Cisco DNA Center 2.2.2 Release Announcement
Available Languages
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
We are excited to announce Cisco DNA Center 2.2.2 release and General Availability (GA). Cisco DNA Center2.2.2 continues the journey to modernize your network operating and security model through innovation in AIOps, automation, and zero trust, helping companies:
● Improve application and infrastructure performance with extensive AI/ML enhancements: Comparative analytics, heatmaps, baselines, and machine reasoning capabilities.
● Lower cost of management: To manage more users and devices with a 2X increase in client endpoint capacity.
● Improve security with Zero-trust architecture improvements that:
◦ Simplify policy creation, viewing, and editing through enhancements to group-based policy analytics and access control.
◦ Enable easy SD-Access with support for existing access VLANs.
● Demonstrate and communicate the time-to-value of your Cisco DNA Center investment through in-product ROI reports.
In this release announcement, you will find feature overviews and details regarding the Cisco DNA Center release methodology and terminology and useful links to additional reference documents.
AIOps with Cisco DNA Assurance and Analytics

“AI Network Analytics is like having an owl in my network, it helps me see in the dark.”
Shai Silberman
Director of Network Services
San Jose State University

Enhanced comparative analytics
Network operators were unable to investigate and isolate the cause of a concern and plan device refresh cycles, as the site comparison feature was limited to comparing network performance across locations and did not offer visibility into the network entities. The network comparison feature now enables network operators to select a Key Performance Indicator (KPI) and cluster network entities such as “AP Models” and “Endpoints” into different performance buckets. This helps network operators expedite the time to identify poorly performing AP models or endpoint types and further optimize overall network performance.
Enhanced network heatmaps
Network operators now have extended visibility into network KPI performance across APs for hours of a day to identify recurring issue surges and maintenance windows. This feature enables network operators to choose a day and view the hourly performance of a selected KPI across APs on the network. It offers improved visibility into the hourly performance of APs for accelerated issue isolation and Root Cause Analysis (RCA).
Additions to the Machine Reasoning Engine (MRE)
Network operators spend a lot of time conducting Root Cause Analysis (RCA) for a set of common issues like authorization, authentication, and accounting (AAA) failures. RCA relies heavily on subject matter expertise and knowledge of the device Command-Line Interface (CLI). Some common issues such as IP address failures, authentication failures, and Power over Ethernet (PoE) failures were not supported by earlier versions of the MRE. The MRE now supports automated RCA for the aforementioned issues. This enables improved issue resolution with automated root cause analysis.
Baselines dashboard
Network operators had no visibility into client onboarding behavior across buildings. Baselines for onboarding KPIs were visible only when a deviation was observed. This made it hard for network operators to identify buildings and SSIDs with subpar onboarding experiences. The interactive dashboard with an end-to-end workflow enables network operators to view and evaluate client onboarding behavior across different buildings and SSIDs, view AI issues, and study the aggregated impact of issues in a 30-day time window. This feature offers improved visibility into the onboarding behavior across buildings and SSIDs.
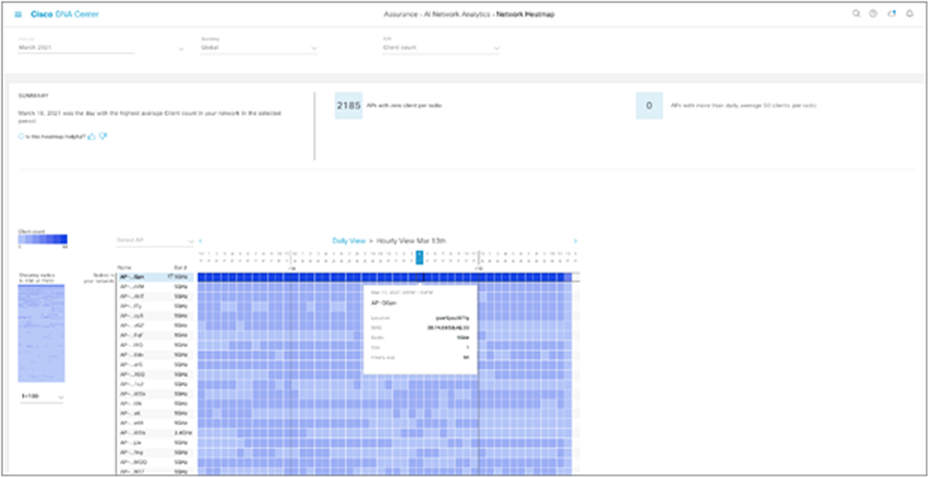
Network heatmap – hourly view
Wireless sensors
Network operators who use proxy in their networks were unable to use sensor web tests and Network Diagnostics Tests (NDTs) because there was no way to configure proxy settings. Prior to this release, network operators could not subscribe to external notifications for sensor issues, which was a real pain point as they would have to go back to Cisco DNA Center to see the sensor issues. Sensors did not support preshared keys (PSK) with hex password wireless security protocols, so network operators using PSK with hex passwords could not join networks.
With this release, sensors can run web tests and NDTs even if the network uses proxy with authentication. Network operators are notified in the event of a global sensor issue related to getting an email or a webhook notification to their central Network Operations Center (NOC) software. This release supports existing standard wireless security protocols (PSK with hex passwords).
Consolidation of notifications to one central NOC enables better issue remediation and a smoother user experience.
ThousandEyes app for Cisco Catalyst 9000 devices
Previously, network operators had to deploy the Cisco ThousandEyes app via the CLI one switch at a time. This was a time-intensive process. The ThousandEyes app required an additional Solid-State Drive (SSD) deployed to switches. This release provides a GUI-supported installation process through Cisco DNA Center. With one click, the app can now be installed on all supported switches at once. Cisco DNA Center automatically downloads the latest upgrades and notifies users for a single-click, networkwide upgrade. Also, the ThousandEyes app now resides on the switch flash storage and does not need an additional SSD. This feature provides significant time and cost savings, reduces inventory management, and simplifies app maintenance.
ThousandEyes dashboards
WAN link availability and utilization
If a WAN link goes down, it is likely that an entire branch or portion of the network is affected. Network operators wanted transparency and visibility into the performance of the WAN links in the network to proactively ensure the health of their WAN links. Network operators on Cisco DNA Center now have the same visibility into their WAN links as is provided by Cisco Prime® Infrastructure. This feature helps prevent issues that result from WAN outages.
Application experience health score customization
The qualitative metrics that Cisco DNA Center reports are not specific to an operational environment. The new ability to customize the health score enables network operators to be notified when performance degradation is relevant to their network. This feature enables network operators to further customize Cisco DNA Center to support their specific operational environment.
Simplify wireless planning with the Ekahau planning tool
Until now, changes made in Cisco DNA Center couldn't be exported to Ekahau Pro projects. Network designers can now edit and augment the maps in Ekahau and reimport the maps back to Cisco DNA Center without losing items such as sensors, markers, and coverage areas that are unrecognized by Ekahau. This feature simplifies life for network designers when making map edits.
Generation of planned AP heatmaps
In earlier releases, network operators weren't able to generate a predictive heatmap for planned APs. This feature optimizes the coverage calculation per floor by supporting planning for access points.
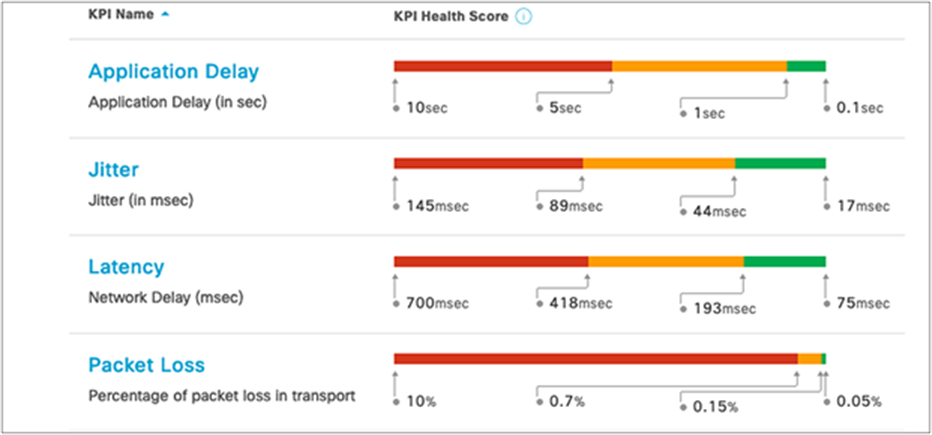
Customize the health score calculation for applications by changing the KPI thresholds on a per-traffic-class basis to support your operational environment
NetOps with Cisco DNA Automation

“We simply log into Cisco DNA Center; it takes us five minutes to do what used to take hours.”
Dustin Metteer
Lead network Engineer
Renown Health
![]()
SWIM scale package
Previously, Software Image Management (SWIM) could upgrade up to 500 devices in a single task, causing longer maintenance windows. As a result, multiple upgrade tasks had to be created for a large network, resulting in loss of productivity. In this release, the SWIM scale package allows for upgrade of up to 1000 Cisco® Catalyst® 9000 devices (running Cisco IOS® XE 17.3 or later) in an hour. This feature minimizes maintenance windows, resulting in productivity improvements, less network downtime, and cost savings.
StackWise Virtual ISSU
Even though a customer network infrastructure runs on In-Service Software Upgrade (ISSU)-supported devices, SWIM was unable to leverage the feature, resulting in longer downtime (which defeats the purpose of using ISSU). ISSU upgrade is now supported out of the box for Catalyst 9000 switches and controllers and ASR routers. Smart checks (via Cisco.com) are in place for successful ISSU upgrades. This feature reduces or avoids downtime. Network operators can manage the ISSU feature in an end-to-end manner and realize their investments in Cisco hardware.
Network Reasoner enhancements
As the Network Reasoner expands with more workflows, it is more difficult to sort through the workflows. The Network Reasoner has a new design that displays the latest workflows. These workflows are easily filtered through the tags assigned to them. Furthermore, network operators can now try a section of preproduction workflows. This feature significantly reduces the Mean Time To Repair (MTTR) and enables network operators to complete frequent troubleshooting tasks.
Security Posture
While network operators have a single view of their device health through Assurance, they previously did not have an aggregated view of their devices’ security posture. The new Security Posture is a single pane of glass for all security applications within Cisco DNA Center. From the Security Posture dashboard, the security application can be launched for further details. The initial release includes integrity verification and security advisories. This feature allows for quick insight into devices that need remediation.
ISSU support for Catalyst 9000 StackWise® Virtual switches in Cisco DNA Center

“Upgrade time reduced 59% from 177 minutes in the manual approach to 73 minutes with DNAC SWIM.”
Dustin Metteer
Lead network Engineer
Renown Health
![]()
Deploying AP-specific configurations on WLCs
In earlier Cisco DNA Center releases, network operators could not perform bulk operations on a group of access points APs, such as renaming APs after onboarding them or deploying N+1 configurations by specifying primary and secondary wireless controllers (WLCs). With this new feature, network operators are able to use a single, simplified workflow to perform bulk operations on a group of APs. Common AP-related network operations that are simplified by this workflow include AP renaming, changing the N+1 configuration by specifying primary and secondary WLCs, and changing radio channels and power levels. This feature improves wireless network robustness and lowers downtime.

Cisco IT DNA Center Example
Configuration drift visibility
Lack of visibility into configuration drift creates inefficiencies in the management of device configurations. Configuration drift visibility allows network operators to compare any two device configuration versions in a very visual manner. Having different versions of a device configuration available allows for accurate accountability of every configuration change.
Rogue rule creation
Network operators are looking for improved detection of sophisticated attacks that could exploit wireless devices and compromise security. The Cisco DNA Center threat dashboard now allows network operators to visualize detection of advanced attacks, providing enhanced context of the threat details in their environment. This feature improves overall network security.
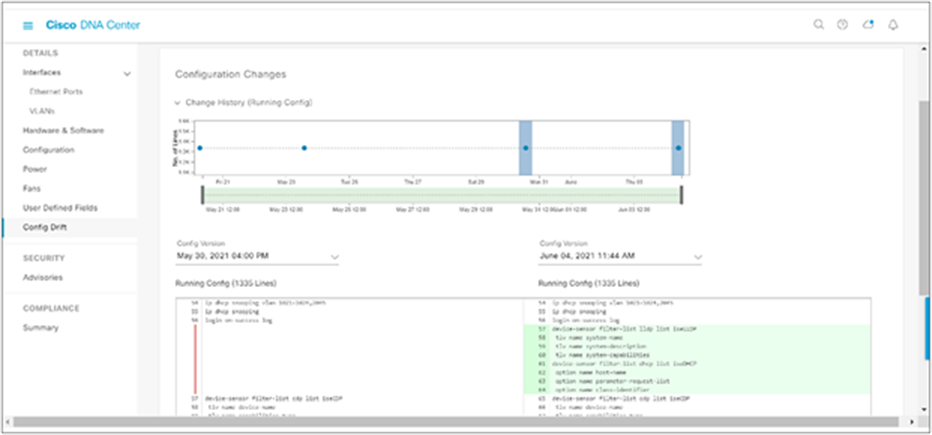
Configuration drift between two running configurations on a given device
Zero-trust workplace with Cisco SD-Access

“…AI Endpoint Analytics is now a centerpiece of our security strategy for the 58,000 medical devices we have in our system.”
Ed Vanderpool
Senior IT Manager
Adventist Health
![]()
Support for existing access VLANs
Integrating existing Layer 2 switching domains with SD-Access has been cumbersome for network operators. It required them to reconfigure VLANs in their infrastructure to match the fabric VLANs. This feature allows network operators to accommodate their existing Layer 2 design without having to change operational VLANs. It provides network operators with the flexibility to define the VLAN ID for their access networks so that the external switching domain can connect to the SD-Access edge node. Support for existing access VLANs reduces the time and expense to get started with SD-Access, thereby simplifying the customer journey toward zero trust.
Macro-segmentation without ISE
Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE) has been a mandatory component to implement SD-Access. This requirement is an impediment for enterprises that don't have endpoints connected to the fabric edge and therefore don't require authentication control. This feature allows network operators to undertake a phased approach to a zero-trust architecture, starting with deploying a fabric network at the core and distribution layers without Cisco ISE. This feature makes it easier for network operators to get started with SD-Access and migrate toward the gold standard (routed access and Cisco ISE as the AAA server) at their own pace and deployment schedule.
Assurance enhancements
A lack of granular fabric insights makes it challenging for network operators to identify and conduct RCA of issues in real time. For example, the absence of AAA and extended node and policy extended node (EN/PEN) reachability checks from fabric nodes makes troubleshooting complex and time consuming.
The enhancements introduce new KPIs and insights for faster issue identification and suggested actions. KPIs organized into categories present the ability to narrow down the issues quickly with a granular level of details. Also, the Client Health dashboard now includes Layer 2 and Layer 3 VN segmentation information for every endpoint connected to the fabric.
These features allow network operators to detect, diagnose, and troubleshoot fabric issues in real time with minimized downtime.
Network Health dashboard provides reachability information for the fabric control plane, external multicast Rendezvous Point (RP), AAA server reachability for fabric edge, and extended node.
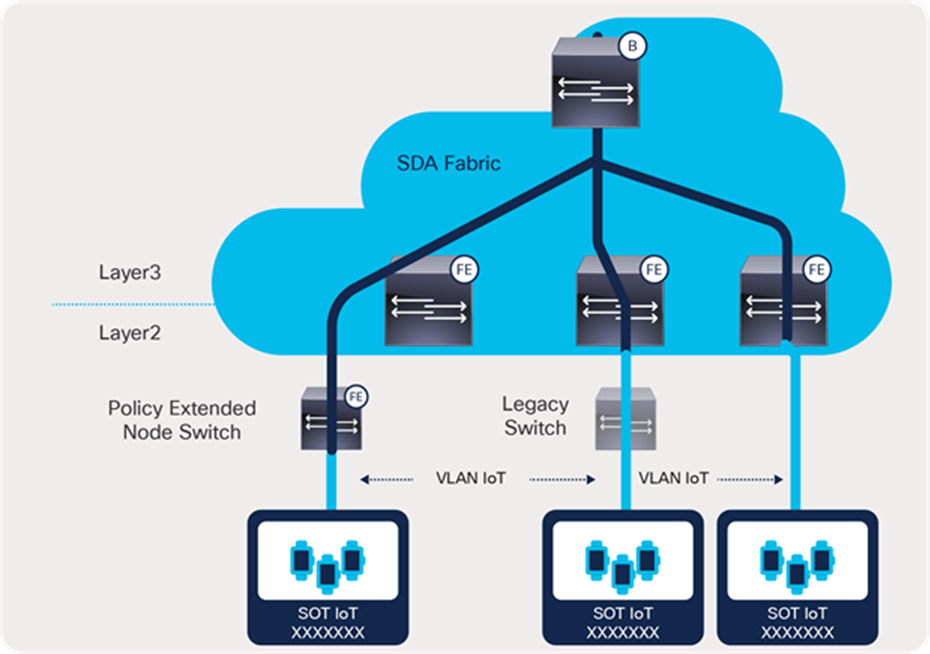
Support for existing access VLANs with SD-Access
Device 360 includes additional fabric information for the device, such as fabric role, fabric domain, and fabric site. New fabric KPIs are grouped under the Fabric Infrastructure, VN Service category to influence the device health.
Network Topology identifies fabric roles associated with a fabric node, such as border, control plane, edge, extended node, and wireless.
Client 360 includes Layer 3 and Layer 2 VN information for clients connected to the Cisco SD-Access environment.
Trust Analytics
It is challenging for enterprises to understand and detect when an endpoint is vulnerable, exhibits anomalous behavior, or is outside the boundaries of an organization’s compliance (posture) requirements. To address this need, enterprises have various products and processes in place that evaluate an endpoint. Aggregating the results from various sources is complex due to an overload of information that is difficult to digest and that offers conflicting insights. Trust Analytics is an aggregation of various inputs and sources into a single, comprehensive, flexible trust score. The feature expedites the detection and containment of untrustworthy endpoints that could lead to a security breach. Trust Analytics simplifies the network and security operator workload by aggregating and simplifying multiple inputs into a single score.
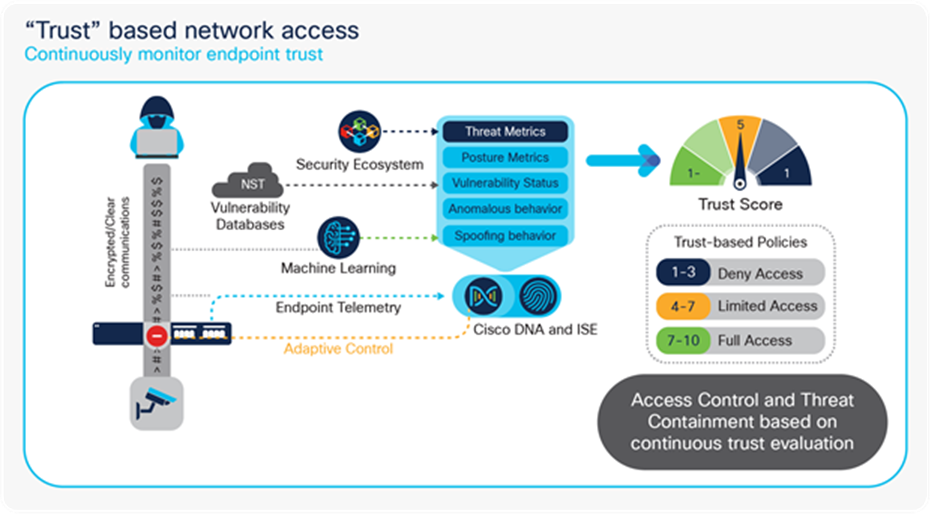
Trust Analytics
AI spoofing detection
Endpoints in the network using MAC and probe spoofing techniques had gone undetected due to a lack of proper detection methods. AI spoofing detection uses cloud-generated behavior models for certain types of endpoints. These models are trained using crowdsourced NetFlow data for known endpoint types functioning under normal operating conditions. When an unauthorized endpoint generates traffic that deviates from the machine learning model, an anomaly is triggered with a low, medium, or high probability of detection. This feature expedites the detection of MAC and probe spoofing techniques that could lead to the identification of security breach.
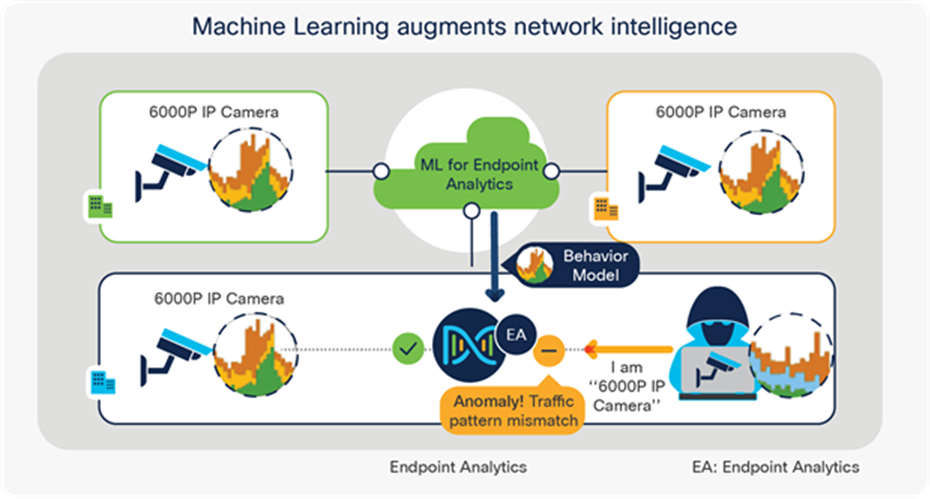
AI Spoofing Detection
Mitigation actions via ANC policy
Network and security operators need the ability to act on the endpoint insights that AI Endpoint Analytics and Trust Analytics provide. Mitigation action via Adaptive Network Control (ANC) policy (predefined in Cisco ISE) allows a network operator to apply a Cisco ISE ANC policy via Cisco DNA Center. This allows network operators to take actions on endpoints, such as blocking endpoint connections, bouncing ports, and reauthenticating endpoints. This feature expedites the containment of untrustworthy endpoints that could lead to a security breach.
AI Endpoint Analytics System Profiling Rule Update
With the rapid proliferation of IoT endpoints, network and security operators are unable to rapidly profile endpoints to mitigate security risk. The AI Endpoint Analytics System Profiling Rule Update keeps profiling rules up to date by applying updates from the cloud. This feature reduces the amount of time network operators spend creating custom profiling rules.
Per-policy enforcement stats
Previously, network operators had no way of telling how their policies were being enforced on the network. This blind spot mad it difficult for them to adjust their policies to the needs of the network. Per-policy enforcement statistics provide enforcement statistics based on policy permits and denies, giving network operators the information to adjust policy behavior over time and comply with audit requests. These statistics take the guesswork out of managing policies, drastically reducing the time it takes to troubleshoot and adjust policies.
Policy modification based on scalable group to scalable group activity
Network operators needed to navigate away from the Group-Based Policy Analytics tool to change a policy. This process was time consuming and tedious. Network operators can now create and modify a policy directly in the Group-Based Policy Analytics tool while viewing traffic flows between scalable groups. This feature drastically reduces the amount of time to create and modify polices.
Custom policy matrix views
In earlier releases, it was time consuming for network operators to navigate the Group-Based Policy Matrix when searching for certain source and destination scalable groups. This became more difficult as the matrix grew and the number of scalable groups expanded. The Custom Policy View feature makes it easy for network operators to quickly navigate and view the Group-Based Policy Matrix based on source and destination scalable groups.
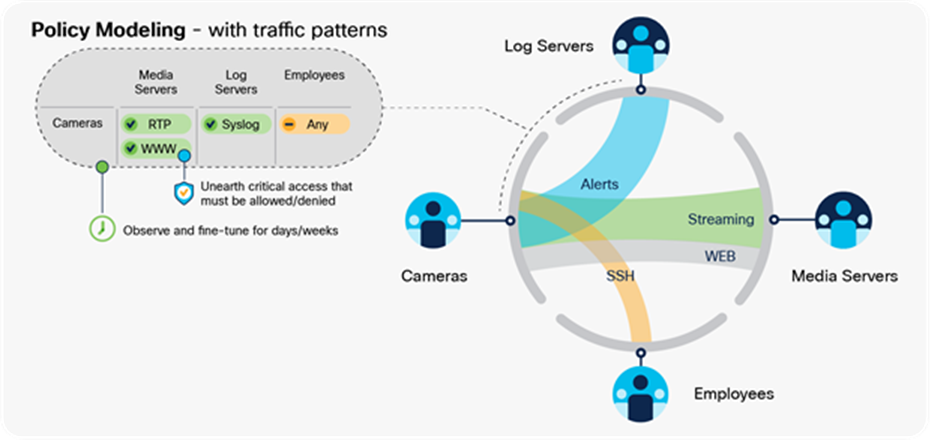
Policy modeling – with traffic patterns
Deployment ready with Cisco DNA Center Platform

“Cisco DNA with Cisco SD-Access, Cisco ACI, and the policy integration between them give us the end-to-end security and a platform we can grow on as we look to the future.”
Mike Everett
VP & Chief Security Officer
Farm Credit Mid-America

Smart Licensing Using Policy (SLP) license management for Smart License-enabled devices
Enterprises using new Cisco IOS XE versions that support SLP could not manage those device licenses with earlier Cisco DNA Center releases. With support for SLP, Cisco DNA Center now automates the workflows necessary to remain in compliance with Cisco licensing policy. Enterprises can more easily understand the license consumption of their network devices that support SLP and adhere to the policies prescribed by Cisco as appropriate.
1-1-1 Disaster Recovery with notifications support
In earlier releases, enterprises had to install Cisco DNA Center in a three-node cluster configuration before they could leverage the benefits of Disaster Recovery. This necessitated an expensive upfront purchase and ongoing costly operations. With the new deployment model, enterprises can now choose to deploy a Disaster Recovery configuration without needing to install a three-node high-availability configuration. By installing a Disaster Recovery infrastructure, enterprises can operate only three nodes, as opposed to seven nodes.
Heartbeat IPAM Network Services
Any large network relies on a robust IP Address Management (IPAM) solution to plan, deploy, monitor, and maintain IP addresses and associated components such as DNS. To monitor for IPAM failures, network operators needed to log in to Cisco DNA Center and monitor the status. With the new feature, Cisco DNA Center monitors the status of the IPAM server and sends an alert/notification via email, webhook, or other mechanism of choice if the IPAM server is offline. The monitoring also applies to third-party IPAM integrations, such as Infoblox and BlueCat. This feature enables faster issue detection and remediation.
2x increase in endpoint scale
Enterprises with large networks and many endpoints under management had to launch an entirely new Cisco DNA Center cluster. Installing a new controller required network operators to split and manage their endpoints separately, leading to operational burden. Support for a larger number of endpoints enables enterprises to provide the same level of service to their end customers (endpoints) at a lower cost per endpoint. This feature minimizes costly errors in governance and policy.
Table 1. Endpoint Scale Table
| Cisco DNA Center Release |
Pre 2.2.1.3 |
2.2.1.3 |
| Wireless endpoints (transient/unique over 14 days) |
250,000 |
500,000 |
| ISE (multi-Cisco DNA Center) |
100,000 |
200,000 |
| NetFlows |
120,000 per second |
250,000 per second |
| DCS endpoints |
100,000 |
200,000 |

Disaster Recovery
Uno for connected enterprise
A lack of context exchange across the various Cisco cloud services/solutions and Cisco DNA Center creates a disjointed and confusing user experience. Additionally, partners must build a point-to-point integration experience with every Cisco solution. Uno is a cloud connector that enables cloud services/solutions to exchange context, data, APIs, and events between cloud and on-premises solutions. This feature enhances the partner integration experience by providing a single integration point for the partner. It offers an enriched, context-driven product experience for users and accelerates faster time to market for partner integration solutions.
In-product ROI reports
Currently, Cisco DNA Center customers are unable to quantify the value of Cisco DNA Center. The value realized by enterprises for each Cisco DNA use case is not clear. The ROI report shows network operators their estimated savings based on product usage telemetry and productivity KPIs set by enterprises. Network operators can use the ROI insights to benchmark themselves against their peers and their historical savings.
Cost savings trend
Enhanced installation experience
Previously, the installation process was lengthy and complicated. Often, network operators were not aware of information they needed to configure the Cisco DNA Center appliance. The new feature brings two options to install a Cisco DNA Center appliance. Network operators can now use an Installer or Advanced Installer feature using a more intuitive web installer or a standard CLI method. The Installer is an abridged workflow to configure a single node, while the Advanced Installer can be used for a three-node cluster. Network operators can install, discover devices, and preview Assurance Health Insights quickly, with a more intuitive workflow to configure devices. This feature simplifies installation and discovery of devices and speeds response times based on Assurance Health Insights.
Inventory UI
To replace faulty line cards or supervisor cards, customers need access to the serial number and other details. This information is not readily available in Inventory. Also, to facilitate the planning or upgrade of network infrastructure, network operators need PoE consumption data, such as how much of the budgeted PoE is available per port and per device. In earlier releases, network operators couldn’t assign a custom name-value pair to a device. Cisco DNA Center now displays the serial number and model number of line cards and supervisor cards on the Inventory UI, along with PoE available per port and device, both as an absolute value and as a percentage. Network operators now have the option to assign up to 10 name-value pairs per device. This feature reduces device replacement time by providing the necessary device details on the UI itself. The additional details help in the planning of an infrastructure upgrade with PoE visibility when upgrading or replacing PoE devices on the network.
Topology
Network operators use a mix of Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) and Cisco Discovery Protocol link discovery to gather details about links between devices. Until now, Cisco DNA Center supported only the proprietary Cisco Discovery Protocol-based link discovery, resulting in incomplete link data and missing links between devices in the topology. In addition to Cisco Discovery Protocol, Cisco DNA Center now supports links running LLDP and helps build the complete network topology (devices and links). This feature reduces troubleshooting time and effort with the availability of a proper network topology showing how the devices and links are connected, regardless of the link discovery method.
Inventory Insights
When onboarding (day 0) a device or entire enterprise network, Cisco DNA Center collects operational data from network devices as part of the Inventory collection. At the time of data collection, Cisco DNA Center has access to configuration anomalies, in which the configuration or operation of a device deviates from Cisco’s recommended best practices.
With Inventory Insights, network operators can be notified about devices and interfaces that have either a speed-duplex or VLAN mismatch across the network. These insights can be viewed and exported per site so that corrective action can be taken. Each insight also provides remediation steps to address the issue.
This feature reduces downtime with visibility into nonstandard device configurations across the network on day 0.
Table 2. New Device support table
| Wireless |
IoT Router |
Switch |
Router |
| C9124AXI-x (UAP) C9124AXD-x (UAP) C9150AXI-EWC-B (EWC) |
IR8140H IR1821-K9 IR1831-K9 IR1833-K9 IR1835-K9 |
C9300X-12Y C9300X-24Y C9300X-NM-8Y C9300X-NM-2C C9300X-NM-8M |
C8200-1N-4T |
New device support
Without support for new platforms in Cisco DNA Center, enterprises would need to deploy other point solutions to manage their Cisco devices, leading to less-than-desired outcomes. By adding new platforms, Cisco DNA Center offers an effective solution for network management coverage for Cisco devices. This feature reduces integration costs and improves the reliability and visibility of network operations.
New APIs
For the corresponding workflows, network operators today must log in to Cisco DNA Center to get the necessary information and manually port the information to other systems of record and reporting. With new APIs, enterprises can plug these capabilities into their existing service orchestration or reporting tool as needed, thereby eliminating some manual overhead. Running Cisco DNA Center in headless mode allows enterprises to use the APIs to scale and automate various Cisco DNA Center functions, such as wireless configuration, license management, and device detail operations.
Disaster Recovery
● GET DR operational status and details.
Wireless
● Configure SSID with advanced parameters.
● Override PSK for existing SSID with support for bulk/singular operations.
● Manage dynamic interfaces.
● Enhanced API documentation for parameters and usage.
System
● Upload controller certificates (PEM, p12) for use by a third party.
● GET health performance indicators for the Cisco DNA Center appliance, including historical information.
License management
● GET license details for devices in the network, including the ability to manage virtual accounts, device registration/deregistration, and Smart Account information.
Device details
● GET PoE interface, stack, and chassis details for devices.
● GET Inventory Insights for devices connected with Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) v3, device link mismatch, line card, and supervisor card details.
Compliance
● Allow northbound applications to receive Cisco DNA Center compliance updates. Also, Cisco partners are now able to generate their own compliance reports through these APIs.
Security advisory
● Allow third-party security monitoring tools to receive device-related security advisories published by Cisco.
Platform configuration
● System version: GET installed Cisco DNA Center version, serial number, core packages, upgrade paths, node configuration, host IP, node names, …
● System health: GET Cisco DNA Center KPIs, such as CPU, memory, and disk utilization.
● Release Notes for Cisco DNA Center 2.2.2.0
● Device Support Compatibility Matrix on Cisco.com