Feedback Feedback
|
Table Of Contents
Cisco 12006 and Cisco 12406 Router Power System Procedures Guide
Power Supply and PDU Compatibility
Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Removing and Replacing an AC PEM
Troubleshooting the AC Power Supply Installation
Removing and Replacing an AC PDU
Removing and Replacing a DC PEM
Troubleshooting the DC Power Supply Installation
Removing and Replacing a DC PDU
Regulatory, Compliance, and Safety Information
Translated Safety Warnings and Agency Approvals
Electromagnetic Compatibility Regulatory Statements
Class A Notice for Taiwan and Other Traditional Chinese Markets
Cisco Product Security Overview
Reporting Security Problems in Cisco Products
Obtaining Technical Assistance
Cisco Technical Support and Documentation Website
Definitions of Service Request Severity
Obtaining Additional Publications and Information
Cisco 12006 and Cisco 12406 Router Power System Procedures Guide
Product Numbers: 12000/6-AC-PEM=, 12000/6-DC-PEM=, 12000/6-AC-PDU=, 12000/6-DC-PDU=, GSR6-AC-PDU=, PWR-GSR6-AC=, PWR-GSR6-DC=, GSR6-DC-PDU=
Upgrade Kits: 12000/6-AC-UP=, 12000/6-DC-UP=This publication contains removal and replacement procedures for the AC and DC power systems used with Cisco 12006 and Cisco 12406 routers.
Note
The illustrations in this guide represent both original and upgraded power supplies and PDUs shipping with the Cisco 12006 and Cisco 12406 routers. Depending on your system, these components may not look exactly like those in your chassis, but the removal and replacement procedures are essentially the same. Illustrations represent original and new models where appropriate. For clarity, most chassis covers are not shown in the illustrations.
Contents
The following sections are included in this publication:
•
Power Supply and PDU Compatibility
•
Prerequisites and Preparation
•
Removing and Replacing an AC PEM
•
Troubleshooting the AC Power Supply Installation
•
Removing and Replacing an AC PDU
•
Removing and Replacing a DC PEM
•
Troubleshooting the DC Power Supply Installation
•
Removing and Replacing a DC PDU
•
Regulatory, Compliance, and Safety Information
•
Obtaining Technical Assistance
•
Obtaining Additional Publications and Information
Power Supply and PDU Compatibility
Cisco 12006 and Cisco 12406 routers are available with either an AC or DC power supply system. The two types of power supplies for these systems are:
•
Original power supplies (rated at 1400 watts) that shipped with earlier systems
•
Enhanced capacity power supplies (rated at 1900 watts) that ship with current systems and upgrade kits
Removal and replacement procedures are the same for either type of power supply, but because of their power capacity and physical differences, you cannot mix different types of power supplies in the chassis.
CautionNewer, 1900 W DC power supplies require the upgraded PDU. You cannot install a new power supply using the old PDU. If you are replacing an old power supply with the new unit, you must perform a complete upgrade by replacing both power supplies, the PDU, and the blower module if you are required to meet NEBS extended temperature range requirements (see the "Power Supply and PDU Compatibility" section for additional information). This also means that you must shut down the router to perform the upgrade. Notify the system administrator and other appropriate personnel that all routing traffic stops while the upgrade takes place.
Before you attempt to install or replace them (Table 1), be sure you know your system power supplies and associated PDU.
Installing Upgrade Kits
When installing a power system upgrade kit, replace the following components.
•
AC power upgrade (12000/6-AC-UP=):
–
Power supplies (Removing and Replacing an AC PEM)
–
PDU (Removing and Replacing an AC PDU)
•
DC power upgrade (12000/6-DC-UP=):
–
Power supplies (Removing and Replacing a DC PEM)
–
PDU (Removing and Replacing a DC PDU)
Note
A blower upgrade (not included in the power upgrade kit) is also required to meet NEBS extended temperature range requirements. To order the blower upgrade (12000/6-BLOWER=), contact your Cisco representative.
Prerequisites and Preparation
Before you perform any of the procedures in this guide, be sure that you:
•
Read the safety and ESD-prevention guidelines in this section.
•
Ensure that you have all of the necessary tools and equipment before beginning the installation (see the "Installation Guidelines" section).
•
Have access to the following documents during the installation:
–
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco 12000 Series Router publication that shipped with the router (78-4347-xx)
–
Cisco 12006 and Cisco 12406 Router Installation and Configuration Guide
For additional information about obtaining documentation see the "Obtaining Documentation" section.
Safety Guidelines
Before you perform any procedure in this publication, review the safety guidelines in this section to avoid injuring yourself or damaging the equipment.
Safety Warnings
Safety warnings appear throughout this publication in procedures that, if performed incorrectly, may harm you. A warning symbol precedes each warning statement. The following warning is an example of a safety warning. It identifies the warning symbol and associates it with a bodily injury hazard.
Warning
This warning symbol means danger. You are in a situation that could cause bodily injury. Before you work on any equipment, be aware of the hazards involved with electrical circuitry and be familiar with standard practices for preventing accidents. To see translations of the warnings that appear in this publication, refer to the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information document that accompanies this device.
Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Many router components can be damaged by static electricity. Not exercising the proper electrostatic discharge (ESD) precautions can result in intermittent or complete component failures. To minimize the potential for ESD damage, always use an ESD-preventive antistatic wrist strap (or ankle strap) and ensure that it makes good skin contact.
Note
You should periodically check the resistance value of the ESD-preventive strap. The measurement should be between 1 and 10 megohms.
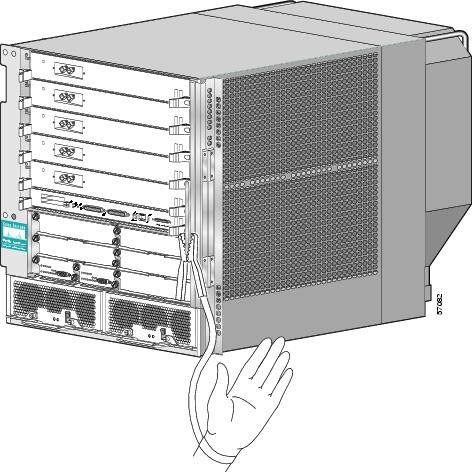
Before performing the procedures in this guide, attach an ESD-preventive strap to your wrist and connect the leash to the chassis or to another grounded, bare metal surface as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 Connecting an ESD-preventive Wrist Strap to the Chassis
Installation Guidelines
Cisco 12006 and Cisco 12406 routers support online insertion and removal (OIR) for power supplies. If you are replacing a redundant power supply, you can remove and install a power supply while the system remains powered on without causing an electrical hazard or damage to the system. This feature enables you to replace a power supply while the system maintains all routing information and ensures session preservation.
However, to maintain operational redundancy, maintain proper cooling, and meet EMI compliance standards, you must have two working power supplies installed. When you remove a failed power supply with the router in operation, perform the replacement as quickly as possible. Before you begin the removal and installation procedure, make sure you have the tools and the replacement power supply ready.
CautionYou cannot mix power supply types within the chassis. If you are replacing a 1400 W power supply from a system with a 1900 W power supply, you must replace both power supplies and the PDUs (see Table 1). You must shut down the router to perform the upgrade. Notify the appropriate personnel that all routing traffic stops while upgrades take place.
CautionRedundancy in 1400 W power systems was not a requirement and used a blank filler (MAS-GSR-PWRBLANK=) in place of a second power supply to ensure EMI compliance. New 1900 W power supplies require redundancy. You must install two power supplies (see Table 1).
Required Tools and Equipment
The following tools and equipment are required to remove and install power equipment:
•
ESD-preventive wrist strap
•
3/16-inch flat-blade screwdriver
•
3/8-inch flat-blade screwdriver
Related Documentation
The following publications contain additional information:
•
Cisco 12006 and Cisco 12406 routers Installation and Configuration Guide
•
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco 12000 Series Router
For additional information about related documentation, see the "Obtaining Documentation" section.
Removing and Replacing an AC PEM
This section contains the procedure to remove and replace an AC PEM from the chassis. Before you begin this procedure, be sure to read the "Installation Guidelines" section.
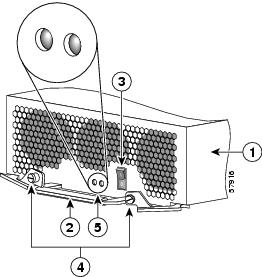
Figure 2 identifies the components of an AC power supply.
Figure 2 AC Power Supply Components
AC PEM
Captive screws/release levers
Handle
AC input/DC output status indicators
Power On/Off switch
Use the following procedure to remove and replace an AC power supply.
CautionYou cannot mix power supply types within the chassis. If you are replacing a 1400 W power supply from an older system with a new 1900 W power supply, you must replace both power supplies, the AC PDU, and the blower module if you are required to meet NEBS extended temperature range requirements (see the "Power Supply and PDU Compatibility" section for additional information). You must shut down the router to perform the upgrade. Notify the system administrator and other appropriate personnel that all routing traffic stops while upgrades take place.
Step 1
Set the power switch to the Off (0) position.
Step 2
Unplug the power supply cord from its AC outlet.
Step 3
Power off the circuit breaker assigned to that AC outlet.
Step 4
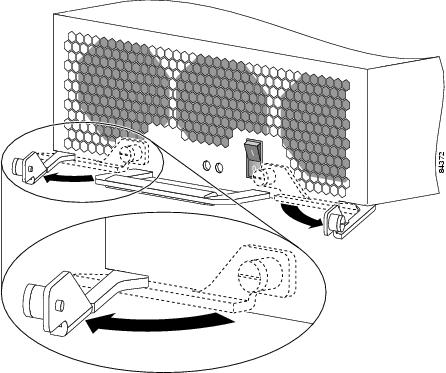
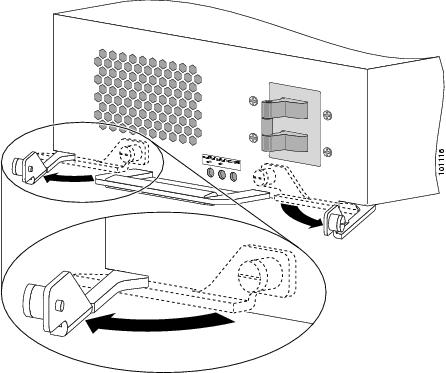
Remove the PEM from the chassis (Figure 3):
a.
Loosen the captive screw on each ejector lever.
b.
Pivot open the levers to eject the power supply.
c.
Slide the power supply out of its bay while supporting it with your other hand.
Warning
The power supply weighs approximately 14 lb (6.35 kg). Use two hands to remove the power supply.
Figure 3 Releasing the AC Power Supply
Step 5
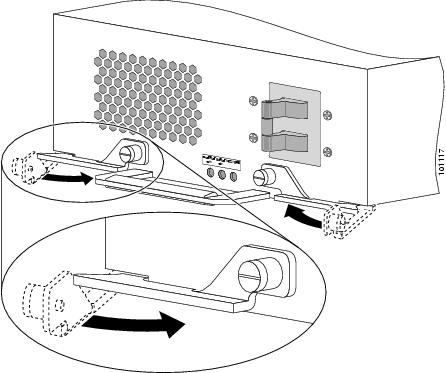
Install the new power supply (Figure 4):
a.
Slide the power supply into the bay until it mates with its backplane connector.
CautionTo prevent damage to the power shelf backplane connector, do not use excessive force when inserting the power supply into the chassis.
b.
Close the ejector levers and tighten the captive screws to securely seat the power supply to the backplane connector.
Figure 4 Seating the AC Power Supply
Step 6
Plug the power supply cable into its AC outlet.
Step 7
Power on the circuit breaker to that AC outlet.
Step 8
Set the power switch to the On (1) position.
The AC Input and DC Output power indicators on the front of the power supply should light. If the indicators do not light, see the "Troubleshooting the AC Power Supply Installation" section.
Troubleshooting the AC Power Supply Installation
Use the following procedure to troubleshoot the AC power supply if it is not operating properly after installation.
Step 1
Make sure the power supply is seated properly:
•
Eject and reseat the power supply. Make sure:
–
The captive screws on the ejector levers are tightened securely.
–
The power switch is set to the On (1) position.
Step 2
Make sure the router is powered on and that all power cords are connected properly:
•
Power cords on the back of the chassis are secured to the PDU with their retention clips.
•
Power cords at the power source end are connected to a dedicated AC power outlet.
–
Each AC power supply operating in the nominal range of 200 to 240 VAC requires a minimum service of 20 A, North America (or 13 A, international).
•
Make sure the source AC circuit breaker is switched on.
Step 3
Check the power supply status indicators:
•
AC Input (green)—Indicates that the power supply is operating normally, and the source AC voltage is within the nominal operating range of 200 VAC to 240 VAC. This indicator lights when the power supply switch is set to the On (1) position.
–
If the AC Input power indicator remains off after checking all of the power sources, replace the power supply with a spare.
–
If the spare power supply does not work, replace the PDU.
•
DC Output (green)—Indicates that the power supply is operating normally, and the output DC voltage is within the nominal operating range of -48 VDC to -60 VDC. This indicator lights when the power switch is set to the On (1) position.
If the indicator is off, toggle the power switch off and then on. If the indicator remains off after several attempts to power it on, replace the power supply with a spare.
Removing and Replacing an AC PDU
Use the following procedure to remove and replace an AC PDU. Before you begin this procedure, read the "Installation Guidelines" section.
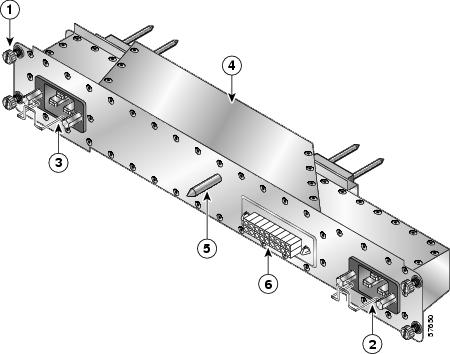
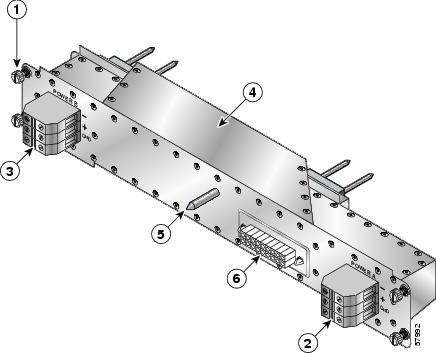
Figure 5 identifies the components of the AC PDU.
Figure 5 AC Power Distribution Unit
Captive screw
AC power distribution unit
AC power cord connector/retention clip (A)
Guide pin
AC power cord connector/retention clip (B)
Blower module connector
CautionThe system must be powered off to remove and replace the PDU. Notify the network administrator and other appropriate personnel that all routing traffic stops while replacements take place.
Step 1
Power off both power supplies by setting the power switches to the Off (0) position.
Step 2
Unplug the power supply cords from their AC outlets.
Step 3
Power off the circuit breakers assigned to the AC outlets.
Step 4
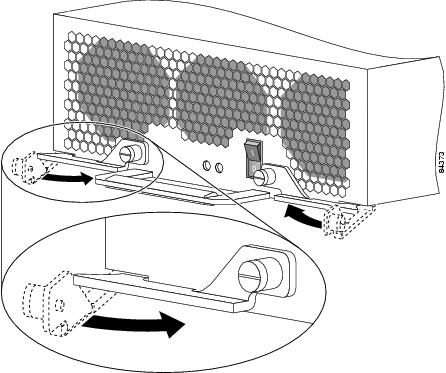
Loosen the captive screw on each ejector lever and pivot the levers open to unseat the power supply from its PDU connector (Figure 6).
•
It is not necessary to remove the power supply from its bay.
•
Repeat this step for the second power supply.
Figure 6 Unseating the AC Power Supply
Step 5
Release the retention clip and disconnect each power supply cord from the PDU (see Figure 5).
Step 6
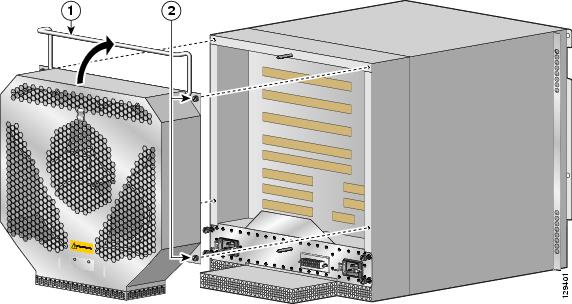
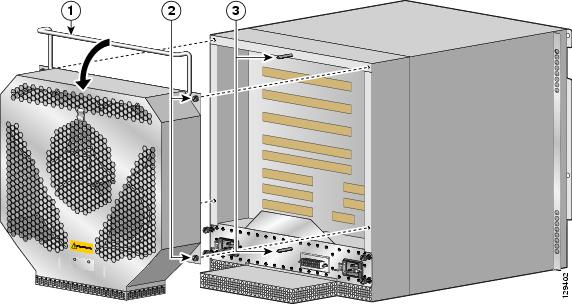
Remove the blower module (Figure 7):
a.
Lift the blower module handle to its raised (carrying) position.
b.
Loosen the (4) captive screws on the blower module.
c.
Remove the blower module by grasping it on each side and pulling it straight back from the chassis.
Figure 7 Removing the Blower Module
Step 7
Remove the PDU from the chassis (Figure 8):
a.
Loosen the (4) captive screws on the PDU.
b.
Grasp the PDU and pull it out slightly.
c.
Move the PDU to the left and pivot the right side through the opening to remove the PDU from the chassis opening.
Note
Tilting the PDU at a slight angle makes it easier to remove it from the chassis.
Figure 8 Removing the AC PDU
Step 8
Install the new PDU and tighten its (4) captive screws to secure it to the chassis.
Step 9
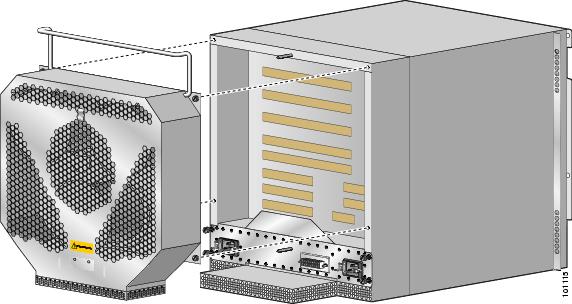
Install the blower module (Figure 9):
a.
Position the alignment holes on the blower module with the guide pins on the chassis and PDU.
b.
Slide the blower over the guide pins toward the chassis until it mates with the PDU connector.
CautionTo prevent damage to the connectors, do not use excessive force when installing the blower module.
c.
Tighten the (4) captive screws to secure the blower module to the chassis.
d.
Lower the carrying handle to its operating position.
Figure 9 Installing the Blower Module
Step 10
Reconnect the power cords to the PDU and secure them using their retention clips.
Step 11
Plug the power cords into their AC outlets.
Step 12
Power on the circuit breakers assigned to the AC outlets.
Step 13
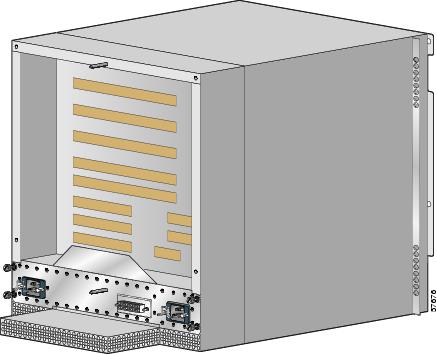
Reinstall the power supplies (Figure 10):
a.
Push the power supply into its bay until it mates with its PDU connector.
CautionTo prevent damage to the connectors, do not use excessive force when inserting the power supply into the chassis.
b.
Close the ejector levers and tighten the captive screws to securely seat the power supply to the chassis.
c.
Repeat steps a. and b. for the second power supply.
Figure 10 Seating the AC Power Supply
Step 14
Set the power switch on both power supplies to the On (1) position.
The AC Input Power and DC Output Power indicators on the power supplies should light. If the indicators do not light, see the "Troubleshooting the AC Power Supply Installation" section.
Removing and Replacing a DC PEM
This section contains the procedure to remove and replace a DC power supply from the chassis. Before you begin this procedure, read the "Installation Guidelines" section.
Figure 11 identifies the components of a DC power supply.
Figure 11 DC Power Entry Module Components
DC PEM
Captive screws/release levers
Handle
Cooling fan
Power on/off switch
DCI/DCO/RVP status indicators
Use the following procedure to remove and replace a DC power supply.
CautionYou cannot mix power supply types within the chassis. If you are replacing a 1400 W power supply with a 1900 W power supply, you must replace both power supplies, the DC PDU, and the blower module if you are required to meet NEBS extended temperature range requirements (see the "Power Supply and PDU Compatibility" section for additional information). You must shut down the router to perform the upgrade. Notify the system administrator and other appropriate personnel that all routing traffic will stop while the upgrade takes place.
Step 1
Set the power switch to the Off position.
Step 2
Power off the circuit breaker assigned to the power supply.
Warning
To ensure that power remains off while you are performing this procedure, tape the circuit breaker switch in the Off (0) position.
Step 3
Remove the power supply from the chassis (Figure 12):
a.
Loosen the captive screw on each ejector lever.
b.
Pivot the levers open to release the power supply from its bay.
c.
Slide the power supply out of its bay while supporting it with your other hand.
Warning
The power supply weighs approximately 10 lb (4.5 kg). Use two hands to remove the power supply.
Figure 12 Releasing the DC Power Supply
Step 4
Install the new power supply:
a.
Slide the power supply into the bay until it mates with its backplane connector.
CautionTo prevent damage to the power shelf backplane connector, do not use excessive force when inserting the power supply into the chassis.
b.
Close the ejector levers and tighten the captive screws to securely seat the power supply to the backplane connector (Figure 13).
Figure 13 Seating the DC Power Supply
Step 5
Power on the circuit breaker.
Step 6
Set the power switch to the On position.
The DCI (DC Input) and DCO (DC Output) power indicators on the front of the power supply should light. If the indicators do not light, or the RVP (Reversed Polarity) indicator is on, see the "Troubleshooting the DC Power Supply Installation" section.
Troubleshooting the DC Power Supply Installation
Use the following procedure to troubleshoot the DC power supply if it is not operating properly after installation.
Step 1
Make sure the power supply is seated properly:
•
Eject and reseat the power supply.
–
The captive screw on the ejector lever are tightened securely.
–
The power switch is set to the On (1) position.
Step 2
Make sure the router is powered on and that all power cables are connected properly:
•
Power leads are securely connected to the power connector block on the PDU.
•
Power cables are securely connected at the DC source connection.
•
The source DC circuit breaker is turned on.
Step 3
Check the power supply status indicators:
•
DCI (green)—Indicates that the power supply is operating normally, and the source DC input voltage is within the nominal operating range of -40.5VDC to -75VDC. This indicator should light when the power supply switch is set to the On (1) position.
–
If the DCI indicator remains off after checking all of the power sources, replace the power supply with a spare.
–
If the spare power supply does not work, replace the PDU.
•
DCO (green)—Indicates that the PEM is operating normally, and the source DC output voltage is within the nominal operating range of -48 to -60 VDC. This indicator should light when the power switch is set to the On (1) position.
If the indicator is off, toggle the power switch off and then on. If the indicator remains off after several attempts to power it on, replace the power supply with a spare.
•
RVP (amber)—Indicates the input wiring is incorrect at the PDU power connection block.
Correct wiring to the DC power connector block (see Figure 20).
Removing and Replacing a DC PDU
Use the following procedure to remove and replace a DC PDU. before beginning this procedure, read the "Installation Guidelines" section.
Figure 14 identifies the components of the DC PDU.
Figure 14 DC Power Distribution Unit
Captive screw
DC power distribution unit
DC power connector block (A)
Guide pin
DC power connector block (B)
Blower module connector
CautionThe system must be powered off to remove and replace the PDU. Notify the network administrator and other appropriate personnel that all routing traffic will stop while the replacement takes place.
Step 1
Power off both power supplies by setting their power switches to the Off (0) position (see Figure 11).
Step 2
Power off the circuit breakers assigned to the power supplies.
Warning
To ensure that power remains off while you are performing this procedure, tape the circuit breaker switches in the Off (0) position.
Step 3
Loosen the captive screw on each ejector lever and pivot the levers open to unseat the power supply from its PDU connector (Figure 15).
•
It is not necessary to remove the power supply from its bay.
•
Repeat this step for the second power supply.
Figure 15 Unseating the DC Power Supply
Step 4
Remove the blower module (Figure 16):
a.
Lift the blower module handle to its raised (carrying) position.
b.
Loosen the (4) captive screws on the blower module.
c.
Remove the blower module by grasping it on each side and pulling it straight back from the chassis.
Figure 16 Removing the Blower Module
Step 5
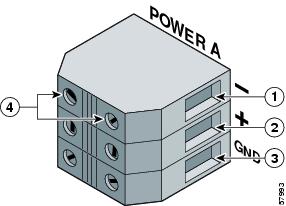
Disconnect the DC power leads from the PDU power connector blocks in the following order (Figure 17):
a.
Negative lead from the top port.
b.
Positive lead from the middle port.
c.
Ground lead from the bottom port.
d.
Repeat these steps for the second power connector block.
Warning
To prevent injury and damage to the equipment, always remove the source DC power leads and ground from the power shelf terminals in the following order: (a) negative (-), (b) positive (+), (c) ground.
Figure 17 Disconnecting the DC Power Leads
Negative terminal port
Ground terminal port
Positive terminal port
Terminal port connector screws
Step 6
Remove the PDU from the chassis (Figure 18):
a.
Loosen the (4) captive screws on the PDU.
b.
Grasp the PDU and pull it out slightly.
c.
Move the PDU to the left and pivot the right side through the opening to remove the PDU from the chassis.
Note
Tilting the PDU at a slight angle makes it easier to remove it from the chassis.
Figure 18 Removing the DC PDU
Step 7
Install the new PDU and tighten its (4) captive screws to secure it to the chassis.
Step 8
Install the blower module (Figure 19):
a.
Position the alignment holes on the blower module with the guide pins on the chassis and PDU.
b.
Slide the blower over the guide pins toward the chassis until it mates with the backplane connector.
CautionTo prevent damage to the connectors, do not use excessive force when installing the blower module.
c.
Tighten the (4) captive screws to secure the blower module to the chassis.
d.
Lower the carrying handle to its operating position.
Figure 19 Installing the Blower Module
Step 9
Reconnect the DC power leads to the PDU power connector blocks in the following order (Figure 20):
a.
Ground lead to the bottom port.
b.
Positive lead to the middle port.
c.
Negative lead to the top port.
d.
Repeat these steps for the second power connector block.
Warning
To prevent injury and damage to the equipment, always attach the ground and source DC power leads to the power block connector in the following order: (a) ground to ground, (b) positive (+) to positive (+), (c) negative (-) to negative (-).
Figure 20 Disconnecting the DC Power Leads
Negative terminal port
Ground terminal port
Positive terminal port
Terminal port connector screws
Step 10
Power on the circuit breakers assigned to the power supplies.
Step 11
Reinstall the power supplies:
a.
Push the power supply into its bay until it mates with its PDU connector.
CautionTo prevent damage to the connectors, do not use excessive force when inserting the power supply into the chassis.
b.
Close the ejector levers and tighten the captive screws to securely seat the power supply to the chassis (Figure 21).
c.
Repeat steps a. and b. for the second power supply.
Figure 21 Seating a DC Power Supply
Step 12
Power on the power supplies.
The output power OK and input power OK indicators on the power supplies should light. If the indicators do not light, see the "Troubleshooting the DC Power Supply Installation" section.
Regulatory, Compliance, and Safety Information
This section includes regulatory, compliance, and safety information in the following sections:
•
Translated Safety Warnings and Agency Approvals
•
Electromagnetic Compatibility Regulatory Statements
Translated Safety Warnings and Agency Approvals
The complete list of translated safety warnings and agency approvals is available in the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for Cisco 12000 Series Routers publication (Document Number 78-4347-xx).
Electromagnetic Compatibility Regulatory Statements
FCC Class A Compliance
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio-frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference, in which case users will be required to correct the interference at their own expense.
Modifying the equipment without Cisco authorization may result in the equipment no longer complying with FCC requirements for Class A digital devices. In that event, your right to use the equipment may be limited by FCC regulation and you may be required to correct any interference to radio or television communication at your own expense.
You can determine whether your equipment is causing interference by turning it off. If the interference stops, it was probably caused by the Cisco equipment or one of its peripheral devices. If the equipment causes interference to radio or television reception, try to correct the interference by using one or more of the following measures:
•
Turn the television or radio antenna until the interference stops.
•
Move the equipment to one side or the other of the television or radio.
•
Move the equipment farther away from the television or radio.
•
Plug the equipment into an outlet that is on a different circuit from the television or radio. (That is, make certain the equipment and the television or radio are on circuits controlled by different circuit breakers or fuses.)
CISPR 22
This apparatus complies with CISPR 22/EN55022 Class B radiated and conducted emissions requirements.
Canada
English Statement of Compliance
This class A digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
French Statement of Compliance
Cet appareil numérique de la classe A est conforme à la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
Europe—EU
This apparatus complies with EN55022 Class B and EN55024 standards when used as ITE/TTE equipment, and EN300386 for Telecommunications Network Equipment (TNE) in both installation environments, telecommunication centers and other indoor locations.
VCCI Class A Notice for Japan
Class A Notice for Hungary
Class A Notice for Taiwan and Other Traditional Chinese Markets
Class A Notice for Korea
Obtaining Documentation
Cisco documentation and additional literature are available on Cisco.com. Cisco also provides several ways to obtain technical assistance and other technical resources. These sections explain how to obtain technical information from Cisco Systems.
Cisco.com
You can access the most current Cisco documentation at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport
You can access the Cisco website at this URL:
You can access international Cisco websites at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/public/countries_languages.shtml
Product Documentation DVD
Cisco documentation and additional literature are available in the Product Documentation DVD package, which may have shipped with your product. The Product Documentation DVD is updated regularly and may be more current than printed documentation.
The Product Documentation DVD is a comprehensive library of technical product documentation on portable media. The DVD enables you to access multiple versions of hardware and software installation, configuration, and command guides for Cisco products and to view technical documentation in HTML. With the DVD, you have access to the same documentation that is found on the Cisco website without being connected to the Internet. Certain products also have .pdf versions of the documentation available.
The Product Documentation DVD is available as a single unit or as a subscription. Registered Cisco.com users (Cisco direct customers) can order a Product Documentation DVD (product number DOC-DOCDVD=) from the Ordering tool or Cisco Marketplace.
Cisco Ordering tool:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/partner/ordering/
Cisco Marketplace:
http://www.cisco.com/go/marketplace/
Ordering Documentation
Beginning June 30, 2005, registered Cisco.com users may order Cisco documentation at the Product Documentation Store in the Cisco Marketplace at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/marketplace/
Cisco supports documentation orders using the Ordering tool:
•
Registered Cisco.com users (Cisco direct customers) can order documentation from the Ordering tool:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/partner/ordering/
•
Instructions for ordering documentation using the Ordering tool are at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/es_inpck/pdi.htm
•
Nonregistered Cisco.com users can order documentation through a local account representative by calling Cisco Systems Corporate Headquarters (California, USA) at 408 526-7208 or, elsewhere in North America, by calling 1 800 553-NETS (6387).
Documentation Feedback
You can rate and provide feedback about Cisco technical documents by completing the online feedback form that appears with the technical documents on Cisco.com.
You can send comments about Cisco documentation to bug-doc@cisco.com.
You can submit comments by using the response card (if present) behind the front cover of your document or by writing to the following address:
Cisco Systems
Attn: Customer Document Ordering
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-9883We appreciate your comments.
Cisco Product Security Overview
Cisco provides a free online Security Vulnerability Policy portal at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/products_security_vulnerability_policy.html
From this site, you can perform these tasks:
•
Report security vulnerabilities in Cisco products.
•
Obtain assistance with security incidents that involve Cisco products.
•
Register to receive security information from Cisco.
A current list of security advisories and notices for Cisco products is available at this URL:
If you prefer to see advisories and notices as they are updated in real time, you can access a Product Security Incident Response Team Really Simple Syndication (PSIRT RSS) feed from this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/products_psirt_rss_feed.html
Reporting Security Problems in Cisco Products
Cisco is committed to delivering secure products. We test our products internally before we release them, and we strive to correct all vulnerabilities quickly. If you think that you might have identified a vulnerability in a Cisco product, contact PSIRT:
•
Emergencies — security-alert@cisco.com
An emergency is either a condition in which a system is under active attack or a condition for which a severe and urgent security vulnerability should be reported. All other conditions are considered nonemergencies.
•
Nonemergencies — psirt@cisco.com
In an emergency, you can also reach PSIRT by telephone:
•
1 877 228-7302
•
1 408 525-6532
Tip
We encourage you to use Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) or a compatible product to encrypt any sensitive information that you send to Cisco. PSIRT can work from encrypted information that is compatible with PGP versions 2.x through 8.x.
Never use a revoked or an expired encryption key. The correct public key to use in your correspondence with PSIRT is the one linked in the Contact Summary section of the Security Vulnerability Policy page at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/products_security_vulnerability_policy.htm
The link on this page has the current PGP key ID in use.
Obtaining Technical Assistance
Cisco Technical Support provides 24-hour-a-day award-winning technical assistance. The Cisco Technical Support & Documentation website on Cisco.com features extensive online support resources. In addition, if you have a valid Cisco service contract, Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC) engineers provide telephone support. If you do not have a valid Cisco service contract, contact your reseller.
Cisco Technical Support and Documentation Website
The Cisco Technical Support and Documentation website provides online documents and tools for troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. The website is available 24 hours a day, at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport
Access to all tools on the Cisco Technical Support & Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. If you have a valid service contract but do not have a user ID or password, you can register at this URL:
http://tools.cisco.com/RPF/register/register.do
Note
Use the Cisco Product Identification (CPI) tool to locate your product serial number before submitting a web or phone request for service. You can access the CPI tool from the Cisco Technical Support & Documentation website by clicking the Tools & Resources link under Documentation & Tools. Choose Cisco Product Identification Tool from the Alphabetical Index drop-down list, or click the Cisco Product Identification Tool link under Alerts & RMAs. The CPI tool offers three search options: by product ID or model name; by tree view; or for certain products, by copying and pasting show command output. Search results show an illustration of your product with the serial number label location highlighted. Locate the serial number label on your product and record the information before placing a service call.
Submitting a Service Request
Using the online TAC Service Request Tool is the fastest way to open S3 and S4 service requests. (S3 and S4 service requests are those in which your network is minimally impaired or for which you require product information.) After you describe your situation, the TAC Service Request Tool provides recommended solutions. If your issue is not resolved using the recommended resources, your service request is assigned to a Cisco engineer. The TAC Service Request Tool is located at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport/servicerequest
For S1 or S2 service requests or if you do not have Internet access, contact the Cisco TAC by telephone. (S1 or S2 service requests are those in which your production network is down or severely degraded.) Cisco engineers are assigned immediately to S1 and S2 service requests to help keep your business operations running smoothly.
To open a service request by telephone, use one of the following numbers:
Asia-Pacific: +61 2 8446 7411 (Australia: 1 800 805 227)
EMEA: +32 2 704 55 55
USA: 1 800 553-2447For a complete list of Cisco TAC contacts, go to this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport/contacts
Definitions of Service Request Severity
To ensure that all service requests are reported in a standard format, Cisco has established severity definitions.
Severity 1 (S1)—Your network is "down," or there is a critical impact to your business operations. You and Cisco will commit all necessary resources around the clock to resolve the situation.
Severity 2 (S2)—Operation of an existing network is severely degraded, or significant aspects of your business operation are negatively affected by inadequate performance of Cisco products. You and Cisco will commit full-time resources during normal business hours to resolve the situation.
Severity 3 (S3)—Operational performance of your network is impaired, but most business operations remain functional. You and Cisco will commit resources during normal business hours to restore service to satisfactory levels.
Severity 4 (S4)—You require information or assistance with Cisco product capabilities, installation, or configuration. There is little or no effect on your business operations.
Obtaining Additional Publications and Information
Information about Cisco products, technologies, and network solutions is available from various online and printed sources.
•
Cisco Marketplace provides a variety of Cisco books, reference guides, documentation, and logo merchandise. Visit Cisco Marketplace, the company store, at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/marketplace/
•
Cisco Press publishes a wide range of general networking, training and certification titles. Both new and experienced users will benefit from these publications. For current Cisco Press titles and other information, go to Cisco Press at this URL:
•
Packet magazine is the Cisco Systems technical user magazine for maximizing Internet and networking investments. Each quarter, Packet delivers coverage of the latest industry trends, technology breakthroughs, and Cisco products and solutions, as well as network deployment and troubleshooting tips, configuration examples, customer case studies, certification and training information, and links to scores of in-depth online resources. You can access Packet magazine at this URL:
•
iQ Magazine is the quarterly publication from Cisco Systems designed to help growing companies learn how they can use technology to increase revenue, streamline their business, and expand services. The publication identifies the challenges facing these companies and the technologies to help solve them, using real-world case studies and business strategies to help readers make sound technology investment decisions. You can access iQ Magazine at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/iqmagazine
or view the digital edition at this URL:
http://ciscoiq.texterity.com/ciscoiq/sample/
•
Internet Protocol Journal is a quarterly journal published by Cisco Systems for engineering professionals involved in designing, developing, and operating public and private internets and intranets. You can access the Internet Protocol Journal at this URL:
•
Networking products offered by Cisco Systems, as well as customer support services, can be obtained at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/index.html
•
Networking Professionals Connection is an interactive website for networking professionals to share questions, suggestions, and information about networking products and technologies with Cisco experts and other networking professionals. Join a discussion at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/discuss/networking
•
World-class networking training is available from Cisco. You can view current offerings at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/learning/index.html
This document is to be used in conjunction with the Cisco 12000/6Router Installation and Configuration Guide.