Cisco HyperFlex - VMware Site Recovery Manager White Paper
Available Languages
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
The purpose of this document is to assist users with VMware Site Recovery Manager (SRM) integrated with Cisco HyperFlex® array-based replication to convert to VMware vSphere replication. Once completed, the conversion process eliminates the use of and dependency on the HyperFlex Storage Replication Adapter (SRA).
Please note that the graphic images and procedural steps included in this document are based on the following product versions:
● Cisco HyperFlex HX Data Platform Release 5.5.1a-43232
● VMware vSphere 7.0.3-22348816
● VMware SRM 8.8.0.22795455
● VMware vSphere Replication 8.8.0.22780241
VMware Site Recovery Manager (SRM)
VMware Site Recovery Manager (SRM) is a disaster-recovery solution that protects Virtual Machines (VMs) and enables recovery of VM workloads at a recovery site. The solution makes it possible to perform test recovery, failover and planned migration and re-protect operations. These operations are performed with VMs that have been replicated from a protected site to a recovery site. SRM currently supports three types of replications, categorized as array-based replication, vSphere replication, and vVol replication.
Within the context of Cisco HyperFlex, vVol replication is not applicable. From a high-level perspective, array-based replication occurs at the storage layer and relies on a HyperFlex-specific SRA deployed on both the protected site and recovery site. vSphere replication is host-based and has no dependency on the underlying storage type. vSphere replication does not include the use of an SRA; instead, it requires the use of vSphere-replication virtual appliances deployed on both the protected site and recovery site.
Documentation for SRM is available from VMware here: https://docs.vmware.com/en/Site-Recovery-Manager/index.html.
Array-based replication
Specific to HyperFlex, SRM array-based replication requires that HyperFlex native replication has been configured, and that the HyperFlex SRA has been properly installed and configured within SRM.
Documentation for HyperFlex, HyperFlex native replication, and the HyperFlex SRA is available from Cisco here: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/hyperconverged_systems/HyperFlex_HX_DataPlatformSoftware/AdminGuide/5-5/b-hxdp-admin-guide-5-5.html.
HyperFlex native 1:1 (NRDR) replication – “other DRO”
HyperFlex integration with SRM for array-based replication requires the use of a HyperFlex SRA. The integrated solution also requires the use of mapped datastores configured as an “other DRO.” The “other DRO” nomenclature refers to non-native “disaster recovery orchestration.” When properly configured, all the VMs residing in a source datastore are replicated to a mapped destination datastore. The mapped datastore configuration also defines the replication schedule. The replication schedule defines an interval that is configurable from a minimum of 5 minutes to a maximum of 24 hours. The interval effectively defines the Recovery Point Objective (RPO) for a given mapped datastore. Deployments with different RPO requirements for different VM workloads may have more than a single mapped datastore configuration.
vSphere replication
vSphere replication has no dependency on the underlying storage architecture and as such does not use an SRA to function. It requires network connectivity between the protected site and the recovery site. At a minimum, this consists of a routed VLAN and gateway for each site. Network configurations can optionally be architected to isolate replication traffic, improve performance, and enhance security.
Important to note is that vSphere replication does not rely on datastore mapping or replication scheduling at the HyperFlex storage level. vSphere replication occurs at a VM level of granularity, where the target datastore and RPO is configured.
The conversion process involves removing protection from the VMs contained within an SRM protection-group type that uses “Datastore groups (array-based replication),” configuring the VMs for vSphere replication, and then adding those VMs to a protection-group type that uses “individual VMs (vSphere replication).” The duration of time between removing protection from VMs and subsequently adding those VMs to a different protection group represents a window during which those VMs are not protected by SRM and cannot be recovered. It should also be understood that once VMs are added to the new protection group, the process of configuring and performing an initial synchronization increases the duration of the time window during which VMs cannot be recovered.
Conversion method
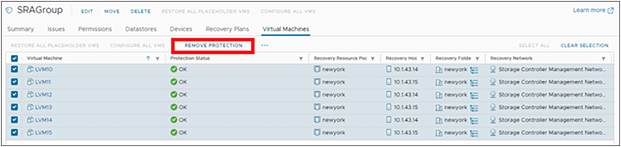
Protection is removed on every VM protected by array-based replication in a protection group.
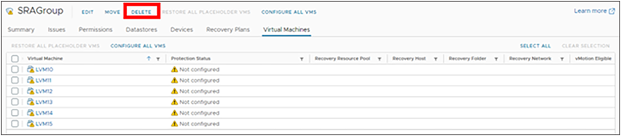
The protection group is then deleted.
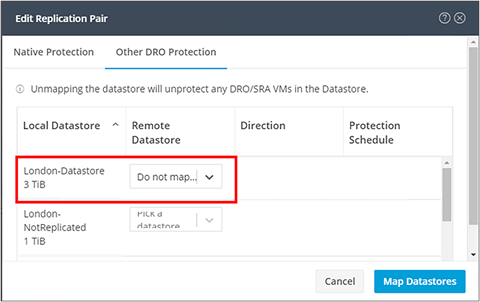
At this point array-based replication is no longer being used. The HyperFlex datastore replication pair is then unmapped.
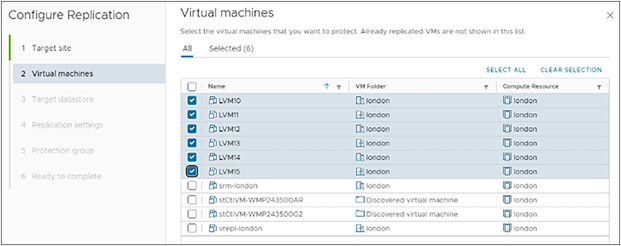
The VMs are then configured for vSphere replication.
Configuration and synchronization will occur, and the VMs are added to a vSphere replication protection group.
During the configuration and synchronization process, increased replication network bandwidth utilization may occur. It is important to understand that, until the configuration and synchronization processes are completed, VMs cannot be recovered.
Not recommended and unsupported
Conversion strategies that include protecting a given VM or VMs by the simultaneous use of both array-based replication and vSphere replication are not supported. VMware documentation states, “Do not attempt to configure vSphere Replication on a virtual machine that resides on a datastore that you replicate by using array-based replication.” The VMware reference for this statement is available here: https://docs.vmware.com/en/Site-Recovery-Manager/8.8/srm-administration/GUID-ECDF095A-5CA4-4F62-A864-603E0FBA75E3.html.
Planning in advance of project execution is advised. If not already present, vSphere replication appliances should be deployed and configured at the protected site and recovery site. One or more SRM protection groups and recovery plans for VMs being converted to use vSphere replication should also be created. HyperFlex VMs currently protected by SRM with array-based replication should be documented.
Adding vSphere replication
VMware documentation should be consulted when deploying and configuring vSphere replication appliances.
● “Deploy the vSphere Replication Virtual Appliance” https://docs.vmware.com/en/vSphere-Replication/8.8/administration-guide/GUID-E654F2D8-7D56-4A81-9568-E85172A7022D.html.
● “Configure the vSphere Replication Appliance to Connect to a vCenter Server” https://docs.vmware.com/en/vSphere-Replication/8.8/administration-guide/GUID-964F4F6C-62B1-4EDA-9B50-E4F55C55CF15.html.
● “Configure vSphere Replication Connections” https://docs.vmware.com/en/vSphere-Replication/8.8/administration-guide/GUID-FFBF959C-5C05-42C0-A2FE-3688AD55B6EF.html.
Creating a protection group for VMs protected by vSphere replication
One or more protection groups can be created in advance of the actual conversion process. VMware documentation should be consulted when creating a protection group.
● “Creating and Managing Protection Groups” https://docs.vmware.com/en/Site-Recovery-Manager/8.8/srm-administration/GUID-294475D7-B136-4492-8F8E-522B8EDA26EA.html.
● “vSphere Replication Protection Groups” https://docs.vmware.com/en/Site-Recovery-Manager/8.8/srm-administration/GUID-CCF2E768-736E-4EAA-B3BE-50182635BC49.html.
Creating a recovery plan for VMs protected by vSphere replication
One or more recovery plans can be created in advance of the actual conversion process. VMware documentation should be consulted when creating a recovery plan.
● “Creating, Testing, and Running Recovery Plans” https://docs.vmware.com/en/Site-Recovery-Manager/8.8/srm-administration/GUID-AF6BF11B-4FB7-4543-A873-329FDF1524A4.html.
Determining which HyperFlex VMs are protected by SRM with array-based replication
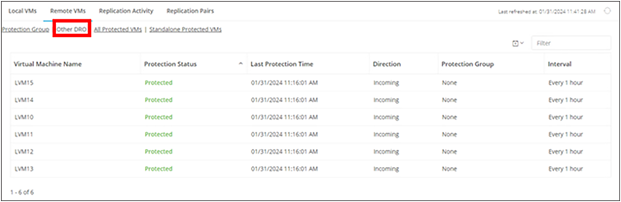
Within the HyperFlex HX Connect user interface, view the list of “other DRO” VMs being replicated.
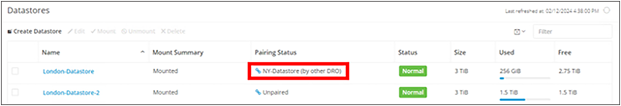
Also view the HyperFlex datastores. Look for datastores that have a pairing status indicating a peer datastore with “(by other DRO).”
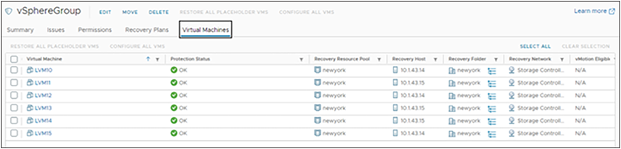
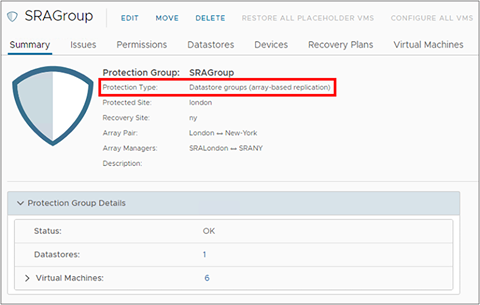
Examine the SRM protection group. The protection group will be of the type “Datastore groups (array-based replication).”
The “Devices” tab will display a device name that should correlate to the HyperFlex datastore name.
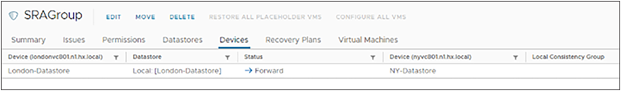
The “Virtual Machines” tab will display a list of protected VMs. This is the list of VMs that will be converted to being protected with vSphere replication.
The conversion procedure assists in converting all HyperFlex VMs residing on an “other DRO”–paired datastore protected by SRM array-based replication to SRM vSphere replication.
1. Within SRM, locate the protection group associated with the “other DRO”–paired datastore. Select all of the VMs, and then select “REMOVE PROTECTION.” A dialog window will present the option to “CANCEL” or “REMOVE.” Select the “REMOVE” option. VM protection status will change from “OK” to “Not Configured.”
2. Delete the protection group. A dialog window will present the option to “CANCEL” or “DELETE.” Select the “DELETE” option.
3. Within the HyperFlex HX Connect user interface, select “Replication” from the left pane. Click “Replication Pairs,” and then click the cluster pair name under the “Name” column. Click the “Edit” button and then click “Other DRO Protection” within the “Edit Replication Pair” window. Locate the datastore pair, and then select “Do not map this datastore” from the pulldown menu. Click the “Map Datastores” button to continue. Note that, at this point any placeholder VMs associated with the datastores should be automatically deleted, and any HyperFlex HX Data Platform snapshots should also be automatically deleted.
4. Within SRM, select the “Replications” tab and then click the “NEW” button. The “Configure Replication” wizard will launch. Auto-assign or manually select the vSphere Replication Server, and click the “Next” button. From the displayed list of VMs, select the VMs that were previously protected by array-based replication and then click the “Next” button. Select a target datastore. This can be the same target datastore that was used with the now unconfigured array-based replication, or a different target datastore. Proceed with the wizard and apply the desired replication settings. Add the VMs to the protection group that was created earlier in the preparation/planning step of the conversion process. Click the “FINISH” button.
5. Refresh the SRM display, and the newly added VMs will have a “Configuring” status. The status will eventually change to “Initial Sync” and then to “OK.” At this point the VMs are protected.
6. Repeat these steps for any additional “other DRO”–paired datastores.
7. If HyperFlex array-based replication is no longer required after successful conversion to vSphere replication, proceed to the section titled “Removing HyperFlex array-based replication.”
Removing HyperFlex array-based replication
Log in to the Site Recovery Manager Appliance management interface as the “admin” user. Select “Storage Replication Adapters” in the left pane. Locate the “Cisco HyperFlex SRA.” Click the ellipsis icon (three vertical dots), and then select “Delete” from the pulldown menu.
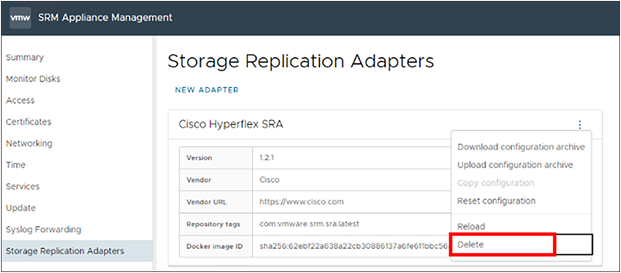
A dialog window will appear with two confirmation check boxes, which should be acknowledged and enabled.
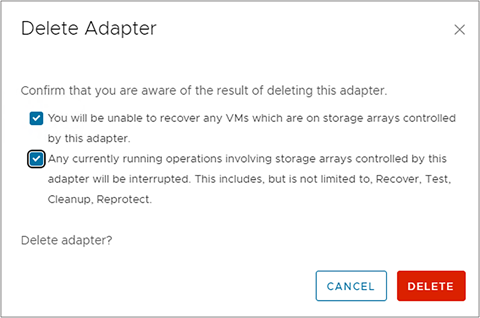
The user then has the option to “CANCEL” or “DELETE.” Select the “DELETE” option. Perform this action on both the protected-site and recovery-site SRM instances.