Feedback Feedback
|
Table Of Contents
Cisco Unifed CallManager Express 3.x Integration Guide for Cisco Unity 4.0
Task List to Create the Integration
Task List to Make Changes to an Integration
Task List to Change the Number of Voice Messaging Ports
Task List to Delete an Existing Integration
Integrations with Multiple Phone Systems
Planning How the Voice Messaging Ports Will Be Used by Cisco Unity
Preparing for Programming the Phone System
Programming the Cisco Unified CallManager Express Phone System
Creating a New Integration with the Cisco Unified CallManager Express Phone System (SCCP)
Changing the Settings for an Existing Integration
Changing the Number of Voice Messaging Ports
Deleting an Existing Integration
Appendix: Using Alternate Extensions and MWIsSetting Up Alternate Extensions
Appendix: Documentation and Technical AssistanceCisco Product Security Overview
Reporting Security Problems in Cisco Products
Obtaining Technical Assistance
Cisco Technical Support & Documentation Website
Definitions of Service Request Severity
Obtaining Additional Publications and Information
Cisco Unifed CallManager Express 3.x Integration Guide for Cisco Unity 4.0
Revised March 6, 2006
This document provides instructions for integrating the Cisco Unified CallManager Express phone system with Cisco Unity.
Note
Cisco Unity failover is not available with the Cisco Unified CallManager Express integration.
AMIS Networking and call loop detection will not function when Cisco Unity is integrated Cisco Unified CallManager Express.
The G.729a codec is not supported.
Some versions of Cisco Unified CallManager Express are not supported. Refer to the Compatibility Matrix: Cisco Unity, the Cisco Unity-CM TSP, Cisco Unified CallManager, and Cisco Unified CallManager Express at http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/voice/c_unity/cmptblty/tspmtrx.htm.
Integration Tasks
Before doing the following tasks to integrate Cisco Unity with the Cisco Unified CallManager Express phone system, confirm that the Cisco Unity server is ready for the integration by completing the applicable tasks in the applicable Cisco Unity installation guide.
The following task lists describe the process for creating, changing, and deleting integrations.
Task List to Create the Integration
Use the following task list to set up a new integration with the Cisco Unified CallManager Express phone system. If you are installing a new Cisco Unity server by using the applicable Cisco Unity installation guide, you may have already completed some of the following tasks.
1.
Review the system and equipment requirements to confirm that all phone system and Cisco Unity server requirements have been met. See the "Requirements" section.
2.
Plan how the voice messaging ports will be used by Cisco Unity. See the "Planning How the Voice Messaging Ports Will Be Used by Cisco Unity" section.
3.
Program Cisco Unified CallManager Express. See the "Programming the Cisco Unified CallManager Express Phone System" section.
4.
Create the integration. See the "Creating a New Integration with the Cisco Unified CallManager Express Phone System (SCCP)" section.
5.
Test the integration. See the "Testing the Integration" section.
Task List to Make Changes to an Integration
Use the following task list to make changes to an integration after it has been created.
1.
Start the Cisco Unity Telephony Integration Manager (UTIM). See the "Changing the Settings for an Existing Integration" section.
2.
Make the changes you want to the existing integration. See the "Changing the Settings for an Existing Integration" section.
Task List to Change the Number of Voice Messaging Ports
Use the following task list to change the number of voice messaging ports for an integration after it has been created.
1.
Change the number of voice messaging ports. See the "Changing the Number of Voice Messaging Ports" section.
2.
Start the Cisco Unity Telephony Integration Manager (UTIM). See the "Changing the Settings for an Existing Integration" section.
3.
Configure the voice messaging ports for Cisco Unity. See the "Changing the Settings for an Existing Integration" section.
Task List to Delete an Existing Integration
Use the following task list to remove an existing integration.
1.
Start the Cisco Unity Telephony Integration Manager (UTIM). See the "Deleting an Existing Integration" section.
2.
Delete the existing integration. See the "Deleting an Existing Integration" section.
Requirements
The Cisco Unified CallManager Express integration supports configurations of the following components:
Phone System
•
For the supported versions of Cisco Unified CallManager Express, refer to the Compatibility Matrix: Cisco Unity, the Cisco Unity-CM TSP, Cisco Unified CallManager, and Cisco Unified CallManager Express at http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/voice/c_unity/cmptblty/tspmtrx.htm.
•
Cisco IOS software version 12.2(15)ZJ3 or later.
•
Cisco Unified CallManager Express feature license.
•
Cisco IP phone feature licenses, and Cisco licenses for other H.323-compliant devices or software (such as Cisco VirtualPhone and Microsoft NetMeeting clients) that will be connected to the network, as well as one license for each Cisco Unity port.
•
For a list of supported Cisco IP phone models, refer to the Specifications document for the applicable version of Cisco Unified CallManager Express at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/voicesw/ps4625/products_documentation_roadmap09186a0080189132.html.
•
Analog phones connected to ATA. (For integration limitations with these phones, see the "Integration Functionality" section.)
•
A LAN connection in each location where you will plug an IP phone into the network.
Cisco Unity Server
•
Cisco Unity installed and ready for the integration, as described in the applicable Cisco Unity installation guide at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/voicesw/ps2237/prod_installation_guides_list.html.
•
The applicable Cisco Unity-CM TSP, installed. For details on compatible versions of the TSP, refer to the Compatibility Matrix: Cisco Unity, the Cisco Unity-CM TSP, Cisco Unified CallManager, and Cisco Unified CallManager Express at http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/voice/c_unity/cmptblty/tspmtrx.htm.
•
A license that enables the appropriate number of voice messaging ports.
Integration Description
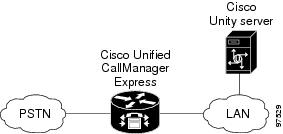
The Cisco Unified CallManager Express integration uses the LAN to connect Cisco Unity and the phone system. The Cisco Unified CallManager Express also provides connections to the PSTN. Figure 1 shows the connections for a system with a single Cisco Unified CallManager Express router.
Figure 1 Connections Between a Single Cisco Unified CallManager Express Router and Cisco Unity
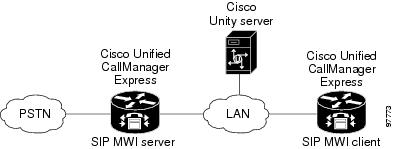
Figure 2 shows the connections for a system with multiple Cisco Unified CallManager Express routers and a single Cisco Unity server. One Cisco Unified CallManager Express router acts as the SIP MWI server, and the remaining Cisco Unified CallManager Express routers act as SIP MWI clients. Note that Cisco Unity voice messaging ports register with only the SIP MWI server (the Cisco Unified CallManager Express router that is on the same LAN as the Cisco Unity server), not with the SIP MWI clients.
Figure 2 Connections Between Multiple Cisco Unified CallManager Express Routers and a Single Cisco Unity Server
Call Information
The phone system sends the following information with forwarded calls:
•
The extension of the called party
•
The extension of the calling party (for internal calls) or the phone number of the calling party (if it is an external call and the system uses caller ID)
•
The reason for the forward (the extension is busy, does not answer, or is set to forward all calls)
Cisco Unity uses this information to answer the call appropriately. For example, a call forwarded to Cisco Unity is answered with the personal greeting of the subscriber. If the phone system routes the call to Cisco Unity without this information, Cisco Unity answers with the opening greeting.
When forwarding calls to greetings, Cisco Unity uses the original redirected number, not the last redirected number. For example, when A calls B and forwards the call to C whose phone forwards to voice mail, the call will go to the voice mailbox for B.
Integration Functionality
The Cisco Unified CallManager Express integration with Cisco Unity provides the following integration features:
•
Call forward to personal greeting
•
Call forward to busy greeting
•
Caller ID
•
Easy message access (a subscriber can retrieve messages without entering an ID because Cisco Unity identifies the subscriber based on the extension from which the call originated; a password may be required)
•
Identified subscriber messaging (Cisco Unity identifies the subscriber who leaves a message during a forwarded internal call, based on the extension from which the call originated)
•
Message waiting indication (MWI)
These integration features are not available to analog phones connected through FXS ports on the Cisco Unified CallManager Express phone system. Analog phones connected to ATA, however, support all integration features, except MWIs (MWI lamps will not light, though the stutter dial tone will sound).
Integrations with Multiple Phone Systems
Depending on the version, Cisco Unity can be integrated with two or more phone systems:
•
Cisco Unity 4.0 and 4.1 can be integrated with a maximum of two phone systems at one time. For information on and instructions for integrating Cisco Unity with two phone systems, refer to the Dual Phone System Integration Guide at http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/voice/c_unity/integuid/multi/itmultin.htm.
•
Cisco Unity 4.2 and later can be integrated with two or more phone systems at one time. For information on the maximum supported combinations and instructions for integrating Cisco Unity with multiple phone systems, refer to the Multiple Phone System Integration Guide at http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/voice/c_unity/integuid/multi/multcu42.htm.
Planning How the Voice Messaging Ports Will Be Used by Cisco Unity
Before programming the phone system, you need to plan how the voice messaging ports will be used by Cisco Unity. The following considerations will affect the programming for the phone system (for example, setting up the hunt group or call forwarding for the voice messaging ports):
•
The number of voice messaging ports installed.
•
The number of voice messaging ports that will answer calls.
•
The number of voice messaging ports that will only dial out, for example, to send message notification, to set message waiting indicators (MWIs), to make AMIS deliveries, and to make telephone record and playback (TRAP) connections.
Table 1 describes the voice messaging port settings in Cisco Unity that can be set in UTIM, and that are displayed as read-only text on the System > Ports page of the Cisco Unity Administrator.
The Number of Voice Messaging Ports to Install
The number of voice messaging ports to install depends on numerous factors, including:
•
The number of calls Cisco Unity will answer when call traffic is at its peak.
•
The expected length of each message that callers will record and that subscribers will listen to.
•
The number of subscribers.
•
The number of ports that will be set to dial out only.
•
The number of calls made for message notification.
•
The number of MWIs that will be activated when call traffic is at its peak.
•
The number of AMIS delivery calls.
•
The number of TRAP connections needed when call traffic is at its peak. (TRAP connections are used by Cisco Unity web applications and e-mail clients to play back and record over the phone.)
•
The number of calls that will use the automated attendant and call handlers when call traffic is at its peak.
It is best to install only the number of voice messaging ports that are needed so that system resources are not allocated to unused ports.
The Number of Voice Messaging Ports That Will Answer Calls
The calls that the voice messaging ports answer can be incoming calls from unidentified callers or from subscribers. Typically, the voice messaging ports that answer calls are the busiest.
You can set voice messaging ports to both answer calls and to dial out (for example, to send message notifications). However, when the voice messaging ports perform more than one function and are very active (for example, answering many calls), the other functions may be delayed until the voice messaging port is free (for example, message notifications cannot be sent until there are fewer calls to answer). For best performance, dedicate certain voice messaging ports for only answering incoming calls, and dedicate other ports for only dialing out. Separating these port functions eliminates the possibility of a collision, in which an incoming call arrives on a port at the same time that Cisco Unity takes the port off-hook to dial out.
The Number of Voice Messaging Ports That Will Only Dial Out, and Not Answer Calls
Ports that will only dial out and will not answer calls can do one or more of the following:
•
Notify subscribers by phone, pager, or e-mail of messages that have arrived.
•
Turn MWIs on and off for subscriber extensions.
•
Make outbound AMIS calls to deliver voice messages from Cisco Unity subscribers to users on another voice messaging system. (This action is available only with the AMIS licensed feature.)
•
Make a TRAP connection so that subscribers can use the phone as a recording and playback device in Cisco Unity web applications and e-mail clients.
Typically, these voice messaging ports are the least busy ports.
CautionIn programming the phone system, do not send calls to voice messaging ports in Cisco Unity that cannot answer calls (voice messaging ports that are not set to Answer Calls). For example, if a voice messaging port is set only to Dialout MWI, do not send calls to it.
Preparing for Programming the Phone System
Record your decisions about the voice messaging ports to guide you in programming the phone system.
Programming the Cisco Unified CallManager Express Phone System
After the Cisco Unified CallManager Express router is installed, do the procedures in the applicable section depending on the number of Cisco Unified CallManager Express routers you will integrate with the Cisco Unity server:
•
Single Cisco Unified CallManager Express router—see the "Programming a Single Cisco Unified CallManager Express Router to Integrate with a Single Cisco Unity Server" section
•
Multiple Cisco Unified CallManager Express routers—see the "Programming Multiple Cisco Unified CallManager Express Routers to Integrate with a Single Cisco Unity Server" section
Programming a Single Cisco Unified CallManager Express Router to Integrate with a Single Cisco Unity Server
Note
Do the procedures in this section only if you are integrating a single Cisco Unified CallManager Express router with a single Cisco Unity server. If you are integrating multiple Cisco Unified CallManager Express routers, see the "Programming Multiple Cisco Unified CallManager Express Routers to Integrate with a Single Cisco Unity Server" section.
To Configure the Message Button Access to Cisco Unity
This procedure configures the Message button on Cisco IP phones to dial the Cisco Unity pilot number when pressed.
Step 1
On the Cisco Unified CallManager Express router, go into the telephony-service configuration mode by entering the following command:
telephony-service
Step 2
Enter the following command:
voicemail <Cisco Unity pilot number>
Step 3
To exit the telephony-service configuration mode, enter the following command:
exit
The following is an example of the configuration:
telephony-servicevoicemail 4001To Configure the Router for Cisco Unity
Step 1
Go into the ephone-dn configuration mode and configure the directory number tag for the Cisco IP phone lines by entering the following command:
ephone-dn <DN tag>
Step 2
To set the extension number for the voice messaging port, enter the following command:
number <Voice messaging port extension>
Note
The voice message port extension must be the Cisco Unity pilot number (configured by the "voicemail" command in the preceding procedure) for all ports dedicated for leaving and retrieving voice messages. Use an extension that cannot be dialed for all ports that are used to set MWIs by Cisco Unity (for example, use "A01").
Step 3
To set the user name for the port (for example, "Voice Port 1" or "MWI Only"), enter the following command:
name <User name of voice messaging port>
Step 4
To disable huntstop, enter the following command:
no huntstop
Step 5
To set the dial-peer preference for the extension, enter the following command:
preference <Preference order>
Step 6
Repeat Step 1 through Step 5 for all remaining ports.
Note
The number of voice messaging ports set up to connect to Cisco Unity must be the same as the number of directory number tags for the Cisco IP phone lines set up by the ephone-dn configuration mode.
Step 7
To exit the ephone-dn configuration mode, enter the following command:
exit
The following is an example of the configuration:
ephone-dn 32number 4001name "Voice Messaging Port 1"no huntstop!ephone-dn 33number 4001name "Voice Messaging Port 2"no huntstoppreference 1!ephone-dn 34number 4001name "Voice Messaging Port 3"no huntstoppreference 2!ephone-dn 35number A01name "MWI Only"In this example, there are four ephone-dns configured to provide four voice messaging ports. Three of the ephone-dns are configured with the same extension number to provide ports dedicated for leaving and retrieving voice messages. The fourth ephone-dn is provided for use as an MWI-only port. The first three ephone-dns are configured with the same extension number (4001), using preferences 0, 1, and 2 to create a hunt group. If the first port is busy, the call goes to the second port, and so on. Port 4 is configured with the extension number A01 and is used to set MWIs by Cisco Unity. Separate ports are required for answering calls and setting MWIs in order to prevent call-collision problems between incoming calls placed by Cisco Unified CallManager Express to Cisco Unity, and MWI calls that Cisco Unity places in the opposite direction.
To Associate the Voice Messaging Port Device
To associate the actual voice messaging port device (vm-device-id) to the phone number, associate the Cisco IP phone with the voice messaging port device.
The vm-device-id name uses the following format:
<Cisco Unity device name prefix><Port number>
The default vm-device-id name is CiscoUM-VI1. The vm-device-id name must match the Cisco Unity voice messaging port name you will use to identify the port in the Cisco Unity Telephony Integration Manager (UTIM) when you create the integration:
•
The Cisco Unity device name prefix part (for example, CiscoUM-VI) must match the Device Name Prefix field in UTIM.
•
The port number part (for example, "1") must match the number part of the Cisco Unity voice messaging port name used to identify the port in UTIM.
To associate a voice mail device to the Cisco Unified CallManager Express router, do the following steps, beginning in ephone configuration mode.
Step 1
Go into the ephone configuration mode and register the Cisco IP phones by entering the following command:
ephone <DN tag>
Step 2
Define the voice messaging port device name, by entering the following command:
vm-device-id <Cisco Unity device name prefix><Port number>
For example, if the Cisco Unity device name prefix is CiscoUM-VI, enter CiscoUM-VI1 for the first port and CiscoUM-VI2 for the second port, and so on.
Note
The vm-device-id name used by Cisco Unified CallManager Express must be the same as the voice messaging port name used by Cisco Unity. Otherwise, the integration will not work.
Step 3
Assign buttons to the Cisco IP phone directory numbers created in the "To Configure the Router for Cisco Unity" procedure by entering the following command:
button <Button number>:<DN tag>
For example, you can use the values 1:1, 2:4, or 3:14. In this example, button 1 corresponds to directory number 1 (ephone-dn 1), button 2 corresponds to directory number 4, and button 3 corresponds to directory number 14. The buttons correspond to the phone lines on the Cisco IP phone.
Step 4
Repeat Step 1 through Step 3 for all remaining voice messaging port device names.
Note
The number of voice messaging port device names configured with the vm-device-id command must be the same as the number of Cisco IP phones registered by the ephone configuration mode.
Step 5
To exit the ephone configuration mode, enter the following command:
exit
Following is an example of the configuration. In this example, the vm-device-id command is used within the ephone configuration in place of the mac-address parameter that is used for configuring a regular Cisco IP phone.
ephone 5vm-device-id CiscoUM-VI1button 1:32!ephone 6vm-device-id CiscoUM-VI2button 1:33!ephone 7vm-device-id CiscoUM-VI3button 1:34!ephone 8vm-device-id CiscoUM-VI4button 1:35To Configure a Directory Number for MWI Notification
MWI configuration on the Cisco Unified CallManager Express is performed by dedicating Cisco IP phone directory numbers (ephone-DNs) to process MWI status notification calls originating from Cisco Unity. You must allocate a minimum of one MWI processing ephone-dn for each MWI ephone-dn voice messaging port. The MWI processing ephone-dn extensions are configured to match the MWI extensions configured on Cisco Unity.
Step 1
Go into the ephone-dn configuration mode and configure the directory numbers for the Cisco IP phone lines by entering the following command:
ephone-dn <DN tag>
Step 2
Configure two valid directory numbers for the Cisco IP phone to be used for MWIs—the first number will turn MWIs on, and the second number will turn MWIs off—by entering the following command:
number <MWI on number> secondary <MWI off number>
Note
The MWI on and off numbers must match the settings of the MWI On Extension and MWI Off Extension fields you enter in UTIM when you create the integration.
Step 3
Configure these two directory numbers to be used for setting MWIs by entering the following command:
mwi on-off
Step 4
To exit the ephone-dn configuration mode, enter the following command:
exit
Following is an example of the configuration.
ephone-dn 32number 8000 secondary 8001mwi on-offIn this example, Cisco Unity calls extensions 8000 and 8001 to turn MWIs on and off. The DN triggers an MWI ON event when 8000 is called, and an MWI OFF event when 8001 is called.
For extensions associated with analog telephone adaptors (ATAs), the MWI is a lit function button on the ATA and a stutter dial tone on the connected analog phone.
Note
After completing the procedures in this section, continue with the "Creating a New Integration with the Cisco Unified CallManager Express Phone System (SCCP)" section.
Programming Multiple Cisco Unified CallManager Express Routers to Integrate with a Single Cisco Unity Server
A single, centralized Cisco Unity server can be used by multiple Cisco Unified CallManager Express routers. This configuration requires that one Cisco Unified CallManager Express router be on the same LAN as the Cisco Unity server, and that this Cisco Unified CallManager Express router register all Cisco Unity voice messaging ports. This Cisco Unified CallManager Express router (the SIP MWI server) is a proxy server that relays SIP MWI messages between the Cisco Unity and all other Cisco Unified CallManager Express routers (the SIP MWI clients). Note that Cisco Unity voice messaging ports register with only the SIP MWI server (the Cisco Unified CallManager Express router that is on the same LAN as the Cisco Unity server), not with the SIP MWI clients.
Do the procedures in this section only if you are integrating multiple Cisco Unified CallManager Express routers with a single Cisco Unity server.
To Configure the Message Button Access to Cisco Unity
Step 1
On the Cisco Unified CallManager Express router, go into the telephony-service configuration mode by entering the following command:
telephony-service
Step 2
Enter the following command:
voicemail <Cisco Unity pilot number>
Step 3
To exit the telephony-service configuration mode, enter the following command:
exit
The following is an example of the configuration:
telephony-servicevoicemail 4001To Configure the Router for Cisco Unity
Step 1
Go into the ephone-dn configuration mode and configure the directory number tag for the Cisco IP phone lines by entering the following command:
ephone-dn <DN tag>
Step 2
To set the extension number for the voice messaging port, enter the following command:
number <Voice messaging port extension>
Note
The voice message port extension must be the Cisco Unity pilot number (configured by the "voicemail" command in the preceding procedure) for all ports dedicated for leaving and retrieving voice messages. Use an extension that cannot be dialed for all ports that are used to set MWIs by Cisco Unity (for example, use "A01").
Step 3
To set the user name for the port (for example, "Voice Port 1" or "MWI Only"), enter the following command:
name <User name of voice messaging port>
Step 4
To disable huntstop, enter the following command:
no huntstop
Step 5
To set the dial-peer preference for the extension, enter the following command:
preference <Preference order>
Step 6
Repeat Step 1 through Step 5 for all remaining ports.
Note
The number of voice messaging ports set up to connect to Cisco Unity must be the same as the number of directory number tags for the Cisco IP phone lines set up by the ephone-dn configuration mode.
Step 7
To exit the ephone-dn configuration mode, enter the following command:
exit
The following is an example of the configuration:
ephone-dn 32number 4001name "Voice Messaging Port 1"no huntstop!ephone-dn 33number 4001name "Voice Messaging Port 2"no huntstoppreference 1!ephone-dn 34number 4001name "Voice Messaging Port 3"no huntstoppreference 2!ephone-dn 35number A01name "MWI Only"In this example, there are four ephone-dns configured to provide four voice messaging ports. Three of the ephone-dns are configured with the same extension number to provide ports dedicated for leaving and retrieving voice messages. The fourth ephone-dn is provided for use as an MWI-only port. The first three ephone-dns are configured with the same extension number (4001), using preferences 0, 1, and 2 to create a hunt group. If the first port is busy, the call goes to the second port, and so on. Port 4 is configured with the extension number A01 and is used to set MWIs by Cisco Unity. Separate ports are required for answering calls and setting MWIs in order to prevent call-collision problems between incoming calls placed by Cisco Unified CallManager Express to Cisco Unity, and MWI calls that Cisco Unity places in the opposite direction.
To Associate the Voice Messaging Port Device
To associate the actual voice messaging port device (vm-device-id) to the phone number, associate the Cisco IP phone with the voice messaging port device.
The vm-device-id name uses the following format:
<Cisco Unity device name prefix><Port number>
The default vm-device-id name is CiscoUM-VI1. The vm-device-id name must match the Cisco Unity voice messaging port name you will use to identify the port in the Cisco Unity Telephony Integration Manager (UTIM) when you create the integration:
•
The Cisco Unity device name prefix part (for example, CiscoUM-VI) must match the Device Name Prefix field in UTIM.
•
The port number part (for example, "1") must match the number part of the Cisco Unity voice messaging port name used to identify the port in UTIM.
To associate a voice mail device with the Cisco Unified CallManager Express router, do the following steps, beginning in ephone configuration mode.
Step 1
Go into the ephone configuration mode and register the Cisco IP phones by entering the following command:
ephone <DN tag>
Step 2
Define the voice messaging port device name, by entering the following command:
vm-device-id <Cisco Unity device name prefix><Port number>
For example, if the Cisco Unity device name prefix is CiscoUM-VI, enter CiscoUM-VI1 for the first port and CiscoUM-VI2 for the second port, and so on.
Note
The vm-device-id name used by Cisco Unified CallManager Express must be the same as the voice messaging port name used by Cisco Unity. Otherwise, the integration will not work.
Step 3
Assign buttons to the Cisco IP phone directory numbers created in the "To Configure the Router for Cisco Unity" procedure by entering the following command:
button <Button number>:<DN tag>
For example, you can use the values 1:1, 2:4, or 3:14. In this example, button 1 corresponds to directory number 1 (ephone-dn 1), button 2 corresponds to directory number 4, and button 3 corresponds to directory number 14. The buttons correspond to the phone lines on the Cisco IP phone.
Step 4
Repeat Step 1 through Step 3 for all remaining voice messaging port device names.
Note
The number of voice messaging port device names configured with the vm-device-id command must be the same as the number of Cisco IP phones registered by the ephone configuration mode.
Step 5
To exit the ephone configuration mode, enter the following command:
exit
Following is an example of the configuration. In this example, the vm-device-id command is used within the ephone configuration in place of the mac-address parameter that is used for configuring a regular Cisco IP phone.
ephone 5vm-device-id CiscoUM-VI1button 1:32!ephone 6vm-device-id CiscoUM-VI2button 1:33!ephone 7vm-device-id CiscoUM-VI3button 1:34!ephone 8vm-device-id CiscoUM-VI4button 1:35If you are integrating with Cisco Unified CallManager Express 3.3 or later, skip to the "To Configure the SIP MWI Server for Cisco Unified CallManager Express 3.3 and Later" procedure.
If you are integrating with Cisco Unified CallManager Express 3.2 or earlier, do the following procedure.
To Configure the SIP MWI Server for Cisco Unified CallManager Express 3.2 and Earlier
Step 1
Go into the telephony-service configuration mode by entering the following command:
telephony-service
Step 2
Configure the IP address and port for the SIP MWI server by entering the following command:
mwi sip-server <MWI server IP address>
[[transport tcp | transport udp] | [port <Port number>] | [reg-e164] [unsolicited]]The SIP MWI server must be in the same LAN as Cisco Unity. This IP address is used in conjunction with the "mwi sip" command in ephone-dn configuration mode to subscribe individual ephone-dn extension numbers to the MWI server notification list. The SIP MWI client runs TCP by default.
This command uses the following keywords:
•
transport tcp—The default setting.
•
transport udp—Allows you to integrate with the SIP MWI client.
•
port—Used to specify the TCP port for the SIP MWI server. The default SIP port number is 5060.
•
reg-e164—The default registration is with an extension number, so the "reg-e164" keyword allows you to register with an E.164 10-digit number.
•
unsolicited—Allows sending SIP NOTIFY for MWIs without the need to send a SUBSCRIBE from the Cisco Unified CallManager Express router.
Step 3
To exit the telephony-service configuration mode, enter the following command:
exit
Step 4
Skip to the "To Configure MWIs for Each Directory Number" procedure.
If you are integrating with Cisco Unified CallManager Express 3.2 or earlier, skip to the "To Configure MWIs for Each Directory Number" procedure.
If you are integrating with Cisco Unified CallManager Express 3.3 or later, do the following procedure.
To Configure the SIP MWI Server for Cisco Unified CallManager Express 3.3 and Later
Step 1
Go into the SIP user-agent configuration mode by entering the following command:
sip-ua
Step 2
Configure the IP address (or DNS name) and port for the SIP MWI server by entering the following command:
mwi-server {ipv4:<MWI server IP address> | dns:<MWI server host-name} [expires <Seconds>]
[port <Port number>] [transport {tcp | udp}] [unsolicited]The SIP MWI server must be in the same LAN as Cisco Unity. This IP address is used in conjunction with the "mwi sip" command in ephone-dn configuration mode to subscribe individual ephone-dn extension numbers to the MWI server notification list. The SIP MWI client runs TCP by default.
This command uses the following keywords:
•
ipv4:—Sets the IP address of the SIP MWI server.
•
dns:—Sets the DNS name of the SIP MWI server.
•
expires—(optional) Subscription expiration time, in seconds. The range is 1 to 999999. The default is 3600.
•
transport tcp—The default setting.
•
transport udp—Allows you to integrate with the SIP MWI client.
•
port—Used to specify the TCP port for the SIP MWI server. The default SIP port number is 5060.
•
unsolicited—Allows sending SIP NOTIFY for MWIs without the need to send a SUBSCRIBE from the Cisco Unified CallManager Express router.
Step 3
To exit the SIP user-agent configuration mode, enter the following command:
exit
Step 4
Go into the telephony-service configuration mode by entering the following command:
telephony-service
Step 5
If you want to keep the default registration with an extension number, continue to Step 6. If you want to register with an E.164 10-digit number, enter the following command:
mwi reg-e164
Step 6
To exit the telephony-service configuration mode, enter the following command:
exit
Step 7
Continue to the next procedure.
To Configure MWIs for Each Directory Number
Step 1
Go into the ephone-dn configuration mode and configure the directory numbers for the Cisco IP phone lines by entering the following command:
ephone-dn <DN tag>
Step 2
Configure a valid directory number for the Cisco IP phone that receives the MWI notification by entering the following command:
number <Directory number>
Step 3
Configure the user name of MWI for the directory number that receives MWI notification by entering the following command:
name MWI
Step 4
Subscribe the extension in a Cisco Unified CallManager Express to receive MWIs from a SIP MWI server by entering the following command:
mwi sip
This command integrates the Cisco Unified CallManager Express with the MWI service based on SIP protocol.
Note
The "mwi sip-server" command under telephony-service configuration mode or the "mwi-server" command under SIP user-agent configuration mode must be set before enabling the "mwi sip" command in ephone configuration mode.
Step 5
To exit the ephone-dn configuration mode, enter the following command:
exit
To Configure a Directory Number for MWI Notification
MWI configuration on the Cisco Unified CallManager Express is performed by dedicating Cisco IP phone directory numbers (ephone-DNs) to process MWI status notification calls originating from Cisco Unity. You must allocate a minimum of one MWI processing ephone-dn for each MWI ephone-dn voice messaging port. The MWI processing ephone-dn extensions are configured to match the MWI extensions configured on Cisco Unity.
Step 1
Go into the ephone-dn configuration mode and configure the directory numbers for the Cisco IP phone lines by entering the following command:
ephone-dn <DN tag>
Step 2
Configure two valid directory numbers for the Cisco IP phone to be used for MWIs—the first number will turn MWIs on, and the second number will turn MWIs off—by entering the following command:
number <MWI on number> secondary <MWI off number>
Note
The MWI on and off numbers must match the settings of the MWI On Extension and MWI Off Extension fields you enter in UTIM when you create the integration on Cisco Unity.
Step 3
Configure these two directory numbers to be used for setting MWIs by entering the following command:
mwi on-off
Step 4
To exit the ephone-dn configuration mode, enter the following command:
exit
Following is an example of the configuration.
ephone-dn 32number 8000 secondary 8001mwi on-offIn this example, Cisco Unity calls extensions 8000 and 8001 to turn MWIs on and off. The DN triggers an MWI ON event when 8000 is called, and an MWI OFF event when 8001 is called.
If you are integrating with Cisco Unified CallManager Express 3.3 or later, skip to the "To Configure MWI Relay for Cisco Unified CallManager Express 3.3 and Later" procedure.
If you are integrating with Cisco Unified CallManager Express 3.2 or earlier, do the following procedure.
To Configure MWI Relay for Cisco Unified CallManager Express 3.2 and Earlier
MWI relay is required when Cisco Unity is integrated with multiple Cisco Unified CallManager Express routers. The Cisco Unified CallManager Express routers use the SIP subscriber and notifier mechanism for MWI relay. The Cisco Unified CallManager Express router that is the SIP MWI relay server acts as the SIP notifier. The other Cisco Unified CallManager Express routers (the SIP MWI clients) act as the SIP subscribers.
Step 1
Go into the telephony-service configuration mode by entering the following command:
telephony-service
Step 2
Enable the Cisco Unified CallManager Express router to relay MWI information to Cisco IP phones on other Cisco Unified CallManager Express routers by entering the following command:
mwi relay
Step 3
Set the expiration time, in seconds, for registration for either the client or the server by entering the following command:
mwi expires <Seconds>
The range for the number of seconds is from 600 to 99999. The default is 86400 (24 hours).
Step 4
Configure the IP address and port for a SIP MWI server by entering the following command:
mwi sip-server <SIP MWI server IP address>
[[transport tcp | transport udp] | [port <Port number>] | [reg-e164] [unsolicited]]The SIP MWI server must be in the same LAN as Cisco Unity. This IP address is used in conjunction with the "mwi sip" command in the ephone-dn configuration mode to subscribe individual extension numbers to the SIP MWI server notification list. The SIP MWI client runs TCP by default.
This command uses the following keywords:
•
transport tcp—The default setting.
•
transport udp—Allows you to integrate with the SIP MWI client.
•
port—Used to specify the TCP port for the SIP MWI server. The default SIP port number is 5060.
•
reg-e164—The default registration is with an extension number, so the "reg-e164" keyword allows you to register with an E.164 10-digit number.
•
unsolicited—Allows sending SIP NOTIFY for MWIs without the need to send a SUBSCRIBE from the Cisco Unified CallManager Express router.
Step 5
To exit the telephony-service configuration mode, enter the following command:
exit
Step 6
Skip to the "To Enable DTMF Relay" procedure.
If you are integrating with Cisco Unified CallManager Express 3.2 or earlier, skip to the "To Enable DTMF Relay" procedure.
If you are integrating with Cisco Unified CallManager Express 3.3 or later, do the following procedure.
To Configure MWI Relay for Cisco Unified CallManager Express 3.3 and Later
MWI relay is required when Cisco Unity is integrated with multiple Cisco Unified CallManager Express routers. The Cisco Unified CallManager Express routers use the SIP subscriber and notifier mechanism for MWI relay. The Cisco Unified CallManager Express router that is the SIP MWI relay server acts as the SIP notifier. The other Cisco Unified CallManager Express routers (the SIP MWI clients) act as the SIP subscribers.
Step 1
Go into the telephony-service configuration mode by entering the following command:
telephony-service
Step 2
Enable the Cisco Unified CallManager Express router to relay MWI information to Cisco IP phones on other Cisco Unified CallManager Express routers by entering the following command:
mwi relay
Step 3
To exit the telephony-service configuration mode, enter the following command:
exit
Step 4
Go into the SIP user-agent configuration mode by entering the following command:
sip-ua
Step 5
Configure the IP address (or DNS name) and port for the SIP MWI server by entering the following command:
mwi-server {ipv4:<MWI server IP address> | dns:<MWI server host-name} [expires <Seconds>]
[port <Port number>] [transport {tcp | udp}] [unsolicited]The SIP MWI server must be in the same LAN as Cisco Unity. This IP address is used in conjunction with the "mwi sip" command in ephone-dn configuration mode to subscribe individual ephone-dn extension numbers to the MWI server notification list. The SIP MWI client runs TCP by default.
This command uses the following keywords:
•
ipv4:—Sets the IP address of the SIP MWI server.
•
dns:—Sets the DNS name of the SIP MWI server.
•
expires—(optional) Subscription expiration time, in seconds. The range is 1 to 999999. The default is 3600.
•
transport tcp—The default setting.
•
transport udp—Allows you to integrate with the SIP MWI client.
•
port—Used to specify the TCP port for the SIP MWI server. The default SIP port number is 5060.
•
unsolicited—Allows sending SIP NOTIFY for MWIs without the need to send a SUBSCRIBE from the Cisco Unified CallManager Express router.
Step 6
To exit the SIP user-agent configuration mode, enter the following command:
exit
Step 7
Go into the telephony-service configuration mode by entering the following command:
telephony-service
Step 8
If you want to keep the default registration with an extension number, continue to Step 9. If you want to register with an E.164 10-digit number, enter the following command:
mwi reg-e164
Step 9
To exit the telephony-service configuration mode, enter the following command:
exit
Step 10
Continue to the next procedure.
To Enable DTMF Relay
In certain situations, DTMF digits are not recognized when processed through VoIP dial-peer gateways. To avoid this problem, certain gateways must be configured to enable DTMF relay. The DTMF relay feature is available in Cisco IOS software version 12.0(5) and later.
Cisco IOS software-based gateways that use H.245 out-of-band signaling (but not the Cisco Unified CallManager Express routers with which Cisco Unity is integrated) must be configured to enable DTMF relay.
The Catalyst 6000 T1/PRI and FXS gateways enable DTMF relay by default and do not need additional configuration to enable this feature.
Step 1
On a VoIP dial-peer that points to a Cisco Unified CallManager Express router integrated with Cisco Unity (the dial-peer must have a session target of the Cisco Unified CallManager Express server, not Cisco Unity), enter the following command:
dtmf-relay h245-signal
Step 2
Create a destination pattern that matches the Cisco Unified CallManager Express voice mail port numbers. For example, if the system has voice mail ports 1001 through 1016, enter the dial-peer destination pattern 10xx.
Step 3
Repeat Step 1 and Step 2 for all remaining VoIP dial-peers that point to Cisco Unified CallManager Express routers integrated with Cisco Unity.
Creating a New Integration with the Cisco Unified CallManager Express Phone System (SCCP)
After ensuring that the Cisco Unified CallManager Express phone system and the Cisco Unity server are ready for the integration, do the following procedures to set up the integration and to enter the port settings.
To Create an Integration
Step 1
If UTIM is not already open, on the Windows Start menu of the Cisco Unity server, click Programs > Cisco Unity > Manage Integrations. UTIM appears.
Step 2
In the left pane of the UTIM window, click Cisco Unity Server.
Step 3
On the Integration menu of the UTIM window, click New. The Telephony Integration Setup Wizard appears.
Step 4
On the Welcome page, click the applicable phone system type, depending on your version of Cisco Unity:
•
Cisco Unity 4.2 or later—SCCP (Cisco Unified CallManager and Cisco Unified CallManager Express only)
•
Cisco Unity 4.0 or 4.1—Cisco CallManager
Step 5
Click Next.
Step 6
On the Name Cisco Unified CallManager Integration and Cluster page, enter the following settings, then click Next.
Step 7
On the Enter Cisco Unified CallManager IP Address and Port page, enter the following settings, then click Next.
You can click Ping Server to confirm that the IP address is correct.
Step 8
On the Enter Secondary Server Settings for Failover page, click Next.
Step 9
On the Enter Cisco Unified CallManager MWI Extensions page, enter the following settings, then click Next.
Step 10
On the Set Number of Voice Messaging Ports page, enter the following settings, then click Next.
You can click Verify to confirm that the CallManager device name prefix is correct.
Step 11
If other integrations already exist, the Enter Trunk Access Code page appears. Enter the extra digits that Cisco Unity must use to transfer calls through the gateway to extensions on the other phone systems with which it is integrated. Then click Next.
Step 12
(Cisco Unity 4.2 and later only) On the Reassign Subscribers page, any subscribers whose phone system integration has been deleted and who are not currently assigned to a phone system integration will appear in the list.
If no subscribers appear in the list, click Next and continue to Step 13.
Otherwise, select the subscribers that you want to assign to this phone system integration and click Next. You can use the following selection controls for selecting subscribers.
Step 13
(Cisco Unity 4.2 and later only) On the Reassign Call Handlers page, any call handlers whose phone system integration has been deleted and that are not currently assigned to a phone system integration will appear in the list.
If no call handlers appear in the list, click Next and continue to Step 14.
Otherwise, select the call handlers that you want to assign to this phone system integration and click Next. You can use the following selection controls for selecting call handlers.
Step 14
On the Completing page, verify the settings you entered, then click Finish.
Step 15
At the prompt to restart the Cisco Unity services, click Yes. The Cisco Unity services restart.
Alternatively, you can restart the Cisco Unity services in UTIM on the Tools menu by clicking Restart Cisco Unity.
To Enter the Voice Messaging Port Settings for the Integration
Step 1
After the Cisco Unity services restart, on the View menu, click Refresh.
Step 2
In the left pane of the UTIM window, expand the phone system integration that you are creating.
Step 3
In the left pane, click the name of the cluster.
Step 4
In the right pane, on the Servers tab, confirm that the Cisco Unified CallManager Security Mode field is set to Non-Secure.
Step 5
Click the Ports tab.
Step 6
Enter the settings shown in Table 8 for the voice messaging ports.
To get the best performance, use the first voice messaging ports for incoming calls and the last ports to dial out. This helps minimize the possibility of a collision, in which an incoming call arrives on a port at the same time that Cisco Unity takes the port off-hook to dial out.
CautionIn programming Cisco Unified CallManager Express, do not send calls to voice messaging ports in Cisco Unity that cannot answer calls (voice messaging ports that are not set to Answer Calls). For example, if a voice messaging port is set only to Dialout MWI, do not send calls to it.
Step 7
Click Save.
Step 8
For Cisco Unity versions 4.0(1) through 4.0(4), exit UTIM, skip the next procedure, and continue with the "Testing the Integration" section.
For Cisco Unity version 4.0(5) and later, continue with the following procedure.
To Identify the Phone System to Cisco Unity as Cisco Unified CallManager Express (Cisco Unity 4.0(5) and Later Only)
Step 1
In the right pane of the UTIM window, click the Servers tab.
Step 2
Under IP Address or Host Name, click the IP address or host name of the Cisco Unified CallManager Express server.
Step 3
Click Modify.
Step 4
In the Modify Server dialog box, in the IP Address or Host Name field, enter the IP address or host name for the Cisco Unified CallManager Express server.
Step 5
Check the This Server Is Cisco Unified CallManager Express check box and click OK.
Step 6
In the UTIM window, click Save.
Step 7
At the prompt to restart the Cisco Unity services, click Yes. The Cisco Unity services restart.
Alternatively, you can restart the Cisco Unity services in UTIM on the Tools menu by clicking Restart Cisco Unity.
Step 8
Exit UTIM.
Testing the Integration
To test whether Cisco Unity and the phone system are integrated correctly, do the following procedures in the order listed.
If any of the steps indicate a failure, refer to the following documentation as applicable:
•
The installation guide for the phone system.
•
Cisco Unity Troubleshooting Guide, available at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/voicesw/ps2237/prod_troubleshooting_guides_list.html.
•
The setup information earlier in this guide.
To Set Up the Test Configuration
Step 1
Set up two test extensions (Phone 1 and Phone 2) on the same phone system that Cisco Unity is connected to.
Step 2
Set Phone 1 to forward calls to the Cisco Unity pilot number when calls are not answered.
CautionThe phone system must forward calls to the Cisco Unity pilot number in no fewer than four rings. Otherwise, the test may fail.
Step 3
In the Cisco Unity Administrator, create a test subscriber to use for testing by doing the applicable substeps below.
If your message store is Microsoft Exchange, do the following:
a.
In the Cisco Unity Administrator, go to the Subscribers > Subscribers > Profile page.
b.
Click the Add icon.
c.
Select New Exchange Subscriber.
d.
On the Add Subscriber page, enter the applicable information.
e.
Click Add.
If your message store is IBM Lotus Domino, do the following:
a.
In the Cisco Unity Administrator, go to the Subscribers > Subscribers > Profile page.
b.
Click the Add icon.
c.
Click Notes.
d.
In the Address Book list, confirm that the address book listed is the one that contains the user data that you want to import.
If the address book that you want to use is not listed, go to the System > Configuration > Subscriber Address Books page and add a different address book.
e.
In the Find Domino Person By list, indicate whether to search by short name, first name, or last name.
f.
Enter the applicable short name or name. You also can enter * to display a list of all users, or enter one or more characters followed by * to narrow your search.
g.
Click Find.
h.
On the list of matches, click the name of the user to import.
i.
On the Add Subscriber page, enter the applicable information.
j.
Click Add.
Step 4
In the Extension field, enter the extension of Phone 1.
Step 5
In the Active Schedule field, click All Hours - All Days.
Step 6
Click the Save icon.
Step 7
In the navigation bar, click Call Transfer to go to the Subscribers > Subscribers > Call Transfer page for the test subscriber.
For more information on transfer settings, refer to the "Subscriber Template Call Transfer Settings" section in the Cisco Unity Administrator Help.
Step 8
Under Transfer Incoming Calls, click Yes, Ring Subscriber's Extension, and confirm that the extension number is for Phone 1.
Step 9
Under Transfer Type, click Release to Switch.
Step 10
Click the Save icon.
Step 11
In the navigation bar, click Messages to go to the Subscribers > Subscribers > Messages page for the test subscriber.
Step 12
Under Message Waiting Indicators (MWIs), check Use MWI for Message Notification.
Step 13
In the Extension field, enter x.
Step 14
Click the Save icon.
Step 15
Open the Status Monitor by doing one of the following:
•
In Internet Explorer, go to http://<Cisco Unity server name>/web/sm.
•
Double-click the desktop shortcut to the Status Monitor.
•
In the status bar next to the clock, right-click the Cisco Unity tray icon and click Status Monitor.
To Test an External Call with Release Transfer
Step 1
From Phone 2, enter the access code necessary to get an outside line, then enter the number outside callers use to dial directly to Cisco Unity.
Step 2
On the Status Monitor, note which port handles this call.
Step 3
When you hear the opening greeting, enter the extension for Phone 1. Hearing the opening greeting means that the port is configured correctly.
Step 4
Confirm that Phone 1 rings and that you hear a ringback tone on Phone 2. Hearing a ringback tone means that Cisco Unity correctly released the call and transferred it to Phone 1.
Step 5
Leaving Phone 1 unanswered, confirm that the state of the port handling the call changes to "Idle." This state means that release transfer is successful.
Step 6
Confirm that, after the number of rings that the phone system is set to wait, the call is forwarded to Cisco Unity and that you hear the greeting for the test subscriber. Hearing the greeting means that the phone system forwarded the unanswered call and the call-forward information to Cisco Unity, which correctly interpreted the information.
Step 7
On the Status Monitor, note which port handles this call.
Step 8
Leave a message for the test subscriber and hang up Phone 2.
Step 9
On the Status Monitor, confirm that the state of the port handling the call changes to "Idle." This state means that the port was successfully released when the call ended.
Step 10
Confirm that the MWI on Phone 1 is activated. The activated MWI means that the phone system and Cisco Unity are successfully integrated for turning on MWIs.
To Test Listening to Messages
Step 1
From Phone 1, enter the internal pilot number for Cisco Unity.
Step 2
When asked for your password, enter the default password. Hearing the request for your password means that the phone system sent the necessary call information to Cisco Unity, which correctly interpreted the information.
Step 3
Confirm that you hear the recorded voice name for the test subscriber (if you did not record a voice name for the test subscriber, you will hear the extension number for Phone 1). Hearing the voice name means that Cisco Unity correctly identified the subscriber by the extension.
Step 4
When asked whether you want to listen to your message, press 1.
Step 5
After listening to the message, press 3 to delete the message.
Step 6
Confirm that the MWI on Phone 1 is deactivated. The deactivated MWI means that the phone system and Cisco Unity are successfully integrated for turning off MWIs.
Step 7
Hang up Phone 1.
Step 8
On the Status Monitor, confirm that the state of the port handling the call changes to "Idle." This state means that the port was successfully released when the call ended.
To Set Up Supervised Transfer on Cisco Unity
Step 1
In the Cisco Unity Administrator, go to the Subscribers > Subscribers > Call Transfer page.
If the name of the test subscriber is not displayed, click the Find icon (the magnifying glass) in the title bar, then click Find, and select the name of the test subscriber in the list that appears.
For more information on transfer settings, refer to the "Subscriber Template Call Transfer Settings" section in the Cisco Unity Administrator Help.
Step 2
Under Transfer Type, click Supervise Transfer.
Step 3
Set the Rings to Wait For field to 3.
Step 4
Click the Save icon.
To Test Supervised Transfer
Step 1
From Phone 2, enter the access code necessary to get an outside line, then enter the number outside callers use to dial directly to Cisco Unity.
Step 2
On the Status Monitor, note which port handles this call.
Step 3
When you hear the opening greeting, enter the extension for Phone 1. Hearing the opening greeting means that the port is configured correctly.
Step 4
Confirm that Phone 1 rings and that you do not hear a ringback tone on Phone 2. Instead, you should hear the indication your phone system uses to mean that the call is on hold (for example, music or beeps).
Step 5
Leaving Phone 1 unanswered, confirm that the state of the port handling the call remains "Busy." This state and hearing an indication that you are on hold mean that Cisco Unity is supervising the transfer.
Step 6
Confirm that, after three rings, you hear the greeting for the test subscriber. Hearing the greeting means that Cisco Unity successfully recalled the supervised-transfer call.
Step 7
During the greeting, hang up Phone 2.
Step 8
On the Status Monitor, confirm that the state of the port handling the call changes to "Idle." This state means that the port was successfully released when the call ended.
To Delete the Test Subscriber
Step 1
In the Cisco Unity Administrator, go to the Subscribers > Subscribers > Profile page.
If the name of the test subscriber is not displayed, click the Find icon (the magnifying glass) in the title bar, then click Find, and select the name of the test subscriber in the list that appears.
Step 2
In the title bar, click the Delete Subscriber icon (the X).
Step 3
Click Delete.
Changing the Settings for an Existing Integration
After the integration is set up, if you want to change any of its settings (for example, to change the MWI settings), do the following procedure.
If you want to change the number of voice messaging ports, see the "Changing the Number of Voice Messaging Ports" section.
To Change the Settings for an Integration
Step 1
On the Cisco Unity server, on the Windows Start menu, click Programs > Cisco Unity > Manage Integrations. The UTIM window appears.
Step 2
In the left pane, double-click Unity Server. The existing integrations appear.
Step 3
Click the integration you want to modify.
Step 4
In the right pane, click the cluster for the integration.
Step 5
In the right pane, click the applicable tab for the integration.
Step 6
Enter new settings in the fields that you want to change.
CautionIf you are adding or removing voice messaging ports, make sure you change the settings for the individual ports so that there are an appropriate number of ports set to answer calls and an appropriate number of ports set to dial out.
Step 7
In the UTIM window, click Save.
Step 8
If prompted, restart the Cisco Unity services.
Changing the Number of Voice Messaging Ports
To change the number of voice messaging ports after you have finished installing and setting up Cisco Unified CallManager Express, do the following procedures.
To Change the Number of Voice Messaging Ports in the Cisco Unified CallManager Express
Step 1
Reprogram the Cisco Unified CallManager Express router for the number of voice messaging ports you want. Each voice messaging port will use one ephone-dn and one e-phone. For details, see the "Programming the Cisco Unified CallManager Express Phone System" section.
Step 2
If you are removing voice messaging ports, skip the remaining steps in this procedure and continue on to the "Changing the Settings for an Existing Integration" section.
If you are not removing voice messaging ports, continue on to Step 3.
Step 3
If you are adding voice messaging ports and the Cisco Unity license does not enable the additional voice messaging ports you added, see your sales representative to request the applicable license file.
Step 4
When you have the license file, on the Cisco Unity server, click Programs > Cisco Unity > Licensing.
Step 5
On the Action menu, click Install License Files.
Step 6
Follow the on-screen instructions.
Note
If you increase the number of voice messaging ports from 32 or fewer to more than 32, you must also install SQL Server 2000 as described in the applicable Cisco Unity installation guide.
Step 7
Continue with the "Changing the Settings for an Existing Integration" section.
Deleting an Existing Integration
If you want to delete an existing integration (for example, you have replaced the phone system with which Cisco Unity originally integrated), do the following procedure.
To Delete an Existing Integration
Step 1
On the Cisco Unity server, on the Windows Start menu, click Programs > Cisco Unity > Manage Integrations. The UTIM window appears.
Step 2
In the left pane, double-click Unity Server. The existing integrations appear.
Step 3
Click the integration that you want to delete.
Step 4
On the Integration menu, click Delete.
Step 5
Follow the on-screen instructions to assign the subscribers of the deleted phone system integration to another phone system integration.
Step 6
At the prompt to restart the Cisco Unity services, click Yes. The Cisco Unity services restart.
Alternatively, you can restart the Cisco Unity services in UTIM on the Tools menu by clicking Restart Cisco Unity.
Step 7
If the integration you deleted used voice cards, remove the voice cards from the Cisco Unity server.
Appendix: Using Alternate Extensions and MWIs
Alternate Extensions
In addition to the "primary" extension that you specify for subscribers, you can assign subscribers up to nine alternate extensions. (The primary extension is the one that you assign to each subscriber when you create his or her subscriber account; it is listed on the Subscribers > Subscribers > Profile page.)
Reasons to Use Alternate Extensions
There are several reasons that you may want to specify alternate extensions for subscribers. For example, if you have more than one Cisco Unity server that accesses a single, corporate-wide directory, you may want to use alternate extensions to simplify addressing messages to subscribers at the different locations. With alternate extensions, the number that a subscriber uses when addressing a message to someone at another location can be the same number that the subscriber dials when calling. You may also want to use alternate extensions to:
•
Handle multiple line appearances on subscriber phones.
•
Offer easy message access on direct calls from a cell phone, home phone, or phone at an alternate work site (assuming that the phone number is passed along to Cisco Unity from these other phone systems). In addition, when such phones are used as alternate extensions, and are set to forward to Cisco Unity, callers can listen to the subscriber greeting, and leave messages for the subscriber just as they would when dialing the primary extension for the subscriber.
Tip
To reduce the number of requests from subscribers who want alternate extensions set up for multiple cell phones, home phones, and other phones, give subscribers class of service (COS) rights to specify their own set of alternate extensions. (See the Subscribers > Class of Service > Profile page.) With proper COS rights, a subscriber can specify up to five alternate extensions in the Cisco Unity Assistant—in addition to the nine that you can specify on the Subscribers > Alternate Extensions page in the Cisco Unity Administrator.
•
Enable URL-based extensions in Cisco Unity for an integration with a SIP phone system.
How Alternate Extensions Work
Before you set up alternate extensions, review the following list for information on how alternate extensions work:
•
Alternate extensions cannot exceed 30 characters in length. By default, each administrator-defined alternate extension must be at least 3 characters in length, while subscriber-defined alternate extensions must be at least 10 characters.
You can use the Advanced Settings tool in Tools Depot to specify a minimum extension length for the extensions entered in the Cisco Unity Administrator and the Cisco Unity Assistant. Refer to the Advanced Settings Tool Help for details on using the settings. Respectively, the settings are Administration—Set the Minimum Length for Locations, and Administration—Set the Minimum Length for Subscriber-Defined Alternate Extensions.
•
You can control whether subscribers can use the Cisco Unity Assistant to view the alternate extensions that you specify in the Cisco Unity Administrator. To do so, see the Subscribers > Class of Service > Profile page. The Subscriber-Defined Alternate Extension table displays the alternate extensions that the subscriber adds.
•
Neither the Cisco Unity Administrator nor the Cisco Unity Assistant will accept an extension that is already assigned to another subscriber (either as a primary or alternate extension), or to a public distribution list, call handler, directory handler, or interview handler. Cisco Unity verifies that each alternate extension is unique—up to the dialing domain level, if applicable—before allowing either an administrator or a subscriber to create it.
•
All alternate extensions use the same transfer settings as the primary extension.
•
In many cases, Cisco Unity can activate a message waiting indicator (MWI) for an alternate extension. However, depending on the phones and phone systems involved, some additional phone system programming may be required to set this up.
Setting Up Alternate Extensions
Do the applicable procedure to add, modify, or delete alternate extensions:
•
To Add Administrator-Defined Alternate Extensions
•
To Modify or Delete Alternate Extension(s)
To Add Administrator-Defined Alternate Extensions
Step 1
In the Cisco Unity Administrator, go to any Subscribers > Alternate Extensions page.
Step 2
In the Administrator-Defined Alternate Extensions table, enter an extension in any row. When entering characters in the Alternate Extensions table, consider the following:
•
You can enter an extension up to 30 characters in length. (SIP integrations can use up to 30 alphanumeric characters.)
•
Each extension must be unique—up to the dialing domain level, if applicable.
•
Enter digits 0 through 9. Do not use spaces, dashes, or parentheses.
•
For SIP integrations, you can also enter a valid alias for a SIP URL. For example, if the URL is SIP:aabade@cisco.com, enter aabade. Do not use spaces.
•
Rows are numbered as a convenience. You can enter alternate extensions in any order, and you can have blank rows.
Step 3
Repeat Step 2 as necessary.
Step 4
Click the Save icon. Alternate extensions are enabled for all rows in the table.
To Modify or Delete Alternate Extension(s)
Step 1
In the Cisco Unity Administrator, go to any Subscribers > Alternate Extensions page.
Step 2
Do any of the following:
•
To modify an extension, change the extension in the Alternate Extensions table.
•
To delete extensions, check the check boxes next to the alternate extensions that you want to delete.
•
To remove all alternate extensions listed in the table, click Select All.
Step 3
Click the Save icon.
Step 4
Repeat Step 2 and Step 3 as necessary.
Note
You can run the Cisco Unity Bulk Import wizard when you want to add alternate extensions for multiple subscribers at once. When you do, the Cisco Unity Bulk Import wizard appends the new alternate extensions to the existing table of alternate extensions, beginning with the first blank row.
Alternate MWIs
You can set up Cisco Unity to activate alternate MWIs when you want a new message for a subscriber to activate the MWIs at up to 10 extensions. For example, a message left at extension 1001 can activate the MWIs on extensions 1001 and 1002.
Cisco Unity uses MWIs to alert the subscriber to new voice messages. MWIs are not used to indicate new e-mail, fax, or return receipt messages.
Setting Up Alternate MWIs
Cisco Unity can activate alternate MWIs. Note that depending on the phones and phone systems, some additional phone system programming may be necessary. Refer to the installation guide for the phone system.
To enable alternate MWIs for extensions, do the following procedure for each subscriber who needs alternate MWIs.
To Set Up Alternate MWIs for Extensions
Step 1
In the Cisco Unity Administrator, go to the applicable Subscribers > Subscribers > Messages page.
Step 2
Confirm that the Use MWI for Message Notification check box is checked.
Step 3
Click the Add button located beneath the MWI Extensions table to add a row to the table. By default, the first row in the table contains an "X" to indicate the primary extension assigned to a subscriber. If you want one more extension and do not need to activate the MWI on the primary extension, you can also modify the first row.
Step 4
Enter the applicable extension in the Extension field of the table. MWIs are automatically enabled for all rows in the table. When entering characters in the MWI Extensions table, consider the following:
•
Enter digits 0 through 9. Do not use spaces, dashes, or parentheses.
•
Enter , (comma) to insert a one-second pause.
•
Enter # and * to correspond to the # and * keys on the phone.
Step 5
Click the Save icon.
Step 6
Repeat Step 3 through Step 5 as necessary.
Note
You can run the Cisco Unity Bulk Import wizard when you want to set up alternate MWIs for multiple subscribers at once.
To change or delete alternate MWIs for extensions, do the following procedure.
To Modify or Delete Alternate MWIs
Step 1
In the Cisco Unity Administrator, go to the applicable Subscribers > Subscribers > Messages page.
Step 2
Do either of the following:
•
To modify an extension, change the extension in the MWI Extensions table.
•
To delete extensions, check the check boxes next to the rows that you want to delete in the MWI Extensions table, and then click the Delete button.
Step 3
Click the Save icon.
Step 4
Repeat Step 2 and Step 3 as necessary.
Appendix: Documentation and Technical Assistance
Conventions
The Cisco Unifed CallManager Express 3.x Integration Guide for Cisco Unity 4.0 uses the following conventions.
The Cisco Unifed CallManager Express 3.x Integration Guide for Cisco Unity 4.0 also uses the following conventions:
Note
Means reader take note. Notes contain helpful suggestions or references to material not covered in the document.
CautionMeans reader be careful. In this situation, you might do something that could result in equipment damage or loss of data.
For descriptions and URLs of Cisco Unity documentation on Cisco.com, see the About Cisco Unity Documentation. The document is shipped with Cisco Unity and is available at http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/voice/c_unity/about/aboutdoc.htm.
Obtaining Documentation
Cisco documentation and additional literature are available on Cisco.com. Cisco also provides several ways to obtain technical assistance and other technical resources. These sections explain how to obtain technical information from Cisco Systems.
Cisco.com
You can access the most current Cisco documentation at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport
You can access the Cisco website at this URL:
You can access international Cisco websites at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/public/countries_languages.shtml
Product Documentation DVD
The Product Documentation DVD is a comprehensive library of technical product documentation on a portable medium. The DVD enables you to access multiple versions of installation, configuration, and command guides for Cisco hardware and software products. With the DVD, you have access to the same HTML documentation that is found on the Cisco website without being connected to the Internet. Certain products also have .PDF versions of the documentation available.
The Product Documentation DVD is available as a single unit or as a subscription. Registered Cisco.com users (Cisco direct customers) can order a Product Documentation DVD (product number DOC-DOCDVD= or DOC-DOCDVD=SUB) from Cisco Marketplace at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/marketplace/
Ordering Documentation
Registered Cisco.com users may order Cisco documentation at the Product Documentation Store in the Cisco Marketplace at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/marketplace/
Nonregistered Cisco.com users can order technical documentation from 8:00 a.m. to 5:00 p.m. (0800 to 1700) PDT by calling 1 866 463-3487 in the United States and Canada, or elsewhere by calling 011 408 519-5055. You can also order documentation by e-mail at tech-doc-store-mkpl@external.cisco.com or by fax at 1 408 519-5001 in the United States and Canada, or elsewhere at 011 408 519-5001.
Documentation Feedback
You can rate and provide feedback about Cisco technical documents by completing the online feedback form that appears with the technical documents on Cisco.com.
You can submit comments about Cisco documentation by using the response card (if present) behind the front cover of your document or by writing to the following address:
Cisco Systems
Attn: Customer Document Ordering
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-9883We appreciate your comments.
Cisco Product Security Overview
Cisco provides a free online Security Vulnerability Policy portal at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/products_security_vulnerability_policy.html
From this site, you will find information about how to:
•
Report security vulnerabilities in Cisco products.
•
Obtain assistance with security incidents that involve Cisco products.
•
Register to receive security information from Cisco.
A current list of security advisories, security notices, and security responses for Cisco products is available at this URL:
To see security advisories, security notices, and security responses as they are updated in real time, you can subscribe to the Product Security Incident Response Team Really Simple Syndication (PSIRT RSS) feed. Information about how to subscribe to the PSIRT RSS feed is found at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/products_psirt_rss_feed.html
Reporting Security Problems in Cisco Products
Cisco is committed to delivering secure products. We test our products internally before we release them, and we strive to correct all vulnerabilities quickly. If you think that you have identified a vulnerability in a Cisco product, contact PSIRT:
•
For Emergencies only — security-alert@cisco.com
An emergency is either a condition in which a system is under active attack or a condition for which a severe and urgent security vulnerability should be reported. All other conditions are considered nonemergencies.
•
For Nonemergencies — psirt@cisco.com
In an emergency, you can also reach PSIRT by telephone:
•
1 877 228-7302
•
1 408 525-6532
Tip
We encourage you to use Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) or a compatible product (for example, GnuPG) to encrypt any sensitive information that you send to Cisco. PSIRT can work with information that has been encrypted with PGP versions 2.x through 9.x.
Never use a revoked or an expired encryption key. The correct public key to use in your correspondence with PSIRT is the one linked in the Contact Summary section of the Security Vulnerability Policy page at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/products_security_vulnerability_policy.html
The link on this page has the current PGP key ID in use.
If you do not have or use PGP, contact PSIRT at the aforementioned e-mail addresses or phone numbers before sending any sensitive material to find other means of encrypting the data.
Obtaining Technical Assistance
Cisco Technical Support provides 24-hour-a-day award-winning technical assistance. The Cisco Technical Support & Documentation website on Cisco.com features extensive online support resources. In addition, if you have a valid Cisco service contract, Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC) engineers provide telephone support. If you do not have a valid Cisco service contract, contact your reseller.
Cisco Technical Support & Documentation Website
The Cisco Technical Support & Documentation website provides online documents and tools for troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. The website is available 24 hours a day, at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport
Access to all tools on the Cisco Technical Support & Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. If you have a valid service contract but do not have a user ID or password, you can register at this URL:
http://tools.cisco.com/RPF/register/register.do
Note
Use the Cisco Product Identification (CPI) tool to locate your product serial number before submitting a web or phone request for service. You can access the CPI tool from the Cisco Technical Support & Documentation website by clicking the Tools & Resources link under Documentation & Tools. Choose Cisco Product Identification Tool from the Alphabetical Index drop-down list, or click the Cisco Product Identification Tool link under Alerts & RMAs. The CPI tool offers three search options: by product ID or model name; by tree view; or for certain products, by copying and pasting show command output. Search results show an illustration of your product with the serial number label location highlighted. Locate the serial number label on your product and record the information before placing a service call.
Submitting a Service Request
Using the online TAC Service Request Tool is the fastest way to open S3 and S4 service requests. (S3 and S4 service requests are those in which your network is minimally impaired or for which you require product information.) After you describe your situation, the TAC Service Request Tool provides recommended solutions. If your issue is not resolved using the recommended resources, your service request is assigned to a Cisco engineer. The TAC Service Request Tool is located at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport/servicerequest
For S1 or S2 service requests, or if you do not have Internet access, contact the Cisco TAC by telephone. (S1 or S2 service requests are those in which your production network is down or severely degraded.) Cisco engineers are assigned immediately to S1 and S2 service requests to help keep your business operations running smoothly.
To open a service request by telephone, use one of the following numbers:
Asia-Pacific: +61 2 8446 7411 (Australia: 1 800 805 227)
EMEA: +32 2 704 55 55
USA: 1 800 553-2447For a complete list of Cisco TAC contacts, go to this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport/contacts
Definitions of Service Request Severity
To ensure that all service requests are reported in a standard format, Cisco has established severity definitions.
Severity 1 (S1)—An existing network is down, or there is a critical impact to your business operations. You and Cisco will commit all necessary resources around the clock to resolve the situation.
Severity 2 (S2)—Operation of an existing network is severely degraded, or significant aspects of your business operations are negatively affected by inadequate performance of Cisco products. You and Cisco will commit full-time resources during normal business hours to resolve the situation.
Severity 3 (S3)—Operational performance of the network is impaired, while most business operations remain functional. You and Cisco will commit resources during normal business hours to restore service to satisfactory levels.
Severity 4 (S4)—You require information or assistance with Cisco product capabilities, installation, or configuration. There is little or no effect on your business operations.
Obtaining Additional Publications and Information
Information about Cisco products, technologies, and network solutions is available from various online and printed sources.
•
The Cisco Product Quick Reference Guide is a handy, compact reference tool that includes brief product overviews, key features, sample part numbers, and abbreviated technical specifications for many Cisco products that are sold through channel partners. It is updated twice a year and includes the latest Cisco offerings. To order and find out more about the Cisco Product Quick Reference Guide, go to this URL:
•
Cisco Marketplace provides a variety of Cisco books, reference guides, documentation, and logo merchandise. Visit Cisco Marketplace, the company store, at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/marketplace/
•
Cisco Press publishes a wide range of general networking, training and certification titles. Both new and experienced users will benefit from these publications. For current Cisco Press titles and other information, go to Cisco Press at this URL:
•
Packet magazine is the Cisco Systems technical user magazine for maximizing Internet and networking investments. Each quarter, Packet delivers coverage of the latest industry trends, technology breakthroughs, and Cisco products and solutions, as well as network deployment and troubleshooting tips, configuration examples, customer case studies, certification and training information, and links to scores of in-depth online resources. You can access Packet magazine at this URL:
•
iQ Magazine is the quarterly publication from Cisco Systems designed to help growing companies learn how they can use technology to increase revenue, streamline their business, and expand services. The publication identifies the challenges facing these companies and the technologies to help solve them, using real-world case studies and business strategies to help readers make sound technology investment decisions. You can access iQ Magazine at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/iqmagazine
or view the digital edition at this URL:
http://ciscoiq.texterity.com/ciscoiq/sample/
•
Internet Protocol Journal is a quarterly journal published by Cisco Systems for engineering professionals involved in designing, developing, and operating public and private internets and intranets. You can access the Internet Protocol Journal at this URL:
•
Networking products offered by Cisco Systems, as well as customer support services, can be obtained at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/index.html
•
Networking Professionals Connection is an interactive website for networking professionals to share questions, suggestions, and information about networking products and technologies with Cisco experts and other networking professionals. Join a discussion at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/discuss/networking
•
World-class networking training is available from Cisco. You can view current offerings at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/learning/index.html
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses. Any examples, command display output, and figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
© 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.