Release Notes for Cisco Intrusion Prevention System 6.0(3)E1
Available Languages
Table Of Contents
Release Notes for Cisco Intrusion Prevention System 6.0(3)E1
IPS Management and Event Viewers
Cisco Security Intelligence Operations
Before Upgrading to Cisco IPS 6.0(3)E.1
Backing Up and Restoring the Configuration File Using a Remote Server
Obtaining Software on Cisco.com
Upgrading to Cisco IPS 6.0(3)E.1
After Upgrading to Cisco IPS 6.0(3)E.1
Service Programs for IPS Products
Obtaining and Installing the License Key
Understanding Password Recovery
Recovering the Appliance Password
Recovering the NM CIDS Password
Recovering the AIP SSM Password
Verifying the State of Password Recovery
Troubleshooting Password Recovery
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
Release Notes for Cisco Intrusion Prevention System 6.0(3)E1
Published: June 27, 2007Revised: August 1, 2012, OL-20145-01
Contents
•
IPS Management and Event Viewers
•
Cisco Security Intelligence Operations
•
Before Upgrading to Cisco IPS 6.0(3)E.1
•
Upgrading to Cisco IPS 6.0(3)E.1
•
After Upgrading to Cisco IPS 6.0(3)E.1
•
Cisco Security Intelligence Operations
•
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request

CautionThe BIOS on Cisco IDS/IPS sensors is specific to Cisco IDS/IPS sensors and must only be upgraded under instructions from Cisco with BIOS files obtained from the Cisco website. Installing a non-Cisco or third-party BIOS on Cisco IDS/IPS sensors voids the warranty. For more information on how to obtain instructions and BIOS files from the Cisco website, see Obtaining Software on Cisco.com.
IPS 6.0(3)E.1 File List
The following files are part of Cisco IPS 6.0(3)E.1:
•
Service Pack Files
–
IPS-K9-6.0-3-E.1.pkg
–
IPS-CS-MGR-K9-6.0-3-E1.zip
•
System Image Files
–
IPS-4215-K9-sys-1.1-a-6.0-3-E.1.img
–
IPS-4240-K9-sys-1.1-a-6.0-3-E.1.img
–
IPS-4255-K9-sys-1.1-a-6.0-3-E.1.img
–
IPS-4260-K9-sys-1.1-a-6.0-3-E.1.img
–
IPS-NM-CIDS-K9-sys-1.1-a-6.0-3-E.1.img
–
WS-SVC-IDSM2-K9-sys-1.1-a-6.0-3-E.1.bin.gz
–
IPS-SSM-K9-sys-1.1-a-6.0-3-E.1.img
•
Recovery Image Files
–
IPS-K9-r-1.1-a-6.0-3-E.1.pkg
•
Readme File
–
IPS-6.0-3-E.1.readme.txt
•
ISO Image
–
IPS-K9-cd-1.1-a-6.0-3-E.1.iso

Note
The ISO Image is for the IDS 4235 and IDS 4250 series sensors only.
For More Information
•
For the procedure for obtaining these files on Cisco.com, see Obtaining Software on Cisco.com.
•
For the procedure for installing service pack files, see Upgrading to 6.0(3)E.1.
•
For the procedure for installing system image files, refer to Upgrading, Downgrading, and Installing System Images.
•
For the procedure for installing recovery image files, refer to Recovering the Application Partition.
•
For the procedure for installing IOS image files, see Installing the ISO Image File.
Supported Platforms

Note
The number of concurrent CLI sessions is limited based on the platform. The IDS 4215 and NM CIDS are limited to three concurrent CLI sessions. All other platforms allow ten concurrent sessions.
Cisco IPS 6.0(3)E.1 is supported on the following platforms:
•
IDS 4215 Series Sensor Appliances
•
IDS 4235 Series Sensor Appliances
•
IPS 4240 Series Sensor Appliances
•
IDS 4250 Series Sensor Appliances
•
IPS 4255 Series Sensor Appliances
•
IPS 4260 Series Sensor Appliances
•
IPS 4270-20 Series Sensor Appliances
•
WS-SVC-IDSM2 series Intrusion Detection System Module (IDSM2)
•
Intrusion Detection System Network Module (NM CIDS)
•
ASA-SSM-AIP-10 series Cisco ASA Advanced Inspection and Prevention Security Service Modules (AIP SSM)
•
ASA-SSM-AIP-20 series Cisco ASA Advanced Inspection and Prevention Security Service Modules (AIP SSM)
Supported Servers
The following FTP servers are supported for IPS software updates:
•
WU-FTPD 2.6.2 (Linux)
•
Solaris 2.8.
•
Sambar 6.0 (Windows 2000)
•
Serv-U 5.0 (Windows 2000)
•
MS IIS 5.0 (Windows 2000)
The following HTTP/HTTPS servers are supported for IPS software updates:
•
CMS - Apache Server (Tomcat)
•
CMS - Apache Server (JRun)

Note
The sensor cannot download software updates from Cisco.com. You must download the software updates from Cisco.com to your FTP server, and then configure the sensor to download them from your FTP server.
ROMMON and TFTP
ROMMON uses TFTP to download an image and launch it. TFTP does not address network issues such as latency or error recovery. It does implement a limited packet integrity check so that packets arriving in sequence with the correct integrity value have an extremely low probability of error. But TFTP does not offer pipelining so the total transfer time is equal to the number of packets to be transferred times the network average RTT. Because of this limitation, we recommend that the TFTP server be located on the same LAN segment as the sensor. Any network with an RTT less than a 100 milliseconds should provide reliable delivery of the image. Be aware that some TFTP servers limit the maximum file size that can be transferred to ~32 MB.
For More Information
•
For the procedure for downloading IPS software updates from Cisco.com, refer to Obtaining Cisco IPS Software.
•
For the procedure for configuring automatic updates, refer to Configuring Automatic Upgrades.
IPS Management and Event Viewers
Use the following tools for configuring IPS 6.0(3)E.1 sensors:
•
IDM 6.0
•
IPS CLI 6.0
•
ASDM 5.2
•
CSM 3.1
Use the following tools for monitoring 6.0(3)E.1 sensors:
•
MARS 4.2 and 4.3(1)
•
IEV 5.2
•
CSM 4.0

Note
Viewers that are already configured to monitor the 5.x sensors may need to be configured to accept a new SSL certificate for the 6.0(3)E.1 sensors.
Cisco Security Intelligence Operations
The Cisco Security Intelligence Operations site on Cisco.com provides intelligence reports about current vulnerabilities and security threats. It also has reports on other security topics that help you protect your network and deploy your security systems to reduce organizational risk.
You should be aware of the most recent security threats so that you can most effectively secure and manage your network. Cisco Security Intelligence Operations contains the top ten intelligence reports listed by date, severity, urgency, and whether there is a new signature available to deal with the threat.
Cisco Security Intelligence Operations contains a Security News section that lists security articles of interest. There are related security tools and links.
You can access Cisco Security Intelligence Operations at this URL:
http://tools.cisco.com/security/center/home.x
Cisco Security Intelligence Operations is also a repository of information for individual signatures, including signature ID, type, structure, and description.
You can search for security alerts and signatures at this URL:
http://tools.cisco.com/security/center/search.x
New and Changed Information
Cisco IPS 6.0(3)E.1 contains the S291 signature update.
MySDN Decommissioned
Because MySDN has been decommissioned, the URL in older versions of IDM and IME is no longer functional. If you are using IPS 6.0 or later, we recommend that you upgrade your version of IDM and IME.
You can upgrade to the following versions to get the functioning MySDN URL:
•
IDM 7.0.3
•
IME 7.0.3
•
IPS 7.0(4), which contains IDM 7.0.4
If you are using version IPS 5.x, you must look up signature information manually at this URL:
http://tools.cisco.com/security/center/search.x
For More Information
For information on MySDN (formerly known as NSDB) in IDM, refer to Configuring Signatures.
Before Upgrading to Cisco IPS 6.0(3)E.1
This section describes what to do before upgrading to IPS 6.0(3)E.1, and contains the following topics:
•
Backing Up and Restoring the Configuration File Using a Remote Server
•
Obtaining Software on Cisco.com
Perform These Tasks
Before you upgrade your sensors to Cisco IPS 6.0(3)E.1, make sure you have performed the following tasks:
•
Created a backup copy of your configuration.
•
Saved the output of the show version command.
If you need to downgrade a service pack or signature update, you will know what versions you had, and you can then apply the configuration you saved when you backed up your configuration.

Note
You cannot use the downgrade command to downgrade from 6.0(3)E.1 to 5.1. You can only downgrade from new service packs and signature updates to the previous version of service pack or signature update.
•
Upgraded the IDS 4215 BIOS to the most recent version.
•
If you are using SNMP set and/or get features, you must configure the read-only-community and read-write-community parameters before upgrading to IPS 6.0(3)E.1.
In IPS 5.x, the read-only-community was set to public by default, and the read-write-community was set to private by default. In IPS 6.0(3)E.1 these two options do not have default values. If you were not using SNMP gets and sets with IPS 5.x (for example, enable-set-get was set to false), there is no problem upgrading to IPS 6.0(3)E.1. If you were using SNMP gets and sets with IPS 5.x (for example, enable-set-get was set to true), you must configure the read-only-community and read-write-community parameters to specific values or the IPS 6.0(3)E.1 upgrade fails. You receive the following error message:
Error: execUpgradeSoftware : Notification Application "enable-set-get" value set to true, but "read-only-community" and/or "read-write-community" are set to null. Upgrade may not continue with null values in these fields.For More Information
•
For the procedure for creating a backup copy of your configuration, see Backing Up and Restoring the Configuration File Using a Remote Server.
•
For the procedure for displaying version information, refer to Displaying Version Information.
•
For the procedure for downgrading your sensor, refer to Upgrading, Downgrading, and Installing System Images.
•
For the procedure for upgrading the sensor, see Upgrading the IDS 4215 BIOS.
•
For the procedure for configuring SNMP, for the CLI procedure, refer to Configuring SNMP. For the IDM procedure, refer to Configuring SNMP.
Backing Up and Restoring the Configuration File Using a Remote Server

Note
We recommend copying the current configuration file to a remote server before upgrading.
Use the copy [/erase] source_url destination_url keyword command to copy the configuration file to a remote server. You can then restore the current configuration from the remote server. You are prompted to back up the current configuration first.
The following options apply:
•
/erase—Erases the destination file before copying.
This keyword only applies to the current-config; the backup-config is always overwritten. If this keyword is specified for destination current-config, the source configuration is applied to the system default configuration. If it is not specified for the destination current-config, the source configuration is merged with the current-config.
•
source_url—The location of the source file to be copied. It can be a URL or keyword.
•
destination_url—The location of the destination file to be copied. It can be a URL or a keyword.
•
current-config—The current running configuration. The configuration becomes persistent as the commands are entered.
•
backup-config—The storage location for the configuration backup.
The exact format of the source and destination URLs varies according to the file. Here are the valid types:
•
ftp:—Source or destination URL for an FTP network server. The syntax for this prefix is:
ftp:[//[username@] location]/relativeDirectory]/filename
ftp:[//[username@]location]//absoluteDirectory]/filename
•
scp:—Source or destination URL for the SCP network server. The syntax for this prefix is:
scp:[//[username@] location]/relativeDirectory]/filename
scp:[//[username@] location]//absoluteDirectory]/filename

Note
If you use FTP or SCP protocol, you are prompted for a password. If you use SCP protocol, you must also add the remote host to the SSH known hosts list.
•
http:—Source URL for the web server. The syntax for this prefix is:
http:[[/[username@]location]/directory]/filename
•
https:—Source URL for the web server. The syntax for this prefix is:
https:[[/[username@]location]/directory]/filename

Note
HTTP and HTTPS prompt for a password if a username is required to access the website. If you use HTTPS protocol, the remote host must be a TLS trusted host.

CautionCopying a configuration file from another sensor may result in errors if the sensing interfaces and virtual sensors are not configured the same.
Backing Up the Current Configuration to a Remote Server
To back up your current configuration to a remote server, follow these steps:
Step 1
Log in to the CLI using an account with administrator privileges.
Step 2 Back up the current configuration to the remote server.sensor# copy current-config scp://user@192.0.2.0//configuration/cfg current-configPassword: ********Warning: Copying over the current configuration may leave the box in an unstable state.Would you like to copy current-config to backup-config before proceeding? [yes]:Step 3 Enter yes to copy the current configuration to a backup configuration.cfg 100% |************************************************| 36124 00:00
Restoring the Current Configuration From a Backup File
To restore your current configuration from a backup file, follow these steps:
Step 1
Log in to the CLI using an account with administrator privileges.
Step 2 Back up the current configuration to the remote server.sensor# copy scp://user@192.0.2.0//configuration/cfg current-configPassword: ********Warning: Copying over the current configuration may leave the box in an unstable state.Would you like to copy current-config to backup-config before proceeding? [yes]:Step 3 Enter yes to copy the current configuration to a backup configuration.cfg 100% |************************************************| 36124 00:00Warning: Replacing existing network-settings may leave the box in an unstable state.Would you like to replace existing network settings (host-ipaddress/netmask/gateway/access-list) on sensor before proceeding? [no]:sensor#Step 4
Enter no to retain the currently configured hostname, IP address, subnet mask, management interface, and access list. We recommend you retain this information to preserve access to your sensor after the rest of the configuration has been restored.
For More Information
•
For the CLI procedure for adding hosts to the SSH known hosts list, refer to Adding Hosts to the SSH Known Hosts List. For the IDM procedure, refer to Defining Known Host Keys.
•
For the CLI procedure for adding TLS trusted hosts, refer to Adding TLS Trusted Hosts. For the IDM procedure, refer to Adding Trusted Hosts.
Obtaining Software on Cisco.com
You can find major and minor updates, service packs, signature and signature engine updates, system and recovery files, firmware upgrades, and readmes on the Download Software site on Cisco.com.

Note
You must be logged in to Cisco.com to download software.
Signature updates are posted to Cisco.com approximately every week, more often if needed. Service packs are posted to Cisco.com as needed. Major and minor updates are also posted periodically. Check Cisco.com regularly for the latest IPS software.

Note
You must have an active IPS maintenance contract and a Cisco.com password to download software. You must have a license to apply signature updates.
Downloading IPS Software
To download software on Cisco.com, follow these steps:
Step 1
Log in to Cisco.com.
Step 2
From the Support drop-down menu, choose Download Software.
Step 3
Under Select a Software Product Category, choose Security Software.
Step 4
Choose Intrusion Prevention System (IPS).
Step 5
Enter your username and password.
Step 6
In the Download Software window, choose IPS Appliances > Cisco Intrusion Prevention System and then click the version you want to download.

Note
You must have an IPS subscription service license to download software.
Step 7
Click the type of software file you need. The available files appear in a list in the right side of the window. You can sort by file name, file size, memory, and release date. And you can access the Release Notes and other product documentation.
Step 8
Click the file you want to download. The file details appear.
Step 9
Verify that it is the correct file, and click Download.
Step 10
Click Agree to accept the software download rules. The first time you download a file from Cisco.com, you must fill in the Encryption Software Export Distribution Authorization form before you can download the software.
•
Fill out the form and click Submit. The Cisco Systems Inc. Encryption Software Usage Handling and Distribution Policy appears.
•
Read the policy and click I Accept. The Encryption Software Export/Distribution Form appears.
If you previously filled out the Encryption Software Export Distribution Authorization form, and read and accepted the Cisco Systems Inc. Encryption Software Usage Handling and Distribution Policy, these forms are not displayed again. The File Download dialog box appears.
Step 11
Open the file or save it to your computer.
Step 12
Follow the instructions in the Readme to install the update.

Note
Major and minor updates, service packs, recovery files, signature and signature engine updates are the same for all sensors. System image files are unique per platform.
IPS Software Versioning
When you download IPS software images from Cisco.com, you should understand the versioning scheme so that you know which files are base files, which are cumulative, and which are incremental.
Major Update
A major update contains new functionality or an architectural change in the product. For example, the IPS 6.0 base version includes everything (except deprecated features) since the previous major release (the minor update features, service pack fixes, and signature updates) plus any new changes. Major update 6.0(1) requires 5.x. With each major update there are corresponding system and recovery packages.

Note
The 6.0(1) major update is only used to upgrade 5.x sensors to 6.0(1). If you are reinstalling 6.0(1) on a sensor that already has 6.0(1) installed, use the system image or recovery procedures rather than the major update.
Minor Update
A minor update is incremental to the major version. Minor updates are also base versions for service packs. The first minor update for 6.0 is 6.1(1). Minor updates are released for minor enhancements to the product. Minor updates contain all previous minor features (except deprecated features), service pack fixes, signature updates since the last major version, and the new minor features being released. You can install the minor updates on the previous major or minor version (and often even on earlier versions). The minimum supported version needed to upgrade to the newest minor version is listed in the Readme that accompanies the minor update. With each minor update there are corresponding system and recovery packages.
Service Packs
Service packs are cumulative following a base version release (minor or major). Service packs are used for the release of defect fixes with no new enhancements. Service packs contain all service pack fixes since the last base version (minor or major) and the new defect fixes being released. Service packs require the minor version. The minimum supported version needed to upgrade to the newest service pack is listed in the Readme that accompanies the service pack. Service packs also include the latest engine update. For example, if service pack 6.0(3) is released, and E3 is the latest engine level, the service pack is released as 6.0(3)E3.
Patch Release
A patch release is used to address defects that are identified in the upgrade binaries after a software release. Rather than waiting until the next major or minor update, or service pack to address these defects, a patch can be posted. Patches include all prior patch releases within the associated service pack level. The patches roll in to the next official major or minor update, or service pack.
Before you can install a patch release, the most recent major or minor update, or service pack must be installed. For example, patch release 5.0(1p1) requires 5.0(1).

Note
Upgrading to a newer patch does not require you to uninstall the old patch. For example, you can upgrade from patch 5.0(1p1) to 5.0(1p2) without first uninstalling 5.0(1p1).
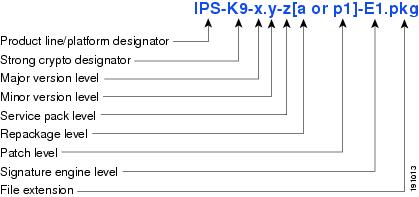
Figure 1 illustrates what each part of the IPS software file represents for major and minor updates, service packs, and patch releases.
Figure 1 IPS Software File Name for Major and Minor Updates, Service Packs, and Patch Releases
Signature Update
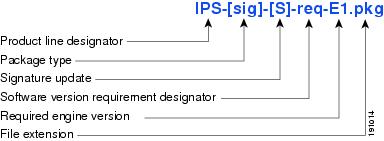
A signature update is a package file containing a set of rules designed to recognize malicious network activities. Signature updates are released independently from other software updates. Each time a major or minor update is released, you can install signature updates on the new version and the next oldest version for a period of at least six months. Signature updates are dependent on a required signature engine version. Because of this, a req designator lists the signature engine required to support a particular signature update.
Figure 2 illustrates what each part of the IPS software file represents for signature/virus updates.
Figure 2 IPS Software File Name for Signature Updates
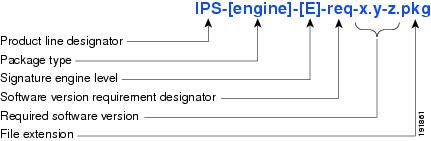
Signature Engine Update
A signature engine update is an executable file containing binary code to support new signature updates. Signature engine files require a specific service pack, which is also identified by the req designator.
Figure 3 illustrates what each part of the IPS software file represents for signature engine updates.
Figure 3 IPS Software File Name for Signature Engine Updates
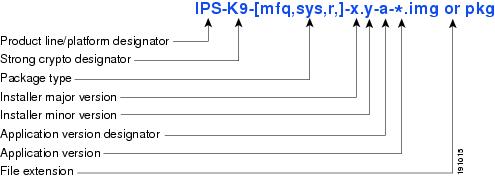
Recovery and System Image Filenames
Recovery and system image files contain separate versions for the installer and the underlying application. The installer version contains a major and minor version field. The major version is incremented by one of any major changes to the image installer, for example, switching from .tar to rpm or changing kernels. The minor version can be incremented by any one of the following:
•
Minor change to the installer, for example, a user prompt added.
•
Repackages require the installer minor version to be incremented by one if the image file must be repackaged to address a defect or problem with the installer.
Figure 4 illustrates what each part of the IPS software file represents for recovery and system image filenames.
Figure 4 IPS Software File Name for Recovery and System Image Filenames
Software Release Examples
Table 1 lists platform-independent IDS 6.x software release examples. Refer to the Readmes that accompany the software files for detailed instructions on how to install the files.
Table 1 Platform-Independent Release Examples
Signature update1
Weekly
sig
S700
IPS-sig-S700-req-E1.pkg
Signature engine update2
As needed
engine
E1
IPS-engine-E1-req-6.1-3.pkg
Service packs3
Semi-annually
or as needed—
6.1(3)
IPS-K9-6.1-3-E1.pkg
Minor version update4
Annually
—
6.1(1)
IPS-K9-6.1-1-E1.pkg
Major version update5
Annually
—
6.0(1)
IPS-K9-6.0-3-E.1.pkg
Patch release6
As needed
patch
6.0(1p1)
IPS-K9-patch-6.0-1pl-E1.pkg
Recovery package7
Annually or as needed
r
1.1-6.0(1)
IPS-K9-r-1.1-a-6.0-3-E.1.pkg
1 Signature updates include the latest cumulative IPS signatures.
2 Signature engine updates add new engines or engine parameters that are used by new signatures in later signature updates.
3 Service packs include defect fixes.
4 Minor versions include new minor version features and/or minor version functionality.
5 Major versions include new major version functionality or new architecture.
6 Patch releases are for interim fixes.
7 The r 1.1 can be revised to r 1.2 if it is necessary to release a new recovery package that contains the same underlying application image. If there are defect fixes for the installer, for example, the underlying application version may still be 6.0(1), but the recovery partition image will be r 1.2.
Table 2 describes platform-dependent software release examples.
Table 2 Platform-Dependent Release Examples
System image1
Annually
sys
Separate file for each sensor platform
IPS-4240-K9-sys-1.1-a-6.0-3-E.1.img
Maintenance partition image2
Annually
mp
IDSM2
c6svc-mp.2-1-2.bin.gz
Bootloader
As needed
bl
NM CIDS
servicesengine-boot-1.0-4.bin
1 The system image includes the combined recovery and application image used to reimage an entire sensor.
2 The maintenance partition image includes the full image for the IDSM2 maintenance partition. The file is installed from but does not affect the IDSM2 application partition.
Table 3 describes the platform identifiers used in platform-specific names.

Note
The IDS 4235 and IDS 4250 do not use platform-specific image files.
For More Information
For instructions on how to access these files on Cisco.com, see Obtaining Software on Cisco.com.
Upgrading the IDS 4215 BIOS
The BIOS/ROMMON upgrade utility (IDS-4215-bios-5.1.7-rom-1.4.bin) upgrades the BIOS of the IDS 4215 to version 5.1.7 and the ROMMON to version 1.4.
To upgrade the BIOS and ROMMON on the IDS 4215, follow these steps:
Step 1
Download the BIOS ROMMON upgrade utility (IDS-4215-bios-5.1.7-rom-1.4.bin) to the TFTP root directory of a TFTP server that is accessible from the IDS 4215.

Note
Make sure you can access the TFTP server location from the network connected to the Ethernet port of the IDS 4215.
Step 2
Boot the IDS 4215.
While rebooting, IDS-4215 runs the BIOS POST. After the completion of POST, the console displays the message:
Evaluating Run Options ...for about 5 seconds.Step 3
Press Ctrl-R while this message is displayed to display the ROMMON menu.
The console display resembles the following:
CISCO SYSTEMS IDS-4215Embedded BIOS Version 5.1.3 05/12/03 10:18:14.84Compiled by ciscouserEvaluating Run Options ...Cisco ROMMON (1.2) #0: Mon May 12 10:21:46 MDT 2003Platform IDS-42150: i8255X @ PCI(bus:0 dev:13 irq:11)1: i8255X @ PCI(bus:0 dev:14 irq:11)Using 1: i82557 @ PCI(bus:0 dev:14 irq:11), MAC: 0000.c0ff.ee01Use ? for help.rommon>Step 4
If necessary, change the port number used for the TFTP download:
rommon> interface port_numberThe port in use is listed just before the rommon prompt. Port 1 (default port) is being used as indicated by the text,
Using 1: i82557 @ PCI(bus:0 dev:14 irq:11), MAC: 0000.c0ff.ee01.
Note
Ports 0 (monitoring port) and 1 (command and control port) are labeled on the back of the chassis.
Step 5
Specify an IP address for the local port on the IDS 4215:
rommon> address ip_address
Note
Use the same IP address that is assigned to the IDS 4215.
Step 6
Specify the TFTP server IP address:
rommon> server ip_addressStep 7
Specify the gateway IP address:
rommon> gateway ip_addressStep 8
Verify that you have access to the TFTP server by pinging it from the local Ethernet port:
rommon> ping server_ip_addressrommon> ping serverStep 9
Specify the filename on the TFTP file server from which you are downloading the image:
rommon> file filenameExample:
rommon> file IDS-4215-bios-5.1.7-rom-1.4.bin
Note
The syntax of the file location depends on the type of TFTP server used. Contact your system or network administrator for the appropriate syntax if the above format does not work.
Step 10
Download and run the update utility:
rommon> tftpStep 11
Enter y at the upgrade prompt and the update is executed. The IDS 4215 reboots when the update is complete.

CautionDo not remove power to the IDS 4215 during the update process, otherwise the upgrade can get corrupted. If this occurs, the IDS 4215 will be unusable and require an RMA.
For More Information
•
For a list of supported TFTP servers, see Supported Servers.
•
For the procedure for locating software on Cisco.com, see Obtaining Software on Cisco.com.
Upgrading to Cisco IPS 6.0(3)E.1
This section provides information on upgrading to IPS 6.0(3)E.1, and contains the following topics:
•
Installing the ISO Image File
Upgrade Notes and Caveats
The following upgrade notes and caveats apply to upgrading to 6.0(3)E.1:
•
If you have 4.x installed on your sensor, you must upgrade to 5.0(1), then upgrade to 6.0(3)E.1.
•
You can upgrade all 5.0 or 5.1 sensors directly to 6.0(3)E.1.

Note
5.1(3) and earlier sensors may display an error message that the upgrade file is not a recognized type. You can ignore this error and continue with the upgrade.
•
If you try to upgrade an IPS 5.x sensor to 6.0(3)E.1, you may receive an error that Analysis Engine is not running:
sensor#upgrade scp://user@10.1.1.1/upgrades/IPS-K9-6.0-3-E.1.pkgPassword: ********Warning: Executing this command will apply a major version upgrade to the application partition. The system may be rebooted to complete the upgrade.Continue with upgrade?: yesError: Analysis Engine is not running. Please reset box and attempt upgrade again.If you receive this error, you must get Analysis Engine running before trying to upgrade again. This error is often caused by a defect in the currently running version. Try rebooting the sensor, and after reboot, run setup and remove the interfaces from the virtual sensor vs0. When it is not monitoring traffic, Analysis Engine usually stays up and running. You can upgrade to 6.0(3)E.1 at this time. After the upgrade to IPS 6.0(3)E.1, add the interfaces back to the virtual sensor vs0 using the setup command.
Or you can use the recovery CD (if your sensor has a CD-ROM) or the system image file to reimage directly to IPS 6.0(3)E.1. You can reimage a 5.x sensor to 6.0(3)E.1 because the reimage process does not check to see Analysis Engine is running.

CautionReimaging using the CD or system image file restores all configuration defaults.
•
You receive SNMP errors if you do not have the read-only-community and read-write-community parameters configured before upgrading to IPS 6.0(3)E.1. If you are using SNMP set and/or get features, you must configure the read-only-community and read-write-community parameters before upgrading to IPS 6.0(3)E.1. In IPS 5.x, the read-only-community was set to public by default, and the read-write-community was set to private by default. In IPS 6.0(3)E.1 these two options do not have default values. If you were not using SNMP gets and sets with IPS 5.x (for example, enable-set-get was set to false), there is no problem upgrading to IPS 6.0(3)E.1. If you were using SNMP gets and sets with IPS 5.x (for example, enable-set-get was set to true), you must configure the read-only-community and read-write-community parameters to specific values or the IPS 6.0(3)E.1 upgrade fails. You receive the following error message:
Error: execUpgradeSoftware : Notification Application "enable-set-get" value set to true, but "read-only-community" and/or "read-write-community" are set to null. Upgrade may not continue with null values in these fields.•
IPS 6.0(3)E.1 denies high risk events by default. This is a change from 5.x. To change the default, create an event action override for the deny packet inline action and configure it to be disabled.
•
In 6.0(3)E.1, you will receive messages indicating the you need to install a license. The sensor functions properly without a license, but you will need a license to install signature updates.
•
After you upgrade any IPS software on your sensor, you must restart the IDM to see the latest software features.
•
Upgrading from 5.x to 6.0(3)E.1 preserves the configuration of the sensor. The upgrade may stop if it comes across a value that it cannot translate. If this occurs, the resulting error message provides enough information to adjust the parameter to an acceptable value. After editing the configuration, try the upgrade again.
•
After you upgrade from 5.x to 6.0(3)E.1, you cannot downgrade using the downgrade command. If you want to return to the previous version, you must reimage your sensor and then copy the backup configuration from a remote server to the reimaged sensor. You cannot use the downgrade command to downgrade from 6.0(3)E.1 to 5.1.
For More Information
•
For more information on running the setup command, refer to Initializing the Sensor.
•
For the procedures for reimaging the sensor, refer to Upgrading, Downgrading, and Installing System Images.
•
For the procedure for obtaining and installing the sensor license, see Licensing the Sensor.
•
For information about SNMP values that must be configured before upgrading from 5.x to 6.0(3)E.1, see Before Upgrading to Cisco IPS 6.0(3)E.1.
•
For the procedure for restoring the configuration file, see Backing Up and Restoring the Configuration File Using a Remote Server.
•
For more information on configuring SNMP, for the CLI procedure, refer to Configuring SNMP. For the IDM procedure, refer to Configuring SNMP.
•
For information on configuring event action overrides, for the CLI procedure, refer to Adding, Editing, Enabling, and Disabling Event Action Overrides. For the IDM procedure, refer to Adding, Editing, Enabling, and Disabling Event Action Overrides.
Upgrading to 6.0(3)E.1

Note
You must have a valid Cisco Service for IPS Maintenance contract per sensor to receive and use software upgrades from Cisco.com.
To upgrade the sensor, follow these steps:
Step 1
Download the major update file (for example, IPS-K9-6.0-3-E.1.pkg) to an FTP, SCP, HTTP, or HTTPS server that is accessible from your sensor.

CautionYou must log in to Cisco.com using an account with cryptographic privileges to download software. The first time you download software on Cisco.com, you receive instructions for setting up an account with cryptographic privileges.

CautionDo not change the filename. You must preserve the original filename for the sensor to accept the update.
Step 2
Log in to the CLI using an account with administrator privileges.
Step 3
Determine the sensor version:
sensor# show version
Note
To install IPS 6.0(3)E.1, the sensor must be at 5.0(1) or later. You must upgrade 4.x and earlier sensors to 5.0(1) before applying 6.0(3)E.1.
Step 4
Enter configuration mode:
sensor# configure terminalStep 5
Upgrade the sensor:
sensor(config)# upgrade scp://tester@10.1.1.1//upgrade/IPS-K9-6.0-3-E.1.pkgStep 6
Enter the password when prompted:
Enter password: ********Step 7
Enter yes to complete the upgrade.

Note
The sensor reboots after installing the service pack.

Note
5.1(3) and earlier sensors may display an error message that the upgrade file is not a recognized type. You can ignore this error and continue with the upgrade.
Step 8
Verify your new sensor version:
sensor# show versionApplication Partition:Cisco Intrusion Prevention System, Version 6.0(3)E1Host:Realm Keys key1.0Signature Definition:Signature Update S291.0 2007-06-18Virus Update V1.2 2005-11-24OS Version: 2.4.30-IDS-smp-bigphysPlatform: ASA-SSM-20Serial Number: P300000220No license presentSensor up-time is 13 days.Using 1039052800 out of 2093682688 bytes of available memory (49% usage)system is using 17.8M out of 29.0M bytes of available disk space (61% usage)application-data is using 49.9M out of 166.6M bytes of available disk space (32% usage)boot is using 37.8M out of 68.5M bytes of available disk space (58% usage)MainApp N-2007_JUN_19_16_45 (Release) 2007-06-19T17:10:20-0500 RunningAnalysisEngine N-2007_JUN_19_16_45 (Release) 2007-06-19T17:10:20-0500 RunningCLI N-2007_JUN_19_16_45 (Release) 2007-06-19T17:10:20-0500Upgrade History:IPS-K9-6.0-3-E.1 15:31:13 UTC Mon Sep 10 2007Recovery Partition Version 1.1 - 6.0(3)E1sensor#
Note
For 5.x, you receive a message saying the upgrade is of unknown type. You can ignore this message.

Note
The operating system is reimaged and all files that have been placed on the sensor through the service account are removed.
For More Information
•
For more information on Cisco service contracts, see Service Programs for IPS Products.
•
For the procedure for locating software on Cisco.com and obtaining an account with cryptographic privileges, see Obtaining Software on Cisco.com.
Installing the ISO Image File

Note
You must create a recovery CD on a Linux system to install the ISO image for the IDS 4235 and IDS 4250.
The Recovery ISO Image is for the IDS 4235 and IDS 4250 sensors only. To create the recovery CD for the ISO image for the IDS 4235 and IDS 4250, follow these steps:
Step 1
Insert a blank CD-R media in to the CD-R recorder of the burn host.
Step 2
Enter the following command:
host# cdrecord -v speed=6 dev=0,0 IPS-K9-cd-1.1-a-6.0-5-E2.isohost# cdrecord -v speed=6 dev=0,0 IPS-K9-cd-1.1-a-6.0-5-E3.isohost# cdrecord -v speed=6 dev=0,0 IPS-K9-cd-1.1-a-6.0-4-E2.isohost# cdrecord -v speed=6 dev=0,0 IPS-K9-cd-1.1-a-6.0-3-E1.isoStep 3
Follow the command line arguments for cdrecord.

Note
The command line arguments are self-explanatory. For more information, refer to the cdrecord man page.
Step 4
Follow the instructions for using a recovery CD to install the ISO image on the IDS 4235 and IDS 4250.
For More Information
For the procedure for using a recovery CD to install images, refer to Using the Recovery/Upgrade CD.
After Upgrading to Cisco IPS 6.0(3)E.1
This section provides information about what to do after you install IPS 6.0(3)E.1. It contains the following topics:
Comparing Configurations
Compare your backed up and saved 5.1 configuration with the output of the show configuration command after upgrading to 6.0(3)E.1 to verify that all the configuration has been properly converted.

CautionIf the configuration is not properly converted, check the list of caveats, or check Cisco.com for any upgrade issues that have been found. Contact the TAC if no DDTS refers to your situation.
For More Information
For a list of IPS 6.0(3)E.1, see Caveats.
SSL Certificate
If necessary, import the new SSL certificate for the upgraded sensor in to each tool being used to monitor the sensor.
For More Information
For the procedure for importing a new SSL certificate, for the CLI procedure, refer to Configuring TLS. For the IDM procedure, refer to Configuring Certificates.
Logging In to IDM
IDM is a web-based, Java Start application that enables you to configure and manage your sensor. The web server for IDM resides on the sensor. You can access it through Internet Explorer or Firefox web browsers.
To log in to IDM, follow these steps:
Step 1
Open a web browser and enter the sensor IP address. A Security Alert dialog box appears.
https://sensor_ip_address
Note
IDM is already installed on the sensor.

Note
The default address is
https://10.1.9.201, which you change to reflect your network environment when you initialize the sensor. When you change the web server port, you must specify the port in the URL address of your browser when you connect to IDM in the formathttps://sensor_ip_ address:port (for example,https://10.1.9.201:1040).
Step 2
Click Yes to accept the security certificate. The Cisco IPS Device Manager Version 6.0 window appears.
Step 3
To launch IDM, click Run IDM. The JAVA loading message box appears, and then the Warning - Security dialog box appears.
Step 4
To verify the security certificate, check the Always trust content from this publisher check box, and click Yes. The JAVA Web Start progress dialog box appears, and then the IDM on ip_address dialog box appears.
Step 5
To create a shortcut for IDM, click Yes. The Cisco IDM Launcher dialog box appears.

Note
You must have JRE 1.4.2 or JRE 1.5 (JAVA 5) installed to create shortcuts for IDM. If you have JRE 1.6 (JAVA 6) installed, the shortcut is created automatically.
Step 6
To authenticate IDM, enter your username and password, and click OK. IDM begins to load. The Status dialog box appears with the following message:
Please wait while IDM is loading the current configuration from the sensor.The main window of IDM appears.

Note
Both the default username and password are cisco. You were prompted to change the password during sensor initialization.

Note
If you created a shortcut, you can launch IDM by double-clicking the IDM shortcut icon. You can also close the The Cisco IPS Device Manager Version 6.0 window. After you launch IDM, is it not necessary for this window to remain open.
For More Information
•
For more information about security and IDM, refer to IDM and Certificates.
•
For the procedure for initializing the sensor, refer to Initializing the Sensor.
Licensing the Sensor
This section describes how to obtain a license key and how to license the sensor using the CLI or IDM. It contains the following topics:
•
Service Programs for IPS Products
•
Obtaining and Installing the License Key
Understanding the License
Although the sensor functions without the license key, you must have a license key to obtain signature updates. To obtain a license key, you must have the following:
•
Cisco Service for IPS service contract—Contact your reseller, Cisco service or product sales to purchase a contract.
•
Your IPS device serial number—To find the IPS device serial number in IDM, choose Configuration > Licensing, or in the CLI use the show version command.
•
Valid Cisco.com username and password
Trial license keys are also available. If you cannot get your sensor licensed because of problems with your contract, you can obtain a 60-day trial license that supports signature updates that require licensing.
You can obtain a license key from the Cisco.com licensing server, which is then delivered to the sensor. Or, you can update the license key from a license key provided in a local file. Go to http://www.cisco.com/go/license and click IPS Signature Subscription Service to apply for a license key.
You can view the status of the license key on the Licensing pane in IDM. Whenever you start IDM, you are informed of your license status—whether you have a trial, invalid, or expired license key. With no license key, an invalid license key, or an expired license key, you can continue to use IDM but you cannot download signature updates.
When you enter the CLI, you are informed of your license status. For example, you receive the following message if there is no license installed:
***LICENSE NOTICE***There is no license key installed on the system.The system will continue to operate with the currently installedsignature set. A valid license must be obtained in order to applysignature updates. Please go to http://www.cisco.com/go/licenseto obtain a new license or install a license.You will continue to see this message until you install a license key.
For More Information
•
For more information on Cisco service contracts, see Service Programs for IPS Products.
•
For the procedure for obtaining and installing the license key, see Obtaining and Installing the License Key.
Service Programs for IPS Products
You must have a Cisco Services for IPS service contract for any IPS product so that you can download a license key and obtain the latest IPS signature updates. If you have a direct relationship with Cisco Systems, contact your account manager or service account manager to purchase the Cisco Services for IPS service contract. If you do not have a direct relationship with Cisco Systems, you can purchase the service account from a one-tier or two-tier partner.
When you purchase the following IPS products you must also purchase a Cisco Services for IPS service contract:
•
IDS 4215
•
IDS 4235
•
IDS 4250
•
IPS 4240
•
IPS 4255
•
IPS 4260
•
IPS 4270-20
•
IDSM2
•
NM CIDS
When you purchase an ASA 5500 series adaptive security appliance product that does not contain IPS, you must purchase a SMARTnet contract.

Note
SMARTnet provides operating system updates, access to Cisco.com, access to TAC, and hardware replacement NBD on site.
When you purchase an ASA 5500 series adaptive security appliance product that ships with the AIP -SSM installed, or if you purchase it to add to your ASA 5500 series adaptive security appliance product, you must purchase the Cisco Services for IPS service contract.

Note
Cisco Services for IPS provides IPS signature updates, operating system updates, access to Cisco.com, access to TAC, and hardware replacement NBD on site.
For example, if you purchased an ASA 5510 and then later wanted to add IPS and purchased an ASA-SSM-AIP-10-K9, you must now purchase the Cisco Services for IPS service contract.
After you have the Cisco Services for IPS service contract, you must also have your product serial number to apply for the license key.

CautionIf you ever send your product for RMA, the serial number will change. You must then get a new license key for the new serial number.
For More Information
For the procedure for obtaining and installing the license key, see Obtaining and Installing the License Key.
Obtaining and Installing the License Key
You can install the license key through the CLI or IDM. This section describes how to obtain and install the license key, and contains the following topics:
Using IDM

Note
In addition to a valid Cisco.com username and password, you must also have a Cisco Services for IPS service contract before you can apply for a license key.
To obtain and install the license key, follow these steps:
Step 1
Log in to IDM using an account with administrator privileges.
Step 2
Choose Configuration > Licensing.
The Licensing pane displays the status of the current license. If you have already installed your license, you can click Download to save it if needed.
Step 3
Obtain a license key by doing one of the following:
•
Check the Cisco Connection Online check box to obtain the license from Cisco.com. IDM contacts the license server on Cisco.com and sends the server the serial number to obtain the license key. This is the default method. Go to Step 4.
•
Check the License File check box to use a license file. To use this option, you must apply for a license key at this URL: www.cisco.com/go/license. The license key is sent to you in e-mail and you save it to a drive that IDM can access. This option is useful if your computer cannot access Cisco.com. Go to Step 7.
Step 4
Click Update License. The Licensing dialog box appears.
Step 5
Click Yes to continue. The Status dialog box informs you that the sensor is trying to connect to Cisco.com. An Information dialog box confirms that the license key has been updated.
Step 6
Click OK.
Step 7
Go to www.cisco.com/go/license.
Step 8
Fill in the required fields. Your license key will be sent to the e-mail address you specified.

CautionYou must have the correct IPS device serial number because the license key only functions on the device with that number.
Step 9
Save the license key to a hard-disk drive or a network drive that the client running IDM can access.
Step 10
Log in to IDM.
Step 11
Choose Configuration > Licensing.
Step 12
Under Update License, check the Update From: License File check box.
Step 13
In the Local File Path field, specify the path to the license file or click Browse Local to browse to the file. The Select License File Path dialog box appears.
Step 14
Browse to the license file and click Open.
Step 15
Click Update License.
For More Information
For more information on Cisco service contracts, see Service Programs for IPS Products.
Using the CLI
Use the copy source-url license_file_name license-key command to copy the license key to your sensor.
The following options apply:
•
source-url—The location of the source file to be copied. It can be a URL or keyword.
•
destination-url—The location of the destination file to be copied. It can be a URL or a keyword.
•
license-key—The subscription license file.
•
license_file_name—The name of the license file you receive.

Note
You cannot install an older license key over a newer license key.
The exact format of the source and destination URLs varies according to the file. Here are the valid types:
•
ftp:—Source or destination URL for an FTP network server. The syntax for this prefix is:
ftp:[//[username@] location]/relativeDirectory]/filename
ftp:[//[username@]location]//absoluteDirectory]/filename
•
scp:—Source or destination URL for the SCP network server. The syntax for this prefix is:
scp:[//[username@] location]/relativeDirectory]/filename
scp:[//[username@] location]//absoluteDirectory]/filename

Note
If you use FTP or SCP protocol, you are prompted for a password. If you use SCP protocol, you must add the remote host must to the SSH known hosts list.
•
http:—Source URL for the web server. The syntax for this prefix is:
http:[[/[username@]location]/directory]/filename
•
https:—Source URL for the web server. The syntax for this prefix is:
https:[[/[username@]location]/directory]/filename

Note
If you use HTTPS protocol, the remote host must be a TLS trusted host.
To install the license key, follow these steps:
Step 1
Apply for the license key at this URL: www.cisco.com/go/license.

Note
In addition to a valid Cisco.com username and password, you must also have a Cisco Services for IPS service contract before you can apply for a license key.
Step 2
Fill in the required fields. Your Cisco IPS Signature Subscription Service license key will be sent by e-mail to the e-mail address you specified.

Note
You must have the correct IPS device serial number because the license key only functions on the device with that number.
Step 3
Save the license key to a system that has a web server, FTP server, or SCP server.
Step 4
Log in to the CLI using an account with administrator privileges.
Step 5
Copy the license key to the sensor:
sensor# copy scp://user@10.89.147.3://tftpboot/dev.lic license-keyPassword: *******Step 6
Verify the sensor is licensed:
sensor# show versionApplication Partition:Cisco Intrusion Prevention System, Version 6.0(3)E.1Host:Realm Keys key1.0Signature Definition:Signature Update S291.0 2007-06-18Virus Update V1.2 2005-11-24OS Version: 2.4.30-IDS-smp-bigphysPlatform: ASA-SSM-20Serial Number: P300000220No license presentSensor up-time is 3 days.Using 1031888896 out of 2093682688 bytes of available memory (49% usage)system is using 17.8M out of 29.0M bytes of available disk space (61% usage)application-data is using 52.4M out of 166.6M bytes of available disk space (33% usage)boot is using 37.8M out of 68.5M bytes of available disk space (58% usage)MainApp N-2007_JUN_19_16_45 (Release) 2007-06-19T17:10:20-0500 RunningAnalysisEngine N-2007_JUN_19_16_45 (Release) 2007-06-19T17:10:20-0500 RunningCLI N-2007_JUN_19_16_45 (Release) 2007-06-19T17:10:20-0500Upgrade History:IPS-K9-6.0-3-E.1 15:36:05 UTC Wed Aug 22 2007Recovery Partition Version 1.1 - 6.0(3)E.1sensor#Step 7
Copy your license key from a sensor to a server to keep a backup copy of the license:
sensor# copy license-key scp://user@10.89.147.3://tftpboot/dev.licPassword: *******sensor#
For More Information
•
For the CLI procedure for adding hosts to the SSH known hosts list, refer to Adding Hosts to the SSH Known Hosts List. For the IDM procedure, refer to Defining Known Host Keys.
•
For the CLI procedure for adding TLS trusted hosts, refer to Adding TLS Trusted Hosts. For the IDM procedure, refer to Adding Trusted Hosts.
•
For more information on Cisco service contracts, see Service Programs for IPS Products.
Restrictions and Limitations
The following restrictions and limitations apply to Cisco IPS 6.0(3)E.1 software and the products that run 6.0(3)E.1:
•
Do not confuse Cisco OS IDS or Cisco IPS (a software-based intrusion-detection/prevention application that runs in the Cisco IOS) with the IPS that runs on the NM CIDS. The NM CIDS runs Cisco IPS 6.0(3)E.1. Because performance can be reduced and duplicate alarms can be generated, we recommend that you do not run Cisco IOS IDS and Cisco PS 6.0(3)E.1 simultaneously.
•
Only one NM CIDS is supported per Cisco 2600, 2811, 2821 2851, 3825, 3845, and 3700 series router.
•
Jumbo frames are not supported on the NM CIDS.
•
The NM CIDS does not run in inline mode.
•
The IDS 4215, and NM CIDS do not support virtualization.
•
Cisco access routers only support one IDS/IPS per router.
•
On IPS sensors with multiple processors (for example, the IPS 4260 and IPS 4270-20), packets may be captured out of order in the IP logs and by the packet command. Because the packets are not processed using a single processor, the packets can become out of sync when received from multiple processors.
•
An IPS appliance can support both promiscuous and inline monitoring at the same time; however you must configure each physical interface in either promiscuous or inline mode. The sensor must contain at least two physical sensing interfaces to perform both promiscuous and inline monitoring. The exceptions to this are AIP SSM-10 and AIP SSM-20. The AIP SSM can support both promiscuous and inline monitoring on its single physical back plane interface inside the adaptive security appliance. The configuration on the main adaptive security appliance can be used to designate which packets/connections should be monitored by the AIP SSM as either promiscuous or inline.
•
When deploying an IPS sensor monitoring two sides of a network device that does TCP sequence number randomization, we recommend using a virtual senor for each side of the device. If you are using the IDS 4125, which does not support virtualization, configure vs0 to track TCP sessions by VLAN and interface.
•
After you upgrade any IPS software on your sensor, you must restart the IDM to see the latest software features.
•
IDM does not support any non-English characters, such as the German umlaut or any other special language characters. If you enter such characters as a part of an object name through IDM, they are turned in to something unrecognizable and you will not be able to delete or edit the resulting object through IDM or the CLI.
This is true for any string that is used by CLI as an identifier, for example, names of time periods, inspect maps, server and URL lists, and interfaces.
•
You can only install eight IDSM2s per switch chassis.
•
The HTML-based IDM has been replaced with a Java applet.
•
When SensorApp is reconfigured, there is a short period when SensorApp is unable to respond to any queries. Wait a few minutes after reconfiguration is complete before querying SensorApp for additional information.
For More Information
For more information on how many modules Cisco access routers support, refer to Interoperability With Other IPS Modules.
Recovering the Password
For most IPS platforms, you can now recover the password on the sensor rather than using the service account or reimaging the sensor. This section describes how to recover the password for the various IPS platforms. It contains the following topics:
•
Understanding Password Recovery
•
Recovering the Appliance Password
•
Recovering the IDSM2 Password
•
Recovering the NM CIDS Password
•
Recovering the AIP SSM Password
•
Verifying the State of Password Recovery
•
Troubleshooting Password Recovery
Understanding Password Recovery
Password recovery implementations vary according to IPS platform requirements. Password recovery is implemented only for the cisco administrative account and is enabled by default. The IPS administrator can then recover user passwords for other accounts using the CLI. The cisco user password reverts to cisco and must be changed after the next login.

Note
Administrators may need to disable the password recovery feature for security reasons.
Table 4 lists the password recovery methods according to platform.
For More Information
For more information on disabling the password recovery feature, see Disabling Password Recovery.
Recovering the Appliance Password
This section describes the two ways to recover the password for appliances. It contains the following topics:
Using the GRUB Menu
For 4200 series appliances, the password recovery is found in the GRUB menu, which appears during bootup. When the GRUB menu appears, press any key to pause the boot process.

Note
You must have a terminal server or direct serial connection to the appliance to use the GRUB menu to recover the password.
To recover the password on appliances, follow these steps:
Step 1
Reboot the appliance.
The following menu appears:
GNU GRUB version 0.94 (632K lower / 523264K upper memory)-------------------------------------------0: Cisco IPS1: Cisco IPS Recovery2: Cisco IPS Clear Password (cisco)-------------------------------------------Use the ^ and v keys to select which entry is highlighted.Press enter to boot the selected OS, 'e' to edit theCommands before booting, or 'c' for a command-line.Highlighted entry is 0:Step 2
Press any key to pause the boot process.
Step 3
Choose 2: Cisco IPS Clear Password (cisco).
The password is reset to cisco. You can change the password the next time you log in to the CLI.
For More Information
For the procedure for connecting the appliance to a terminal server, refer to Connecting an Appliance to a Terminal Server.
Using ROMMON
For the IPS 4240 and IPS 4255 you can use the ROMMON to recover the password. To access the ROMMON CLI, reboot the sensor from a terminal server or direct connection and interrupt the boot process.
To recover the password using the ROMMON CLI, follow these steps:
Step 1
Reboot the appliance.
Step 2
To interrupt the boot process, press ESC or Control-R (terminal server) or send a BREAK command (direct connection).
The boot code either pauses for 10 seconds or displays something similar to one of the following:
•
Evaluating boot options•
Use BREAK or ESC to interrupt bootStep 3
Enter the following commands to reset the password:
confreg 0x7bootSample ROMMON session:
Booting system, please wait...CISCO SYSTEMSEmbedded BIOS Version 1.0(11)2 01/25/06 13:21:26.17...Evaluating BIOS Options...Launch BIOS Extension to setup ROMMONCisco Systems ROMMON Version (1.0(11)2) #0: Thu Jan 26 10:43:08 PST 2006Platform IPS-4240-K9Use BREAK or ESC to interrupt boot.Use SPACE to begin boot immediately.Boot interrupted.Management0/0Link is UPMAC Address:000b.fcfa.d155Use ? for help.rommon #0> confreg 0x7Update Config Register (0x7) in NVRAM...rommon #1> boot
Recovering the IDSM2 Password
To recover the password for the IDSM2, you must install a special password recovery image file. This installation only resets the password, all other configuration remains intact. The password recovery image is version-dependent and can be found on the Cisco Download Software site. For IPS 6.x, download WS-SVC-IDSM2-K9-a-6.0-password-recovery.bin.gz. For IPS 7.x, download WS-SVC-IDSM2-K9-a-7.0-password-recovery.bin.gz.
FTP is the only supported protocol for image installations, so make sure you put the password recovery image file on an FTP server that is accessible to the switch. You must have administrative access to the Cisco 6500 series switch to recover the password on the IDSM2.
During the password recovery image installation, the following message appears:
Upgrading will wipe out the contents on the hard disk.Do you want to proceed installing it [y|n]:This message is in error. Installing the password recovery image does not remove any configuration, it only resets the login account.
Once you have downloaded the password recovery image file, follow the instructions to install the system image file but substitute the password recovery image file for the system image file. The IDSM2 should reboot in to the primary partition after installing the recovery image file. If it does not, enter the following command from the switch:
hw-module module module_number reset hdd:1
Note
The password is reset to cisco. Log in to the CLI with username cisco and password cisco. You can then change the password.
For More Information
•
For the procedure for installing system images on the IDSM2, refer to Installing the IDSM2 System Image.
•
For more information on downloading Cisco IPS software, see Obtaining Software on Cisco.com.
Recovering the NM CIDS Password
To recover the password for the NM CIDS, use the clear password command. You must have console access to the NM CIDS and administrative access to the router.

Note
There is no minimum IOS release requirement for password recovery on the NM CIDS.

Note
Recovering the password for the NM CIDS requires a new bootloader image.
To recover the password for the NM CIDS, follow these steps:
Step 1
Session in to the NM CIDS:
router# service-module ids module_number/0 sessionStep 2
Press Control-shift-6 followed by x to navigate to the router CLI.
Step 3
Reset the NM CIDS from the router console:
router# service-module ids module_number/0 resetStep 4
Press Enter to return to the router console.
Step 5
When prompted for boot options, enter *** quickly. You are now in the bootloader.
Step 6
Clear the password:
ServicesEngine boot-loader# clear passwordStep 7
Restart the NM CIDS:
ServicesEngine boot-loader# boot disk
CautionDo not use the reboot command to start the NM CIDS. This causes the password recovery action to be ignored. Make sure you use the boot disk command.
For More Information
For the procedure for installing a new bootloader image, refer to Installing the NM CIDS System Image.
Recovering the AIP SSM Password
You can reset the password to the default (cisco) for the AIP SSM using the CLI or the ASDM. Resetting the password causes it to reboot. IPS services are not available during a reboot.

Note
To reset the password, you must have ASA 7.2.2 or later.
Use the hw-module module slot_number password-reset command to reset the password to the default cisco. If the module in the specified slot has an IPS version that does not support password recovery, the following error message is displayed:
ERROR: the module in slot <n> does not support password recovery.Resetting the Password Using the CLI
To reset the password on the AIP SSM, follow these steps:
Step 1
Log into the adaptive security appliance and enter the following command to verify the module slot number:
asa# show moduleMod Card Type Model Serial No.--- -------------------------------------------- ------------------ -----------0 ASA 5510 Adaptive Security Appliance ASA5510 JMX1135L0971 ASA 5500 Series Security Services Module-40 ASA-SSM-40 JAF1214AMRLMod MAC Address Range Hw Version Fw Version Sw Version--- --------------------------------- ------------ ------------ ---------------0 001b.d5e8.e0c8 to 001b.d5e8.e0cc 2.0 1.0(11)2 8.4(3)1 001e.f737.205f to 001e.f737.205f 1.0 1.0(14)5 7.0(7)E4Mod SSM Application Name Status SSM Application Version--- ------------------------------ ---------------- --------------------------1 IPS Up 7.0(7)E4Mod Status Data Plane Status Compatibility--- ------------------ --------------------- -------------0 Up Sys Not Applicable1 Up UpStep 2
Reset the password for module 1.
asa# hw-module module 1 password-resetReset the password on module in slot 1? [confirm]Step 3
Press Enter to confirm.
Password-Reset issued for slot 1.Step 4
Verify the status of the module. Once the status reads Up, you can session to the AIP SSM.
asa# show module 1Mod Card Type Model Serial No.--- -------------------------------------------- ------------------ -----------1 ASA 5500 Series Security Services Module-40 ASA-SSM-40 JAF1214AMRLMod MAC Address Range Hw Version Fw Version Sw Version--- --------------------------------- ------------ ------------ ---------------1 001e.f737.205f to 001e.f737.205f 1.0 1.0(14)5 7.0(7)E4Mod SSM Application Name Status SSM Application Version--- ------------------------------ ---------------- --------------------------1 IPS Up 7.0(7)E4Mod Status Data Plane Status Compatibility--- ------------------ --------------------- -------------1 Up UpStep 5
Session to the AIP SSM.
asa# session 1Opening command session with slot 1.Connected to slot 1. Escape character sequence is 'CTRL-^X'.Step 6
Enter the default username (cisco) and password (cisco) at the login prompt.
login: ciscoPassword: ciscoYou are required to change your password immediately (password aged)Changing password for cisco.(current) password: ciscoStep 7
Enter your new password twice.
New password: new passwordRetype new password: new password***NOTICE***This product contains cryptographic features and is subject to United States and local country laws governing import, export, transfer and use. Delivery of Cisco cryptographic products does not imply third-party authority to import, export, distribute or use encryption. Importers, exporters, distributors and users are responsible for compliance with U.S. and local country laws. By using this product you agree to comply with applicable laws and regulations. If you are unable to comply with U.S. and local laws, return this product immediately.A summary of U.S. laws governing Cisco cryptographic products may be found at: http://www.cisco.com/wwl/export/crypto/tool/stqrg.htmlIf you require further assistance please contact us by sending email to export@cisco.com.***LICENSE NOTICE***There is no license key installed on this IPS platform. The system will continue to operate with the currently installed signature set. A valid license must be obtained in order to apply signature updates. Please go to http://www.cisco.com/go/license to obtain a new license or install a license.aip_ssm#
Using the ASDM
To reset the password in the ASDM, follow these steps:
Step 1
From the ASDM menu bar, choose Tools > IPS Password Reset.

Note
This option does not appear in the menu if there is no IPS present.
Step 2
In the IPS Password Reset confirmation dialog box, click OK to reset the password to the default (cisco). A dialog box displays the success or failure of the password reset. If the reset fails, make sure you have the correct ASA and IPS software versions.
Step 3
Click Close to close the dialog box. The sensor reboots.
Disabling Password Recovery

CautionIf you try to recover the password on a sensor on which password recovery is disabled, the process proceeds with no errors or warnings; however, the password is not reset. If you cannot log in to the sensor because you have forgotten the password, and password recovery is set to disabled, you must reimage your sensor.
Password recovery is enabled by default. You can disable password recovery through the CLI or IDM.
Disabling Password Recovery Using the CLI
To disable password recovery in the CLI, follow these steps:
Step 1
Log in to the CLI using an account with administrator privileges.
Step 2
Enter global configuration mode:
sensor# configure terminalStep 3
Enter host mode:
sensor(config)# service hostStep 4
Disable password recovery:
sensor(config-hos)# password-recovery disallowed
Disabling Password Recovery Using IDM
To disable password recovery in IDM, follow these steps:
Step 1
Log in to the CLI using an account with administrator privileges.
Step 2
Choose Configuration > Sensor Setup > Network. The Network pane appears.
Step 3
To disable password recovery, uncheck the Allow Password Recovery check box.
For More Information
•
If you are not certain about whether password recovery is enabled or disabled, see Verifying the State of Password Recovery.
•
For more information about troubleshooting password recovery, see Troubleshooting Password Recovery.
Verifying the State of Password Recovery
Use the show settings | include password command to verify whether password recovery is enabled.
To verify whether password recovery is enabled, follow these steps:
Step 1
Log in to the CLI.
Step 2
Enter service host submode:
sensor# configure terminalsensor (config)# service hostsensor (config-hos)#Step 3
Verify the state of password recovery by using the include keyword to show settings in a filtered output:
sensor(config-hos)# show settings | include passwordpassword-recovery: allowed <defaulted>sensor(config-hos)#
Troubleshooting Password Recovery
To troubleshoot password recovery, pay attention to the following:
•
You cannot determine whether password recovery has been disabled in the sensor configuration from the ROMMON prompt, GRUB menu, switch CLI, or router CLI. If password recovery is attempted, it always appears to succeed. If it has been disabled, the password is not reset to cisco. The only option is to reimage the sensor.
•
You can disable password recovery in the host configuration. For the platforms that use external mechanisms, such as the NM CIDS bootloader, ROMMON, and the maintenance partition for the IDSM2, although you can run commands to clear the password, if password recovery is disabled in the IPS, the IPS detects that password recovery is not allowed and rejects the external request.
•
To check the state of password recovery, use the show settings | include password command.
•
When performing password recovery for the NM CIDS, do not use the reboot command to restart the NM CIDS. This causes the recovery action to be ignored. Use the boot disk command.
•
When performing password recovery on IDSM2, you see the following message:
Upgrading will wipe out the contents on the storage media. You can ignore this message. Only the password is reset when you use the specified password recovery image.For More Information
•
For information on reimaging the sensor, refer to Upgrading, Downgrading, and Installing System Images.
•
For the procedure for disabling password recovery, see Disabling Password Recovery.
•
For the procedure for checking the state of password recovery, see Verifying the State of Password Recovery.
Caveats
This section lists the caveats, and contains the following topics:
Bug Toolkit
For the most complete and up-to-date list of caveats, use the Bug Toolkit to refer to the caveat release note. You can use the Bug Toolkit to search for known bugs based on software version, feature set, and keywords. The resulting matrix shows when each bug was integrated, or fixed if applicable. It also lets you save the results of a search in Bug Groups, and also create persistent Alert Agents that can feed those groups with new defect alerts.

Note
You must be logged in to Cisco.com to access the Bug Toolkit.
If you are a registered Cisco.com user, you can view the Bug Toolkit at this URL:
http://tools.cisco.com/Support/BugToolKit/action.do?hdnAction=searchBugs
To become a registered cisco.com user, go to this URL:
http://tools.cisco.com/RPF/register/register.do
Resolved Caveats
The following known issues have been resolved in Cisco IPS 6.0(3)E.1:
•
CSCsj03856—Upgrade from 6.0(1)E1 to IPS-K9-6.0-2-E1.7.pkg missing policies conf.
•
CSCsi58602—IPS evasion using Unicode encoding for HTTP-based attacks +
•
CSCsi42159—IPS mainapp memory leak due to SNMP
Known Caveats
The following known issues are found in Cisco IPS 6.0(3)E.1:
•
CSCeh12238H225 sig 12505 subsig 5 is not alarming
•
CSCse40651—Config operation on heavily loaded system may cause unresponsive system
•
CSCsg09619—IPS accepts RSA keys with exponent 3 which are vulnerable to forgery
•
CSCsg21826—CISCO-CIDS-MIB v3.5 does not have denyPacket and blockHost defined
•
CSCsg24632—String.TCP sigs may fire out of order
•
CSCsg38169—IPS SNMP interface reports incorrect sensing interface stats
•
CSCsg96871—AnalysisEngine InspectorServiceAICWeb::ToServiceInspect abort
•
CSCsh05168—sensorApp fault during oversubscribed, heavily fragmented traffic input
•
CSCsh17891—Sensor should not allow an assigned interface to be subdivided
•
CSCsh31034—SensorApp crashes when file copy attempt failed (libhoard + fork)
•
CSCsh50205—IPS 5.1(4) 4215 imaged as CF based system because of HD failure
•
CSCsh50760—NAC causes high mainApp usage
•
CSCsh61309—IPS - Passwords presented in clear text for network devices
•
CSCsh75673—valid NTP key values stored as -1
•
CSCsh81056—Add port 443 to IM sigs
•
CSCsh89645—Unexpected behaviour while processing configuration in Service RPC
•
CSCsi10673—Modification to signature 5829
•
CSCsi24004—AICWeb: searchContentType abort
•
CSCsi27886—Meta Signatures do not retire
•
CSCsi40687—Defaulting Sig0 causes sensorApp to stop repsonding
•
CSCsi42747—Memory leak in mainApp when checking license status
•
CSCsi43787—Memory leak in mainApp when log event initiated remotely
•
CSCsi45329—Meta component signature not firing when enabled
•
CSCsi45463—6.0(3) TCP SYN Flood Cookies not functioning on XL platform
•
CSCsi48979—Sig 2152:0 false alarms after tunings or restore defaults
•
CSCsi50951—ARC IPS cannot access blocking device with 'usage' in the banner
•
CSCsi51947—telnet login script causes sensor telnet service to fail
•
CSCsi55663—5840.0 additional CLSID
•
CSCsi56228—Signature 5858-4 modification
•
CSCsi56291—service-mssql does not count usernames correctly
Related Documentation
Refer to the following documentation for more information on IPS 6.0(3)E.1 found at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/vpndevc/ps4077/tsd_products_support_series_home.html
•
Documentation Roadmap for Cisco Intrusion Prevention System 6.0
•
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco Intrusion Detection and Prevention System 4200 Series Appliance Sensor
•
Installing and Using Cisco Intrusion Prevention System Device Manager 6.0
•
Command Reference for Cisco Intrusion Prevention System 6.0
•
Configuring the Cisco Intrusion Prevention System Sensor Using the Command Line Interface 6.0
•
Installing Cisco Intrusion Prevention System Appliances and Modules 6.0
•
Installing and Removing Interface Cards in Cisco IPS-4260 and IPS 4270
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
For information on obtaining documentation, submitting a service request, and gathering additional information, see the monthly What's New in Cisco Product Documentation, which also lists all new and revised Cisco technical documentation, at:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html
Subscribe to the What's New in Cisco Product Documentation as an RSS feed and set content to be delivered directly to your desktop using a reader application. The RSS feeds are a free service. Cisco currently supports RSS Version 2.0.
This document is to be used in conjunction with the documents listed in the "Related Documentation" section.
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Copyright © 2007-2012 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback