RDMA Over Converged Ethernet (RoCE) version 2
Introduction
RDMA Over Converged Ethernet (RoCEv2)
Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) over Converged Ethernet (RoCEv2) allows direct memory access over the network. It does this by encapsulating an Infiniband (IB) transport packet over Ethernet. There are two RoCE versions: RoCEv1 and RoCEv2. RoCEv1 is an Ethernet link layer protocol and hence allows communication between any two hosts in the same Ethernet broadcast domain. RoCEv2 is an internet layer protocol, which means that RoCEv2 packets can be routed.
The RoCEv2 protocol exists on top of either the UDP/IPv4 or the UDP/IPv6 protocol. The UDP destination port number 4791 has been reserved for RoCEv2. Since RoCEv2 packets are routable, the RoCEv2 protocol is sometimes called Routable RoCE.
RoCEv2 is supported on the Windows and Linux platforms.
This document provides information to configure RoCEv2 in Mode 1 and Mode 2 using Cisco Integrated Management Controller (Cisco IMC). This document does not provide detailed steps to configure vNIC properties. For detailed steps to configure vNIC properties, refer the configuration guide for your Cisco IMC release.
NVMe over Fibre
NVMe over Fabrics (NVMeoF) is a communication protocol that allows one computer to access NVMe namespaces available on another computer. The commands for discovering, connecting, and disconnecting a NVMeoF storage device are integrated into the nvme utility provided in Linux. The NVMeoF fabric that Cisco supports is RDMA over Converged Ethernet version 2 (RoCEv2). The eNIC RDMA driver works in conjunction with the eNIC driver, which must be loaded first when configuring NVMeoF.
Configuring SMB Direct with RoCEv2 in Windows
Guidelines for Using SMB Direct with RoCEv2
General Guidelines and Limitations
-
Cisco IMC 4.1.x and later releases support Microsoft SMB Direct with RoCEv2 on Windows. Cisco recommends that you have all KB updates from Microsoft. See Windows Requirements.

Note
RoCEv2 is not supported on Windows Server 2016.
-
Cisco recommends you check UCS Hardware and Software Compatibility specific to your Cisco IMC release to determine support for Microsoft SMB Direct with RoCEv2 on Microsoft 2019.
-
Microsoft SMB Direct with RoCEv2 is supported only with Cisco UCS VIC 14xx series adapters. RoCEv2 is not supported on UCS VIC 12xx Series and 13xx Series adapters.

Note
RoCE v1 is not supported with Cisco UCS VIC 14xx adapters.
-
RoCEv2 configuration is supported only between Cisco adapters. Interoperability between Cisco adapters and third party adapters is not supported.
-
RoCEv2 supports two RoCEv2 enabled vNIC per adapter and four virtual ports per adapter interface, independent of SET switch configuration.
-
RoCEv2 cannot be used on the same vNIC interface as Geneve Offload, NVGRE, NetFlow, and VMQ features.

Note
RoCEv2 cannot be configured if Geneve Offload feature is enabled on any of the interfaces of a specific adaptor.
-
Support for RoCEv2 protocol for Windows 2019 NDKPI mode 1 and mode 2, with both IPV4 and IPV6.
-
RoCEv2 enabled vNIC interfaces must have the no-drop QoS system class enabled in Cisco IMC.
-
The RoCEv2 properties queue pairs setting must be a minimum of 4 Queue pairs.
-
Maximum number of queue pairs per adapter is 2048.
-
The maximum number of memory regions per RNIC interface is 131072.
-
Cisco IMC does not support fabric failover for vNICs with RoCEv2 enabled.
-
QOS no-drop class configuration needs to be configured correctly on upstream switches. For example: N9K
QOS configurations will vary between different upstream switches.
-
Configuration of RoCEv2 on the Windows platform requires first configuring RoCEv2 Mode 1, then configuring RoCEv2 Mode 2. Modes 1 and 2 relate to the implementation of Network Direct Kernel Provider Interface (NDKPI): Mode 1 is native RDMA, and Mode 2 involves configuration for the virtual port with RDMA.
MTU Properties
-
MTU in Windows is derived from the Jumbo Packet advanced property, rather than from the Cisco IMC configuration.
-
In older versions of the VIC driver, the MTU was derived from Cisco IMC in standalone mode. This behavior changed for VIC 14xx series adapters, where MTU is controlled from the Windows OS Jumbo Packet advanced property. A value configured from Cisco IMC has no effect.
-
The RoCEv2 MTU value is always power-of-two and the maximum limit is 4096.
-
RoCEv2 MTU is derived from the Ethernet MTU.
-
RoCEv2 MTU is the highest power-of-two that is less than the Ethernet MTU. For example:
-
If the Ethernet value is 1500, then the RoCEv2 MTU value is 1024.
-
If the Ethernet value is 4096, then the RoCEv2 MTU value is 4096.
-
If the Ethernet value is 9000, then the RoCEv2 MTU value is 4096.
-
RoCEv2 Modes of Operation
Cisco IMC provides two modes of RoCEv2 configuration depending on the release:
-
From Cisco IMC Release 4.1(1c) onwards, RoCEv2 can be configured with Mode 1 and Mode 2.
Mode 1 uses the existing RoCEv2 properties with Virtual Machine Queue (VMQ).
Mode 2 introduces additional feature to configure Multi-Queue RoCEv2 properties.
RoCEv2 enabled vNICs for Mode2 operation require that the Trust Host CoS is enabled.
RoCEv2 Mode1 and Mode2 are mutually exclusive: RoCEv2 Mode1 must be enabled to operate RoCEv2 Mode2.
-
In Cisco IMC releases prior to 4.1(1c), only mode 1 is supported and could be configured from VMQ RoCE properties.
Downgrade Limitations
Cisco recommends you remove the RoCEv2 configuration before downgrading to any non-supported RoCEv2 release. If the configuration is not removed or disabled, downgrade may fail.
Windows Requirements
Configuration and use of RDMA over Converged Ethernet for RoCEv2 in Windows Server requires the following:
-
Windows Server 2019 or Windows Server 2022 with latest Microsoft updates.
-
VIC Driver version 5.4.0.x or later
-
UCS M5 C-Series servers with VIC 1400 Series adapters: only Cisco UCS VIC 1400 Series adapters are supported.
Configuring vNIC Properties in Mode 1
Follow this procedure to configure vNIC Properties using the VMQ RoCEv2 properties.
Before you begin
Ensure that you are familiar with Cisco IMC GUI interface.
SUMMARY STEPS
- In the Navigation pane, click the Networking menu.
- In the Adapter Card pane, click the vNICs tab.
- In the vNICs pane, select the vNIC (either the default eth0 or eth1, or any other newly created vNIC).
- Configure the vNIC properties as desired. See the configuration guide for detailed procedures. In addition to configuring RoCEv2 in Mode 1, perform the remaining steps.
- In the vNIC Properties pane, under the Ethernet Interrupt area, update the following fields:
- In the vNIC Properties, under the RoCE Properties area, update the following fields:
DETAILED STEPS
| Step 1 |
In the Navigation pane, click the Networking menu. |
||||||||||||
| Step 2 |
In the Adapter Card pane, click the vNICs tab. |
||||||||||||
| Step 3 |
In the vNICs pane, select the vNIC (either the default eth0 or eth1, or any other newly created vNIC). |
||||||||||||
| Step 4 |
Configure the vNIC properties as desired. See the configuration guide for detailed procedures. In addition to configuring RoCEv2 in Mode 1, perform the remaining steps. |
||||||||||||
| Step 5 |
In the vNIC Properties pane, under the Ethernet Interrupt area, update the following fields:
|
||||||||||||
| Step 6 |
In the vNIC Properties, under the RoCE Properties area, update the following fields:
|
What to do next
Perform the host verification to ensure that the Mode 1 is configured correctly. See Verifying the Configurations on the Host.
Configuring RoCEv2 Mode 1 on the Host System
Perform this procedure to configure connection between smb-client and smb-server on two host interfaces. For each of these servers, smb-client and smb-server, configure the RoCEv2-enabled vNIC.
Before you begin
Configure RoCEv2 for Mode 1 from Cisco IMC. See Configuring vNIC Properties in Mode 1.
Procedure
| Step 1 |
In the Windows host, go to the Device Manager and select the appropriate Cisco VIC Internet Interface. |
| Step 2 |
Select the Advanced tab and verify that the Network Direct Functionality property is Enabled. If not, enable it and click OK. Perform this step for both the smb-server and smb-client vNICs. |
| Step 3 |
Select and select . |
| Step 4 |
Verify that RoCEv2 is enabled on the host operating system using PowerShell.
|
| Step 5 |
Bring up Powershell and execute the SmbClientNetworkInterface command. |
| Step 6 |
Enter enable - netadapterrdma [-name] ["Ethernetname"] |
| Step 7 |
Verify the overall RoCEv2 Mode 1 configuration at the host:
|
| Step 8 |
In the Powershell command window, check the connection entries with the netstat -xan output command to ensure they are displayed. |
| Step 9 |
By default, SMB Direct of Microsoft establishes two RDMA connections per RDMA Interface. You can change the number of RDMA connections per RDMA interface to one or any number of connections. To increase the number of RDMA connections to 4, execute the following command in PowerShell: |
What to do next
Configure RoCEv2 Mode 2. See Configuring vNIC Properties in Mode 2.
Configuring vNIC Properties in Mode 2
Follow this procedure to configure vNIC Properties in Mode 2. You can perform this procedure using Cisco IMC release 4.1(1c) or higher.
Before you begin
-
Ensure that you are familiar with Cisco IMC GUI interface.
-
Ensure that you are using Cisco IMC release 4.1(1c) or higher.
SUMMARY STEPS
- In the Navigation pane, click the Networking menu.
- In the Adapter Card pane, click the vNICs tab.
- In the vNICs pane, select the vNIC (either the default eth0 or eth1, or any other newly created vNIC).
- Configure the vNIC properties as desired. See the configuration guide for detailed procedures. In addition to configuring RoCEv2 in Mode 1, perform the remaining steps.
- In the vNIC Properties pane, under the General area, update the following :
- In the vNIC Properties pane, under the Ethernet Interrupt area, update the following fields:
- In the vNIC Properties pane, under the Multi Queue area, update the following fields:
- In the vNIC Properties pane, under the RoCE Properties area, update the following fields:
DETAILED STEPS
| Step 1 |
In the Navigation pane, click the Networking menu. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Step 2 |
In the Adapter Card pane, click the vNICs tab. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Step 3 |
In the vNICs pane, select the vNIC (either the default eth0 or eth1, or any other newly created vNIC). |
||||||||||||||||||
| Step 4 |
Configure the vNIC properties as desired. See the configuration guide for detailed procedures. In addition to configuring RoCEv2 in Mode 1, perform the remaining steps. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Step 5 |
In the vNIC Properties pane, under the General area, update the following :
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Step 6 |
In the vNIC Properties pane, under the Ethernet Interrupt area, update the following fields:
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Step 7 |
In the vNIC Properties pane, under the Multi Queue area, update the following fields:
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Step 8 |
In the vNIC Properties pane, under the RoCE Properties area, update the following fields:
|
What to do next
Perform the host verification to ensure that the Mode 2 is configured correctly. See Verifying the Configurations on the Host.
Configuring RoCEv2 Mode 2 on the Host System
Before you begin
-
Configure and confirm the connection for RoCEv2 Mode 2 for both Cisco IMC and the host.
-
Configure RoCEv2 Mode 2 connection for Cisco IMC.
-
Enable Hyper-V at the Windows host server.
Procedure
| Step 1 |
Go to the Hyper-V switch manager. |
| Step 2 |
Create a new Virtual Network Switch (vSwitch) for the RoCEv2-enabled Ethernet interface.
|
| Step 3 |
Bring up the Powershell interface. |
| Step 4 |
Configure the non-default vPort and enable RDMA with the following Powershell commands: |
| Step 5 |
Configure IPv4 addresses for the vPorts. |
| Step 6 |
Create a share in smb-server and map the share in the smb-client.
|
| Step 7 |
Verify the Mode 2 configuration.
|
Verifying the Configurations on the Host
Once the configurations are done, you should perform the following:
-
Host verification of Mode 1 and Mode 2 configurations
-
Host verification for RDMA capable ports
-
Verification of RDMA capable ports using Advanced Property
-
V port assignment on each PF
SUMMARY STEPS
- NIC driver creates Kernal Socket Listeners on each RDMA capable ports in Mode 1 and V ports in Mode 2 to accept incoming remote RDMA requests.
- Host verification for RDMA capable ports at host.
- Netstat-xan output shows established connections in addition to Listeners. If output shows only listeners with traffic, it indicates traffic is passing only on TCP path. If connections are created on PF or vPorts, traffic is passing on RDMA Path.
- Verification of RDMA capable port using Advanced Property. According to the driver, Network Direct functionality to be enabled on RDMA Capable VNIC.
- Verify V Port assignment on each PF.
DETAILED STEPS
| Step 1 |
NIC driver creates Kernal Socket Listeners on each RDMA capable ports in Mode 1 and V ports in Mode 2 to accept incoming remote RDMA requests. Example: |
| Step 2 |
Host verification for RDMA capable ports at host. Example: |
| Step 3 |
Netstat-xan output shows established connections in addition to Listeners. If output shows only listeners with traffic, it indicates traffic is passing only on TCP path. If connections are created on PF or vPorts, traffic is passing on RDMA Path. Example: |
| Step 4 |
Verification of RDMA capable port using Advanced Property. According to the driver, Network Direct functionality to be enabled on RDMA Capable VNIC. |
| Step 5 |
Verify V Port assignment on each PF. Example: |
Removing RoCEv2 on vNIC Interface Using Cisco IMC GUI
You must perform this task to remove RoCEv2 on the vNIC interface.
Procedure
| Step 1 |
In the Navigation pane, click Networking. |
| Step 2 |
Expand Networking and select the adapter from which you want to remove RoCEv2 configuration. |
| Step 3 |
Select vNICs tab. |
| Step 4 |
Select the vNIC from which you want to remove RoCEv2 configuration. |
| Step 5 |
Expand RoCE Properties tab and uncheck the RoCE check box. |
| Step 6 |
Click Save Changes. |
| Step 7 |
Reboot the server for the above changes to take effect. |
Configuring NVMe Over Fabrics (NVMeoF) with RoCEv2 in Linux
Guidelines for using NVMe over Fabrics (NVMeoF) with RoCEv2 on Linux
General Guidelines and Limitations
-
Cisco IMC Release 4.1(1x) and later releases support RoCEv2 on Redhat Enterprise Linux 7.6 with Linux Z-Kernel 3.10.0-957.27.2 and Redhat Enterprise Linus 7.7 with Linux Z-kernel-3.10.0-1062.9.1. Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.7 supports both IPv4 and IPv6.

Note
Additional Linux distributions will be supported in later Cisco IMC 4.1.x releases.
-
Cisco recommends that you check UCS Hardware and Software Compatibility specific to your Cisco IMC release to determine support for NVMeoF. NVMeoF is supported on Cisco UCS C-Series M5 and later servers.
-
NVMeoF with RoCEv2 is supported only with the Cisco UCS VIC 14xx series adapters. NVMeoF is not supported on Cisco UCS VIC 12xx or 13xx series adapters.
-
When creating RoCEv2 interfaces, use Cisco IMC provided Linux-NVMe-RoCE adapter policy.
-
Only two RoCEv2 enabled vNICs per adapter are supported.
-
Booting from an NVMeoF namespace is not supported.
-
Layer 3 routing is not supported.
-
RoCEv2 does not support bonding.
-
Saving a crashdump to an NVMeoF namespace during a system crash is not supported.
-
NVMeoF cannot be used with usNIC, VMFEX, VxLAN, VMQ, VMMQ, NVGRE, Geneve offload and DPDK features.
-
Netflow monitoring is not supported on RoCEv2 interfaces.
-
In the Linux-NVMe-RoCE policy, do not change values of Queue Pairs, Memory Regions, Resource Groups, and Priority settings other than to Cisco provided default values. NVMeoF functionality may not be guaranteed with different settings for Queue Pairs, Memory Regions, Resource Groups, and Priority.
-
The QoSno drop class configuration must be properly configured on upstream switches such as Cisco Nexus 9000 series switches. QoS configurations vary between different upstream switches.
-
Set MTU size correctly on the VLANs and QoS policy on upstream switches.
-
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) may cause temporary loss of network connectivity when a failover or failback event occurs. To prevent this issue from occurring, disable STP on uplink switches.
Interrupts
-
Linux RoCEv2 interface supports only MSIx interrupt mode. Cisco recommends that you avoid changing interrupt mode when the interface is configured with RoCEv2 properties.
-
The minimum interrupt count for using RoCEv2 with Linux is 8.
Downgrade Limitations
Cisco recommends that you remove the RoCEv2 configuration before downgrading to any non-supported RoCEv2 release.
Linux Requirements
Configuration and use of RoCEv2 in Linux requires the following:
-
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.6 with Z-Kernel 3.10.0-957.27.2 and Redhat Enterprise Linux 7.7 with Linux Z-kernel-3.10.0-1062.9.1 and above

Note
Additional Linux distributions will be supported in later releases.
-
InfiniBand kernel API module ib_core
-
Cisco IMC Release 4.1(1x) or later
-
VIC firmware - Minimum requirement is 5.1(1x) for IPv4 support and 5.1(2x) for IPv6 support
-
UCS C-Series M5 servers with Cisco UCS VIC 14xx series adapters
-
eNIC driver version 4.0.0.6-802-21 or later provided with the 4.1(1x) release package
-
enic_rdma driver version 1.0.0.6-802-21 or later provided with the 4.1(1x) release package

Note
Use eNIC driver version 4.0.0.10-802.34 or later and enic_rdma driver version 1.0.0.10-802.34 or later for IPv6 support.
-
A storage array that supports NVMeoF connection
Configuring RoCEv2 for NVMeoF using Cisco IMC GUI
Procedure
| Step 1 |
In the Navigation pane, click Networking. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Step 2 |
Expand Networking and click on the adapter to configure RoCEv2 vNIC. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Step 3 |
Select the vNICs tab. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Step 4 |
Perform one the following:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Step 5 |
Expand RoCE Properties. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Step 6 |
Select RoCE checkbox. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Step 7 |
Modify the following vNIC properties:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Step 8 |
Click Save Changes. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Step 9 |
Select Reboot when prompted. |
Enabling an SRIOV BIOS Policy
Use these steps to configure the server with RoCEv2 vNIC to enable the SRIOV BIOS policy before enabling the IOMMU driver in the Linux kernel.
Procedure
| Step 1 |
In the Navigation pane, click Compute. |
| Step 2 |
Expand BIOS > Configure BIOS > I/O. |
| Step 3 |
Select Intel VT for direct IO to Enabled. |
| Step 4 |
Click Save. |
| Step 5 |
Reboot the host for the changes to take effect. |
Configuring RoCEv2 for NVMeoF on the Host System
Before you begin
Configure the server with RoCEv2 vNIC and the SRIOV-enabled BIOS policy.
Procedure
| Step 1 |
Open the |
| Step 2 |
Add |
| Step 3 |
Save the file. |
| Step 4 |
Run the following command to generate a new
|
| Step 5 |
Reboot the server for the changes to take effect after enabling IOMMU. |
| Step 6 |
Use the following to check the output file and verify that the server is booted with the
Note its inclusion at the end of the output. Example:  |
What to do next
Download the enic and enic_rdma drivers.
Installing Cisco enic and enic_rdma Drivers
The enic_rdma driver requires enic driver. When installing enic and enic_rdma drivers, download and use the matched set of enic and enic_rdma drivers from here. Do not attempt to use the binary enic_rdma driver downloaded from cisco.com with an inbox enic driver.
Procedure
| Step 1 |
Run the following command to tnstall the enic and enic_rdma rpm packages: The enic_rdma driver is now installed but not loaded in the running kernel. During enic_rdma installation, enic_rdmalibnvdimm module might fail to install on RHEL 7.7 because the nvdimm-security.conf dracut module requires spaces in the add_drivers value. For the workaround, follow the instructions from the following links: |
||
| Step 2 |
Reboot the server to load enic_rdma driver into the running kernel. |
||
| Step 3 |
Run the following command to verify the installation of enic_rdma driver and RoCEv2 interface: |
||
| Step 4 |
Run the following command to load the nvme-rdma kernel module: After the server reboots, nvme-rdma kernel module is unloaded. To load nvme-rdma kernel module on every server reboot, create
nvme_rdma.conf file using:
|
What to do next
Discover targets and connect to NVMe namespaces. If your system needs multipath access to the storage, see Setting Up Device Mapper Multipath.
Discovering the NVMe Target
Use this procedure to discover the NVMe target and connect NVMe namespaces.
Before you begin
-
Ensure that you have nvme-cli version 1.6 or later.
-
Configure the IP address on the RoCEv2 interface and make sure the interface can ping the target IP.
Procedure
| Step 1 |
Perform the following to create an nvme folder in /etc, and then manually generate hostnqn. |
||
| Step 2 |
Perform the following to create a settos.sh file and run the script to set priority flow control (PFC) in IB frames.
|
||
| Step 3 |
Run the following command to discover the NVMe target: Example:
|
||
| Step 4 |
Run the following command to connect to the discovered NVMe target: Example: |
||
| Step 5 |
Use the nvme list command to verify the mapped namespaces: |
Setting Up Device Mapper Multipath
If your system is configured with Device Mapper Multipathing (DM Multipath), use this procedure to set up device mapper multipath.
Procedure
| Step 1 |
Install the |
| Step 2 |
Perform the following to enable and start multipathd: |
| Step 3 |
Edit the etc/multipath.conf file to use the following values: 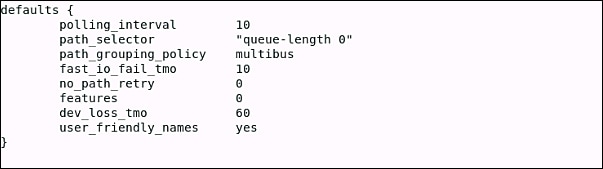 |
| Step 4 |
Perform the following to flush with the updated multipath device maps: |
| Step 5 |
Perform the following to restart multipath service: |
| Step 6 |
Perform the following to rescan multipath devices: |
| Step 7 |
Perform the following to check the multipath status: |
Removing RoCEv2 on vNIC Interface using Cisco IMC GUI
Perform this procedure to remove RoCEv2 on the vNIC interface.
Procedure
| Step 1 |
In the Navigation pane, click Networking. |
| Step 2 |
Expand Networking and select the adapter from which you want to remove RoCEv2 configuration. |
| Step 3 |
Select vNICs tab. |
| Step 4 |
Select the vNIC from which you want to remove RoCEv2 configuration. |
| Step 5 |
Expand RoCE Properties tab. |
| Step 6 |
Uncheck the RoCE check box. |
| Step 7 |
Click Save Changes. |
| Step 8 |
Reboot the server for the above changes to take effect. |
Using the Cisco IMC CLI to Configure the RoCEv2 Interface
Configuring RoCEv2 Interface Using Cisco IMC CLI
Use the following steps to configure RoCEv2 interface using Cisco IMC CLI interface.
Before you begin
-
Ensure that you are familiar with Cisco IMC CLI interface.
-
You must log in with admin privileges.
SUMMARY STEPS
- server # scope chassis
- server/chassis # scope adapter index_number
- server/chassis/adapter # create host-eth-if vNIC_name
- server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if *# set rocev2 enabled
- server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if *# set rdma-cos 5
- server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if *# set rdma_mr 131072
- server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if *# set rdma_qp 1024
- server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if *# set rdma_resgrp 8
- server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if *# scope comp-queue
- server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if/comp-queue *# set cq-count 2
- server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if/comp-queue *# exit
- server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if *# scope trans-queue
- server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if/trans-queue *# set wq-count 1
- server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if/trans-queue *# set wq-ring-size 256
- server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if/trans-queue *# exit
- server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if *# scope interrupt
- server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if/interrupt *# set interrupt-count 256
- server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if/interrupt *# set interrupt-mode MSIx
- server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if/interrupt *# commit
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
server # scope chassis |
Enters chassis command mode. |
||
| Step 2 |
server/chassis # scope adapter index_number |
Enters the command mode for the adapter card at the PCI slot number specified by index_number.
|
||
| Step 3 |
server/chassis/adapter # create host-eth-if vNIC_name |
Creates a vNIC. |
||
| Step 4 |
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if *# set rocev2 enabled |
Enables RoCEv2 on vNIC. |
||
| Step 5 |
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if *# set rdma-cos 5 |
Sets RDMA CoS 5 for RoCEv2 vNIC. |
||
| Step 6 |
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if *# set rdma_mr 131072 |
Sets RDMA Memory Region as 131072 for RoCEv2 vNIC. |
||
| Step 7 |
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if *# set rdma_qp 1024 |
Sets RDMA Queue Pairs as 1024 for RoCEv2 vNIC. |
||
| Step 8 |
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if *# set rdma_resgrp 8 |
Sets RDMA Resource Groups as 8 for RoCEv2 vNIC. |
||
| Step 9 |
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if *# scope comp-queue |
Enters the Completion Queue command mode. |
||
| Step 10 |
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if/comp-queue *# set cq-count 2 |
Sets Completion Queue Count as 2 for vNIC. |
||
| Step 11 |
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if/comp-queue *# exit |
Exits to host Ethernet interface command mode. |
||
| Step 12 |
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if *# scope trans-queue |
Enters the Transmit Queue command mode. |
||
| Step 13 |
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if/trans-queue *# set wq-count 1 |
Sets Transmit Queue Count as 1 for vNIC. |
||
| Step 14 |
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if/trans-queue *# set wq-ring-size 256 |
Sets Transmit Queue Ring Buffer Size as 256 for vNIC. |
||
| Step 15 |
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if/trans-queue *# exit |
Exits to host Ethernet interface command. |
||
| Step 16 |
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if *# scope interrupt |
Enters Interrupt command mode. |
||
| Step 17 |
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if/interrupt *# set interrupt-count 256 |
Sets Interrupt Count as 256 for vNIC. |
||
| Step 18 |
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if/interrupt *# set interrupt-mode MSIx |
Sets the Interrupt Mode as MSIx |
||
| Step 19 |
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if/interrupt *# commit |
Commits the transaction to the system configuration.
|
Example
server# scope chassis
server/chassis # scope adapter 1
server/chassis/adapter # create host-eth-if vNIC_Test
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if *# set rocev2 enabled
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if *# set rdma-cos 5
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if *# set rdma_mr 131072
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if *# set rdma_qp 1024
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if *# set rdma_resgrp 8
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if *# scope comp-queue
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if/comp-queue *# set cq-count 2
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if/comp-queue *# exit
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if *# scope trans-queue
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if/trans-queue *# set wq-count 1
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if/trans-queue *# set wq-ring-size 256
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if/trans-queue *# exit
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if *# scope interrupt
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if/interrupt *# set interrupt-count 256
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if/interrupt *# set interrupt-mode MSIx
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if/interrupt *# commit
Deleting RoCEv2 Interface Using Cisco IMC CLI
SUMMARY STEPS
- server # scope chassis
- server/chassis # scope adapter index_number
- server/chassis/adapter # scope host-eth-if vNIC_name
- server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if # set rocev2 disabled
- server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if *# commit
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
server # scope chassis |
Enters the chassis command mode. |
||
| Step 2 |
server/chassis # scope adapter index_number |
Enters the command mode for the adapter card at the PCI slot number specified by index_number.
|
||
| Step 3 |
server/chassis/adapter # scope host-eth-if vNIC_name |
Enters the command mode for the vNIC specified by vNIC_name. |
||
| Step 4 |
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if # set rocev2 disabled |
Disables RoCE properties on the vNIC. |
||
| Step 5 |
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if *# commit |
Commits the transaction to the system configuration.
|
Example
server# scope chassis
server/chassis # scope adapter 1
server/chassis/adapter # scope host-eth-if vNIC_Test
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if # set rocev2 disabled
server/chassis/adapter/host-eth-if *# commit
Known Limitations and Behavior
The following known issues are found in the RoCEv2 release.
|
Symptom |
Conditions |
Workaround |
|---|---|---|
|
When sending high bandwidth NVMe traffic on some Cisco Nexus 9000 switches, the switch port connected to the storage sometimes reaches the max PFC peak and does not automatically clear the buffers. In Nexus 9000 switches, the nxos command "show hardware internal buffer info pkt-stats input peak" shows that the Peak_cell or PeakQos value for the port reaches more than 1000. |
The NVMe traffic will drop. |
To recover the switch from this error mode.
|
|
On VIC 1400 Series adapters, the neNIC driver for Windows 2019 can be installed on Windows 2016. And the Windows 2016 driver can be installed on Windows 2019. However, this is an unsupported configuration. |
Case 1: Installing Windows 2019 nenic driver on Windows 2016 succeeds, but on Windows 2016,RDMA is not supported. Case 2: Installing Windows 2016 nenic driver on Windows 2019 succeeds, but on Windows 2019, RDMA comes with default disabled state, instead of enabled state. |
The driver binaries for Windows 2016 and Windows 2019 are in folders that are named accordingly. Install the correct binary on the platform that is being built/upgraded. |
 Feedback
Feedback