configuration mode:
policy-template policy-template-name
The policy-template-name argument specifies the name of the policy template. See Table 7-1 for more information.
The following example shows how to enter http policy template configuration mode:
user@GUARD-conf-zone-scannet# policy-template httpuser@GUARD-conf-zone-scannet-policy_template-http#To display the parameters of a specific policy template, use the show command in policy template configuration mode.
This section contains the following topics:
•
Configuring the Maximum Number of Services
•
Configuring the Minimum Threshold
•
Configuring Policy Template States
•
Configuring All Policy Template Parameters Simultaneously
Configuring the Maximum Number of Services
The maximum number of services parameter defines the maximum number of services (protocol numbers or port numbers) for which the policy template selects and creates policies. The Guard ranks the services that the policy template relates to by the level of traffic volume for each service. The Guard then selects the services that have the highest traffic volume and that have exceeded the defined minimum threshold (as defined by the min-threshold parameter), and it creates policies for each service. The Guard may add an additional policy with a service of any to handle all other traffic flows with the characteristics of the policy template.
Note
The higher the maximum number of services, the more Guard memory the zone requires.
You can only define the maximum number of services parameter for policy templates that detect services: tcp_services, tcp_services_ns, udp_services, and other protocols. You cannot configure it for policy templates that monitor a specific service, such as dns_tcp, which monitors service 53, or for policy templates that relate to a specific traffic characteristic, such as fragments.
The Guard measures the traffic rate of the service based on the policy traffic characteristics. The traffic characteristic can be the source IP addresses or the destination IP addresses. A policy that monitors the service any measures the rate of source IP addresses on all services that are not handled by a specific policy.
By limiting the service number, you can configure the Guard policies to your preferred traffic flow requirements.
To configure the maximum number of services, use the following command in policy template configuration mode:
max-services max-services
The max-services argument is an integer greater than 1 that defines the maximum number of services that the Guard selects. We recommend that you do not exceed the maximum of 10 services.
The following example shows how to configure the maximum number of services that the Guard monitors to 5:
user@GUARD-conf-zone-scannet-policy_template-tcp_services# max-services 5Configuring the Minimum Threshold
The minimum threshold parameter defines the minimum traffic volume for a service. When the threshold is exceeded, the Guard constructs policies that relate to the service traffic according to the particular traffic flow that exceeded the threshold. By setting the threshold, you can adapt the protection operation to the traffic volume of the zone services.
You cannot configure the minimum threshold parameter for policy templates that are essential for proper zone protection and that always construct a policy such as the following policy templates: tcp_services, tcp_services_ns, udp_services, other_protocols, http, and fragments.
To configure the minimum threshold, use the following command in policy template configuration mode:
min-threshold min-threshold
The min-threshold argument is a real number (a floating point number with two decimal places), equal to or greater than 0, that defines the minimum threshold rate in packets per second (pps). When measuring concurrent connections and the SYN/FIN ratio, the threshold is an integer that defines the total number of connections.
The following example shows how to configure the minimum threshold of the policy template http:
user@GUARD-conf-zone-scannet-policy_template-http# min-threshold 12.3Configuring Policy Template States
The policy template state parameter defines whether the policy template is enabled or disabled. If you disable a policy template, it is prevented from producing policies when the Guard is in the policy construction phase.
CautionDisabling a policy template may seriously compromise zone protection. If you disable a policy template, the Guard cannot protect the zone from the traffic to which the policy template relates. For example, disabling the dns_udp policy template prevents the Guard from creating zone policies that manage DNS (UDP) attacks.
To disable a policy template, use the disable command in policy template configuration mode.
To enable a policy template, use the enable command in policy template configuration mode.
The following example shows how to disable the policy template http:
user@GUARD-conf-zone-scannet-policy_template-http# disableConfiguring All Policy Template Parameters Simultaneously
You can configure all policy template operational parameters with a single command by entering the following command in zone configuration mode:
policy-template policy-template-name max-services min-threshold {disabled | enabled}
Table 7-4 provides the arguments and keywords for the policy-template command.
Table 7-4 Arguments and Keywords for the policy-template Command
policy-template-name
Policy template name. See Table 7-5 for more information.
max-services
Maximum number of services for which the Guard selects and constructs policies from the specific policy template.
To prevent the Guard from changing the current value, enter a value of -1.
See the "Configuring the Maximum Number of Services" section for more information.
min-threshold
Minimum threshold that must be exceeded for the Guard to rank the service.
To prevent the Guard from changing the current value, enter a value of -1.
See the "Configuring the Minimum Threshold" section for more information.
disabled
Disables the policy template from producing policies. See the "Configuring Policy Template States" section for more information.
enabled
Enables the policy template. See the "Configuring Policy Template States" section for more information.
The following example shows how to set the parameters of the tcp_services policy template. The maximum number of services is set to 3, the policy state is set to enabled, and the minimum threshold is unchanged (-1).
user@GUARD-conf-zone-scannet# policy-template tcp_services 3 -1 enabledUnderstanding the Policy Path
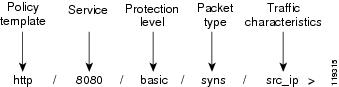
The name of the policy is composed of sections that describe the traffic characteristic that it measures. For example, the policy http/80/analysis/syns/src_ip measures traffic flows of HTTP SYN packets destined to port 80 that were authenticated by the Guard analysis protection level functions and aggregated according to source IP addresses.
Figure 7-1 provides an example of a zone policy name.
Figure 7-1 Policy Name
Table 7-5 describes the policy name sections.
Table 7-5 Policy Name Sections
Policy template
Policy template that was used to construct the policy. Each policy template deals with the characteristics that the Guard requires to protect against a specific DDoS threat. See the "Understanding and Configuring Policy Templates" section for more information.
Service
Port number or protocol number in the traffic flow that the policy monitors. You can add or delete services from the policies.
Protection level
Protection level that the Guard applies to the traffic flow. Protection levels have a static configuration and cannot be configured manually.
Packets type
Packet types that the Guard monitors.
Traffic characteristics
Traffic characteristics that the Guard uses to aggregate the policy.
The first four sections of the policy name (policy template, service, protection level, and packet type) define the type of traffic that is analyzed. The last section of the policy path (traffic characteristics) defines how to analyze the flow.
This section describes each of the policy path sections as follows:
•
Understanding and Managing the Policy Services
•
Understanding the Guard Protection Levels
•
Understanding the Packet Types that the Guard Monitors
•
Understanding the Traffic Characteristics that the Guard Monitors
Understanding and Managing the Policy Services
The service section defines the zone application port or protocol to which each policy relates. Policies have cross dependencies and priorities. If two different policies define the same traffic flow, the Guard analyzes the flow using the policy that is more specific. The service any relates to all traffic that does not specifically match other services created from the same policy template.
We recommend that you define specific policies for the zone main services to obtain protection that is most suited to your individual needs.
CautionDo not add the same service (port number) to more than one policy because it may decrease the performance of the Guard.
When you add or delete a service from the zone policies, the Guard marks the zone policies as untuned. If you enabled zone protection and the learning process, the Guard cannot detect anomalies in the zone traffic until you perform one of the following actions:
•
Perform the threshold tuning phase of the learning process and accept the results (see the "Activating the Threshold Tuning Phase" section on page 8-6).
•
Mark the zone policies tuned (see the "Marking the Policies as Tuned" section on page 8-10).
This section contains the following topics:
Adding a Service
You can add services to all policies that were created from a specific policy template. The new service is an addition to the services that were discovered during the policy construction phase and is defined with default values. You can define the threshold manually, but we recommend that you run the threshold tuning phase of the learning process to tune the policies to the zone traffic. See the "Activating the Threshold Tuning Phase" section on page 8-6 for more information.
You can add a new service to policies that were created from the following policy templates:
•
tcp_services, udp_services, or tcp_services_ns
The service designates a port number.
•
other_protocols
The service designates a protocol number.
Note
If you activate the policy construction phase after adding a service, new services might override the manually added service.
Unless you enable the policy construction phase, you may need to add a service manually in the following situations:
•
A new application or service was added to the zone network.
•
The policy construction phase was activated for a short period, so it does not reflect all the network services (for instance, if there are known applications or services that are active only once a week or during the night).
To add a service, use one of the following commands:
•
add-service service-num (in policy template configuration mode)
•
policy-template policy-template-name add-service service-num (zone configuration mode)
Table 7-6 provides the arguments for the add-service command.
Table 7-6 Arguments for the add-service Command
service-num
Protocol or port number.
policy-template-name
Policy template name. See Table 7-1 for more information.
The following example shows how to add a service to all the policies that were created from the policy template tcp_services:
user@GUARD-conf-zone-scannet-policy_template-tcp_services# add-service 25Deleting a Service
You can delete a specific service for any policy template. The Guard will delete the service from all policies that were created from the specific policy template.
To delete a service, use one of the following commands:
•
remove-service service-num (in policy template configuration mode)
•
policy-template policy-template-name remove-service service-num (in zone configuration mode)
Table 7-7 provides the arguments for the remove-service command.
Table 7-7 Arguments for the remove-service Command
service-num
Protocol or port number to remove.
policy-template-name
Policy template name. See Table 7-1 for more information.
CautionIf you delete a service, the Guard policies cannot monitor the traffic of that service, which may compromise zone protection.
You can remove services from the following policy templates:
•
tcp_services, udp_services, or tcp_services_ns
The service is a port number.
•
other_protocols
The service is a protocol number.
If you do not activate the policy construction phase of the learning process, you may need to remove a service manually in the following situations:
•
An application or service was removed from the network.
•
An application or service that you do not want to enable (because it is uncommon for the network environment) but was identified during the policy construction phase.
Note
If you activate the policy construction phase after removing a service, the Guard may add the same service to the zone configuration.
The following example shows how to delete a service from all policies that were created from the policy template tcp_services:
user@GUARD-conf-zone-scannet-policy_template-tcp_services# remove-service 25Understanding the Guard Protection Levels
The Guard applies three protection levels in which it applies different processes to the traffic flow. The Guard has the following three protection levels:
•
Analysis protection level—The Guard allows the traffic to flow monitored, but unhindered, during zone protection, as long as no anomalies are traced. Once the Guard traces anomalies, it directs the traffic to the appropriate protection level.
•
Basic protection level—The Guard activates anti-spoofing and anti-zombie functions to authenticate the traffic by inspecting the suspicious traffic flow to verify its source. The Guard performs authentication for each host. The authentication is valid for a predefined period of time only. When the time expires, the Guard authenticates the host again.
•
Strong protection level—The Guard activates severe anti-spoofing functions that inspect the traffic flow packets to verify the flow legitimacy.
The Guard performs authentication for each connection.
After activating a protection function, the Guard continues to analyze the traffic. If the Guard can still spot traffic abnormalities in traffic destined to the zone, it applies a stronger protection level.
Note
Protection levels have a static configuration and cannot be configured manually.
Understanding the Packet Types that the Guard Monitors
The Guard monitors packet characteristics, which can be one of the following:
•
Packet type (for example, TCP-SYN packets)
•
Packet analysis (for example, authenticated packets, which are packets that the Guard has verified their connection by performing a TCP handshake)
•
Packet direction (for example, incoming connections)
Table 7-8 describes the packet types that the Guard monitors.
Understanding the Traffic Characteristics that the Guard Monitors
Traffic characteristics define how to analyze the traffic flow and what characteristics were used to aggregate the policies. Different policies can analyze the same traffic flow but measure the rate based on different characteristics, as shown in this example:
dns_tcp/53/analysis/pkts/dst_ip and dns_tcp/53/analysis/pkts/src_ip.
Table 7-9 describes the traffic characteristics that the Guard monitors.
Configuring Policy Parameters
After completing the learning process, you can display specific policy parameters (policy state, policy threshold, policy timeout, policy action, and policy interactive status) to determine if the policy parameters suit the zone traffic. You can configure the policy parameters of a single policy or a group of policies to adapt to zone traffic requirements.
To display the configuration of the policy parameters, use the show command in policy configuration mode.
To enter policy configuration mode, use the following command in zone configuration mode:
policy policy-path
The policy-path argument specifies the policy path sections. The path can be a partial path that includes only part of the policy sections. See the "Understanding Zone Policies" section for more information.
Note
To move up one level in the policy path hierarchy, enter policy .. at the policy path prompt.
The following example shows how to enter the dns_tcp/53/analysis/syns/global policy configuration mode:
user@GUARD-conf-zone-scannet# policy dns_tcp/53/analysis/syns/global user@GUARD-conf-zone-scannet-policy-/dns_tcp/53/analysis/syns/global#You can change the policy action, timeout, threshold, and learning parameters at every section of the policy path. However, more policies are affected if you change these parameters at the higher-level policy sections (such as policy template or service sections). If you configure these parameters at a high-level policy path hierarchy, these parameters change in all the subpolicy paths.
You can use an asterisk (*) as a wildcard character in each policy path section. If you do not specify a policy path section, the Guard relates to the unspecified section as a wildcard (*). For example, the tcp_services//analysis//global policy uses a wildcard for the service and the packet type.
This section contains the following topics:
•
Configuring the Policy Threshold
•
Configuring the Policy Timeout
•
Configuring the Policy Action
•
Configuring the Policy Interactive Status
Changing the Policy State
The zone policies have three possible states as follows:
•
Active—The policy monitors the traffic and performs an action once the threshold is exceeded.
•
Inactive—The policy monitors the traffic and obtains the threshold, but it takes no action when a threshold is exceeded. You can inactivate a policy to avoid reactivating the threshold-tuning phase of the learning process.
•
Disabled—The policy does not monitor the traffic flow, so no threshold is obtained.
Note
We recommend that you activate the threshold tuning phase of the learning process to ensure that the Guard monitors the correct thresholds for the other policies.
CautionWhen you disable a policy, the active zone policies assume responsibility for the traffic that would normally be monitored by the disabled policy. To adjust the thresholds of the active policies, we recommend that you activate the threshold tuning phase before you activate zone protection.
To change the policy state, use the following command in policy configuration mode:
state {active | disabled | inactive}
The following example shows how to set the policy state:
user@GUARD-conf-zone-scannet-policy-/dns_tcp/53/analysis/syns# state disabledThe following example shows how to set the state of all global policies:
user@GUARD-conf-zone-scannet-policy-/*/*/*/global# state inactive
CautionIf you deactivate or disable a zone policy, the active zone policies may not assume the protection capabilities that the deactivated policy provided, which may compromise zone protection.
If you activate the policy construction phase after disabling a zone policy, all zone policies are reconfigured according to the current traffic flow and the policy may be reactivated.
Configuring the Policy Threshold
The policy threshold defines the threshold traffic rate for a specific policy and is adjusted by the threshold tuning phase. The threshold is set, by default, to a value that is appropriate for on-demand protection. When this threshold is exceeded, the policy takes action to protect the zone.
The threshold is measured in packets per second except for policies that are constructed from the following policy templates:
•
num_soruces—The threshold is measured in the number of IP addresses or ports.
•
tcp_connections—The threshold is measured in the number of connections.
•
tcp_ratio—The threshold is measured as the ratio number.
You can configure the policy threshold in the following ways:
•
Set the threshold—You can set the value of the policy threshold. See the "Setting the Policy Threshold" section.
•
Multiply the threshold—The Guard multiplies the current policy thresholds by a factor. The new value may change in subsequent threshold tuning phases if you do not set it as fixed. See the "Multiplying a Threshold by a Factor" section.
•
Configure specific IP thresholds—The Guard sets thresholds for specific IP source addresses within the zone address range. See the "Configuring Specific IP Thresholds" section.
•
Configure a proxy threshold—The Guard sets a threshold for traffic of clients that connect to the zone in HTTP through proxies. See the "Configuring the Proxy Threshold" section.
The policy threshold may change if you perform additional threshold tuning phases. You can modify how a threshold may change in subsequent threshold tuning phases in the following ways:
•
Set the threshold as fixed—The Guard will not change the value of the policy threshold, proxy-threshold, and threshold-list in subsequent threshold tuning phases. See the "Setting the Threshold as Fixed" section.
•
Set a fixed multiplier for the policy threshold—The Guard calculates the policy threshold in subsequent threshold tuning phases based on the current policy threshold, the learned threshold, and the fixed multiplier. See the "Configuring a Threshold Multiplier" section.
This section contains the following topics:
•
Setting the Threshold as Fixed
•
Configuring a Threshold Multiplier
•
Multiplying a Threshold by a Factor
•
Configuring Specific IP Thresholds
•
Configuring the Proxy Threshold
Setting the Policy Threshold
To configure the policy threshold, use the following command in policy configuration mode:
threshold threshold
The threshold argument is a positive number that specifies the policy threshold.
The following example shows how to set the threshold value of the policy dns_tcp/53/analysis/syns/global to 300:
user@GUARD-conf-zone-scannet-policy-/dns_tcp/53/analysis/syns/ global# threshold 300Setting the Threshold as Fixed
You can set a policy threshold, proxy-threshold, and threshold-list as fixed. The Guard ignores new thresholds in the threshold tuning phase of the learning process and maintains the current thresholds. Setting a threshold as fixed enables you to configure the thresholds of a policy but continue learning the thresholds of other policies.
To set a policy threshold as fixed, use the following command in policy configuration mode:
learning-params fixed-threshold
The following example shows how to set the threshold of the policy dns_tcp/53/analysis/syns/global as fixed:
user@GUARD-conf-zone-scannet-policy-/dns_tcp/53/analysis/syns/ global# learning-params fixed-thresholdYou can set the threshold of several policies as fixed in a single command by entering the command in zone configuration mode. To set a policy threshold as fixed while in zone configuration mode, use the following command:
policy policy-path learning-params fixed-threshold
The policy-path argument specifies the policy path. The path can be a partial path that includes only part of the policy sections. See the "Understanding Zone Policies" section for more information.
The following example shows how to set the thresholds of all policies that were created from the dns_tcp policy template as fixed:
user@GUARD-conf-zone-scannet# policy dns_tcp learning-params fixed-thresholdTo display the policy learning parameters, use the show learning-params command in policy configuration mode, or use the show policies policy-path learning-params command in zone configuration mode.
Configuring a Threshold Multiplier
You can set a multiplier for a policy threshold. The Guard calculates a new policy threshold by multiplying the learned threshold by the specified multiplier before accepting the result of subsequent threshold tuning phases. The Guard accepts the results of the threshold tuning phase using the configured threshold selection method. See the "Configuring the Threshold Selection Method" section on page 8-9.
To set a multiplier for the policy threshold, use the following command in zone configuration mode:
policy policy-path learning-params threshold-multiplier threshold-multiplier
Table 7-10 provides the arguments and keywords for the policy learning-params threshold-multiplier command.
Table 7-10 Arguments and Keywords for the policy learning-params threshold-multiplier Command
policy-path
Policy path for which to multiply the thresholds. The path can be a partial path that includes only part of the policy sections. See the "Understanding Zone Policies" section for more information.
learning-params
Configures the learning parameters.
threshold-multiplier threshold-multiplier
Multiplies the policy threshold. The threshold-multiplier is a real positive number (a floating point number with two decimal places) by which the policy threshold is multiplied. Enter a number less than 1 to decrease the policy threshold.
To set a multiplier for the policy threshold in policy configuration mode, use the learning-params threshold-multiplier threshold-multiplier command.
The following example shows how to configure a threshold multiplier so that the Guard decreases the thresholds of policies that were created from the policy template dns_tcp by half in subsequent threshold tuning phases:
user@GUARD-conf-zone-scannet# policy dns_tcp learning-params threshold-multiplier 0.5To display the policy learning parameters, use the show learning-params command in policy configuration mode, or use the show policies policy-path learning-params command in zone configuration mode.
Multiplying a Threshold by a Factor
You can multiply the thresholds of a policy or a group of policies by a factor, which enables you to increase or decrease the threshold of a policy or a group of policies if the traffic volume does not represent the zone traffic. You can enable the Guard to multiply the policy thresholds, the proxy thresholds, and the thresholds that were defined by the policy threshold-list command.
To multiply policy thresholds by a factor, use the following command in zone configuration mode:
policy policy-path thresh-mult threshold-multiply-factor
Table 7-11 provides the arguments and keywords for the policy thresh-mult command.
Table 7-11 Arguments and Keywords for the policy thresh-mult Command
policy-path
Policy template name. See Table 7-1 for more information.
thresh-mult threshold-multiply-factor
Specifies a real positive number (a floating point number with 4 decimal places) by which to multiply the threshold. Enter a number less than 1 to decrease the policy threshold.
The following example shows how to decrease the thresholds of policies that were created from the policy template dns_tcp by half:
user@GUARD-conf-zone-scannet# policy */*/*/*/src_ip thresh-mult 0.5
Note
The Guard may change the threshold value in subsequent threshold tuning phases. To prevent the Guard from changing the threshold value, set the threshold value as fixed. See the "Setting the Threshold as Fixed" section.
To display the policy learning parameters, use the show learning-params command in policy configuration mode, or use the show policies policy-path learning-params command in zone configuration mode.
Configuring Specific IP Thresholds
You can avoid false attack detections by the Guard when traffic increases on a known high traffic source or destination IP address by configuring a policy with a threshold for traffic that is associated with that IP address.
You should consider configuring a specific IP threshold if one of the following situations occurs:
•
When there is known high-volume traffic from a source IP address, you can configure a threshold to apply to traffic that originates from the specific source IP address.
•
When there is a nonhomogeneous zone (a zone that has more than a single IP address defined) and there is known high-volume traffic flowing to part of the zone only, you can configure a threshold to apply to traffic that targets the specific destination IP address within the zone.
You can configure specific IP thresholds only for the following policies:
•
Policies with traffic characteristic of destination IP (dst_ip).
•
Policies with traffic characteristics of source IP address (src_ip) where the default policy action is drop. The default policy action is the action that the Guard applies to the policy when you create a new zone. You can configure the threshold list for such policies even if you change the policy action.
To configure a specific IP threshold, use one of the following commands:
•
policy policy-path threshold-list ip threshold [ip threshold ...] (in zone configuration mode)
•
threshold-list ip threshold [ip threshold ...] (in policy configuration mode)
Table 7-12 provides the arguments for the threshold-list command.
Table 7-12 Arguments for the policy threshold-list Command
Policy template name. See Table 7-1 for more information.
Specific IP address.
Threshold traffic rate in packets per second, except for policies that measure concurrent connections and SYN-by-FIN ratio, where the threshold is the number of connections.
You can add a maximum of 10 specific IP thresholds for each policy. You can enter all specific IP thresholds in a single command.
The Guard might change the policy thresholds in subsequent threshold tuning phases if the threshold selection method is set to new-thresholds. See the "Configuring the Threshold Selection Method" section on page 8-9 for more information.
The following example shows how to set specific IP thresholds for IP addresses 10.10.10.2 and 10.10.15.2 for the policy http/80/analysis/syns/src_ip:
user@GUARD-conf-zone-scannet-policy-/http/80/analysis/syns/src_ip# threshold-list 10.10.10.2 500 10.10.15.2 500Configuring the Proxy Threshold
The proxy threshold parameter defines the traffic rate for clients that connect to the zone in HTTP through proxies and enables the Guard to adapt the policy to traffic volumes that come from different sources. The Guard uses the proxy thresholds to block traffic only, so you can configure them only for policies in the DEFAULT zone template with a strong protection level and for policies in the TCP_NO_PROXY zone template with a basic protection level.
A proxy threshold is available for the http, http_ns, tcp_connections, and tcp_connections_ns policies only and is effective for tcp_connections or tcp_connections_ns policy templates if the zone has active http or http_ns policies only.
To configure the proxy-threshold, use the following command in policy configuration mode:
proxy-threshold proxy-threshold
The proxy-threshold argument specifies the proxy-threshold traffic rate in packets per second for http and http_ns policies. It specifies the proxy-threshold in the number of connections for tcp_connections and tcp_connections_ns policies.
Because proxy servers handle much more traffic than network clients that are part of the zone, we recommend that when you configure a proxy threshold, you configure the proxy-threshold argument with a higher value than the threshold argument.
The following example shows how to set the proxy threshold for the http/80/strong/syns/src_ip policy to 20:
user@GUARD-conf-zone-scannet-policy-/http/80/strong/syns/src_ip# proxy-threshold 20Configuring the Policy Timeout
The timeout parameter defines the minimum time for dynamic filters that are produced by the policy to apply their action. When the timeout expires, the Guard determines whether or not to deactivate the dynamic filters that were produced by the policy. If the Guard decides not to deactivate the dynamic filters, the filter activation timeout resumes for another time span. To change the criteria for dynamic filter deactivation, use the filter-termination command. See the "Deactivating Dynamic Filters" section on page 6-23 for more information.
To configure the policy timeout, use the following command in policy configuration mode:
timeout {forever | timeout}
Table 7-13 provides the arguments and keywords for the timeout command.
The following example shows how to set the timeout of the policy http/80/analysis/syns/src_ip to 100 seconds:
user@GUARD-conf-zone-scannet-policy-/http/80/analysis/syns/src_ip# timeout 100To change the timeout of a group of policies simultaneously, use the policy set-timeout command in zone configuration mode.
The following example shows how to set the timeout of all policies that were produced from the HTTP policy template and measure source IP addresses to 100:
user@GUARD-conf-zone-scannet# policy http/*/*/*/src_ip set-timeout 100Configuring the Policy Action
The action parameter defines the type of action that the policy takes once its threshold is exceeded.
Configure the policy action so that it enhances the protection that the policy defines. For example, configure the policy action to to-user-filters for policies with a protection level of analysis, or configure the policy action to filter/drop for policies with a protection level of strong. Do not configure the policy action so that it reduces the protection level that the policy defines. For example, do not configure the policy action to to-user-filters for policies with a protection level of basic or strong.
To configure the policy action, use the following command in policy configuration mode:
action policy-action
Table 7-14 describes the policy actions.
Table 7-14 Policy Actions
block-unauthenticated
Adds a filter that blocks traffic that was not authenticated by the anti-spoofing functions, such as an ACK with no prior handshake.
Configure this policy action for policies with a packet type of in_unauth_pkts and unauth_pkts only.
filter/strong
Adds a filter that applies the strong protection level to the traffic flow.
Configure this policy action for policies with a protection level of analysis and basic. We recommend that you use this policy action on TCP (incoming) policies with traffic characteristics of src_ip only and do not use it on policies with traffic characteristics of global because it may cause network problems in networks that use a load balancer or an ACL1 to manage traffic.
to-user-filters
Adds a filter directing the traffic to the user filters.
Configure this policy action for policies with a protection level of analysis.
filter/drop
Adds a filter that directs the Guard to drop the specified traffic.
Configure this policy action for policies that monitor traffic after the Guard has applied the anti-spoofing functions (policies with a protection level of basic and strong). We do not recommend that you use this action for policies with a protection level of analysis because this might cause the Guard to deplete all the Guard filters when mitigating a spoofed attack.
redirect/zombie
Adds a filter that enhances authentication for all user filters with an action of redirect.
This policy action applies to the tcp_connections/any/basic/num_sources/global policy only.
notify
Notifies you when its threshold is exceeded.
1 ACL = Access Control List
The following example shows how to set the action of the policy http/80/analysis/syns/src_ip:
user@GUARD-conf-zone-scannet-policy-/http/80/analysis/syns/src_ip# action dropTo change the action of a group of policies simultaneously, use the policy set-action command in zone configuration mode.
Note
Not all actions are valid for all policies. If you modify the policy action to an action that is not valid for the specific policy, the Guard displays an error message.
The following example shows how to set the action of all dns_tcp policies:
user@GUARD-conf-zone-scannet# policy dns_tcp/ set-action filter/dropset action of dns_tcp/ to filter/drop:16 policy actions set.Configuring the Policy Interactive Status
The interactive status parameter defines the interactive status that the pending dynamic filters, which are created by the zone policy, will assume. The interactive status applies only to zones if you enable zone protection, and the zone is in interactive protect mode. See Chapter 10, "Using Interactive Protect Mode," for more information.
To modify the status of the pending dynamic filters that a policy produces after you have set the interactive status of a recommendation to always-accept or always-ignore, use the interactive-status command.
For example, if you have defined the status of a recommendation to always-accept, the recommendation and the pending dynamic filters of the recommendation are no longer displayed. To ignore the recommendation or the pending dynamic filters that the recommendation produces, change the policy interactive status to interactive or always-accept.
To configure the policy interactive status, use the following command in policy configuration mode:
interactive-status {always-accept | always-ignore | interactive}
Table 7-15 provides the keywords for the interactive-status command.
The following example shows how to configure the interactive status of policy dns_tcp/53/analysis/pkts/src_ip to always-accept:
user@GUARD-conf-zone-scannet-policy-/dns_tcp/53/analysis/pkts/ src_ip# interactive-status always-acceptMonitoring Policies
You can monitor the policies to see how well they are suited to the zone traffic volume and services.
This section describes the following topics:
Displaying Policies
You can display the zone policies to verify that they are adapted to the zone traffic characteristics. You might want to view the zone-constructed policies to verify that these policies are customized for the traffic characteristics of the zone. You can configure only policies that appear in this list.
The Guard displays only current zone policies. If a policy template was disabled during the policy construction phase, the Guard does not create policies from that policy template, and you do not see these policies when you enter the show policies command.
To display the zone policies, use the following command in zone configuration mode:
show policies policy-path
The policy-path argument specifies a group of policies. You can use an asterisk (*) as a wildcard character in each policy path section. If you do not specify a policy path section, the Guard considers the unspecified section to be a wildcard (*). For example, the policy tcp_services//analysis//global uses wildcards for the service and the packet type sections.
To display the statistics of all policies, enter an asterisk (*) for the policy path.
See the "Understanding Zone Policies" section for more information about the policy path sections.
The following example shows how to display all the zone policies:
user@GUARD-conf-zone-scannet# show policies *The following example shows how to display all policies that monitor DNS-over-TCP synchronization packets on port 53:
user@GUARD-conf-zone-scannet# show policies dns_tcp/53/*/syns/*Table 7-16 describes the fields in the show policies command output.
Table 7-16 Field Descriptions of the show policies Command Output
Policy
Policy name. See the "Understanding Zone Policies" section for more information about the policy path sections.
State
Policy state. See the "Changing the Policy State" section for more information.
act = active, inact = inactive, disab= disabled
IStatus
Policy interactive status. See the "Configuring the Policy Interactive Status" section for more information.
a-accept = always-accept, a-ignor = always-ignore,
interac = interactiveThreshold
Policy threshold. When this threshold is exceeded, the Guard takes action to protect the zone. See the "Configuring the Policy Threshold" section for more information.
Proxy
Policy proxy-threshold. See the "Configuring the Proxy Threshold" section for more information.
List
Number of specific IP thresholds defined for the policy. See the "Configuring Specific IP Thresholds" section for more information.
Action
Action that the policy takes when the threshold is exceeded. See the "Configuring the Policy Action" section for more information.
Timeout
Minimum time span that the policy action is valid. The Guard determines, according to the filter-termination thresholds, whether or not the dynamic filter that was produced by the policy is to be inactivated. See the "Configuring the Policy Timeout" section for more information.
Displaying Policy Statistics
You can display the rate of the traffic flowing through a zone policy or a group of zone policies, and you can determine whether the type of services and volume represent the zone traffic. The Guard displays the traffic flows forwarded to the zone with the highest rates as measured by the policies. The rate is calculated based on traffic samples.
To display the policy statistics, use the following command in zone configuration mode:
show policies policy-path statistics [num-entries]
Table 7-17 provides the arguments for the show policies statistics command output.
Table 7-17 Arguments for the show policies statistics Command
Group of policies for which to display statistics.
You can use an asterisk (*) as a wildcard character in each policy path section. If you do not specify a policy path section, the Guard relates to the unspecified section as a wildcard (*). For example, the policy tcp_services//analysis//global uses wildcards for the service and the packet type sections.
To display the statistics of all policies, enter an asterisk (*) for the policy-path.
See the "Understanding Zone Policies" section for more information about the policy path sections.
(Optional) Number of entries to display. Enter a number from 1 to 100. The Guard displays the policies with the highest values.
The following example shows how to display the statistics of all the zone policies:
user@GUARD-conf-zone-scannet# show policies * statisticsThe following example shows how to display the statistics of all policies that monitor DNS-over-TCP synchronization packets on port 53:
user@GUARD-conf-zone-scannet# show policies dns_tcp/53/*/syns/*The following example shows how to display the statistics of the zone global traffic:
user@GUARD-conf-zone-scannet# show policies */*/*/*/global statisticsThe Guard displays the information in three tables. The information in each table is sorted by value, with the highest values appearing at the top of the table.
Table 7-18 displays the fields in the tables in the show policies statistics command output.
Table 7-18 Field Descriptions of the show policies statistics Command Output Tables
Key
Key that is the traffic characteristic used to aggregate the policies.
For example, in the tcp_services/any/analysis/syns/dst_ip policy, the key is the destination IP address (dst_ip). If the traffic characteristic that was used to aggregate the policies is global, the key displays N/A.
See Table 7-8 for more information.
Policy
Policy name. See the "Understanding Zone Policies" section for more information.
Rate
Rate of the traffic that flows through the policy and is measured in packets per second (pps). The rate is calculated based on traffic samples.
Connection
Number of concurrent connections.
This information is available for tcp_connections policies and for the following packet types:
•
in_conns—For the strong protection level
•
in_nodata_conns—For the analysis protection level
Ratio
Ratio between the number of SYN flagged packets and the number of FIN/RST flagged packets. This information is available for syn_by_fin policies only.
Note
The Guard does not display tables that contain no data.
Backing Up the Policy Configuration
You can back up the current zone policies at any time by using the snapshot threshold-selection cur-thresholds command in zone configuration mode.
The following example shows how to create a snapshot to back up the current policy configuration:
user@GUARD-conf-zone-scannet# snapshot threshold-selection cur-thresholds

 Feedback
Feedback