Feedback Feedback
|
Table Of Contents
Managing and Troubleshooting NextPort Services on the UPC
Port Configuration Mode Commands
SPE Configuration Mode Commands
Disable a Port from Dial-Up Services
Upgrading SPE Firmware and Cisco IOS Images
Displaying SPE Firmware Versions
Upgrading SPE Firmware from the Cisco CCO TFTP Server
Download SPE Firmware from the Cisco CCO TFTP Server to a Local TFTP Server
Copy the SPE Firmware File from Local TFTP Server to the SPEs
Upgrading SPE Firmware from Diskettes
Copy the SPE Firmware to Your PC Hard Disk
Copy the SPE Firmware from Your PC to the SPEs
Using the SPE Firmware Bundled with Cisco IOS Software
Managing and Troubleshooting NextPort Services on the UPC
The Cisco AS5800 universal access servers support universal port carrier cards, and DMM modem cards. For details on these modem carrier cards, refer to the Cisco AS5800 Universal Access Server Hardware Installation Guide and Cisco AS5800 Universal Access Server Dial Shelf Card Guide. The universal port card (UPC) supports NextPort hardware and software interfaces. A port is defined as the binding of a TDM channel, service, and data queue to support a bidirectional service on the UPC. A universal port is a port on a UPC that can be switched freely between two or more services without changing the TDM channel.
You can manage port connections at the UPC, service proccessing element (SPE—the processor on the slot card that executes protocols to process in-band data) or port level using monitoring, polling, and troubleshooting commands. NextPort management functions are very similar to MICA modem (DMM) management functions. This document discusses procedures and commands similar in both types of services and procedures, and some unique to the NextPort architecture.
NextPort introduces shelf, slot, and SPE software hierarchies. On the Cisco AS5800, the hierarchy is shelf/slot/spe. The user can perform the following functions on an SPE:
•
General configuration such as busyout, shutdown, or clear
•
View statistics and states
•
Configure auto and manual diagnostic tests and recovery process
•
Upgrade firmware
•
Retrieve trace information for ports running on an SPE
This document includes the following sections:
•
Upgrading SPE Firmware and Cisco IOS Images
SPE Performance Statistics
Configuration
By default, event logging is enabled, and SPEs are polled every 12 sec. The log contains raw data in binary form, which must be viewed using the show commands listed in the "Viewing Statistics" section.You may configure some aspects of how the record is kept using the following global configuration mode commands [at the AS5800(config)# prompt]:
•
spe poll auto—Enables the UPC to immediately send statistics data when its event buffers get filled, instead of waiting until the next polling interval. Use the no form of this command to disable this option. When this option is disabled, data will be dropped if the event buffers get filled before the next polling interval. Enter this command in global configuration mode which applies to all available SPEs. It is used in the same way the modem poll command is used for MICA modems. Enter this command, which applies to all available SPE's, in Global Configuration Mode.
•
spe poll time seconds—Sets the frequency with which performance statistics are retrieved from the SPEs and added to the log. Use the no form to disable this type of polling. The default is 12 seconds. This replaces the modem poll time command. If the number of attempts to retrieve port status or statistics exceeds the number you define, the port is removed from operation. In this case, you must reset the port using the clear port command. It is used in the same way the modem poll command is used for MICA modems.
•
spe call-record max-userid — Requests that the access server generate a modem call record after a call is terminated, and add it to the log. To disable this function, use the no form. This replaces the modem call-record command.
•
spe log-event-size number—This command allows the user to configure the size of the history event queue buffer for manageable SPEs in the access server. The default is 100 events per port. Use the show port log command to view port events. It is used in the same way the modem buffer-size command is used for MICA modems.
The following Enable Mode (also called Privileged EXEC Mode) commands allow you to clear some or all of the log events relating to the SPEs (at the AS5800# prompt):
•
clear spe log—This command allows a user to clear all event entries in the slot history event log.
•
clear spe counters—This command clears statistical counters for all types of services for the specified SPE, SPE range, or all the SPEs. If the user does not specify the range of SPEs or a SPE, all SPEs' statistics are cleared. It is used in the same way the clear modem counters command is used for MICA modems.
•
show port log—This command allows a user to clear event entries in the port level history event log.
Viewing Statistics
You can view SPE statistics using the Cisco IOS software with the Cisco AS5800. To view performance statistics for the UPCs, enter one or more of the following commands in Enable Mode (also called Privileged EXEC Mode), at the AS5800# prompt:
•
show modem config—This command displays the configuration information for specified ports or the specified port range. The port should have an active session associated at the time the command is executed.
•
show modem operational-status—This command displays the operational status of the specified ports or the specified port range. The port should have an active session associated at the time the command is executed.
•
show port config—This command displays the configuration information for specified ports or the specified port range. The port should have an active session associated at the time the command is executed.
•
show port log—This command displays the oldest event first from the port history event log. It is used in the same way the show modem log command is used for MICA modems.
•
show port log reverse—This command displays the latest event first from the port history event log.
•
show port modem log—This command displays the oldest event first from the port history event log. It is used in the same way the show modem log command is used for MICA modems. (The show modem log command is not supported on the Cisco AS5800.)
•
show port modem log reverse—This command displays the latest event first from the port history event log.
•
show port modem test—This command displays the test log for the specified SPE port range or all the SPE ports.
•
show port operational-status—This command displays the operational status of the specified ports or the specified port range. The port should have an active session associated at the time the command is executed.
•
show spe or show spe modem—This command displays the history statistics of all SPEs, a specified SPE, or the specified SPE range. It is used in the same way the show modem command is used for MICA modems.
•
show spe digital active—This command displays active digital statistics of all SPEs, specified SPE or the specified SPE range.
•
show spe digital disconnect-reason—This command displays the digital disconnect reasons for the specified SPE or SPE range. The disconnect reasons are displayed with Class boundaries.
•
show spe digital csr—This command displays the digital call success rate statistics for a specific SPE, range of SPEs or all the SPEs.
•
show spe digital summary—This command displays digital history statistics of all SPEs, specified SPE or the specified SPE range for all service types.
•
show spe modem active—This command displays the active statistics of all SPEs, a specified SPE or a specified SPE range serving modem traffic. It is used in the same way the show modem command is used for MICA modems. (The show modem command is not supported on the Cisco AS5800.)
•
show spe modem csr—This command displays the call success rate statistics for a specific SPE, range of SPEs, or all the SPEs.
•
show spe modem summary—This command displays the history statistics of all SPEs, specified SPE or the specified SPE range. It is used in the same way the show modem command is used for MICA modems. (The show modem command is not supported on the Cisco AS5800.)
•
show spe modem disconnect-reason—This command displays the disconnect reasons for the specified SPE or SPE range. The disconnect reasons are displayed with Class boundaries. It is used in the same way the show modem call-stats command is used for MICA modems.
•
show spe version—List all SPEs and the SPE firmware files used. This will help you decide if you need to update your SPE firmware files. It is used in the same way the show modem mapping command is used for MICA modems.
•
show spe modem speed—This command shows the connect-speeds negotiated within each high/low speed modulation or codecs for a specific range of SPEs or all the SPEs.
•
show spe log—This command displays the oldest event first from the slot history event log.
•
show spe log reverse —This command displays the latest event first from the log.
Managing Ports
This section describes how to manage NextPort ports by clearing ports, entering port configuration mode, removing ports from service, and disabling ports from dial-up service. For details on disabling a port from dial-up services, see the section, "Troubleshooting" on page 6.
Clear Ports
Ports may need to be cleared if polling attempts have failed and the port is removed from operation.This is done using the clear port command.
Use the show spe shelf/slot/spe command to view the active ports on an SPE. To clear ports on an SPE, enter the following command in Enable Mode (also called Privileged EXEC Mode). The user can clear all ports on the NAS, all ports on a slot, or a port. This replaces the clear modem command.
•
The example below clears all ports on SPE 1 on slot 4 of shelf 1 on the Cisco AS5800.
AS5800# clear port 1/4/1AS5800#•
The example below clears all active ports on slot 4 of shelf 1 on the Cisco AS5800.
AS5800# clear port 1/4AS5800#Port Configuration Mode
Port configuration mode allows the user to enter a mode similar to the line configuration mode. This mode allows individual ports or ranges of ports to be shut down or put in busyout mode. Port configuration mode commands replace the modem range, modem busyout, and modem shutdown commands used with MICA modems.
•
The example below demonstrates how to enter port configuration mode for a single port on the Cisco AS5800.
AS5800# configure terminalEnter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.AS5800(config)# port 1/3/1AS5800(config-port)#•
The example below demonstrates how to enter port configuration mode for a range of ports on the Cisco AS5800.
AS5800# configure terminalEnter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.AS5800(config)# port 1/3/1 1/3/18AS5800(config-port)#Port Configuration Mode Commands
The following commands are available in port configuration mode:
•
busyout—This command gracefully disables a port by waiting for the active services on the specified ports to terminate. Use the no form of this command to re-enable the ports. This replaces the modem busyout command.
•
shutdown—This command clears active calls on the specified ports. No more calls can be placed on the port. The SPE state is changed to the Out-of-Service state. The state of the SPEs are reflected in the show spe command display. Use the no form of this command to re-enable the ports. This command replaces the modem shutdown command.
Managing SPEs
This section describes how to manage SPEs by setting the SPE country code, clearing the SPEs, entering SPE configuration mode, upgrading the SPE firmware, and performing busyout on SPEs.
SPE Country
Enter this global configuration mode command to specify the country to set the UPC parameters (including country code and encoding) for UPCs. The default is usa if the access server is configured with T1 interfaces and e1-default if the access server has E1 interfaces. Use the no form of this command to set the country code to the default of domestic.
Note
All sessions on all slot cards in all slots must be IDLE (no calls are active) for this command to execute.
A list of all supported countries is displayed in the help file. This replaces the modem country command.
•
The command below sets the country code to E1 default.
AS5800(config)# spe country e1-defaultSPE Configuration Mode
SPE configuration mode allows the user to enter the SPE configuration mode, which is similar to the line configuration mode. The user can configure an SPE by specifying a slot and an SPE associated with the slot or, the user can choose to configure a range of SPEs by specifying the first & last SPE in the range.
•
The example below demonstrates how to enter SPE configuration mode on the Cisco AS5800.
AS5800# config tEnter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.AS5800(config)# spe 1/1 1/18AS5800(config-SPE)#SPE Configuration Mode Commands
The following commands are available in SPE configuration mode:
•
firmware location filename—This command allows the user to upgrade firmware for SPEs after the new SPE firmware image. This command cannot be performed on the SPEs that are in Bad state. For further information on firmware upgrades, see the "Upgrading SPE Firmware and Cisco IOS Images" section.
•
firmware upgrade busyout | download-maintenance | reboot—This command allows the user to specify the upgrade method. Three methods of upgrade are available. Reboot requests the NAS to upgrade firmware at the next reboot. Busyout waits until all calls are terminated on a SPE before upgrading the SPE to the designated firmware. Download-maintenance upgrades the firmware during the download maintenance time. For further information on firmware upgrades, see the "Upgrading SPE Firmware and Cisco IOS Images" section.
•
busyout—This command gracefully disables an SPE by waiting for all the active services on the specified SPE to terminate. If there are active ports on the specified SPE, the BusyoutPending state is assigned to the SPE and the same will be reflected in the show SPE command. When all calls terminate on the BusyoutPending SPE, the state of the SPE is changed to Out-of-Service. Auto-diagnostic test, and firmware upgrade functions can be performed while SPEs are in OutofService state. This implies SPEs that are in Busyout state can transition to Bad state because they failed auto-diagnostic test or firmware upgrade. User actions are logged into syslog. Additionally, shutdown will override busyout. Use the no form of this command to re-enable the SPEs.
•
shutdown—This command clears active calls on all ports on the SPE. No more calls can be placed on these ports. The SPE state is changed to the Out-of-Service state. The state of the SPEs are reflected in the show spe command display. Use the no form of this command to re-enable the ports. This command replaces the modem shutdown command.
Troubleshooting
This section describes how to perform diagnostic testing on installed ports or SPEs, test two ports back-to-back, disable ports from service, and recover a port that is frozen.
Configure SPE Self Tests
To perform self-diagnostic testing on all the installed ports during the system's initial startup or rebooting process, or during service, enter the following command in global configuration mode [the prompt is displayed as AS5800(config)#]:
•
modem autotest—Perform back to back diagnostic testing for all ports.
The results of the SPE self test are displayed in the Status column of the output from the show spe modem and show spe modem active commands. Ports that pass the diagnostic test are marked as Idle, Busy, Downloading, and Reset, and are put into service. Ports that fail the diagnostic test are marked as Bad, and are not put into service or tested again until they are no longer marked as Bad. If all the ports of an SPE are bad, the corresponding SPE is also marked bad. These ports cannot be used for call connections. Depending on how many ports are present and not marked Bad, this diagnostic test may take from 5 to 15 minutes to complete. You may perform additional testing on an inoperative port by executing the test modem back-to-back command. The no port modem autotest command disables testing.
You may additionally configure the following options:
•
modem autotest minimum ports —Define the minimum number of free ports available for autotest to begin.
•
modem autotest time hh:mm interval — Enable autotesting time and interval.
Test Two Ports Back-to-Back
When a port has tested as being Bad, you may perform additional testing by conducting a series of internal back-to-back connections and data transfers between two ports. All port test connections occur inside the access server. For example, if mobile users cannot dial into port 1/2/5 (which is the sixth port on the UPC in the second chassis slot oof shelf 1), attempt a back-to-back test with port 1/2/5 and a known-functioning port such as port 1/2/6.
Enter the following command in enable mode (the prompt is displayed as 5800#) to perform internal back-to-back port tests between two ports:
•
test modem back-to-back shelf/slot/port shelf/slot/port size—Perform internal back-to-back port tests between two ports, sending test packets of the specified size.
You might need to enable this command on several different combinations of ports to determine which one is not functioning properly. A pair of operable ports successfully connect and complete transmitting data in both directions. An operable port and an inoperable port do not successfully connect with each other.
A sample back-to-back test might look like the following:
AS5800# test modem back-to-back 1/6/7 1/6/100AS5800#.Feb 10 16:56:19.536: %PM_MODEM_MAINT-5-B2BCONNECT: Modems (1/6/07) and (1/6/100) connected in back-to-back test: CONNECT33600/V34/LAP.Feb 10 16:56:25.708: %PM_MODEM_MAINT-5-B2BMODEMS: Modems (1/6/100) and (1/6/07) completed back-to-back test: success/packets = 200/200If you attempt a back to back test on a port that is in use, the output will resemble the following example:
AS5800# test modem back-to-back 1/6/7 1/6/100Repetitions (of 10-byte packets) [1]: 100Modem 1/6/07 is currently busy, Back-to-back Test will be delayed.A port that has been confirmed to have problems can often be fixed using the clear spe command. For more information, see the "Clear an SPE" section.
Disable a Port from Dial-Up Services
To disable ports from dialing or answering calls, enter one of the following commands in port configuration mode [the prompt is displayed as AS5800(config-port)#]:
•
busyout—Gracefully disable a port from dial-up services.
•
shutdown—Abruptly shut down a port from dial-up services.
The busyout command is not executed until the active port is idle. No active connections are interrupted when you use this command. In contrast, the shutdown command immediately terminates all active connections on the specified port. The resulting port status for both these commands is the same. Enable the no form of these commands to restore a port for dial-up services.
You can still configure the following commands on a disabled port:
•
test modem back-to-back
•
clear port
You may also disable ports on specified SPEs in SPE configuration mode [the prompt is displayed as AS5800(config-SPE)#]. Some problems with ports require a reload of SPE firmware, and all ports on an SPE will need to be out of service to reload the firmware.
SPE Recovery
Configure automatic recovery (removal from service and reloading of SPE firmware) of ports on an SPE at any available time from global configuration mode as shown [the prompt is displayed as 5800(config)#]:
•
spe recovery <disable | recover> port-threshold num-failures}
When an SPE port fails to connect for a certain number of consecutive times, it indicates that a problem exists in a specific part or the whole of SPE/firmware. Such SPEs have to be recovered by downloading firmware. Any port failing to connect num-failures times will be moved to a state based on port-action, where you can choose to disable (mark the port as Bad) or recover the port when the SPE is in IDLE and has no active calls. The default for num-failures is 30.
You may also schedule recovery using the spe download maintenance configuration command.
SPE Download Maintenance
Configure a scheduled recovery of SPEs from global configuration mode as shown [the prompt is displayed as 5800(config)#]:
•
spe download maintenance time hh:mm | stop-time hh:mm | max-spes num-of-spes | window time-period | expired-window {disable | drop-call | reschedule
Download maintenance starts at time, steps through all the SPEs that need recovery and SPEs that need a firmware upgrade and starts maintenance on max-spes at a time. It waits for the window delay time for all the ports on the SPE to become inactive before moving the SPE to the Idle state. It will download firmware immediately after the SPE moves to idle. If the ports are still in use by the end of (window), depending on the expired-window setting, the port marked for recovery can be set to be moved to the disabled state by choosing the disable option, connections on the SPE ports will be shutdown and the firmware will downloaded by choosing the drop-call option, or the firmware download is rescheduled to the next download maintenance time by choosing the reschedule option. This process continues until the number of SPEs under maintenance are below max-spes, or until stop-time (if set), or until all SPEs marked for recovery or upgrade have had their firmware reloaded.
Clear an SPE
The clear spe Enable Mode (also called Privileged EXEC Mode) command allows the user to manually recover a port that is frozen in a suspended state. This command causes the firmware configured for that SPE to be downloaded to the specified SPE or the range of SPEs and Power on Self Test (POST) to be executed. This command can be executed regardless of the state of the SPEs. All active ports running on the SPE are prematurely terminated and messages are logged into the appropriate log. This replaces the clear modem command.
The following example shows a coldstart on SPE 1 on slot 1.
AS5800# clear spe 1/1/1AS5800# Are you sure you want to clear SPE 1/1/1(Y/N)? YUpgrading SPE Firmware and Cisco IOS Images
Cisco IOS Release 12.1(2)XD or later is required for using UPCs on the Cisco AS5800. Matching Cisco IOS images are needed for both the router shelf and the dial shelf. The required images should have been shipped with your UPC, and the Cisco IOS software may be upgraded using the same instructions as are used for upgrading unbundled firmware files.
At startup, UPCs copy a Cisco IOS software-compatible version of SPE firmware to the installed SPEs. By default, the SPE firmware version bundled with the current version of the Cisco IOS is loaded, but the SPEs may be configured to use unbundled SPE firmware files.
Note
You do not have to take any action to use the pre-installed version of SPE firmware with new systems using Cisco IOS Release 12.1(2)XD or later.
You can acquire new SPE firmware in several ways:
•
Cisco periodically releases new SPE firmware versions (with bug fixes or new port features) that improve your system's overall performance.
•
Cisco also might ship SPE firmware on diskette with spare boards or offer SPE firmware for purchase with spare boards.
•
SPE firmware is also available on the Cisco Software Center.
After you have the new firmware, you can configure different firmware versions onto individual SPEs or ranges of SPEs on a UPC. You can also configure different upgrade methods.
This section describes how to upgrade SPE firmware handling your access server ports by:
1.
Understanding the SPE firmware scenarios possible for your access server.
2.
Choosing an upgrade strategy.
3.
Finding out the SPE firmware version installed on your access server.
4.
Upgrading the SPE firmware.
How to Obtain SPE Firmware
You can obtain SPE firmware in one of two ways:
•
Bundled in regular Cisco IOS releases. See "Using the SPE Firmware Bundled with Cisco IOS Software" on page 24.
•
Unbundled from Cisco Connection Online (CCO) or supplied on diskette. This can be either a more up-to-date version of SPE firmware released before the next Cisco IOS release (when the SPE firmware will be bundled with the Cisco IOS release), or a special version of SPE firmware shipped with a new board. See "Upgrading SPE Firmware from the Cisco CCO TFTP Server" and "Upgrading SPE Firmware from Diskettes" for details.
Important Upgrade Commands
There are several commands you use to upgrade SPE firmware. For examples on using the commands, see "Upgrading SPE Firmware from the Cisco CCO TFTP Server," "Upgrading SPE Firmware from Diskettes," and "Using the SPE Firmware Bundled with Cisco IOS Software" on page 24.
•
Use the copy tftp flash filename command to copy any version of SPE firmware (no matter how it is obtained) into system Flash memory. You can store several versions of the SPE firmware in system Flash memory under different filenames.
•
Use the firmware location filename SPE configuration command to transfer a specified version (filename) of SPE firmware from system Flash memory to the SPEs named upon entering SPE configuration mode.
•
Use the firmware upgrade busyout | download-maintenance | reboot SPE configuration command to configure when the file named in the firmware location filename command will be loaded to the SPEs. Three methods of upgrade are available. Reboot request the NAS to upgrade firmware at the next reboot. Busyout waits until all calls are terminated on a SPE before upgrading the SPE to the desired firmware. Recovery requests firmware download as configured by the recovery method command (see "SPE Recovery" section).
Note
The copy ios-bundled command is not necessary with UPCs. By default, the version of SPE firmware bundled with the Cisco IOS software release transfers to all SPEs not specifically configured for a different SPE firmware file.
Choosing an Update Strategy
Because of multiple versions of SPE firmware and the way Cisco IOS software processes these versions, Cisco suggests that you choose one of the following two strategies:
•
Always allow Cisco IOS software to select the version of SPE firmware.
•
Always control the version of SPE firmware used by the slot cards, independent of Cisco IOS software selections.
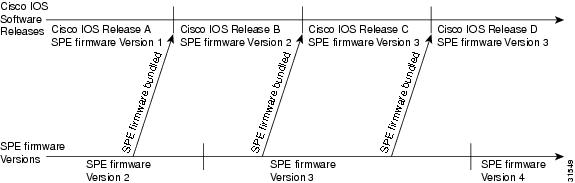
To help with the decision, Figure 3 shows a hypothetical release process. Using the SPE firmware bundled with Cisco IOS software is the easier strategy and enables you to take advantage of new SPE firmware whenever you upgrade your Cisco IOS software. You can control the SPE firmware by using the copy command as discussed later.
Figure 3 Release Timeline for Cisco IOS Software and SPE Firmware
SPE Firmware Scenarios
Table 5 provides scenarios that can occur when you upgrade Cisco IOS software or SPE firmware.
Table 5 Cisco IOS and SPE firmware upgrade scenarios
Step 1
You receive a new access server from the Cisco factory.
•
No action needed. The factory loads and maps a compatible version of SPE firmware.1
Step 2
You update Cisco IOS software, and you decide to use the version of SPE firmware selected by Cisco IOS software.
•
Update Cisco IOS software.
•
No further action needed—Cisco IOS software automatically downloads either its bundled version or a mapped version from system Flash memory.2
Step 3
You update Cisco IOS software, and you decide not to use the SPE firmware selected by Cisco IOS software.
•
Update Cisco IOS software.
•
Copy the desired version of SPE firmware file to system Flash memory, then configure the desired SPEs to use the firmware. See "Copy the SPE Firmware from Your PC to the SPEs," later in this document, for details.
Step 4
The SPEs are running a version of SPE firmware from system Flash memory that is different than the version bundled with Cisco IOS software. You decide to revert to the bundled version.
•
Use the no form of the firmware filename SPE configuration command to revert to the bundled image.3
Step 5
Cisco releases new SPE firmware, which is a later version than the version currently running on the SPEs. You decide to use Cisco's newest SPE firmware.4
•
Copy the desired version of SPE firmware file to system Flash memory, then configure the SPEs to use that firmware file. See "Copy the SPE Firmware File from Local TFTP Server to the SPEs," later in this document, for details.
1 To find out the version of SPE firmware in your system, use the show spe version command. This command displays the versions running on the SPEs.
2 In part, Cisco IOS software bases this decision on the last copy command issued.
3 The copy ios-bundled command is not necessary with UPCs. By default, the version of SPE firmware bundled with the Cisco IOS software release transfers to all SPEs not specifically configured for a different SPE firmware file.
4 Cisco might ship this SPE firmware on a diskette packed with the spare carrier card.
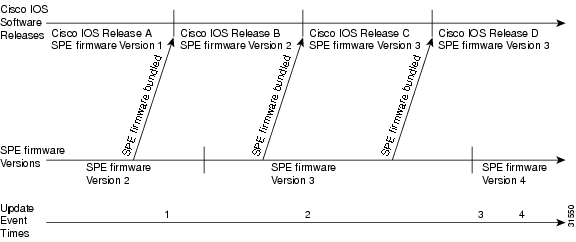
Figure 4 shows a location on the release timeline where updates might take place, and Table 6 explains the resulting versions of Cisco IOS software and SPE firmware.
Figure 4 Release Timeline for Cisco IOS Software and SPE Firmware
Table 6 Cisco IOS and SPE firmware results
Cisco IOS Software
and SPE FirmwareStep 1
You upgrade Cisco IOS software to Release B.
•
If there is no previous copy command (Cisco IOS software uses the bundled version).
•
If invalid mapping (Cisco IOS software uses the bundled version).
•
If last copy command was copy flash modem and SPE firmware Version 1 was specified.
•
Cisco IOS Release B
SPE firmware Version 2•
Cisco IOS Release B
SPE firmware Version 2•
Cisco IOS Release B
SPE firmware Version 1Step 2
You upgrade Cisco IOS software to Release C. (Cisco IOS software uses mapping from last copy command at Time 1).1
Cisco IOS Release C
SPE firmware Version 1Step 3
New SPE firmware Version 4 is released, you copy the file to system Flash memory, enter copy flash modem, and specify SPE firmware Version 4.
Cisco IOS Release C
SPE firmware Version 4Step 4
You upgrade Cisco IOS software to Release D.
Cisco IOS Release D
SPE firmware Version 4
1 This example assumes the last copy command was copy flash modem, and SPE firmware Version 1 was specified.
Displaying SPE Firmware Versions
Use the show spe version command to list the versions of SPE firmware running on the SPEs, residing in system Flash memory, and bundled with Cisco IOS software. This will help you decide if you need to change the version running on the modems.
The following example shows an example of the show SPE command for a system with one 324 universal port card.
AS5800# show spe versionAS5800#show spe versionIOS-Bundled Default Firmware-Filename Version Firmware-Type===================================== ======= =============system:/ucode/np_spe_firmware1 0.6.6.9 SPE firmwareOn-Flash Firmware-Filename Version Firmware-Type========================== ======= =============slot0:np.spe_36 0.6.6.5 SPE firmwareSPE-# SPE-Type SPE-Port-Range Version UPG Firmware-Filename1/04/00 CSMV6 0000-0005 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled default1/04/01 CSMV6 0006-0011 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled default1/04/02 CSMV6 0012-0017 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled default1/04/03 CSMV6 0018-0023 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled default1/04/04 CSMV6 0024-0029 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled default1/04/05 CSMV6 0030-0035 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled default1/04/06 CSMV6 0036-0041 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled default1/04/07 CSMV6 0042-0047 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled default1/04/08 CSMV6 0048-0053 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled default1/04/09 CSMV6 0054-0059 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled default1/04/10 CSMV6 0060-0065 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled default...1/04/30 CSMV6 0180-0185 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled default1/04/31 CSMV6 0186-0191 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled default1/04/32 CSMV6 0192-0197 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled default1/04/33 CSMV6 0198-0203 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled default1/04/34 CSMV6 0204-0209 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled default1/04/35 CSMV6 0210-0215 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled default1/04/36 CSMV6 0216-0221 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled default1/04/37 CSMV6 0222-0227 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled default1/04/38 CSMV6 0228-0233 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled default1/04/39 CSMV6 0234-0239 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled default1/04/40 CSMV6 0240-0245 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled default1/04/41 CSMV6 0246-0251 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled default1/04/42 CSMV6 0252-0257 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled default1/04/43 CSMV6 0258-0263 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled default1/04/44 CSMV6 0264-0269 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled default1/04/45 CSMV6 0270-0275 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled default1/04/46 CSMV6 0276-0281 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled default1/04/47 CSMV6 0282-0287 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled default1/04/48 CSMV6 0288-0293 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled default1/04/49 CSMV6 0294-0299 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled default1/04/50 CSMV6 0300-0305 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled default1/04/51 CSMV6 0306-0311 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled default1/04/52 CSMV6 0312-0317 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled default1/04/53 CSMV6 0318-0323 0.6.6.9 N/A ios-bundled defaultUpgrading SPE Firmware from the Cisco CCO TFTP Server
Upgrading SPE firmware from the Cisco CCO TFTP server is a two-step process:
•
Downloading the SPE firmware from Cisco CCO TFTP server to a local TFTP server
•
Copying the SPE firmware file to the access server and SPEs
Note
Cisco IOS software contains bundled SPE firmware, which can differ from the version of SPE firmware you download. For more information about how Cisco IOS software processes multiple SPE firmware versions, refer to the earlier sections "Choosing an Update Strategy" on page 10 and "SPE Firmware Scenarios" on page 11.
Download SPE Firmware from the Cisco CCO TFTP Server to a Local TFTP Server
Note
You must be a registered Cisco user to log in to Cisco's Software Center.
You can download software from the Cisco Systems CCO TFTP server using an Internet browser or using an FTP application. Both procedures are described.
Note
To download SPE firmware from CCO to a PC and then upgrade the SPE firmware to an access server connected to your PC via an Ethernet hub, you need to set up a TFTP application on your PC, establish a HyperTerminal session, and make sure your PC and access server are correctly connected and talking before downloading the SPE firmware from CCO. All these procedures are described in "Upgrading SPE Firmware from Diskettes," later in this document.
Using an Internet Browser
Step 1
Launch an Internet browser.
Step 2
Bring up Cisco's Software Center home page at the following URL (this is subject to change without notice):
http://www.cisco.com/kobayashi/sw-center/
Step 3
Click Access Products (under Cisco Software Products) to open the Access Products window.
Step 4
Click Cisco AS5800 Series Software.
Step 5
Click the SPE firmware you want and download it to your workstation or PC. For example, to download SPE firmware for the NextPort, click Download NextPort Images.
Step 6
Click the SPE firmware file you want to download, and then follow the remaining download instructions. If you are downloading the SPE firmware file to a PC, make sure you download it to the c:\tftpboot directory; otherwise, the download process will not work.
Step 7
When the SPE firmware is downloaded to your workstation, transfer the file to a TFTP server in your LAN using a terminal emulation software application.
Step 8
When the SPE firmware is downloaded to your workstation, transfer the file to a TFTP server somewhere in your LAN using a terminal emulation software application.
Using an FTP Application
Note
The directory path leading to the SPE firmware files on cco.cisco.com is subject to change without notice. If you cannot access the files using an FTP application, try the Cisco Systems URL http://www.cisco.com/kobayashi/sw-center/.
Step 1
Log in to the Cisco CCO FTP server, called cco.cisco.com:
terminal> ftp cco.cisco.comConnected to cio-sys.cisco.com.220-220- Cisco Connection Online | | Cisco Systems, Inc.220- Email: cco-team@cisco.com ||| ||| 170 West Tasman Drive220- Phone: +1.800.553.2447 .:|||||:..:|||||:. San Jose, CA 95134220-220- NOTE: As of February 1,1997 ftp.cisco.com will now point to this220- service. Please be advised. To use the former ftp.cisco.com after220- February 1, connect to ftpeng.cisco.com220-220- You may login with:220- + Your CCO username and password, or220- + A special access code followed by your e-mail address, or220- + "anonymous" followed by your e-mail address for guest access.220-220 cio-sys FTP server (CIOESD #103 Sun Dec 15 14:43:43 PST 1996) ready.Step 2
Enter your CCO registered username and password (for example, harry and letmein):
Name (cco.cisco.com:harry): harry331 Password required for harry.Password: letmein230-#############################################################230-# Welcome to the Cisco Systems CCO FTP server.230-# This server has a number of restrictions. If you are not familiar230-# with these, please first get and read the /README or /README.TXT file.230-# http://www.cisco.com/acs/info/cioesd.html for more info.230-#############################################################230-230- ***** NOTE: As of February 1, 1997, "cco.cisco.com", *****230- ***** "www.cisco.com" and "ftp.cisco.com" are now all *****230- ***** logical names for the same machine. *****230- ***** *****230- ***** The old "ftp.cisco.com" is an entirely *****230- ***** different machine, which is now known as *****230- ***** "ftpeng.cisco.com" or "ftp-eng.cisco.com". *****230- ***** *****230- ***** In general, "ftpeng.cisco.com" is used only for ****230- ***** distribution of Cisco Engineering-controlled *****230- ***** projects, such as beta programs, early field *****230- ***** trials, developing standards documents, etc. *****230- ***** *****230- ***** Be sure to confirm you have connected to *****230- ***** the machine you need to interact with. *****230-230- If you have any odd problems, try logging in with a minus sign (-) as230- the first character of your password. This will turn off a feature230- that may be confusing your ftp client program.230- Please send any questions, comments, or problem reports about this230- server to cco-team@cisco.com.230-230- NOTE:230- o To download files from CCO, you must be running a *passive-mode*230- capable FTP client.230- o To drop files on this system, you must cd to the /drop directory.230- o Mirrors of this server can be found at230-230- + ftp://www-europe.cisco.com European (Amsterdam)230- + ftp://www-fr.cisco.com France (Paris)230- + ftp://www-au.cisco.com Australia (Sydney)230- + ftp://www-jp.cisco.com Japan (Tokyo)230- + ftp://www-kr.cisco.com Korea (Seoul)230-230-Please read the file README230- it was last modified on Sat Feb 1 12:49:31 1997 - 163 days ago230 User harry logged in. Access restrictions apply.Remote system type is UNIX.Using binary mode to transfer files.Step 3
Specify the directory path that holds the SPE firmware you want to download. For example, the directory path for the Cisco AS5800 SPE firmware is /cisco/access/5800:
ftp> cd /cisco/access/5800250-Please read the file README250- it was last modified on Tue May 27 10:07:38 1997 - 48 days ago250-Please read the file README.txt250- it was last modified on Tue May 27 10:07:38 1997 - 48 days ago250 CWD command successful.Step 4
View the contents of the directory with the ls command:
ftp> ls227 Entering Passive Mode (192,31,7,130,218,128)150 Opening ASCII mode data connection for /bin/ls.total 2688drwxr-s--T 2 ftpadmin ftpcio 512 Jun 30 18:11 .drwxr-sr-t 19 ftpadmin ftpcio 512 Jun 23 10:26 ..lrwxrwxrwx 1 root 3 10 Aug 6 1996 README ->README.txt-rw-rw-r-- 1 root ftpcio 2304 May 27 10:07 README.txt-r--r--r-- 1 ftpadmin ftpint 377112 Jul 10 18:08 SPE-firmware.x.x.x.bin-r--r--r-- 1 ftpadmin ftpint 635 Jul 10 18:08 SPE-firmware.3.1.30.readme226 Transfer complete.Step 5
Specify a binary image transfer:
ftp> binary200 Type set to I.Step 6
Copy the SPE firmware files or Cisco IOS images from the ftp server to your local environment with the get command.
Step 7
Quit your terminal session:
ftp> quitGoodbye.Step 8
Verify you successfully transferred the files to your local directory:
server% ls -altotal 596-r--r--r-- 1 280208 Jul 10 18:08 SPE-firmware.x.x.x.binserver% pwd/auto/tftpbootStep 9
Transfer these files to a local TFTP or RCP server that your access server can access.
Copy the SPE Firmware File from Local TFTP Server to the SPEs
The procedure for copying the SPE firmware file from your local TFTP server to the UPCs is a two-step process. First, transfer the SPE firmware to the access server's Flash memory. Then, configure the SPEs to use the upgrade firmware. The upgrade will occur automatically, either as you leave configuration mode, or as specified in the configuration.
These two steps are performed only once. After you copy the SPE firmware file into Flash memory for the first time, you should not have to perform these steps again. Because the SPE firmware is configurable for individual SPEs or ranges of SPEs, the Cisco IOS software automatically copies the SPE firmware to each SPE whenever-- the access server restarts.
The following procedure assumes your terminal is connected directly to the console port on the AS5800 router shelf. Use these steps to download the NextPort SPE firmware to flash:
Step 1
Check the image in the router shelf Flash memory:
AS5800# show flashSystem flash directory:File Length Name/status1 4530624 c5800-js-mx[498776 bytes used, 16278440 available, 16777216 total]16384K bytes of processor board System flash (Read/Write)Step 2
Enter the copy tftp flash command to download the code file or IOS image from the TFTP server into the router shelf Flash memory. You are prompted for the download destination and the remote host name.
AS5800# copy tftp flashSystem flash directory:File Length Name/status1 4530624 images/c5800-js-mx[498776 bytes used, 16278440 available, 16777216 total]Address or name of remote host [255.255.255.255]? juraiSource file name? SPE-firmware.x.x.x.x.binDestination file name [SPE-firmware.x.x.x.x.bin]?Accessing file 'SPE-firmware.x.x.x.x.bin' on 255.255.255.255...Loading SPE-firmware.x.x.x.x.bin from 2.2.0.1 (via Ethernet0): ! [OK]Erase flash device before writing? [confirm] noCopy 'SPE-firmware.x.x.x.x.bin' from serveras 'SPE-firmware.x.x.x.x.bin' into Flash WITHOUT erase? [yes/no] yesLoading images/SPE-firmware.x.x.x.x.bin from 2.2.0.1 (via Ethernet0):!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!![OK - 249108/16278440 bytes]Verifying checksum... OK (0xE009)Flash device copy took 00:00:02 [hh:mm:ss]Step 3
Verify the file has been copied into the router shelf Flash memory:
AS5800# show flashSystem flash directory:File Length Name/status1 4530624 c5800-js-mz2 210104 SPE-firmware.x.x.x.x.bin[747948 bytes used, 16029268 available, 16777216 total]16384K bytes of processor board System flash (Read/Write)Step 4
Disconnect the terminal from the router shelf, and connect it to the console port on the dial shelf's dial shelf controller card.
Step 5
Enter the copy tftp flash command to download the code file from the TFTP server into the dial shelf Flash memory. You are prompted for the download destination and the remote host name.
AS5800# copy tftp flashSystem flash directory:File Length Name/status1 4530624 images/c5800-js-mx[498776 bytes used, 16278440 available, 16777216 total]Address or name of remote host [255.255.255.255]? juraiSource file name? SPE-firmware.x.x.x.x.binDestination file name [SPE-firmware.x.x.x.x.bin]?Accessing file 'SPE-firmware.x.x.x.x.bin' on 255.255.255.255...Loading SPE-firmware.x.x.x.x.bin from 2.2.0.1 (via Ethernet0): ! [OK]Erase flash device before writing? [confirm] noCopy 'SPE-firmware.x.x.x.x.bin' from serveras 'SPE-firmware.x.x.x.x.bin' into Flash WITHOUT erase? [yes/no] yesLoading images/SPE-firmware.x.x.x.x.bin from 2.2.0.1 (via Ethernet0):!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!![OK - 249108/16278440 bytes]Verifying checksum... OK (0xE009)Flash device copy took 00:00:02 [hh:mm:ss]To configure the SPEs to use an upgraded firmware file:
Step 1
Enter the enable command.
AS5800# enableStep 2
Enter your password.
Password: passwordAS5800#You are in privileged EXEC mode when the prompt changes to AS5800#
Step 3
Enter global configuration mode by typing the configure command. The example uses the terminal configuration option.
AS5800# configure terminalEnter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.AS5800(config)#You are in global configuration mode when the prompt changes to AS5800(config)#.
Step 4
Enter SPE configuration mode, which is similar to the line configuration mode. You can choose to configure a single SPE or range of SPEs by specifying the first and last SPE in the range.
AS5800(config)# spe shelf/slot/speorAS5800(config)# spe shelf/slot/spe shelf/slot/speYou are in SPE configuration mode when the prompt changes to AS5800(config-SPE)#.
Step 5
Specify the SPE firmware file in Flash memory to use the for the selected SPEs.
AS5800(config-SPE)# firmware location filenameStep 6
Specify when the SPE firmware upgrade will occur.
AS5800(config-SPE)# firmware upgrade busyout | download-maintenance | rebootStep 7
Type the exit command to exit out of SPE config mode.
AS5800(config-SPE)# exitAS5800(config)#Step 8
Press the Return key to verify your command registers, then type Ctrl-Z to return to privileged EXEC mode.
AS5800(config)# Ctrl-ZAS5800#Step 9
Save your changes when ready.
AS5800# copy running-config startup-configUpgrading SPE Firmware from Diskettes
This section describes how to copy SPE firmware from diskettes to your hard disk in a PC environment, and then upload the SPE firmware to the SPEs. The steps are similar if you are using a Macintosh or UNIX workstation.
Note
If you loaded Cisco IOS software from a feature pack CD-ROM using Router Software Loader (RSL), note that the CD contains a TFTP server program for PCs using Microsoft Windows. Run the TFTP server program from the directory where you installed the RSL program. Remember to set the root directory to the directory where the Cisco AS5800 SPE firmware is located. The RSL and the TFTP applications are also available on CCO in the software library in the Access Products section.
Copy the SPE Firmware to Your PC Hard Disk
This section describes how to copy the SPE firmware file to your hard disk in a PC environment. The steps are similar if you are using a Macintosh or a UNIX workstation.
Step 1
Insert the SPE firmware diskette into the disk drive.
Step 2
Create a folder named tftpboot at your hard disk root c:.
Step 3
Copy the SPE firmware file into the c:/tftpboot folder.
Copy the SPE Firmware from Your PC to the SPEs
If you are using a PC running Microsoft Windows, upgrading SPE firmware from a hard drive onto a Cisco AS5800 involves installing a TFTP application on your PC, connecting your PC and the access server, establishing a HyperTerminal session on your PC, pinging the PC and access server to make sure they are talking to each other, and finally, copying the SPE firmware from the PC to the access server. See the following sections for details.
Note
The steps are similar if you are using a Macintosh or a UNIX workstation.
Set Up a TFTP Application on the PC
Step 1
Install the TFTP application on the PC.
Note
You can use any TFTP or rcp application available from independent software vendors. A number of TFTP programs are also available as shareware from public sources on the World Wide Web. If you are using Microsoft Windows, you can also download a TFTP application (as zipped files) from the Cisco web site at http://www.cisco.com/public/sw-center/sw-other.shtml.
Step 2
Launch the TFTP application. You commonly do this by double-clicking the application icon or its filename.
Step 3
Set your TFTP server root directory:
•
Choose Server Root Directory from the Options menu.
•
Choose c:\tftpboot from the Drives and [...] list boxes.
•
Click OK.
CautionIf you do not select the c:\tftpboot directory as your TFTP server directory, you will not be able to perform the copy procedure. This also applies if you are using RCP on your system.
Connect your PC and the Access Server
Step 1
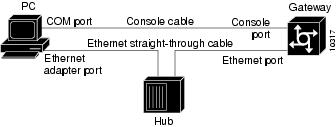
Use straight-through cables to connect the PC and access server via a 10BaseT hub, as shown in Figure 5. Also note that both Ethernet ports must have the same baseband.
Figure 5 Connecting a PC and an Access Server
Note
You can also connect your PC Ethernet port to the Cisco AS5800 Ethernet port using the 10BaseT crossover cable provided.
Step 2
Connect your PC COM port to the Cisco AS5800 console port, as shown in Figure 5.
Step 3
Make sure your PC and access server are powered ON.
Establish a HyperTerminal Session
Use the steps in this section to establish a HyperTerminal session from your local PC to the Cisco AS5800. You will use the HyperTerminal session to talk to the access server.
Step 1
In Microsoft Windows, choose Start/Programs/Accessories/HyperTerminal.
Step 2
Double-click Hypertrm.exe to display the Connection Description dialog box.
Step 3
Enter a name for your connection, for example, Console and then click OK. HyperTerminal displays the Phone number dialog box.
Step 4
Choose the COM port connecting the PC and the access server in the Connect Using list box. You have options to connect directly to one of four COM ports.
Step 5
Click OK. HyperTerminal displays the COM Properties dialog box.
Step 6
Choose these options in the COM Properties dialog box:
•
Bits per second: 9600
•
Data bits: 8
•
Parity: None
•
Stop bits: 1
•
Flow control: None
Step 7
Click OK. The HyperTerminal dialog box appears.
Step 8
Press Enter to display the AS5800# prompt.
Note
If the access server prompt does not appear, you may have selected the wrong COM port, the cable connections could be incorrect or bad, or the access server may not be powered on.
Ping the PC and Access Server
Ping the access server and the PC to make sure they are talking to each other and there are no configuration problems on your access server.
Step 1
Choose the correct Ethernet adapter connecting to the access server and note the PC's IP address:
a.
Choose Start/Run to display the Run dialog.
b.
Enter winipcfg and click OK to display the IP Configuration dialog box.
c.
Choose the PC Ethernet adapter connector used for the connection to the access server if you have more than one Ethernet adapter connector installed on your PC.
d.
Make a note of the PC IP address, and then click OK.
Note
Enter the show running config command at the AS5800# prompt to verify the access server has an IP address assigned. If the access server does not have an IP address, assign an IP address before continuing.
Step 2
In the HyperTerminal dialog box (see the previous section "Establish a HyperTerminal Session" on page 21), enter the access server enable mode (the prompt is displayed as AS5800#):
AS5800# enablePassword: passwordAS5800#Step 3
Enter the ping command with your PC's IP address.
AS5800# ping 172.16.1.1The access server displays five exclamation points (!) if everything is working and it displays five dots (.) if there is a problem. In the latter case, check the cabling between the router and the PC and check the access server configuration.
Upload SPE Firmware to the Access Server
The procedure for copying the SPE firmware file from your PC set up as a local TFTP server to the access server system Flash memory is a two-step process:
•
Transfer the SPE firmware to the access server.
•
Transfer the SPE firmware to the SPEs.
Perform these two steps only once. After you copy the SPE firmware file into system Flash memory for the first time, you should not have to perform these steps again. Because the code runs from the SPEs, the Cisco IOS software must automatically copy the SPE firmware to each SPE whenever the access server restarts.
Use these steps to download the NextPort SPE firmware to Flash memory:
Step 1
Check the image in the access server Flash memory:
AS5800# show flashSystem flash directory:File Length Name/status1 4530624 c5800-js-mx[498776 bytes used, 16278440 available, 16777216 total]16384K bytes of processor board System flash (Read/Write)Step 2
Enter the copy tftp flash command to download the code file from the TFTP server into the access server Flash memory. You are prompted for the download destination and the remote host name.
AS5800# copy tftp flashSystem flash directory:File Length Name/status1 4530624 images/c5800-js-mx[498776 bytes used, 16278440 available, 16777216 total]Address or name of remote host [255.255.255.255]? juraiSource file name? SPE-firmware.x.x.x.x.binDestination file name [SPE-firmware.x.x.x.x.bin]?Accessing file 'SPE-firmware.x.x.x.x.bin' on 255.255.255.255...Loading SPE-firmware.x.x.x.x.bin from 2.2.0.1 (via Ethernet0): ! [OK]Erase flash device before writing? [confirm] noCopy 'SPE-firmware.x.x.x.x.bin' from serveras 'SPE-firmware.x.x.x.x.bin' into Flash WITHOUT erase? [yes/no] yesLoading images/SPE-firmware.x.x.x.x.bin from 2.2.0.1 (via Ethernet0):!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!![OK - 249108/16278440 bytes]Verifying checksum... OK (0xE009)Flash device copy took 00:00:02 [hh:mm:ss]Step 3
Verify the file has been copied into the access server Flash memory:
AS5800# show flashSystem flash directory:File Length Name/status1 4530624 c5800-js-mz2 210104 SPE-firmware.x.x.x.x.bin[747948 bytes used, 16029268 available, 16777216 total]16384K bytes of processor board System flash (Read/Write)To configure the SPEs to use an upgraded firmware file:
Step 1
Enter the enable command.
AS5800# enableStep 2
Enter your password.
Password: passwordAS5800#You are in privileged EXEC mode when the prompt changes to AS5800#
Step 3
Enter global configuration mode by typing the configure command. The example uses the terminal configuration option.
AS5800# configure terminalEnter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.AS5800(config)#You are in global configuration mode when the prompt changes to AS5800(config)#.
Step 4
Enter SPE configuration mode, which is similar to the line configuration mode. You can choose to configure a single SPE or range of SPEs by specifying the first & last SPE in the range.
AS5800(config)# spe shelf/slot/speorAS5800(config)# spe shelf/slot/spe shelf/slot/speYou are in SPE configuration mode when the prompt changes to AS5800(config-SPE)#.
Step 5
Specify the SPE firmware file in flash to use the for the selected SPEs.
AS5800(config-SPE)# firmware filename location filenameStep 6
Specify when the SPE firmware upgrade will occur.
AS5800(config-SPE)# firmware filename upgrade busyout | download-maintenance | rebootStep 7
Type the exit command to exit out of SPE config mode.
AS5800(config-SPE)# exitAS5800(config)#Step 8
Press the Return key to verify your command registers, then type Ctrl-Z to return to privileged EXEC mode.
AS5800(config)# Ctrl-ZAS5800#Step 9
Save your changes when ready.
AS5800# copy running-config startup-configUsing the SPE Firmware Bundled with Cisco IOS Software
Use this procedure to update SPE firmware on the SPEs in your access server if you decide to use the version of SPE firmware bundled with Cisco IOS software instead of the version already mapped to your ports.
To set the SPE firmware mapping to the SPE firmware version bundled with Cisco IOS software, enter the following commands:
Step 1
Enter the enable command.
AS5800# enableStep 2
Enter your password.
Password: passwordAS5800#You are in privileged EXEC mode when the prompt changes to AS5800#
Step 3
Enter global configuration mode by typing the configure command. The example uses the terminal configuration option.
AS5800# configure terminalEnter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.AS5800(config)#You are in global configuration mode when the prompt changes to AS5800(config)#.
Step 4
Enter SPE configuration mode, which is similar to the line configuration mode. You can choose to delete the configuration for a single SPE or range of SPEs by specifying the first & last SPE in the range. The SPE firmware used by the SPEs will automatically revert to the version bundled with the current Cisco IOS image.
AS5800(config)# spe shelf/slot/speorAS5800(config)# spe shelf/slot/spe shelf/slot/speYou are in SPE configuration mode when the prompt changes to AS5800(config-SPE)#.
Step 5
Change the Specify the SPE firmware file in flash to use the for the selected SPEs.
AS5800(config-SPE)# no firmware filename location filenameStep 6
Specify when the SPE firmware upgrade will occur (if used).
AS5800(config-SPE)# firmware filename upgrade busyout | download-maintenance | rebootStep 7
Type the exit command to exit out of SPE config mode.
AS5800(config-SPE)# exitAS5800(config)#Step 8
Press the Return key to verify your command registers, then type Ctrl-Z to return to privileged EXEC mode.
AS5800(config)# Ctrl-ZAS5800#Step 9
Save your changes when ready.
AS5800# copy running-config startup-configThis process does not delete any existing SPE firmware that resides in system Flash memory in case you later want to revert to it. If you decide to delete the code from system Flash memory, remember that all files in system Flash memory will be deleted, therefore save and restore any important files (for example, the Cisco IOS software image).
Note
If the new Cisco IOS image contains the same SPE firmware as the old one, no new code will be downloaded to the SPEs.