Introducción
Este documento describe cómo configurar los controladores LAN inalámbricos (WLC) de AireOS para sincronizar la fecha y la hora con un servidor de protocolo de tiempo de la red (NTP).
Prerequisites
Requirements
Asegúrese de cumplir estos requisitos antes de intentar esta configuración:
Componentes Utilizados
La información que contiene este documento se basa en las siguientes versiones de software y hardware.
La información que contiene este documento se creó a partir de los dispositivos en un ambiente de laboratorio específico. Todos los dispositivos que se utilizan en este documento se pusieron en funcionamiento con una configuración verificada (predeterminada). Si tiene una red en vivo, asegúrese de entender el posible impacto de cualquier comando.
Gestión de la fecha y hora del sistema en el controlador de LAN inalámbrica
En un WLC, la fecha y la hora del sistema se pueden configurar manualmente desde el WLC o configurarse para obtener la fecha y la hora de un servidor NTP.
La fecha y la hora del sistema se pueden configurar manualmente en el asistente de configuración de CLI o en la GUI/CLI del WLC.
Este documento proporciona un ejemplo de configuración para sincronizar la fecha y hora del sistema WLC a través de un servidor NTP.
NTP es un protocolo de red para la sincronización de reloj entre sistemas informáticos a través de redes de datos de latencia variable para sincronizar los relojes de los equipos con alguna referencia de tiempo. Los documentos RFC 1305 y RFC 5905 proporcionan información detallada sobre la implementación de NTPv3 y NTPv4, respectivamente.
Una red NTP normalmente recibe su hora de una fuente de tiempo autorizada, como un reloj de radio o un reloj atómico conectado a un servidor de tiempo. NTP luego distribuye este tiempo a través de la red.
Un cliente NTP realiza una transacción con su servidor durante el intervalo de sondeo, que cambia dinámicamente con el tiempo y depende de las condiciones de red entre el servidor NTP y el cliente.
NTP utiliza el concepto de un estrato para describir cuántos saltos NTP fuera de una máquina es de una fuente de tiempo autoritativa. Por ejemplo, un servidor de tiempo de estrato 1 tiene una radio o un reloj atómico conectados directamente a él. Luego envía su tiempo a un servidor de tiempo de estrato 2 a través de NTP, y así sucesivamente.
Para obtener más información sobre las prácticas recomendadas para la implementación de NTP, consulte Uso de prácticas recomendadas para el protocolo de tiempo de la red.
El ejemplo de este documento utiliza un switch Cisco Catalyst 3560-CX Series L3 Switch como servidor NTP. El WLC se configura para sincronizar su fecha y hora con este servidor NTP.
Configurar
Diagrama de la red
WLC ---- 3560-CX L3 Switch ---- NTP server
Configuraciones
Configure el switch L3 como un servidor NTP autorizado
Utilice este comando en el modo de configuración global si desea que el sistema sea un servidor NTP autorizado, incluso si el sistema no está sincronizado con una fuente de hora externa:
#ntp master !--- Makes the system an authoritative NTP server
Configuración de la autenticación NTP
Si desea autenticar las asociaciones con otros sistemas por motivos de seguridad, utilice los siguientes comandos. El primer comando habilita la función de autenticación NTP.
El segundo comando define cada una de las claves de autenticación. Cada clave tiene un número, un tipo y un valor. Actualmente, el único tipo de clave admitido es md5.
En tercer lugar, se define una lista de claves de autenticación de confianza. Si una clave es de confianza, este sistema está listo para sincronizarse con un sistema que la utilice en sus paquetes NTP. Para configurar la autenticación NTP, utilice estos comandos en el modo de configuración global:
#ntp authenticate
!--- Enables the NTP authentication feature
#ntp authentication-key number md5 value
!--- Defines the authentication keys
#ntp trusted-key key-number
!--- Defines trusted authentication keys
Este es un ejemplo de configuración del servidor NTP en el switch 3560-CX L3. El switch es el NTP master, lo que significa que el router actúa como el servidor NTP autorizado pero él mismo obtiene el tiempo de otro servidor NTP xxxx.xxx.
(config)#ntp authentication-key 1 md5 1511021F0725 7
(config)#ntp authenticate
(config)#ntp trusted-key 1
(config)#ntp master
(config)#ntp server xxxx.xxx
Configure el WLC para el servidor NTP
Desde la versión 8.6 puede habilitar NTPv4. También puede configurar un canal de autenticación entre el controlador y el servidor NTP.
Para configurar la autenticación NTP en la GUI del controlador, realice estos pasos:
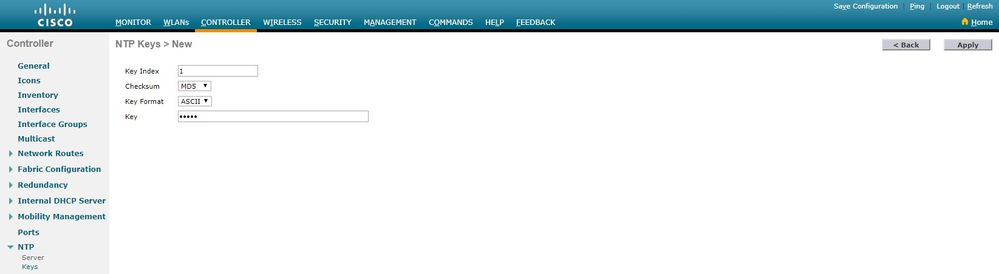
1. Elija Controlador > NTP > Claves.
2. Haga clic en Nuevo para crear una clave.
3. Introduzca el índice de clave en el cuadro de texto Índice de Claves.
4. Seleccione la suma de comprobación de clave (MD5 o SHA1) y la lista desplegable Formato de clave.
5. Introduzca la clave en el cuadro de texto Clave:
6. Seleccione Controlador > NTP > Servidores para abrir la página Servidores NTP. Seleccione la versión 3 o 4 y, a continuación, haga clic en Nuevo para agregar un servidor NTP. Aparecerá la página Servidores NTP > Nuevo.
7. Seleccione el índice de servidor (prioridad).
8. Introduzca la dirección IP del servidor NTP en el cuadro de texto Dirección IP del servidor.
9. Active la autenticación del servidor NTP, active la casilla de control Autenticación del Servidor NTP y seleccione el Índice de Claves configurado anteriormente.
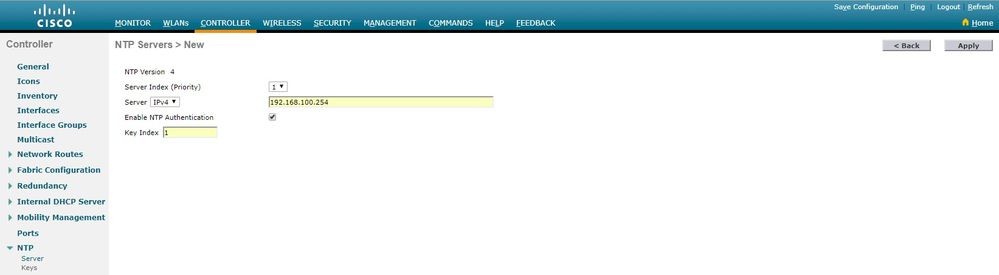
10. Haga clic en Aplicar.
Para configurar la autenticación NTP a través de la CLI del controlador, haga un seguimiento de este árbol de comandos:
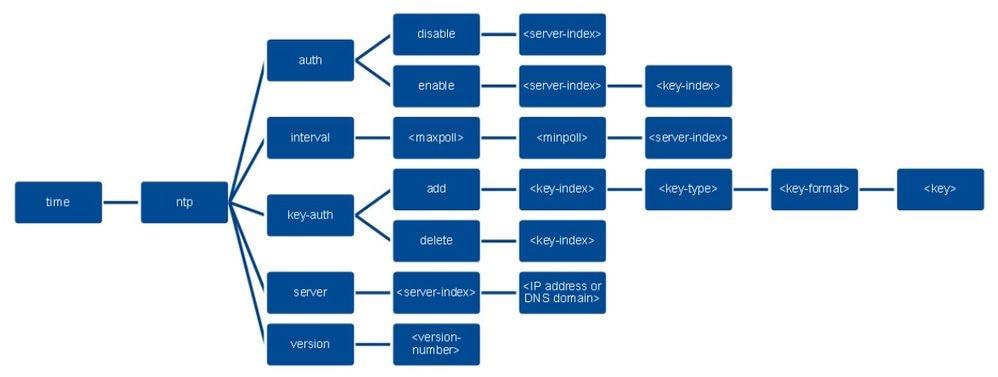
>config time ntp version 4
>config time ntp key-auth add 1 md5 ascii cisco
>config time ntp server 1 192.168.100.254
>config time ntp auth enable 1 1
Verificación
En el servidor NTP
#show ntp status
Clock is synchronized, stratum 3, reference is x.x.x.x
nominal freq is 286.1023 Hz, actual freq is 286.0901 Hz, precision is 2**21
ntp uptime is 6591900 (1/100 of seconds), resolution is 3496
reference time is E007C909.80902653 (09:23:21.502 UTC Fri Feb 8 2019)
clock offset is 0.3406 msec, root delay is 59.97 msec
root dispersion is 25.98 msec, peer dispersion is 1.47 msec
loopfilter state is 'CTRL' (Normal Controlled Loop), drift is 0.000042509 s/s
system poll interval is 128, last update was 7 sec ago.
#show ntp associations
address ref clock st when poll reach delay offset disp
*~x.x.x.x y.y.y.y 2 20 1024 17 13.634 0.024 1.626
~127.127.1.1 .LOCL. 7 9 16 377 0.000 0.000 0.232
* sys.peer, # selected, + candidate, - outlyer, x falseticker, ~ configured
#show ntp information
Ntp Software Name : Cisco-ntpv4
Ntp Software Version : Cisco-ntpv4-1.0
Ntp Software Vendor : CISCO
Ntp System Type : Cisco IOS / APM86XXX
En el WLC
En la GUI
Mientras que el WLC establece la comunicación:
Después de establecer la conexión:
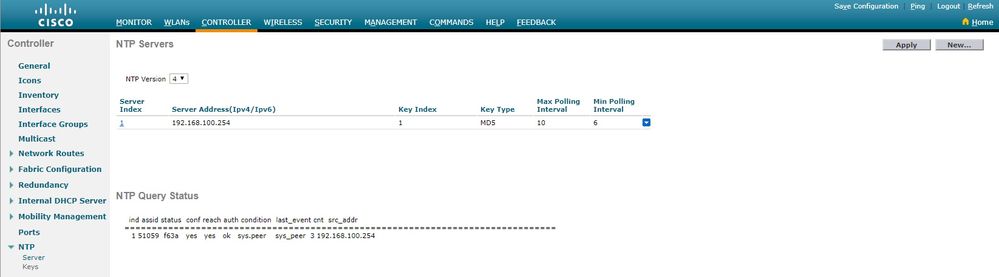
En la CLI del WLC
(Cisco Controller) >show time
Time............................................. Fri Feb 8 10:14:47 2019
Timezone delta................................... 0:0
Timezone location................................
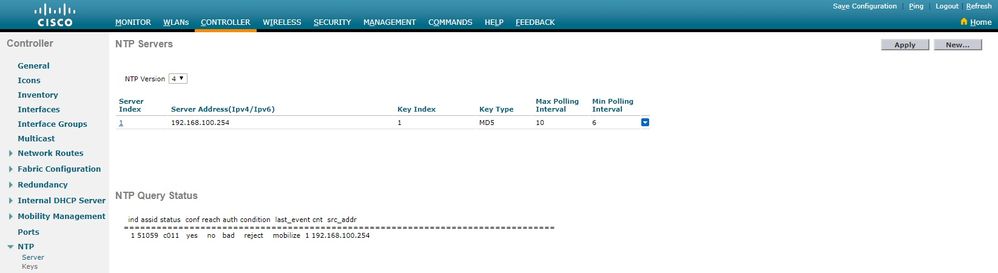
NTP Servers
NTP Version.................................. 4
Index NTP Key NTP Server NTP Key Polling Intervals
Index Type Max Min
-----------------------------------------------------------
1 1 192.168.100.254 MD5 10 6
NTPQ status list of NTP associations
assoc
ind assid status conf reach auth condition last_event cnt src_addr
===============================================================================
1 1385 f63a yes yes ok sys.peer sys_peer 3 192.168.100.254
(Cisco Controller) >
Troubleshoot
En el lado del servidor NTP que ejecuta Cisco IOS, puede utilizar eldebug ntp all enable comando:
#debug ntp all
NTP events debugging is on
NTP core messages debugging is on
NTP clock adjustments debugging is on
NTP reference clocks debugging is on
NTP packets debugging is on
#
(communication between SW and NTP server xxxx.xxx)
Feb 8 09:52:30.563: NTP message sent to x.x.x.x, from interface 'Vlan1' (192.168.1.81).
Feb 8 09:52:30.577: NTP message received from x.x.x.x on interface 'Vlan1' (192.168.1.81).
Feb 8 09:52:30.577: NTP Core(DEBUG): ntp_receive: message received
Feb 8 09:52:30.577: NTP Core(DEBUG): ntp_receive: peer is 0x0D284B34, next action is 1.
(communication between SW and WLC)
Feb 8 09:53:10.421: NTP message received from 192.168.100.253 on interface 'Vlan100' (192.168.100.254).
Feb 8 09:53:10.421: NTP Core(DEBUG): ntp_receive: message received
Feb 8 09:53:10.421: NTP Core(DEBUG): ntp_receive: peer is 0x00000000, next action is 3.
Feb 8 09:53:10.421: NTP message sent to 192.168.100.253, from interface 'Vlan100' (192.168.100.254).
(communication between SW and NTP server xxxx.xxx)
Feb 8 09:53:37.566: NTP message sent to x.x.x.x, from interface 'Vlan1' (192.168.1.81).
Feb 8 09:53:37.580: NTP message received from x.x.x.x on interface 'Vlan1' (192.168.1.81).
Feb 8 09:53:37.580: NTP Core(DEBUG): ntp_receive: message received
Feb 8 09:53:37.580: NTP Core(DEBUG): ntp_receive: peer is 0x0D284B34, next action is 1.
(communication between SW and WLC)
Feb 8 09:54:17.421: NTP message received from 192.168.100.253 on interface 'Vlan100' (192.168.100.254).
Feb 8 09:54:17.421: NTP Core(DEBUG): ntp_receive: message received
Feb 8 09:54:17.421: NTP Core(DEBUG): ntp_receive: peer is 0x00000000, next action is 3.
Feb 8 09:54:17.421: NTP message sent to 192.168.100.253, from interface 'Vlan100' (192.168.100.254).
En el lado del WLC:
>debug ntp ?
detail Configures debug of detailed NTP messages.
low Configures debug of NTP messages.
packet Configures debug of NTP packets.
(at the time of writte this doc there was Cisco bug ID CSCvo29660
on which the debugs of ntpv4 are not printed in the CLI. The below debugs are using NTPv3.)
(Cisco Controller) >debug ntp detail enable
(Cisco Controller) >debug ntp packet enable
(Cisco Controller) >*emWeb: Feb 08 11:26:53.896: ntp Auth key Info = -1
*emWeb: Feb 08 11:26:58.143: ntp Auth key Info = -1
*emWeb: Feb 08 11:26:58.143: ntp Auth key Info = -1
*emWeb: Feb 08 11:26:58.143: Key Id = 1 found at Local Index = 0
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.143: Initiating time sequence
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.143: Fetching time from:192.168.100.254
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.143: Started=3758614018.143350 2019 Feb 08 11:26:58.143
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.143: hostname=192.168.100.254 hostIdx=1 hostNum=0
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.143: Looking for the socket addresses
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.143: NTP Polling cycle: accepts=0, count=5, attempts=1,
retriesPerHost=6. Outgoing packet on NTP Server on socket 0:
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.143: sta=0 ver=3 mod=3 str=15 pol=8 dis=0.000000 ref=0.000000
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.143: ori=0.000000 rec=0.000000
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.143: tra=3758614018.143422 cur=3758614018.143422
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.143: Host Supports NTP authentication with Key Id = 1
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.143: NTP Auth Key Id = 1 Key Length = 5
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.143: MD5 Hash and Key Id added in NTP Tx packet
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.143: 00000000: 1b 0f 08 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ................
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.143: 00000010: 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ................
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.143: 00000020: 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 e0 07 e6 02 24 b7 50 00 ............$.P.
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.143: 00000030: 00 00 00 01 e4 35 f3 1a 89 f0 93 c5 51 c7 c5 23 .....5......Q..#
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.143: 00000040: 01 dd 67 e0 ..g.
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.143: Flushing outstanding packets
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.143: Flushed 0 packets totalling 0 bytes
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.143: Packet of length 68 sent to ::ffff:192.168.100.254 UDPport=123
*emWeb: Feb 08 11:26:58.143: ntp Auth key Info = 0
*emWeb: Feb 08 11:26:58.143: idx != 0 : ntp key Id = 1 Msg auth Status = 66
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.146: Packet of length 68 received from ::ffff:192.168.100.254 UDPport=123
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.146: Incoming packet on socket 0: has Authentication Enabled
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.146: 00000000: 1c 04 08 eb 00 00 0e a0 00 00 0b 2e c3 16 11 07 ................
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.146: 00000010: e0 07 e5 f8 d3 21 bf 57 e0 07 e6 02 24 b7 50 00 .....!.W....$.P.
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.146: 00000020: e0 07 e6 02 24 e5 e3 b4 e0 07 e6 02 24 f3 c7 5a ....$.......$..Z
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.146: 00000030: 00 00 00 01 32 e4 26 47 33 16 50 bd d1 37 63 b7 ....2.&G3.P..7c.
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.146: KeyId In Recieved NTP Packet 1
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.146: KeyId 1 found in recieved NTP packet exists as part of the trusted Key/s
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.146: The NTP trusted Key Id 1 length = 5
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.146: NTP Message Authentication - SUCCESS
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.146: sta=0 ver=3 mod=4 str=4 pol=8 dis=0.043671 ref=3758614008.824734
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.146: ori=3758614018.143422 rec=3758614018.144133
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.146: Offset=-0.000683+/-0.002787 disp=1.937698
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.146: best=-0.000683+/-0.002787
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.146: accepts=1 rejects=0 flushes=0
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.146: Correction: -0.000683 +/- 0.002787 disp=1.937698
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.146: Setting clock to 2019 Feb 08 11:26:58.145 + 0.001 +/- 1.940 secs
*sntpReceiveTask: Feb 08 11:26:58.146: correction -0.001 +/- 1.938+0.003 secs - ignored
(Cisco Controller) >
Información Relacionada






 Comentarios
Comentarios