Using Cisco Unified Communications Manager to Configure Transcoding and Media Termination Point
Available Languages
Table Of Contents
Using Cisco Unified Communications Manager to Configure Transcoding and Media Termination Point
Prerequisites for Transcoding and MTP for Cisco VGD 1T3 Voice Gateway
Restrictions for Transcoding and MTP for the Cisco VGD 1T3 Voice Gateway
Information About Transcoding and MTP for the Cisco VGD 1T3 Voice Gateway
Allocation of DSP Resources Within the Voice Network Module
Allocation of DSP Resources Within the DSP Farm
Transcoding Session Capacities
Configuring Transcoding and MTP for the Cisco VGD 1T3 Voice Gateway
Determining DSP Resource Requirements
Enabling SCCP on the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Interface
Configuring Transcoding and MTP
Configuration Examples for Transcoding and MTP
DSP-Farm Services on the Cisco VGD 1T3: Example
Out-Band to In-Band DTMF Relay: Example
Out-Band to In-Band DTMF Relay for MTP Device: Example
Using Cisco Unified Communications Manager to Configure Transcoding and Media Termination Point
This chapter describes the steps for enabling transcoding and media termination point (MTP) support on Cisco VGD 1T3 voice gateways in a Cisco Unified Communications Manager network. This feature provides enhanced multiservice support by enabling transcode functions and MTP in voice gateway routers. Using transcoding services reduces bandwidth needs resulting in tangible cost savings.
Digital signal processor (DSP) farms provide transcoding services using DSP resources on high-density digital voice/fax network modules. This chapter contains the following sections:
•
Prerequisites for Transcoding and MTP for Cisco VGD 1T3 Voice Gateway
•
Restrictions for Transcoding and MTP for the Cisco VGD 1T3 Voice Gateway
•
Information About Transcoding and MTP for the Cisco VGD 1T3 Voice Gateway
•
Configuring Transcoding and MTP for the Cisco VGD 1T3 Voice Gateway
•
Configuration Examples for Transcoding and MTP
Prerequisites for Transcoding and MTP for Cisco VGD 1T3 Voice Gateway
The prerequisites defined in the sections below apply to the configuration of transcoding and MTP for the Cisco VGD 1T3 Voice Gateway:
DSP Resources
The Cisco VGD 1T3 voice gateway uses PVDM2 modules to provide DSP resources for transcoding and hardware MTP services. Use Cisco Unified Communications Manager 5.0 (formerly known as Cisco CallManager 5.0) or later for transcoding and for MTP. You must have Cisco IOS Release 12.4(20)YA or later.
Codecs
End-user devices must be equipped with one of the following codecs:
G.711 a-law, G.711 mu-law
10, 20, or 30
G.729, G.729A, G.729B, G.729AB
10, 20, 30, 40, 50, or 60
Restrictions for Transcoding and MTP for the Cisco VGD 1T3 Voice Gateway
•
DSP farm services communicate with Cisco Unified Communications Manager using Skinny Client Control Protocol (SCCP); other protocols are not supported.
•
DSP farm services are not supported for Cisco Survivable Remote Site Telephony (SRST) or Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express.
•
Hardware MTPs support only G.711 a-law and G.711 u-law. If you configure a profile as a hardware MTP, and you want to change the codec to other than G.711, you must first remove the hardware MTP by using the no maximum sessions hardware command.
•
Only one codec is supported for each MTP profile. To support multiple codecs, you must define a separate MTP profile for each codec.
•
If an MTP call is received but MTP is not configured, transcoding is used if resources are available.
•
Dynamic conference and transcoding resource allocation is not supported.
•
Fax is not supported for transcoding.
Information About Transcoding and MTP for the Cisco VGD 1T3 Voice Gateway
To configure transcoding, you should understand the following concepts:
•
Transcoding Session Capacities
DSP Farms
A DSP farm is the collection of DSP resources available for transcoding and MTP services. DSP farms are configured on the voice gateway and managed by Cisco Unified Communications Manager through Skinny Client Control Protocol (SCCP).
The DSP farm can support a combination of transcoding sessions and MTP sessions simultaneously. The DSP farm maintains the DSP resource details locally. Cisco Unified Communications Manager requests transcoding services from the gateway, which either grants or denies these requests, depending on resource availability. The details of whether DSP resources are used, and which DSP resources are used, are transparent to Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
The DSP farm uses the DSP resources in network modules on Cisco routers to provide transcoding and hardware MTP services.

Tip
To determine how many DSP resources your router supports, see the "Allocation of DSP Resources" section.
DSP Farm Profiles
DSP-farm profiles are created to allocate DSP-farm resources. Under the profile you select the service type (transcode or MTP), associate an application, and specify service-specific parameters such as codecs and maximum number of sessions. A DSP-farm profile allows you to group DSP resources based on the service type. Applications associated with the profile, such as SCCP, can use the resources allocated under the profile. You can configure multiple profiles for the same service, each of which can register with one Cisco Unified Communications Manager group. The profile ID and service type uniquely identify a profile, allowing the profile to uniquely map to a Cisco Unified Communications Manager group that contains a single pool of Cisco Unified Communications Manager servers.
Transcoding and MTP
Transcoding compresses and decompresses voice streams to match endpoint-device capabilities. Transcoding is required when an incoming voice stream is digitized and compressed (by means of a codec) to save bandwidth, but the local device does not support that type of compression. Ideally, all IP telephony devices would support the same codecs, but this is not the case. Rather, different devices support different codecs.
Transcoding is processed by DSPs on the DSP farm; sessions are initiated and managed by Cisco Unified Communications Manager which also refers to transcoders as hardware MTPs.
This feature provides transcoding at the remote site, without the need for access to the central site (see Figure 1).
Figure 1 Transcoding Service
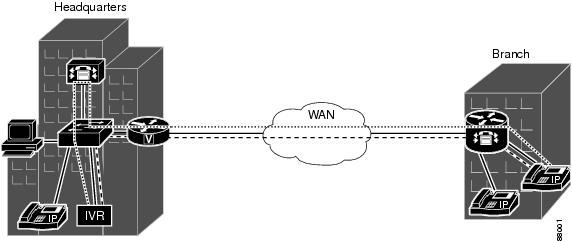
Media Termination Point
A Media Termination Point (MTP) bridges the media streams between two connections allowing Cisco Unified Communications Manager to relay calls that are routed through SIP or H.323 endpoints.
The following MTP resources are supported for Cisco Unified Communications Manager 4.0 (formerly known as Cisco CallManager 4.0) and later releases:
•
Software MTP—Software-only implementation that does not use a DSP resource for endpoints using the same codec and the same packetization time.
•
Hardware MTP—Hardware-only implementation that uses a DSP resource for endpoints using the same G.711 codec but a different packetization time. The repacketization requires a DSP resource so it cannot be done by software only. Cisco Unified Communications Manager also uses the term software MTP when referring to a hardware MTP.
For MTP and transcoding, the DSP farm supports only two IP streams connected to each other at a time. If more than two streams need connecting, the streams must be connected using conferencing.
Allocation of DSP Resources
You must allocate DSP resources on two levels:
•
Within the voice network module, between the DSP farm and your voice trunk group that handles standard voice termination
•
Within the DSP farm, between transcoding and voice-conferencing services
Allocation of DSP Resources Within the Voice Network Module
You allocate DSP resources either to voice termination of the voice trunk group or to the DSP farm. Occasionally these allocations can conflict.
If you previously allocated DSP resources to voice termination and you now try to configure a DSP farm, you might find that insufficient DSP resources are available. Conversely, if you previously allocated DSP resources to a DSP farm and you now try to configure a trunk group, you might find that insufficient DSP resources are available.
If your requested configuration is rejected, you have two options:
•
Insert more DSPs on the voice network module (NM-HDV or NM-HDV2)
•
Allocate a different voice network module for either the DSP farm or the trunk group
Allocation of DSP Resources Within the DSP Farm
You should know the following about your system:
•
Number of DSPs required to handle your anticipated number of conference calls and transcoding sessions
•
Number of DSPs that your system can support
DSP resources can reside in packet-voice DSP modules (PVDM2s) installed in voice network modules or directly in the network module. Cisco VGD 1T3 voice gateway routers have onboard DSP resources located on PVDM2s installed directly on the motherboard. Your router supports up to six voice network modules.
Transcoding Session Capacities
Each DSP is individually configurable to support transcoding and standard voice termination. The total number of transcoding and voice termination sessions is limited by the capacity of the entire system, which includes the DSPs, hardware platform, physical voice interface, and Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
Table 1 and Table 2 list the maximum number of conference calls and transcoding sessions that DSPs can handle, in theory. Actual capacity may be less based on the total system design.
Table 2 Theoretical System Capacities for One DSP
16 sessions
—
—
8 sessions
8 sessions
6 sessions
Configuring Transcoding and MTP for the Cisco VGD 1T3 Voice Gateway
This section contains the procedures for configuring transcoding and MTP support on Cisco VGD 1T3 voice gateways. The procedures that you perform depend on the type of voice network module you are using to allocate DSP resources:
•
Determining DSP Resource Requirements (required)
•
Enabling SCCP on the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Interface (required)
•
Configuring Transcoding and MTP (required)
Determining DSP Resource Requirements
DSPs reside on PVDM2s that are installed in a voice network module or on PVDM2s that are installed directly onto the motherboard. You must determine the number of PVDM2s or network modules that are required to support your transcoding services and install the modules on your router.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
Determine performance requirements.
2.
Determine the number of DSPs that are required.
3.
Verify your solution.
4.
Install hardware.
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Determine the number of transcoding sessions and conference calls that your router must support.
Establishes your performance requirements.
Step 2
Determine the number of DSPs that are required to support the transcoding sessions. If voice termination is also required, determine the additional DSPs required.
Example:8 G.711 conferences and 32 transcoding sessions require 1 PVDM2-64 (4 DSPs).
Establishes your hardware requirements.
Step 3
Ensure that your requirements fall within router capabilities, taking into account whether your router supports multiple network modules. If necessary, reassess performance requirements.
Verifies your proposed solution.
Step 4
Install PVDM2s and network modules, as needed (see the "Connecting Voice Network Modules" chapter in the Cisco Network Modules Hardware Installation Guide, and the Cisco Network Modules and Interface Cards Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information).
Prepares your system for DSP-farm configuration.
Enabling SCCP on the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Interface
Perform this task to enable SCCP on the local interface that the voice gateway uses to communicate with Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
sccp ccm {ip-address | dns} identifier identifier-number [port port-number] [version version-number]
4.
sccp local interface-type interface-number
5.
sccp ip precedence value
6.
sccp
7.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring Transcoding and MTP
For detailed instructions on how to configure Transcoding on Cisco Unified Communications Manager, refer to the Transcoder Configuration section in the Media Resource Configuration chapter in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration Guide.
For detailed instructions on how to configure MTP on Cisco Unified Communications Manager, refer to the Media Termination Point Configuration section in the Media Resource Configuration chapter in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration Guide.
Configuration Examples for Transcoding and MTP
This section provides the following configuration examples:
•
DSP-Farm Services on the Cisco VGD 1T3: Example
•
Out-Band to In-Band DTMF Relay: Example
•
Out-Band to In-Band DTMF Relay for MTP Device: Example
DSP-Farm Services on the Cisco VGD 1T3: Example
The following example shows a configuration of transcoding services on a PVDM2. DSP farm profile 6, which supports transcoding, is assigned to Cisco Unified Communications Manager group 988.

Note
This configuration requires Cisco IOS Release 12.4(20)YA or later.
Current configuration : 2661 bytes!version 12.4service timestamps debug datetime msecservice timestamps log datetime msecno service password-encryption!hostname sjl23!boot-start-markerboot-end-marker!!no aaa new-modelip subnet-zero!!!ip host boating 223.255.254.254no ftp-server write-enable!voice-card 1no dspfarmdsp services dspfarm!!voice service voiph323!!!interface FastEthernet0/0ip address 10.4.20.7 255.255.255.0no ip mroute-cachespeed autohalf-duplexno cdp enable!interface FastEthernet0/1no ip addressno ip mroute-cacheshutdownduplex autospeed autono cdp enable!ip default-gateway 10.4.0.1ip classlessip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 FastEthernet0/0ip route 223.255.254.254 255.255.255.255 10.4.0.1no ip http server!!no cdp run!!control-plane!!sccp local FastEthernet0/0sccp ccm 10.4.20.24 identifier 1 version 4.0sccp ccm 10.4.20.25 identifier 2 version 4.0sccp ccm 10.4.20.26 identifier 3 version 4.0sccp ip precedence 3sccp!sccp ccm group 988associate ccm 1 priority 1associate ccm 2 priority 2associate ccm 3 priority 3associate profile 6 register MTP123456789988keepalive retries 5switchover method immediateswitchback method immediateswitchback interval 15!dspfarm profile 6 transcodecodec g711ulawcodec g711alawcodec g729ar8codec g729abr8codec gsmfrmaximum sessions 4associate application SCCP!!dial-peer cor custom!!dial-peer voice 200 voipdestination-pattern 111....session target ipv4:10.4.205.24!dial-peer voice 2600 voipdestination-pattern 666....session target ipv4:10.4.205.24codec g711ulaw!dial-peer voice 100 voipdestination-pattern 5550...session target ipv4:10.4.205.24codec g711ulaw!dial-peer voice 10 potsdestination-pattern 7770000forward-digits 0!dial-peer voice 11 potsdestination-pattern 7771111!dial-peer voice 999 voipsession target ipv4:10.4.205.8!gatewaytimer receive-rtp 1200!!line con 0exec-timeout 0 0line aux 0line vty 0 4password testlogin!!endOut-Band to In-Band DTMF Relay: Example
In the following configuration, the voice gateway acts as both a H.323 gateway and DSP farm.
Building configuration...Current configuration :2091 bytes!version 12.4service timestamps debug datetime msecservice timestamps log datetime msecno service password-encryption!hostname vgd 1t3!boot-start-markerboot-end-marker!no logging console!no network-clock-participate wic 1network-clock-participate wic 2no network-clock-participate wic 3network-clock-participate wic 4mmi polling-interval 60no mmi auto-configureno mmi pvcmmi snmp-timeout 180no aaa new-modelip subnet-zeroip cef!!!no ftp-server write-enableisdn switch-type primary-net5voice-card 0dsp services dspfarm!!!controller T1 2/0:1shutdownframing esflinecode b8zs!controller T1 3/0:1framing esflinecode b8zs!!!interface FastEthernet0/0ip address 192.168.12.21 255.255.255.0duplex autospeed auto!interface FastEthernet0/1no ip addressshutdownduplex autospeed auto!interface BRI4/0no ip addressisdn switch-type basic-net3!interface BRI4/1no ip addressisdn switch-type basic-net3!ip classlessip http server!!!control-plane!!!voice-port 3/0:1!voice-port 3/1:1!voice-port 4/0:1!voice-port 4/1:1!!sccp local FastEthernet0/0sccp ccm 192.168.12.131 identifier 1 version 4.0sccp ip precedence 4sccp!sccp ccm group 1bind interface FastEthernet0/0associate ccm 1 priority 1associate profile 2 register amalthea-mtpassociate profile 1 register amalthea-xcoderegistration retries 20registration timeout 30keepalive retries 10connect retries 30connect interval 30!dspfarm profile 1 transcodedescription xcode funccodec g711ulawcodec g711alawcodec g729ar8codec g729abr8codec gsmfrcodec g729r8maximum sessions 2associate application SCCP!dspfarm profile 2 mtpcodec g711ulawmaximum sessions hardware 2maximum sessions software 2associate application SCCP!!dial-peer voice 1 potsdestination-pattern 4444port 3/0!dial-peer voice 2 voipdestination-pattern 52..session target ipv4:192.168.12.131dtmf-relay h245-alphanumeric!gatewaytimer receive-rtp 1200!!line con 0line aux 0line vty 0 4login!endOut-Band to In-Band DTMF Relay for MTP Device: Example
The following running configuration example shows the MTP device configuration.
Building configuration...Current configuration : 1435 bytes!version 12.3service timestamps debug uptimeservice timestamps log uptimeno service password-encryption!hostname router1!voice-card 1no dspfarmdsp services dspfarm!voice-card 2dspfarm!no aaa new-modelip subnet-zero!ip host sample 10.10.10.5mpls ldp logging neighbor-changesno ftp-server write-enableno scripting tcl initno scripting tcl encdir!no voice hpi capture bufferno voice hpi capture destination!interface FastEthernet0/0ip address 10.4.118.13 255.255.255.255duplex autospeed auto!interface FastEthernet0/1no ip addressshutdownduplex autospeed auto!ip default-gateway 10.4.0.10ip classlessip route 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 FastEthernet0/0ip route 223.255.255.255 255.255.255.255 FastEthernet0/0!ip http server!sccp local FastEthernet0/0sccp ccm 10.40.10.10 identifier 10 version 4.0sccp ccm 10.10.10.51 identifier 20 version 4.0sccp!sccp ccm group 999associate ccm 10 priority 1associate ccm 20 priority 2associate profile 12 register MTP123456789associate profile 2 register XCODT123456!dspfarm profile 2 transcodecodec g711ulawcodec g711alawcodec g729ar8codec g729abr8codec gsmfrmaximum sessions 2associate application SCCP!dspfarm profile 12 mtpcodec g711ulawmaximum sessions hardware 4maximum sessions software 40associate application SCCP!SIP Gateway: Example
The following running configuration example shows the SIP gateway configuration for the Out-Band to In-Band DTMF Relay feature.
Building configuration...Current configuration : 2051 bytes!version 12.4service timestamps debug uptimeservice timestamps log uptimeno service password-encryption!hostname cisco_sip_gw!logging buffered 6000000 debugging!voice-card 2dspfarm!no aaa new-modelip subnet-zero!!ip domain name cisco.comip host sample 10.10.10.5ip host myhost 10.4.175.2mpls ldp logging neighbor-changesno ftp-server write-enableno scripting tcl initno scripting tcl encdir!!no voice hpi capture bufferno voice hpi capture destination!!ccm-manager mgcpccm-manager music-on-holdccm-manager config server 10.4.175.2ccm-manager config!!controller T1 2/0:1framing esflinecode b8zsds0-group 1 timeslots 1-24 type e&m-fgb!controller T1 2/0:2framing sflinecode ami!!!interface FastEthernet0/0ip address 10.4.175.14 255.255.0.0duplex autospeed auto!interface FastEthernet0/1no ip addressshutdownduplex autospeed auto!interface BRI1/0no ip address!ip default-gateway 10.4.0.1ip classlessip route 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet0/0ip route 223.255.254.254 255.255.255.255 FastEthernet0/0!ip http server!!voice-port 1/0:0!voice-port 1/0:1!voice-port 1/1:0!voice-port 2/0:1!mgcp profile default!!dial-peer voice 1 voipdestination-pattern 2000session protocol sipv2session target ipv4:10.4.175.2dtmf-relay rtp-ntecodec g711ulaw!dial-peer voice 3 potsapplication mgcpappport 2/0:1!dial-peer voice 999201 potsapplication mgcpappport 2/0:1!dial-peer voice 2 potsdestination-pattern 2005port 1/0/0!dial-peer voice 5 potsdestination-pattern 2001port 1/0/0!!line con 0line aux 0line vty 0 4login!!end
CCDE, CCENT, CCSI, Cisco Eos, Cisco HealthPresence, Cisco IronPort, the Cisco logo, Cisco Lumin, Cisco Nexus, Cisco Nurse Connect, Cisco Pulse, Cisco StackPower, Cisco StadiumVision, Cisco TelePresence, Cisco Unified Computing System, Cisco WebEx, DCE, Flip Channels, Flip for Good, Flip Mino, Flipshare (Design), Flip Ultra, Flip Video, Flip Video (Design), Instant Broadband, and Welcome to the Human Network are trademarks; Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn, Cisco Capital, Cisco Capital (Design), Cisco:Financed (Stylized), Cisco Store, and Flip Gift Card are service marks; and Access Registrar, Aironet, AllTouch, AsyncOS, Bringing the Meeting To You, Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP, CCIE, CCIP, CCNA, CCNP, CCSP, CCVP, Cisco, the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, Cisco Press, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo, Cisco Unity, Collaboration Without Limitation, Continuum, EtherFast, EtherSwitch, Event Center, Explorer, Fast Step, Follow Me Browsing, FormShare, GainMaker, GigaDrive, HomeLink, iLYNX, Internet Quotient, IOS, iPhone, iQuick Study, IronPort, the IronPort logo, Laser Link, LightStream, Linksys, MediaTone, MeetingPlace, MeetingPlace Chime Sound, MGX, Networkers, Networking Academy, Network Registrar, PCNow, PIX, PowerKEY, PowerPanels, PowerTV, PowerTV (Design), PowerVu, Prisma, ProConnect, ROSA, ScriptShare, SenderBase, SMARTnet, Spectrum Expert, StackWise, The Fastest Way to Increase Your Internet Quotient, TransPath, WebEx, and the WebEx logo are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the United States and certain other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned in this document or website are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (0908R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
© 2008-2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback