简介
本文档介绍 bgp deterministic-med 命令并解释它如何影响基于多出口标识符(MED)的路径选择。
先决条件
要求
本文档没有任何特定的要求。
使用的组件
本文档不限于特定的软件和硬件版本。
本文档中的信息都是基于特定实验室环境中的设备编写的。本文档中使用的所有设备最初均采用原始(默认)配置。如果您的网络处于活动状态,请确保您了解所有命令的潜在影响。
规则
有关文档规则的详细信息,请参阅 Cisco 技术提示规则。
MED 属性
MED 是一个可选的非传递性属性。MED 用于提示外部邻居,进入具有多个入口点的自治系统 (AS) 的首选路径是什么。MED 也称为路由器的外部量度。低 MED 值优先于高 MED 值。
本部分举例说明如何使用 MED 影响相邻 AS 采取的路由决策。
网络拓扑
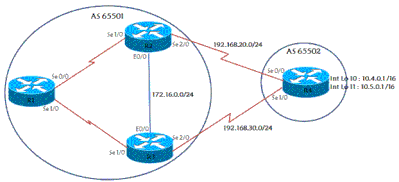 网络拓扑
网络拓扑
示例
在此场景中,AS 65502是具有AS 65501的ISP的用户。R4连接到ISP端的两台不同的路由器以实现冗余,并将两个网络通告给ISP - 10.4.0.0/16和10.5.0.0/16。本部分显示了一些相关配置。
| R4 |
!
version 12.3
!
hostname r4
!
ip cef
!
!
interface Loopback10
ip address 10.4.0.1 255.255.0.0
!
interface Loopback11
ip address 10.5.0.1 255.255.0.0
!
interface Serial0/0
ip address 192.168.20.4 255.255.255.0
!
interface Serial1/0
ip address 192.168.30.4 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 65502
no synchronization
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 10.4.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0
network 10.5.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0
neighbor 192.168.20.2 remote-as 65501
neighbor 192.168.30.3 remote-as 65501
no auto-summary
!
ip classless
!
!
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
exec-timeout 0 0
login
!
!
end |
| R2 |
!
version 12.3
!
hostname r2
!
ip cef
!
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 172.16.0.2 255.255.255.0
!
interface Serial1/0
ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
serial restart-delay 0
!
interface Serial2/0
ip address 192.168.20.2 255.255.255.0
serial restart-delay 0
!
router ospf 1
log-adjacency-changes
redistribute connected
passive-interface Serial2/0
network 10.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 area 0
network 172.16.0.2 0.0.0.0 area 0
network 192.168.1.2 0.0.0.0 area 0
network 192.168.20.2 0.0.0.0 area 0
!
router bgp 65501
no synchronization
bgp log-neighbor-changes
neighbor 10.1.1.1 remote-as 65501
neighbor 10.1.1.1 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 10.3.3.3 remote-as 65501
neighbor 10.3.3.3 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 192.168.20.4 remote-as 65502
no auto-summary
!
ip classless
!
!
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
transport preferred all
transport output all
line aux 0
transport preferred all
transport output all
line vty 0 4
exec-timeout 0 0
login
transport preferred all
transport input all
transport output all
!
end |
R1 和 R3 的配置类似于 R2。R3 有一个与 R4 配对的 eBGP,还有一个与 R1 配对的 iBGP。
R1 有一个与 R2 配对的 iBGP,还有一个与 R3 配对的 iBGP。查看R1、R2和R3 BGP表对于R4通告的两个网络的显示内容:
r2# show ip bgp 10.4.0.1
BGP routing table entry for 10.4.0.0/16, version 7
Paths: (2 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table)
Advertised to non peer-group peers:
10.1.1.1 10.3.3.3
65502
192.168.20.4 from 192.168.20.4 (10.4.4.4)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, external, best
65502
192.168.30.4 (metric 74) from 10.3.3.3 (10.3.3.3)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal
r2# show ip bgp 10.5.0.1
BGP routing table entry for 10.5.0.0/16, version 6
Paths: (2 available, best #2, table Default-IP-Routing-Table)
Advertised to non peer-group peers:
10.1.1.1 10.3.3.3
65502
192.168.30.4 (metric 74) from 10.3.3.3 (10.3.3.3)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal
65502
192.168.20.4 from 192.168.20.4 (10.4.4.4)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, external, best
r3# show ip bgp 10.4.0.1
BGP routing table entry for 10.4.0.0/16, version 8
Paths: (2 available, best #2, table Default-IP-Routing-Table)
Advertised to non peer-group peers:
10.1.1.1 10.2.2.2
65502
192.168.20.4 (metric 74) from 10.2.2.2 (10.2.2.2)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal
65502
192.168.30.4 from 192.168.30.4 (10.4.4.4)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, external, best
r3# show ip bgp 10.5.0.1
BGP routing table entry for 10.5.0.0/16, version 10
Paths: (2 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table)
Advertised to non peer-group peers:
10.1.1.1 10.2.2.2
65502
192.168.30.4 from 192.168.30.4 (10.4.4.4)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, external, best
65502
192.168.20.4 (metric 74) from 10.2.2.2 (10.2.2.2)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal
r1# show ip bgp 10.4.0.1
BGP routing table entry for 10.4.0.0/16, version 11
Paths: (2 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table)
Not advertised to any peer
65502
192.168.20.4 (metric 128) from 10.2.2.2 (10.2.2.2)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal, best
65502
192.168.30.4 (metric 128) from 10.3.3.3 (10.3.3.3)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal
r1# show ip bgp 10.5.0.1
BGP routing table entry for 10.5.0.0/16, version 10
Paths: (2 available, best #2, table Default-IP-Routing-Table)
Not advertised to any peer
65502
192.168.30.4 (metric 128) from 10.3.3.3 (10.3.3.3)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal
65502
192.168.20.4 (metric 128) from 10.2.2.2 (10.2.2.2)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal, best
R2和R3都根据BGP最佳路径选择算法从R4中选择期望的外部路由作为最佳路径。有关详细信息,请参阅 BGP 最佳路径选择算法。
同样,R1选择R2访问两个网络,这符合BGP最佳路径规则 — 选择路由器ID最低的路径。由于R2路由器ID是10.2.2.2,而R3路由器ID是10.3.3.3,因此选择R2。在此基本配置中,默认情况下,发往AS 65502中两个网络的所有流量从R1通过R2,然后到R4。现在,假设R4希望对从AS 65501接收的流量进行负载均衡。 要在不修改任何R4 ISP的情况下完成此操作,请将R4配置为使用MED将一个网络的流量强制移至另一路径,而将另一网络的流量强制移至另一路径。
以下是R4在应用必要配置后的配置:
| R4 |
!
version 12.3
!
hostname r4
!
ip cef
!
!
!
interface Loopback10
ip address 10.4.0.1 255.255.0.0
!
interface Loopback11
ip address 10.5.0.1 255.255.0.0
!
interface Serial0/0
ip address 192.168.20.4 255.255.255.0
!
interface Serial1/0
ip address 192.168.30.4 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 65502
no synchronization
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 10.4.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0
network 10.5.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0
neighbor 192.168.20.2 remote-as 65501
neighbor 192.168.20.2 route-map setMED-R2 out
neighbor 192.168.30.3 remote-as 65501
neighbor 192.168.30.3 route-map setMED-R3 out
no auto-summary
!
ip classless
no ip http server
!
!
access-list 1 permit 10.4.0.0 0.0.255.255
access-list 2 permit 10.5.0.0 0.0.255.255
!
route-map setMED-R3 permit 10
match ip address 1
set metric 200
!
route-map setMED-R3 permit 20
match ip address 2
set metric 100
!--- The route-map MED-R3 is applying a MED of 200 to the 10.4.0.0/16
!--- network and a MED of 100 to the 10.5.0.0/16 network.
!--- The route-map is being applied outbound towards R3. ! route-map setMED-R2 permit 10 match ip address 1 set metric 100 ! route-map setMED-R2 permit 20 match ip address 2 set metric 200 !--- The route-map MED-R2 is applying a MED of 100 to the 10.4.0.0/16
!--- network and a MED of 200 to the 10.5.0.0/16 network.
!--- The route-map is being applied outbound towards R2. ! ! ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 line aux 0 line vty 0 4 exec-timeout 0 0 login ! ! end |
注意:您需要使用 clear ip bgp * soft out 命令,例如,使这些配置生效。
现在,R1 将经过 R2 的路由视为网络 10.4.0.0/16 的最佳路径,因为从 R2 收到的更新中的 MED 为 100,而 R3 通告的 MED 则为 200。同样,R1 使用 R3 和 R3 - R4 链路访问 10.5.0.0/16:
r1# show ip bgp 10.4.0.1
BGP routing table entry for 10.4.0.0/16, version 14
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table)
Flag: 0x800
Not advertised to any peer
65502
192.168.20.4 (metric 128) from 10.2.2.2 (10.2.2.2)
Origin IGP, metric 100, localpref 100, valid, internal, best
r1#sh ip bgp 10.5.0.1
BGP routing table entry for 10.5.0.0/16, version 13
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table)
Flag: 0x800
Not advertised to any peer
65502
192.168.30.4 (metric 128) from 10.3.3.3 (10.3.3.3)
Origin IGP, metric 100, localpref 100, valid, internal, best
查看R2的显示:
r2# show ip bgp 10.4.0.1
BGP routing table entry for 10.4.0.0/16, version 10
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table)
Advertised to non peer-group peers:
10.1.1.1 10.3.3.3
65502
192.168.20.4 from 192.168.20.4 (10.4.4.4)
Origin IGP, metric 100, localpref 100, valid, external, best
r2# show ip bgp 10.5.0.1
BGP routing table entry for 10.5.0.0/16, version 11
Paths: (2 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table)
Advertised to non peer-group peers:
192.168.20.4
65502
192.168.30.4 (metric 74) from 10.3.3.3 (10.3.3.3)
Origin IGP, metric 100, localpref 100, valid, internal, best
65502
192.168.20.4 from 192.168.20.4 (10.4.4.4)
Origin IGP, metric 200, localpref 100, valid, external
R2只显示10.4.0.0/16的一条路径的原因是,R3在注意到R3使用R2访问10.4.0.0/16(在所有可用路径上运行BGP最佳路径后)后撤消(发送带有不可达度量的更新)10.4.0.0/16的更新:
r3# show ip bgp 10.4.0.0
BGP routing table entry for 10.4.0.0/16, version 20
Paths: (2 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table)
Advertised to non peer-group peers:
192.168.30.4
65502
192.168.20.4 (metric 74) from 10.2.2.2 (10.2.2.2)
Origin IGP, metric 100, localpref 100, valid, internal, best
65502
192.168.30.4 from 192.168.30.4 (10.4.4.4)
Origin IGP, metric 200, localpref 100, valid, external
因为不必存储这些无用的信息,R2 由此可以节省一些内存。如果R2和R4之间的BGP会话失败,R2会向R3发送有关10.4.0.0/16的不可达更新。此更新将触发 R3 对 10.4.0.0/16 使用 R3 路由,通过 R4 向 R2 发送更新。R2 可以开始通过 R3 进行路由。
bgp deterministic-med 命令
如果启用 bgp deterministic-med 命令,删除基于MED的最佳路径决策的任何临时相关性。它可以确保在从同一自治系统 (AS) 收到的所有路由间进行准确的 MED 比较。
如果禁用 bgp deterministic-med ,路由的接收顺序可能会影响基于MED的最佳路径决策。如果从多个 AS 或联盟的子 AS 处接收具有完全相同的路径长度、不同 MED 的相同路由,则可能会发生这种情况。
Examples
例如,考虑以下路由:
entry1: ASPATH 1, MED 100, internal, IGP metric to NEXT_HOP 10
entry2: ASPATH 2, MED 150, internal, IGP metric to NEXT_HOP 5
entry3: ASPATH 1, MED 200, external
接收到 BGP 路由的顺序是 entry3、entry2 和 entry1(entry3 是 BGP 表中最早的条目,而 entry1 则是最新的条目)。
禁用了 bgp deterministic-med 的 BGP 路由器
BGP路由器 bgp deterministic-med disabled选择entry2而不是entry1,因为到达NEXT_HOP的IGP度量较低(在本决定中未使用MED,因为entry1和entry2来自两个不同的AS)。然后,它会首选entry3,而不是entry2,因为它是外部的。但是,entry3 比 entry1 的 MED 更高。有关BGP路径选择标准的详细信息,请参阅BGP最佳路径选择算法。
启用了 bgp deterministic-med 的 BGP 路由器
在这种情况下,来自同一 AS 的路由器被分为一组,并且每组中的最佳项会进行比较。在给定的示例中,有两个 AS:AS 1 和 AS 2。
Group 1: entry1: ASPATH 1, MED 100, internal, IGP metric to NEXT_HOP 10
entry3: ASPATH 1, MED 200, external
Group 2: entry2: ASPATH 2, MED 150, internal, IGP metric to NEXT_HOP 5
在 Group 1 中,最佳路径是 entry1,因为它的 MED 更低(由于所有路径都来自同一 AS,因此在此决策中使用了 MED)。在 Group 2 中,只有一项 (entry2)。然后,通过比较各组优胜者确定最佳路径(默认情况下,此比较不使用MED,因为各组的优胜者来自不同的AS。当您启用 bgp always-compare-med 它更改此默认行为)。现在,当您比较entry1(来自组1的优胜者)和entry2(来自组2的优胜者)时,entry2可能是优胜者,因为它具有通向下一跳的更好的IGP度量。
如果 bgp always-compare-med 当您比较entry1(组1的优胜者)和entry 2(组2的优胜者)时,因为较低的MED,entry 1可能是优胜者。
思科建议您启用 bgp always-compare-med 所有新网络部署中。此外,如果 bgp always-compare-med 已启用,BGP MED决策始终具有确定性。
有关 bgp deterministic-med 和 bgp always-compare-med 命令,请参阅bgp deterministic-med命令与bgp always-compare-med命令有何区别。
相关信息