Ejemplo de Configuración de MP-EBGP
Contenido
Introducción
Este documento proporciona información sobre cómo configurar el Protocolo de gateway fronterizo extendido multiprotocolo (MP-EBGP) en los routers Cisco IOS. MP-BGP es un BGP extendido que permite a BGP transportar información de ruteo para varios protocolos de capa de red IPv6, VPNv4 y otros. MP-BGP le permite tener una topología de ruteo unicast diferente de una topología de ruteo multicast, que ayuda a controlar la red y los recursos.
Prerequisites
Requirements
No hay requisitos específicos para este documento.
Componentes Utilizados
Este documento no tiene restricciones específicas en cuanto a versiones de software y de hardware.
Las configuraciones de este documento se basan en el Cisco 3700 Series Router que ejecuta Cisco IOS® Software Release 12.4 (15)T 13.
Convenciones
Configurar
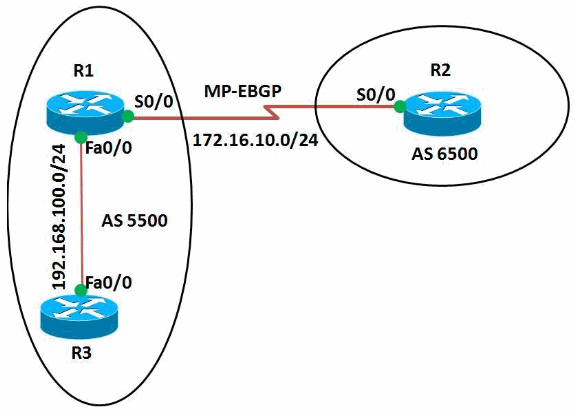
En este ejemplo, los routers R1 y R3 están configurados para estar en AS 5500 formando iBGP. El router R2 está configurado para estar en AS 6500. Los routers R1 y R2 se comunican entre sí mediante MP-EBGP. Todos los routers se configuran con direcciones de loopback.
Nota: Utilice la herramienta de búsqueda de comandos (solo para clientes registrados) para obtener más información sobre los comandos utilizados en este documento.
Diagrama de la red
En este documento, se utiliza esta configuración de red:
Configuraciones
En este documento, se utilizan estas configuraciones:
| Configuración en el Router R1 |
|---|
R1#show run Building configuration... ! version 12.4 ! hostname R1 ! ip cef ! ! interface Loopback0 ip address 10.10.10.10 255.255.255.0 ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 192.168.100.10 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ! interface Serial0/0 ip address 172.16.10.1 255.255.255.0 mpls ip clock rate 2000000 ! router bgp 5500 no synchronization bgp router-id 10.10.10.10 bgp log-neighbor-changes network 192.168.100.0 redistribute connected neighbor 172.16.10.2 remote-as 6500 neighbor 172.16.10.2 soft-reconfiguration inbound neighbor 192.168.100.11 remote-as 5500 no auto-summary ! address-family vpnv4 neighbor 172.16.10.2 activate neighbor 172.16.10.2 send-community both !--- Sends the community attribute to a BGP neighbor. exit-address-family ! ! end |
| Configuración en el Router R2 |
|---|
R2#show run Building configuration... ! version 12.4 ! hostname R2 ! ip cef ! ip vrf WAN rd 2020:1 route-target export 2020:1 route-target import 2020:1 ! ! interface Loopback0 ip vrf forwarding WAN !--- Associates a VRF instance with an interface or subinterface. ip address 20.20.20.20 255.255.255.255 ! interface Serial0/0 ip vrf forwarding WAN ip address 172.16.10.2 255.255.255.0 mpls ip clock rate 2000000 ! router bgp 6500 no synchronization bgp router-id 20.20.20.20 bgp log-neighbor-changes neighbor 172.16.10.1 remote-as 5500 no auto-summary ! ! address-family vpnv4 neighbor 172.16.10.1 activate neighbor 172.16.10.1 send-community both exit-address-family ! address-family ipv4 vrf WAN redistribute connected redistribute static neighbor 172.16.10.1 remote-as 5500 neighbor 172.16.10.1 activate no synchronization exit-address-family ! ! ! end |
| Configuración en el Router R3 |
|---|
R3#show run Building configuration... ! version 12.4 ! hostname R3 ! ip cef ! ! ! interface Loopback0 ip address 11.11.11.11 255.255.255.255 ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 192.168.100.11 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ! router bgp 5500 no synchronization bgp router-id 11.11.11.11 bgp log-neighbor-changes neighbor 192.168.100.10 remote-as 5500 no auto-summary ! end |
Verificación
Para mostrar las entradas en la tabla de ruteo (BGP), utilice el comando show ip bgp.
| show ip bgp |
|---|
En el router R1 R1#show ip bgp 172.16.10.2
BGP routing table entry for 172.16.10.2/32, version 14
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table)
Advertised to update-groups:
1 2
Local
0.0.0.0 from 0.0.0.0 (10.10.10.10)
Origin incomplete, metric 0, localpref 100, weight 32768, valid, sourced, best
!--- Displays the routing table entries for the host 172.16.10.2
R1#sh ip bgp 192.168.100.11
BGP routing table entry for 192.168.100.0/24, version 4
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table)
Advertised to update-groups:
1 2
Local
0.0.0.0 from 0.0.0.0 (10.10.10.10)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, weight 32768, valid, sourced, local, best
!--- Displays the entries for the host 192.168.100.11
En el router R3 R3#sh ip bgp 192.168.100.10
BGP routing table entry for 192.168.100.0/24, version 4
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table, RIB-failure(17))
Not advertised to any peer
Local
192.168.100.10 from 192.168.100.10 (10.10.10.10)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal, best
!--- Displays the entries for the host 192.168.100.10
|
En el router R2, utilice el comando show ip bgp vpnv4 para mostrar la información de dirección (VPNv4) de la tabla (BGP).
| show ip bgp vpnv4 |
|---|
En el router R2 R2#sh ip bgp vpnv4 vrf WAN
BGP table version is 24, local router ID is 20.20.20.20
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, I - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: I - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
Route Distinguisher: 2020:1 (default for vrf WAN)
*> 10.10.10.0/24 172.16.10.1 0 0 5500 ?
*> 20.20.20.20/32 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ?
* 172.16.10.0/24 172.16.10.1 0 0 5500 ?
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ?
r> 172.16.10.2/32 172.16.10.1 0 0 5500 ?
*> 192.168.100.0 172.16.10.1 0 0 5500 I
!--- Displays prefixes associated with the (VRF) instance WAN.
R2#show ip bgp vpnv4 vrf WAN 172.16.10.1
BGP routing table entry for 2020:1:172.16.10.0/24, version 7
Paths: (2 available, best #2, table WAN)
Advertised to update-groups:
1
5500
172.16.10.1 from 172.16.10.1 (10.10.10.10)
Origin incomplete, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, external
Extended Community: RT:2020:1
mpls labels in/out 18/nolabel
Local
0.0.0.0 from 0.0.0.0 (20.20.20.20)
Origin incomplete, metric 0, localpref 100, weight 32768, valid, sourced, best
Extended Community: RT:2020:1
mpls labels in/out 18/aggregate(WAN)
!--- Displays prefixes associated with neighbor 172.16.10.1
|
MP-EBGP se establece entre los routers R1 y R2. Utilice el comando ping para verificar el alcance de R1 a R2 y viceversa.
| ping |
|---|
En el router R1 R1#ping 172.16.10.2 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.10.2, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 12/64/208 ms R1#ping 192.168.100.11 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.100.11, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 12/41/96 ms !--- Router R1 can successfully ping the routers R2 and R3.En el router R2 R2#ping vrf WAN 172.16.10.1 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.10.1, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 4/32/96 ms R2#ping vrf WAN 192.168.100.11 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.100.11, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 32/73/204 ms !--- Router R2 can successfully reach router R1 and R3. |
Información Relacionada
Historial de revisiones
| Revisión | Fecha de publicación | Comentarios |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
23-May-2012
|
Versión inicial |
Contacte a Cisco
- Abrir un caso de soporte

- (Requiere un Cisco Service Contract)
 Comentarios
Comentarios