Feedback Feedback
|
Table Of Contents
E1 R2 Signaling for the Cisco AS5800
Configuring E1 R2 Signaling for the Cisco AS5800
E1 R2 Signaling for the Cisco AS5800
The following sections are provided:
•
Configuring E1 R2 Signaling for the Cisco AS5800
Feature Summary
E1 R2 signaling allows a Cisco AS5800 universal access server to talk to central office trunks that also use E1 R2 Signaling. Only MICA modems support R2 functionality. R2 signaling is an international signaling standard that is common to channelized E1 networks. There is no single standard for R2 signaling. The ITU-T Q.400-Q.490 recommendation defines R2, but a number of countries implement R2 in entirely different ways. Cisco Systems addresses this challenge by supporting many localized implementations of R2 signaling in its Cisco IOS software.
Benefits
Cisco Systems' E1 R2 signaling default is ITU, which supports the following countries: Denmark, Finland, Germany, Russia (ITU variant), Hong Kong (ITU variant), and South Africa (ITU variant). The expression "ITU variant" means there are multiple R2 signaling types in the specified country.
Countries Supported
Cisco Systems also supports specific local variants of E1 R2 signaling in the following regions, countries, and corporations:
Note
Country names and regions followed by an asterisk (*) were first supported in Cisco IOS Release 11.3(2)T.
•
Argentina *
•
Australia
•
Bolivia
•
Brazil
•
Bulgaria
•
China
•
Columbia
•
Costa Rica
•
Crotia
•
East Europe (includes Croatia, Russia, and Slovak Republic) *
•
Ecuador ITU *
•
Ecuador LME *
•
Greece
•
Guatemala *
•
Hong Kong (uses the China variant) *
•
Indonesia
•
Israel
•
ITU
•
Korea
•
Laos
•
Malaysia
•
Malta
•
New Zealand
•
Paraguay
•
Peru *
•
Philippines
•
Saudi Arabia *
•
Singapore
•
South Africa (Panaftel variant)*
•
Telmex corporation (Mexico)
•
Telnor corporation (Mexico)
•
Thailand
•
Uruguay
•
Venezuela
•
Vietnam
Platforms
This feature is now supported on the Cisco AS5800.
Supported MIBs and RFCs
None.
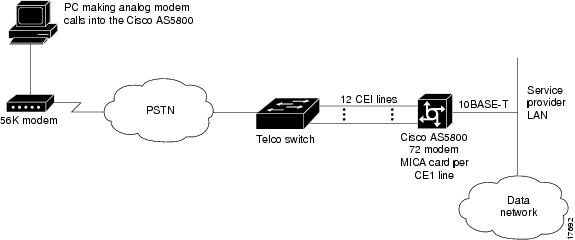
Sample Network Topology
shows a sample network topology for using E1 R2 signaling with a Cisco AS5800. All four controllers on the access server are configured with R2 digital signaling. Additionally, localized R2 country settings are enabled on the access server. For a sample configuration, see the "Configuration Example" section.
Figure 1 Service Provider using E1 R2 Signaling and a Cisco AS5800
Configuring E1 R2 Signaling for the Cisco AS5800
This section describes how to configure E1 R2 signaling.
R2 signaling is channelized E1 signaling used in Europe, Asia, and South America. It is equivalent to channelized T1 signaling in North America. There are two types of R2 signaling: line signaling and interregister signaling. R2 line signaling includes R2 digital, R2 analog, and R2 pulse. R2 interregister signaling includes R2 compelled, R2 non compelled, and R2 semi compelled. These signaling types are configured using the cas-group (controller e1) command.
Many countries have their own E1 R2 variant specifications, which supplement the ITU-T Q.400-Q.490 recommendation for R2 signaling. Unique E1 R2 signaling parameters for specific countries are set by issuing the cas-custom channel command followed by the country name command.
Cisco's implementation of R2 signaling has DNIS support turned on by default. If you enable the ani option, the collection of DNIS information is still performed. Specifying the ani option does not disable DNIS collection. DNIS is the number being called. ANI is the caller's number. For example, if you are configuring router A to call router B, then the DNIS number is assigned to router B, the ConfigureANI number is assigned to router A. ANI is similar to Caller ID.
Configure
1

controller e1 number
Specify the E1 controller that you want to configure with R2 signaling.
2

cas-group channel timeslots range type {r2-analog | r2-digital | r2-pulse} [dtmf | r2-compelled [ani] | r2-non-compelled [ani] | r2-semi-compelled [ani]]
Configure R2 channel associated signaling on the E1 controller. For a complete description of the available R2 options, see the cas-group (controller e1) command reference page.
3

cas-custom channel
Enter cas-custom mode. In this mode, you can localize E1 R2 signaling parameters, such as specific R2 country settings for Hong Kong.
For the customization to take effect, the channel number used in the cas-custom command must match the channel number specified by the cas-group command.
4

The following signaling commands are available:
•
ani-digits
•
answer-signal
•
caller-digits
•
category
•
country
•
default
•
dnis-digits
•
invert-abcd
•
ka
•
kd
•
metering
•
nc-congestion
•
unused-abcd
(Optional) Customize E1 R2 signaling parameters for your E1 networking environment. Cisco strongly recommends that you specify your country type using the country command. Otherwise, the default will be ITU.
See the cas-custom command reference page for more information about each signaling command.
For an E1 R2 configuration example, see the "Configuration Example" section.
Verify
To verify your E1 R2 signaling configuration, do the following:
•
Enter the show controller e1 command to view the status for all controllers, or enter the show controller e1 number command to view the status for a particular controller. Make sure the status indicates the controller is up (line 2 in the following example) and no alarms (line 4 in the following example) or errors (lines 9 and 10 in the following example) have been reported.
5800# show controller e1 1/1/1E1 0 is up.Applique type is Channelized E1 - balancedNo alarms detected.Framing is CRC4, Line Code is HDB3, Clock Source is Line Primary.Data in current interval (785 seconds elapsed):0 Line Code Violations, 0 Path Code Violations0 Slip Secs, 0 Fr Loss Secs, 0 Line Err Secs, 0 Degraded Mins0 Errored Secs, 0 Bursty Err Secs, 0 Severely Err Secs, 0 Unavail SecsTotal Data (last 13 15 minute intervals):0 Line Code Violations, 0 Path Code Violations,0 Slip Secs, 12 Fr Loss Secs, 0 Line Err Secs, 0 Degraded Mins,0 Errored Secs, 0 Bursty Err Secs, 0 Severely Err Secs, 12 Unavail Secs•
Enter the show modem csm [slot/modem-port] command to view status for a specific modem:
5800# show modem csm 1/4/1VDEV_INFO:slot 4, port 1vdev_status(0x00000001):VDEV_STATUS_ACTIVE_CALL.csm_state(0x00000205)=CSM_IC5_CONNECTED, csm_event_proc=0x60665CB0, current call thru Channelize lineinvalid_event_count=0, wdt_timeout_count=0watchdog timer is not activatedwait_for_dialing:False, wait_for_bchan:pri_chnl=(E1 1/1/0:1), vdev_chnl=(s4, c1)start_chan_p=0, chan_p=61994BC4, time_slot=1The calling party phone number =The called party phone number = 7789ring_no_answer=0, ic_failure=0, ic_complete=1dial_failure=0, oc_failure=0, oc_complete=0oc_busy=0, oc_no_dial_tone=0, oc_dial_timeout=0remote_link_disc=0, busyout=0, modem_reset=0call_duration_started=1d16h, call_duration_ended=00:00:00, total_call_duration=00:00:00...Troubleshoot
If the connection does not come up, check the following:
•
Loose wires, splices, connectors, shorts, bridge taps, and grounds
•
Backwards transmit and receive
•
Mismatched framing types (for example, CRC-4 verses no-CRC-4)
•
Transmit and receive pair separation (crosstalk)
•
Faulty line cards or repeaters
•
Noisy lines (for example, power and crosstalk)
If you see errors on the line, or the line is going up and down, check the following:
•
Mismatched line codes (HDB3 vs. AMI)
•
Receive level
•
Frame slips due to poor clocking plan
If you are still having trouble, enable the modem management Call Switching Module (CSM) debug mode using the debug modem csm command. The following is the debug output for an incoming call:
5800# debug csm 1/1/0deb csmCall Switching Module debugging is onRouter#*Dec 11 12:51:10.687:allocate slot 4 and port 0 is allocated*Dec 11 12:51:10.687:CSM v(4/0) c(E1 1/1/0:17):CSM_PROC_IDLE: ev_DSX0_CALL.*Dec 11 12:51:10.703:CSM v(4/0) c(E1 1/1/0:17):CSM_PROC_IC1_RING: ev_MODEM_OFFHOOK.*Dec 11 12:51:16.239:CSM v(4/0) c(E1 1/1/0:17):CSM_PROC_IC2_COLLECT_ADDR_INFO: ev_IC_ADDR_INFO_COLLECTED.*Dec 11 12:51:16.635:CSM v(4/0) c(E1 1/1/0:17):CSM_PROC_IC4_WAIT_FOR_CARRIER: ev_DSX0_CONNECTED...When the E1 controller comes up, you will see the following messages:
..00:06:04:Msm1:MSM_IN_SERVICE:n_ring_ind:cc0x200 si3 dc2 ms0 cr56000,7500:06:04:Msm1:MSM_PREPARE:m_state_trans:newst MODEM_STATE_SETUP00:06:04:Msm1:MSM_COLLECTING_R2:m_dig_det:di=0x36(6)00:06:04:Msm1:MSM_COLLECTING_R2:r2_gen_dig:Generate digits:1.00:06:04:Msm1:MSM_COLLECTING_R2:r2_gen_dig:Save Generate digits:#.00:06:04:Msm1:MSM_COLLECTING_R2:m_digit_gen:st=000:06:04:Msm1:MSM_COLLECTING_R2:m_digit_gen:Generate saved digits #00:06:04:Msm1:MSM_COLLECTING_R2:m_digit_gen:st=000:06:04:Msm1:MSM_COLLECTING_R2:m_dig_det:di=0x23(#)00:06:04:Msm1:MSM_COLLECTING_R2:r2_gen_dig:Generate digits:#.00:06:04:Msm1:MSM_COLLECTING_R2:m_digit_gen:st=000:06:04:Msm1:MSM_COLLECTING_R2:m_dig_det:di=0x37(7)00:06:04:Msm1:MSM_COLLECTING_R2:r2_gen_dig:Generate digits:1.00:06:04:Msm1:MSM_COLLECTING_R2:r2_gen_dig:Save Generate digits:#.00:06:04:Msm1:MSM_COLLECTING_R2:m_digit_gen:st=000:06:04:Msm1:MSM_COLLECTING_R2:m_digit_gen:Generate saved digits #00:06:05:Msm1:MSM_COLLECTING_R2:m_digit_gen:st=000:06:05:Msm1:MSM_COLLECTING_R2:m_dig_det:di=0x23(#)00:06:05:Msm1:MSM_COLLECTING_R2:r2_gen_dig:Generate digits:#.00:06:05:Msm1:MSM_COLLECTING_R2:m_digit_gen:st=0...Configuration Example
This section shows a sample configuration of E1 R2 signaling. In most cases, the same R2 signaling type is configured on each E1 controller. The following example configures R2 signaling and customizes R2 parameters on controller E1 2 of a Cisco AS5800:
Step 1
Enter global configuration mode using the configure terminal command:
as5800# configure terminalEnter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.Step 2
Specify the E1 controller that you want to configure with R2 signaling using the controller e1 number global configuration command. A controller informs the access server how to distribute or provision individual timeslots for a connected channelized E1 line. You must configure one E1 controller for each E1 line.
as5800(config)# controller e1 2/1/2Step 3
Configure channel-associated signaling with the cas-group channel timeslots range type signal command. The signaling type forwarded by the connecting telco switch must match the signaling configured on the Cisco AS5800. The Cisco IOS configuration options are r2-analog, r2-digital, or r2-pulse.
as5800(config-controller)# cas-group 1 timeslots 1-31 type ?e&m-fgb E & M Type II FGBe&m-fgd E & M Type II FGDe&m-immediate-start E & M Immediate Startfxs-ground-start FXS Ground Startfxs-loop-start FXS Loop Startp7 P7 Switchr2-analog R2 ITU Q411r2-digital R2 ITU Q421r2-pulse R2 ITU Supplement 7sas-ground-start SAS Ground Startsas-loop-start SAS Loop StartThe following example specifies R2 ITU Q421 digital line signaling (r2-digital). This example also specifies R2 compelled register signaling and provisions the ANI ADDR option.
as5800(config-controller)# cas-group 1 timeslots 1-31 type r2-digital r2-compelled anias5800(config-controller)#%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 1 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 2 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 3 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 4 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 5 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 6 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 7 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 8 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 9 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 10 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 11 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 12 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 13 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 14 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 15 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 17 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 18 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 19 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 20 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 21 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 22 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 23 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 24 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 25 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 26 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 27 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 28 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 29 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 30 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 31 is up
Note
For a description of the supported R2 signaling options, see the cas-group (controller e1) command reference page. The actual R2 channel-associated signaling is configured on the 16th timeslot, which is the reason the timeslot does not come up in the example output.
Step 4
Customize some of the E1 R2 signaling parameters with the cas-custom channel controller configuration command. This example specifies the default R2 settings for Argentina. See the cas-custom command reference page for a detailed description of these options.
as5800(config-controller)# cas-custom 1as5800(config-ctrl-cas)# ?CAS custom commands:ani-digits Expected number of ani digitsanswer-signal Answer signal to be usedcaller-digits Digits to be collected before requesting CallerIDcategory Category signalcountry Country Namedefault Set a command to its defaultsdnis-digits Expected number of DNIS digitsexit Exit from cas custom modeinvert-abcd invert the ABCD bits before tx and after rxka KA Signalkd KD Signalmetering R2 network is sending metering signalnc-congestion Non Compelled Congestion signalno Negate a command or set its defaultsunused-abcd Unused ABCD bit valuesas5800(config-ctrl-cas)# country ?argentina Argentinaaustralia Australiabrazil Brazilchina Chinacolumbia Columbia...as5800(config-ctrl-cas)# country argentina ?use-defaults Use Country defaults<cr>as5800(config-ctrl-cas)# country argentina use-defaults
Note
Cisco highly recommends that you specify your country's default settings. To display a list of supported countries, issue the country ? command. The default setting for all countries is ITU.
Command Reference
This section documents new or modified commands. All other commands used with this feature are documented in the Cisco IOS Release 11.3 command references.
The following commands are modified:
cas-custom
To customize E1 R2 signaling parameters for a particular E1 channel group on a channelized E1 line, use the cas-custom controller configuration command. Use the no form of this command to disable the signaling customization.
cas-custom channel
no cas-custom channelSyntax Description
channel
Specifies a single channel group number, which can be between 0 and 30. This channel group number must match the channel number specified in the cas-group command.
Default
No customized signaling parameters are set. If you do not specify a country name using the country name command, which is described in , ITU is the selected default signal.
Command Mode
Controller configuration
Usage Guidelines
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 11.2 P.
The customization parameters set by the cas-custom channel command are applied to the same channel group number used in the cas-group channel timeslots range type signal command. These channel group numbers must match. Otherwise, the customized features specified by the cas-custom command will not be applied to the cas-group command's configuration. The signaling customization will not take effect. See Example 1.
However, you will not need to configure or set more than one channel group number per E1 line in most cases. Though rarely used, it is possible to split a single E1 (timeslots 1 to 31) into two groups (for example, 1 to 15 on group 1 and timeslots 17 to 31 in group 2).
Cisco strongly recommends that you use the use-defaults option when specifying a particular country type. See the country name command in . This additional keyword ensures that all the local country settings are correctly enabled. For example, issue the country greece use-defaults command. If the use-defaults option is not specified, generic ITU will be the default setting for all countries. See Example 2.
You can configure the system to deviate from a country's default settings as defined by Cisco. To do this, choose from the following list of commands described in : ani-digits min number max number, answer-signal {group-a | group-b} number, caller-digits number, category number, dnis-digits min number max number, invert-abcd, ka number, kd number, metering, nc-congestion, and unused-abcd value. To return a country back to its country specific default settings, issue the country name use-defaults command. To return a country back to the ITU standard, issue the default country name use-defaults command. See Example 3 and Example 4.
Note
Only integrated MICA modems support E1 R2 signaling on Cisco access servers.
shows a list of command options in cas-custom mode, which is used to customize R2 signaling settings.
Example 1
The following example displays the available signaling parameters after you enter cas-custom mode. Notice that the same channel group 1 is specified in the cas-group command and the cas-custom command.
router# configure terminalEnter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Zrouter(config)# controller e1 1router(config-controller) cas-group 1 timeslots 1-31 type r2-digital r2-compelledrouter(config-controller) cas-custom 1router(config-ctrl-cas)# ?CAS custom commands:ani-digits Expected number of ANI digitsanswer-signal Answer signal to be usedcaller-digits Digits to be collected before requesting CallerIDcategory Category signalcountry Country Namedefault Set a command to its defaultsdnis-digits Expected number of DNIS digitsexit Exit from cas custom modeinvert-abcd invert the ABCD bits before tx and after rxka KA Signalkd KD Signalmetering R2 network is sending metering signalnc-congestion Non Compelled Congestion signalno Negate a command or set its defaultsunused-abcd Unused ABCD bit valuesExample 2
You can localize your R2 configuration for a specific country. Don't forget to include the use-defaults option as described in . For example, use the country argentina use-defaults command for a R2 scenario in Argentina.
Router(config-ctrl-cas)#country ?argentina Argentinaaustralia Australiabolivia Boliviabrazil Brazilbulgaria Bulgariachina Chinacolombia Colombiacostarica Costa Ricacroatia Croatiaeasteurope East Europeecuador-itu Ecuador ITUecuador-lme Ecuador LMEgreece Greeceguatemala Guatemalahongkong-china Hong Kong (China variant)india Indiaindonesia Indonesiaisrael Israelitu ITUkorea Korealaos LAOS Network (Thailand Variant)malaysia Malaysiamalta Maltanewzealand New Zealandparaguay Paraguayperu Peruphilippines Philippinessaudiarabia Saudi Arabiasingapore Singaporesouthafrica-panaftel South Africa Panafteltelmex Telmextelnor Telnorthailand Thailanduruguay Uruguayvenezuela Venezuelavietnam Vietnamrouter(config-ctrl-cas)# country argentina ?use-defaults Use Country defaults<cr>router(config-ctrl-cas)# country argentina use-defaultsExample 3
The following example customizes the signaling for channel group 1. The configuration collects 3 digits before it requests ANI information for analog calls received on a Cisco AS5800 in Argentina.
router(config-controller)# cas-custom 1router(config-ctrl-cas)# country argentina use-defaultsrouter(config-ctrl-cas)# caller-digits 3router(config-controller)# ^zrouter(config)#Example 4
Because cas-custom mode gives you the flexibility to customize R2 parameters, the margin for user error increases. Therefore, the Cisco IOS software enables you to return a country back to its default R2 settings using the use-defaults option. The following example begins by bringing up Argentina's default settings, changing a few customization parameters, then returning the Argentina R2 setting back to its original state.
router(config-ctrl-cas)# country argentina use-defaultsrouter(config-ctrl-cas)# caller-digits 3router(config-ctrl-cas)# unused-abcd 1router(config-ctrl-cas)# meteringrouter(config-ctrl-cas)# country argentina use-defaultsRelated Command
cas-group (controller E1)
cas-group (controller e1)
To configure channel associated signaling on an E1 controller, use the cas-group controller configuration command. Use the no form of this command to disable channel associated signaling for one or more timeslots.
cas-group channel timeslots range type signal
no cas-group channel timeslots range type signalSyntax Description
Default
No channel associated signaling is configured on the controller. All R2 signaling types have DNIS turned on by default.
Command Mode
Controller configuration
Usage Guidelines
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 11.2 P.
Use this command to configure support for incoming and outgoing call signals (such as on-hook and off-hook) on each E1 controller.
If you specify the timeslot range 1-31, the system software automatically uses the 16th timeslot to transmit the channel associated signaling.
The signaling you configure on the access server must match the signaling used by the central office. For example if the central office switch is forwarding R2 analog signaling to a Cisco AS5800, then the access server's E1 controller must also be configured for R2 analog signaling (r2-analog).
All R2 signaling options have DNIS support turned on by default. If you enable the ani option, the collection of DNIS information is still performed. Specifying the ani option does not disable DNIS. DNIS is the number being called. ANI is the caller's number. For example, if you are configuring router A to call router B, then the DNIS number is router B, the ANI number is router A. ANI is very similar to Caller ID.
To customize the R2 signaling parameters, refer to the cas-custom controller configuration command. When you enable the cas-group command, the cas-custom command is automatically setup to be polled for configuration information. However, unless you enable or turn on specific features with the cas-custom command, the cas-custom feature has an empty set of signaling parameters.
Note
Only integrated MICA modems support E1 R2 signaling on Cisco access servers.
DNIS is automatically collected for modem pools and R2 tone signaling. You do not need to specify the collection of DNIS information with the cas-group command. However, if you are using non-R2 tone signaling, the system must be manually configured to collect DNIS information. For non-R2 cas signaling, DNIS collection is done only for E&M-fgb.
Examples
In most cases, you will configure the same channel associated signaling on each E1 controller. The following examples configure signaling and customized parameters on controller E1 2 using the cas-group and cas-custom controller configuration commands.
The actual channel associated signaling is configured on the 16th timeslot, which is the reason why this timeslot does not come up in the following output.
router# configure terminalEnter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.router(config)# controller e1 2/1/0router(config-controller)# cas-group 1 timeslots 1-31 type r2-digital r2-compelled anirouter(config-controller)#%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 1 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 2 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 3 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 4 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 5 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 6 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 7 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 8 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 9 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 10 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 11 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 12 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 13 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 14 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 15 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 17 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 18 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 19 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 20 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 21 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 22 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 23 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 24 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 25 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 26 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 27 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 28 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 29 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 30 is up%DSX0-5-RBSLINEUP: RBS of controller 0 timeslot 31 is upThe following example shows all the supported E1 signaling types on a Cisco AS5800:
router(config-controller)# cas-group 1 timeslots 1-31 type ?e&m-fgb E & M Type II FGBe&m-fgd E & M Type II FGDe&m-immediate-start E & M Immediate Startfxs-ground-start FXS Ground Startfxs-loop-start FXS Loop Startp7 P7 Switchr2-analog R2 ITU Q411r2-digital R2 ITU Q421r2-pulse R2 ITU Supplement 7sas-ground-start SAS Ground Startsas-loop-start SAS Loop Startrouter(config-controller)# cas-group 1 timeslots 1-31 type r2-analog ?dtmf DTMF tone signallingr2-compelled R2 Compelled Register Signallingr2-non-compelled R2 Non Compelled Register Signallingr2-semi-compelled R2 Semi Compelled Register Signalling<cr>R2 signaling parameters can be customized with the cas-custom controller configuration command:
router(config-controller)# cas-custom 1router(config-ctrl-cas)# ?CAS custom commands:caller-digits Digits to be collected before requesting CallerIDcategory Category signalcountry Country Namedefault Set a command to its defaultsexit Exit from cas custom modeinvert-abcd invert the ABCD bits before tx and after rxmetering R2 network is sending metering signalnc-congestion Non Compelled Congestion signalno Negate a command or set its defaultsWhat to Do Next
For additional dial-related software configuration information, see the following publications:
•
Dial Solutions Configuration Guide (Cisco IOS Release 11.3)
•
Cisco AS5800 Universal Access Server Software Configuration Guide