-
Troubleshooting Guide for Cisco CallManager, Release 4.1(3)
-
Index
-
Preface
-
Troubleshooting Overview
-
Troubleshooting Tools
-
Installation, Backup, and Restore Issues
-
Cisco CallManager System Issues
-
Directory Issues
-
Device Issues
-
Dial Plans and Routing Issues
-
Cisco CallManager Services Issues
-
Voice Messaging Issues
-
Opening a Case With TAC
-
Case Study: Troubleshooting Intracluster Phone Calls
-
Case Study: Troubleshooting Cisco IP Phone to Cisco IOS Gateway Calls
-
Case Study: Troubleshooting Intercluster Phone Calls
-
Table Of Contents
Cisco CallManager System Issues
Cisco CallManager System Not Responding
Cisco CallManager System Stops Responding
Checking Settings on the Backup Utility to Avoid High CPU
Setting up Performance Monitor Counter Logs
Cisco CallManager Administration Page Does Not Display
Errors Occur When Attempting to Access the Cisco CallManager Administration Page from the Browser
You Are Not Authorized to View This Page
Problems Displaying or Adding Users With Cisco CallManager
Name to Address Resolution Failing
Unable to Change the Server Name for Cisco CallManager
Default Web Site Under IIS Has Improper Setting
You Attempt to Access a Machine Where Access Is Explicitly Denied
Improper Network Setting Exists in the Remote Machine Where You Are Browsing
Replication Fails Between the Publisher and the Subscriber
Cannot Update Data Because the Publisher Is Not Available
Subscriber Stops Replicating Data From the Publisher
Mismatched Duplex Port Settings
JTAPI Subsystem Startup Problems
JTAPI Subsystem is OUT_OF_SERVICE
MIVR-SS_TEL-4-ModuleRunTimeFailure
MIVR-SS_TEL-1-ModuleRunTimeFailure
JTAPI Subsystem is in PARTIAL_SERVICE
Changing IIS Parameters for Security
Cisco CallManager System Issues
This section covers solutions for the following most common issues related to a Cisco CallManager system.
•
Cisco CallManager System Not Responding
•
Replication Fails Between the Publisher and the Subscriber
•
JTAPI Subsystem Startup Problems
Cisco CallManager System Not Responding
This section covers the following issues for a Cisco CallManager system not responding:
•
Cisco CallManager System Stops Responding
•
Cisco CallManager Administration Page Does Not Display
•
Errors Occur When Attempting to Access the Cisco CallManager Administration Page from the Browser
•
You Are Not Authorized to View This Page
•
Name to Address Resolution Failing
•
Default Web Site Under IIS Has Improper Setting
•
You Attempt to Access a Machine Where Access Is Explicitly Denied
•
Improper Network Setting Exists in the Remote Machine Where You Are Browsing
•
Replication Fails Between the Publisher and the Subscriber
Cisco CallManager System Stops Responding
Symptom
The Cisco CallManager system does not respond.
Possible Cause
When the Cisco CallManager service (ccm.exe) crashes, the following message displays in the System Event log:
The Cisco CallManager service terminated unexpectedly.It has done this 1 time. The following corrective actionwill be taken in 60000 ms. Restart the service.Other messages you may see in the event of a crash are:
Timeout 3000 milliseconds waiting forCisco CallManager service to connect.The Cisco CallManager failed to start due to the following error:
The service did not respond to the start or control request in a timely fashion.At this time, when devices such as the Cisco IP Phones and gateways unregister from the Cisco CallManager, users receive delayed dial tone, and/or the Cisco CallManager server freezes due to high CPU usage. For event log messages not included here, view the Cisco CallManager Event Logs.
The Cisco CallManager service can crash due to one of the following reasons:
–
An unexpected event occurs in the Cisco CallManager service. This crash adds an entry to the existing Dr.Watson log and a user.dmp is generated in the C:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Documents\DrWatson folder. Refer to the "Unexpected Event" section.
–
The Cisco CallManager service does not have enough resources such as CPU or memory to function. Generally, the CPU utilization in the server is 100 percent at that time. Refer to the "Lack of Resources" section.
Depending on what type of crash you experience, you will need to gather different data that will help determine the root cause of the crash.
Related Topics
•
"Checking Settings on the Backup Utility to Avoid High CPU" section
•
"Setting up Performance Monitor Counter Logs" section
Unexpected Event
Use the following procedure as a guide for what information to gather and provide to TAC in the event of Cisco CallManager crash.
Procedure
Step 1
Collect Cisco CallManager traces 15 minutes before and after the crash. The traces are located at C:\Program Files\cisco\trace\ccm.
Step 2
Collect SDL traces 15 minutes before and after the crash. Traces are located at C:\Program Files\cisco\trace\sdl\ccm.
Step 3
Locate the System and Application Event log files in the Event Viewer by selecting Start > Programs > Administrative Tools > Event Viewer, clicking on System Log, and selecting Action > Save Log as and save the log. Also do this for the Application Log.
Step 4
Ensure that the SdlMaxUnhandledExceptions parameter is set to 0 (zero) for each Cisco CallManager.
Step 5
Locate the Dr. Watson log file located at
C:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Documents\DrWatson.The file is named Drwtsn32.log.
Step 6
Locate the user.dmp file at C:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Documents\DrWatson.
Note
These files can be very large. Zip them before sending them to the TAC. It is important to note that these files hold the information the TAC engineer and developers need to determine the cause of the crash.
Step 7
Open the Dr. Watson log file in Notepad and view the most recent entry to see if an entry for the ccm.exe has been added. Begin at the bottom of the file, and search for Application exception occurred, which takes you to the latest crash.
The following is an example of the header of a crash entry in the Drwtsn32.log file.
Application exception occurred:App: (pid=680)When: 3/8/2003 @ 14:01:06.978Exception number: e06d7363Along with the date of the crash, there is a PID. If that PID corresponds to the PID for ccm.exe in the task list, then you know that Cisco CallManager crashed.
Note
In the following example, the PID = 680. From the list, you see that this also corresponds to ccm.exe.
The task list in the Drwtsn32.log looks similar to the following:
Example
PID PROCESS8 System.exe212 SMSS.exe240 CSRSS.exe264 WINLOGON.exe292 SERVICES.exe304 LSASS.exe424 termsrv.exe520 svchost.exe560 msdtc.exe696 DLLHOST.exe736 Ipvmsapp.exe752 DLLHOST.exe824 AudioTranslator.exe848 RisDC.exe860 LogoutService.E.exe884 DCX500.exe936 svchost.exe980 LLSSRV.exe1028 sqlservr.exe1112 ntpd.exe1140 rcmdsvc.exe1172 regsvc.exe1176 mstask.exe1204 SNMP.exe1244 WinMgmt.exe1260 cpqnimgt.exe1284 cqmgserv.exe1296 cqmgstor.exe1308 sysdown.exe1372 cqmghost.exe1524 aupair.exe1552 sqlagent.exe276 svchost.exe2400 inetinfo.exe2412 explorer.exe2752 sqlmangr.exe2700 taskmgr.exe2704 mmc.exe680 ccm.exe868 DRWTSN32.exeIf there is no list of the PIDs, look at the timestamp of the last entry of the Drwtsn32.log and the timestamp of the error in the Event Log (refer to the Cisco CallManager Service Crash Description section). If they are the exact same time, it is likely that you experienced an Unexpected Event Cisco CallManager crash.
What makes a crash unique is the stack trace. This is why you will see the requested complete Drwtsn32.log file in the Unexpected Event section.
If the PID for the day of the crash is not ccm.exe or the timestamp did not correspond, then you are most likely experiencing a lack-of- resource crash or a crash of another process.
Lack of Resources
Use the following procedure if there is a lack of resources crash.
Procedure
Step 1
Collect Cisco CallManager traces 15 minutes before and after the crash. The traces are located at C:\Program Files\cisco\trace\ccm.
Step 2
Collect SDL traces 15 minutes before and after the crash. Traces are located at C:\Program Files\cisco\trace\sdl\ccm .
Step 3
Collect perfmon traces if available.
Step 4
If the traces are not available, start collecting the perfmon traces and track memory and CPU usage for each process running on the server. To set up perfmon traces go to the Setting up Performance Monitor Counter Logs section. These will help in the event of another lack of resources crash.
Checking Settings on the Backup Utility to Avoid High CPU
To avoid a system crash due to the Cisco IP Telephony Applications Backup running for an extended time at high CPU utilization, ensure that you are running the latest Cisco IP Telephony Applications Backup.
If you are running Cisco CallManager 3.1(3a)spC and later or Cisco CallManager 3.2(1)spA and later, per Cisco bug ID CSCdt91655 ( registered customers only) , the new Backup utility runs at low priority by default.
Registered customers can download the latest version of Cisco IP Telephony Applications Backup from the Voice Software download page under Cisco CallManager.
Prior to this change, the previous versions used a tab called Performance to change the Base Priority of the process running the Cisco IP Telephony Applications Backup application. Changing the performance to below normal or low ensures that this process does not compete with other processes (that are running at normal Base Priority) for CPU, such as ccm.exe.
Setting up Performance Monitor Counter Logs
In order to verify the processes running, and the amount of CPU and memory that are being consumed, use the following procedure to gather counters for the crash.
Procedure
Step 1
Choose Start > Programs > Administrative Tools > Performance.
Step 2
Choose Performance Logs > Alerts > Counter Logs from the Performance Monitor.
Step 3
Choose Action > New log settings and enter a name for the counter log.
Step 4
Click Add in the counters page.
Use the local computer counters and make sure that you are configuring this directly on the Cisco CallManager that is experiencing the crash.
Step 5
Choose Process in the Performance Object.
Step 6
Choose List > Select Instances in the Select Counters and click the following counters and associated instances:
% Processor Time / All Instances
ID Process / All Instance
Virtual Bytes / All Instances
Private Bytes / All Instances
Step 7
Set the interval to 2 and the units as seconds in the Sample Data Every.
From the Log Files tab, make sure that the log file type is Text File - CSV. Also note where these are located. The default is C:\PerfLogs. Select a log file limit of 20,000 Kb.
Step 8
Click the Schedule tab.
Step 9
Choose Start Log Manually to start the log.
Step 10
Choose When the 20,000 Kb Log File is Full to stop the log.
Step 11
Choose Start a new log file and then click OK when the log closes.
Step 12
Start logging by selecting the created counter log.
Step 13
Choose Action > Start.
Note
Over time, enabling these performance monitor logs generates a large number of files and utilizes a large amount of disk space. Therefore, you need to monitor this activity and, if it is generating large files, zip up the older logs and/or move them from the local drive.
Step 14
The event log data may or may not be necessary. However, you should proactively dump both the System and Application events and filter out only the events from the last 30 minutes before the crash. Investigate these events before sending them to the TAC. You might see something that warrants more attention.
Note
Within a highly utilized system, using Event Viewer (a built-in Microsoft utility) to dump these events to a text file can easily starve all other processes from the CPU, including the Cisco CallManager KeepAlive process used to maintain phone registrations. Save the event log file in the .csv file format.
Step 15
In the following order, zip all files before e-mailing and copying them using WinZip version 8. In general, files are copied to a local machine for faster evaluation. Zipped files use less space and can be moved around faster than raw file formats.
a.
Zip the USER.DMP and DRWTSN32.LOG together. Send and copy this Zip file immediately with a descriptive symptom definition and include the exact Cisco CallManager version, appropriate device loads, and Cisco IOS versions. If any special patches are in use, ensure this fact is made clear.
b.
Zip and send the Cisco CallManager and SDL trace files together.
c.
Zip and send the Performance Monitor logs together.
d.
Zip and send the event log entries together.
Cisco CallManager Administration Page Does Not Display
Symptom
Administration web page does not display.
Possible Cause
The Cisco CallManager service stopped.
Recommended Action
Use the following procedure to verify that the Cisco CallManager service is active on a server that is local or remote.
1.
From Cisco CallManager Administration, choose Application > Cisco CallManager Serviceability.
The Cisco CallManager Serviceability window displays.
2.
Choose Tools > Service Activation.
3.
From the Servers column, choose a server.
The server that you chose displays next to the Current Server title, and a box with configured services displays.
Activation Status column displays either Activated or Deactivated in the Cisco CallManager line.
If Activated, the Cisco CallManager is active on the chosen server and you need to contact TAC for further assistance.
If Deactivated, continue with the following steps.
4.
Check the Cisco CallManager check box.
5.
Click the Update button.
The Activation Status column displays Activated in the Cisco CallManager line.
Cisco CallManager is now active for the chosen server.
Perform the following procedure if the Cisco CallManager has been in service and you want to check if it is currently active.
1.
From Cisco CallManager Administration, choose Application > Cisco CallManager Serviceability.
The Cisco CallManager Serviceability window displays.
2.
Choose Tools > Control Center.
3.
From the Servers column, choose the server.
The server that you chose displays next to the Current Server title, and a box with configured services displays.
The Activation Status column displays Activated in the Cisco CallManager line.
Cisco CallManager is active for the chosen server. Contact TAC for further assistance.
If Deactivated, continue with the following steps.
4.
Check the Cisco CallManager check box.
5.
Click the Update button.
The Activation Status column displays Activated in the Cisco CallManager line.
Cisco CallManager is now active for the chosen server.
Repeat the preceding procedure to verify that the Cisco CallManager service is activated.
Errors Occur When Attempting to Access the Cisco CallManager Administration Page from the Browser
Symptom
One of the following error messages displays when you are trying to access the administration page from the same server where the Cisco CallManager resides.
•
Internet Explorer—The page cannot be displayed.
•
Netscape—Warning box displays: There was no response. The server could be down or is not responding.
Possible Cause
The IIS Admin service or the WWW publishing service does not start automatically as expected. One of these services stopping represents the most frequent reason for the pages not displaying locally.
Recommended Action
Use the following procedure to start the IIS.
Note
If the IIS is stopped, the WWW publishing services may also be stopped. Start the WWW publishing services, which automatically starts the IIS .
1.
From the Start menu, choose Start > Programs > Administration Tools > Services.
A window displays listing IIS Administration.
2.
Right-click IIS Admin Service.
3.
Choose Start.
4.
Click Yes.
The IIS starts.
Start the other services using the following procedure.
1.
From the Start menu, choose Start > Programs > Administration Tools > Services.
2.
Right-click the service.
3.
Choose Start.
4.
Click Yes.
The service starts.
Verification
Use the following procedure to verify that IIS is started.
1.
From the Start menu, choose Start > Programs > Administration Tools > Services.
2.
Right-click the service.
3.
Verify the status, which should display Started.
4.
If any service is stopped, perform the following procedures to start the service(s).
Use the following procedure to start the IIS.
Note
If the IIS is stopped, WWW publishing services may also be stopped. Start the WWW publishing services, which automatically starts the IIS .
1.
From the Start menu, choose Start > Programs > Administration Tools > Services.
A window displays listing IIS Admin Service.
2.
Right-click IIS Admin Service.
3.
Choose Start.
4.
Click Yes.
5.
The IIS starts.
Start the other services using the following procedure.
1.
From the Start menu, choose Start > Programs > Administration Tools > Services.
2.
Right-click the service.
3.
Choose Start.
4.
Click Yes.
5.
The service starts.
Viruses can also cause the IIS service to stop and display strange messages when attempting to access the administration page. See the Virus Protection section for more information.
You Are Not Authorized to View This Page
Symptom
When accessing the administration page, the following error message displays.
Error Message You Are Not Authorized to View This Page
and other similar error messages that may occur include:
–
You do not have permission to view this directory or page using the credentials you supplied.
–
HTTP 401.3 Access denied by ACL on resource Internet Information Services.
–
Server Application Error. The server has encountered an error while loading an application during the processing of your request. Please refer to the event log for more detailed information. Please contact the server administrator for assistance.
–
Error: Access is Denied.
Possible Cause
The NTFS permissions have been modified on your C drive off the root directory to propagate into child directories on the Cisco CallManager server.
NTFS permissions have been changed from the default settings on the server and are no longer sufficient for IIS to run properly.
Recommended Action
Visit the Microsoft site for details on the issue: Q271071 "Minimum NTFS Permissions Required for IIS 5.0 to Work" at the following URL:
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?ln=EN-GB&pr=kbinfo&
Verification
Use the following procedure to verify that IIS is started.
1.
From the Start menu, choose Start > Programs > Administration Tools > Services.
2.
Right-click the service.
3.
Verify the status, which should display Started.
4.
If any service is stopped, perform the following procedures to start the service(s).
Use the following procedure to start the IIS.
Note
If the IIS is stopped, the WWW publishing services may also be stopped. Start the WWW publishing services, which starts the IIS automatically.
1.
From the Start menu, choose Start > Programs > Administration Tools > Services.
A window displays listing IIS Admin Service.
2.
Right-click IIS Admin Service.
3.
Choose Start.
4.
Click Yes.
The IIS starts.
Start the other services using the following procedure.
1.
From the Start menu, choose Start > Programs > Administration Tools > Services.
2.
Right-click the service.
3.
Choose Start.
4.
Click Yes.
The service starts.
Errors Occur When Attempting to Access the Cisco CallManager Administration Page from a Browser on a Remote Server
If you can access the Administration Web page locally on the Cisco CallManager server, but not when you browse from a remote machine, verify whether one of the following situations applies to you. They appear in order, from the most frequent reason to the least frequent reason.
Problems Displaying or Adding Users With Cisco CallManager
Symptom
You are not able to add a user or conduct a search on the Cisco CallManager Administration user pages.
Possible Cause
You may encounter the following problems if you are working with Cisco CallManager 3.x installed on a server that has a special character (such as an underscore) in its hostname, or MS Internet Explorer 5.5 with SP2 and a Q313675 patch or above.
–
When you conduct a basic search and hit submit, the page returns the same page.
–
When you try to insert a new user, the following error message appears.
The following error occurred while trying to execute the command.Sorry, your session object has timed out.Click here to Begin a New SearchRecommended Action
You may not be able to add a user or do a search on the Cisco CallManager Admin user pages, if your Cisco CallManager hostname contains any special characters such as underscore or period (for example, Call_Manager). Domain Name System (DNS)-supported characters include all letters (A-Z, a-z), numbers (0-9), and hyphen (-), and any special characters are not allowed. If the Q313675 patch is installed on your browser, make sure that the URL does not contain any non-DNS supported characters.
For more information about the Q313675 patch, refer to MS01-058: File Vulnerability Patch for Internet Explorer 5.5 and Internet Explorer 6.
To resolve this problem, you have the following options:
–
Access the Cisco CallManager Admin pages using the IP address of the server.
–
Do not use non-DNS characters in the Server Name.
–
Use the localhost or IP address in the URL.
SQLSvc User Cannot Log In
Symptom
The SQLSvc user cannot log in, and dependent services do not start.
Possible Cause
The SQLSvc user must log in to the local system before the Cisco CallManager, SQLServerAgent, MSSQLServer, and COM+ Event System services can start and execute their specific functions. If the SQLSvc password is not configured correctly, both locally and within the cluster, the SQLSvc user cannot log in and these dependent services do not start. Cisco CallManager and its basic functionality can be affected.
Note
The SQLSvc password should be the same across the entire cluster.
This problem affects the following:
–
Cisco CallManager
–
Microsoft SQL server for Cisco Call Manager
–
Cisco Music on Hold (MOH) Audio Translator
–
Cisco Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP)
Recommended Action
Use the following procedure to recover an SQLSvc account password.
1.
Choose Start > Programs > Administrative Tools > Computer Management.
2.
Click + (the plus sign) beside Local Users and Groups in the left column.
3.
Click Users.
4.
Right-click SQLSvc in the right column and choose Set Password.
5.
Enter the new password and confirm the password.
6.
Click OK to confirm and close the Change Password dialog box.
7.
Click + (the plus sign) beside Services and Applications in the left column.
8.
Click Services.
9.
In the right column click to highlight MSSQLServer 2000.
10.
Right-click MSSQLServer 2000 and choose Properties.
11.
Click the Log On tab.
12.
Change the password and confirm that the password matches the SQLSvc user password set in step 5.
13.
Click OK to return to the Services List.
14.
Click to highlight SQLServerAgent.
15.
Right-click SQLServerAgent and choose Properties.
16.
Click the Log On tab.
17.
Change the password to match the SQLSvc user password set in step 5.
18.
Click OK to return to the Services List.
19.
Close the Computer Management window.
20.
Choose Start > Programs > Administrative Tools > Component Services.
21.
Click + (the plus sign) beside Component Services.
22.
Click + (the plus sign) beside Computers.
23.
Click + (the plus sign) beside My Computer.
24.
Click + (the plus sign) beside COM+ Applications.
25.
Right-click DBL and choose Properties.
26.
Click the Identity tab.
27.
Change the password and confirm that the password matches the SQLSvc user password set in step 5.
28.
Click OK to go back to the Component Manager.
29.
Right-click DBL and click Shut Down.
30.
Right-click DBL and click Start.
31.
Close the Component Manager window.
Name to Address Resolution Failing
Symptom
One of the following error messages displays when you try to access the following URL:
http://your-cm-server-name/ccmadmin
Internet Explorer: This page cannot be displayed
Netscape: Not Found. The requested URL /ccmadmin was not found on this server.
If you try to access the same URL using the Cisco CallManager IP address (http://10.48.23.2/ccmadmin) instead of the name, the page displays.
Possible Cause
The name that you entered as "your-cm-server-name" is mapping to the wrong IP address in DNS or hosts file.
Recommended Action
1.
If you have configured the use of DNS, check in the DNS to see whether the entry for the your-cm-server-name has the correct IP address of the Cisco CallManager server. If it is not correct, change it.
2.
If you are not using DNS, your local machine will check in the "hosts" file to see whether there is an entry for the your-cm-server-name and an IP address associated to it. Open the file and add the Cisco CallManager server name and the IP address.
You can find the "hosts" file at C:\WINNT\system32\drivers\etc\hosts on your Windows station.
Unable to Change the Server Name for Cisco CallManager
Symptom
You attempt to change the name of the Cisco CallManager server and the service fails. Other services , such as CTI Manager, Extended Functions, and Voice Media Streaming, also fail.
Possible Cause
Cisco does not support changing the name of a Cisco CallManager server.
Recommended Action
Use the following procedure to change the IP address instead of changing the name of a Cisco CallManager server.
Note
You must change the IP address in all applications.
1.
From Customer Response Applications Administration, choose System > Engine to access the Engine web page.
Note
These steps are required if the Customer has installed Extended Services (required in version 3.2 and below for Extension Mobility and required in all versions for IP-Auto Attendant or TAPS, which are free applications) or a co-resident installation of CRS on the machine whose IP address is being changed.
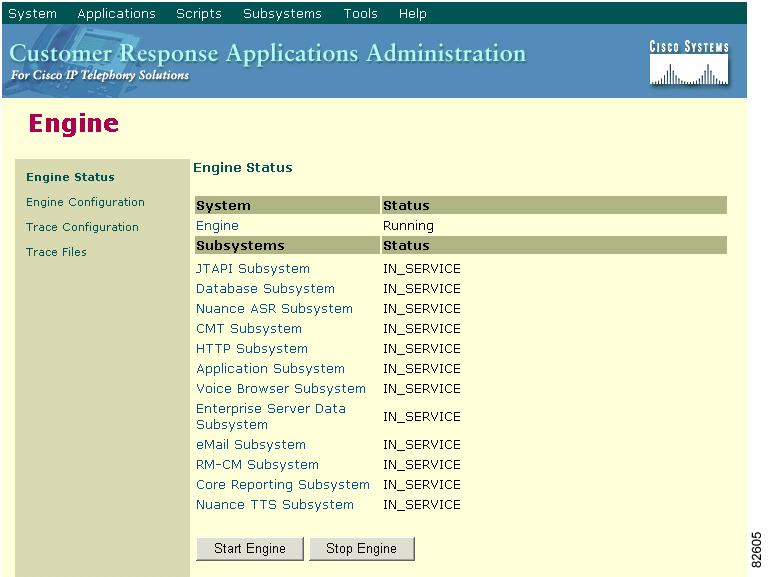
Figure 4-1 Engine Window—Engine Status Area
The Engine Status area displays information about the CRS system and its subsystems.
2.
Click the Stop Engine button to stop the CRS Engine.
Note
You can also control the CRS Engine from the Windows Service window, which you display by choosing Start > Programs > Administrative Tools > Services.
3.
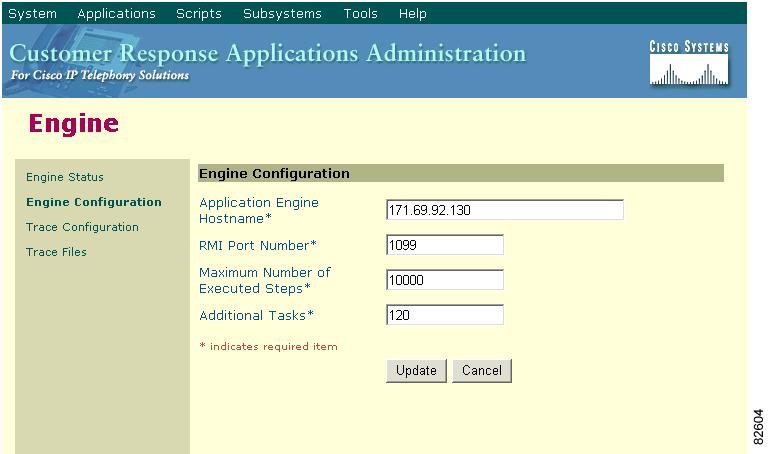
Click the Engine Configuration hyperlink on the navigation bar of the Engine web page to access the Engine Configuration area, which displays information you specified during user profile creation.
Figure 4-2 Engine Window—Engine Configuration Area
4.
In the Application Engine Hostname field, enter the new IP address of the server.
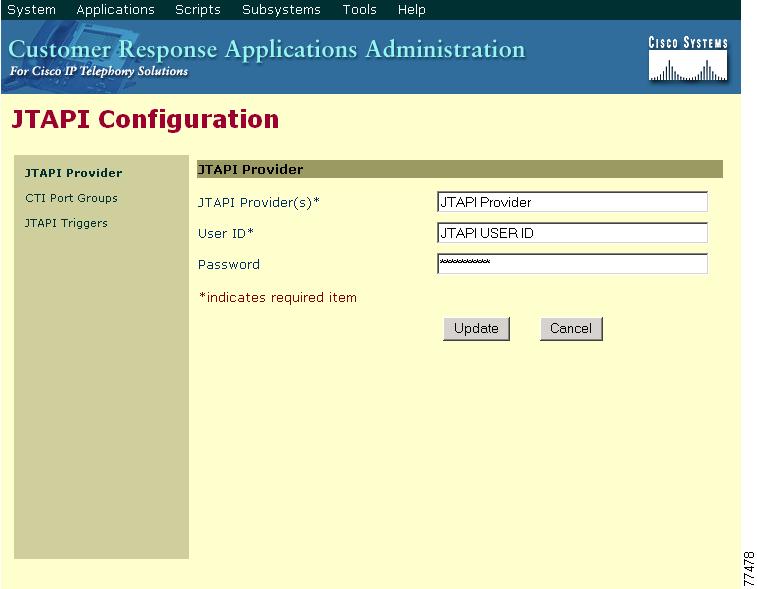
5.
From the Customer Response Applications Administration, choose Subsystems > JTAPI.
The JTAPI Configuration web page displays.
Figure 4-3 JTAPI Configuration Window
6.
In the JTAPI Provider(s) field, enter the new IP address of the Cisco Media Convergence server (Cisco MCS) running Cisco CallManager CTI Manager.
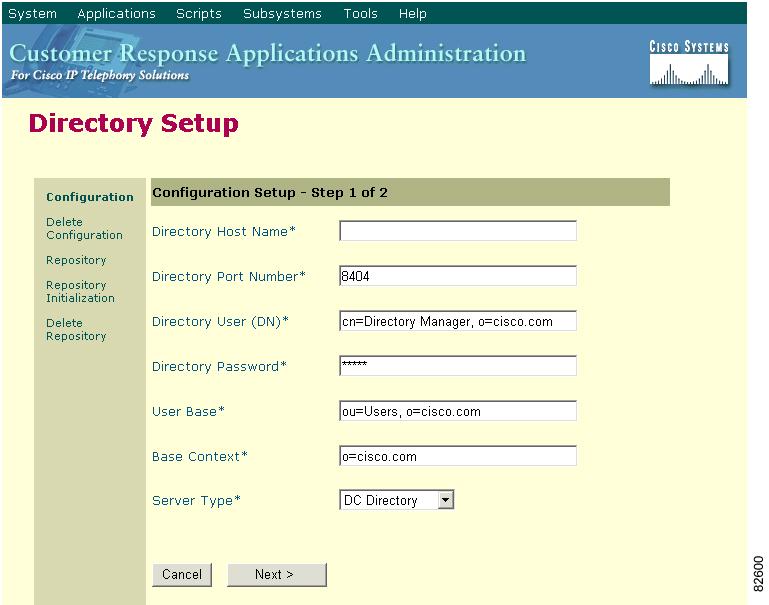
7.
From Customer Response Applications Administration, choose System > Configuration and Repository.
The Directory Setup Window displays.
Figure 4-4 Directory Setup Window—Configuration Setup Area
8.
In the Directory Host Name field, enter the new IP address.
9.
Click the Repository hyperlink on the navigation bar of the Directory Setup window.
The Repository Setup area displays.
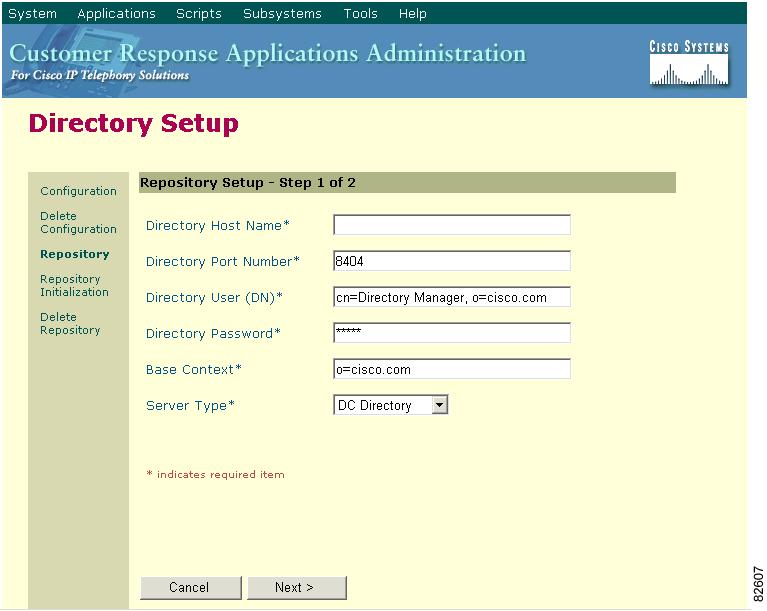
Figure 4-5 Directory Setup Window—Repository Setup Area
10.
In the Directory Host Name field, enter the new IP address.
11.
Stop the DC Directory Service on the server by choosing Control Panel > Administrative Tools > Services.
12.
Select Start > Programs > DC Directory Administrator Directory Manager.
13.
Enter the directory manager password that you entered during the installation.
14.
Choose Directory > cisco.com > CCN > systemProfile.
15.
Double-click Hoteling Profile.
16.
Click Modify and enter the new IP address.
17.
In the Cisco CallManager Administration, choose System > Server and enter the new IP address.
18.
In the Cisco CallManager Administration, choose System > Enterprise Parameters and enter the new IP addresses for the URL Directories. There are multiple URL entries that may need to be changed. Help, Authentication, Directories, Information, and Services all have URLs under Enterprise Parameters.
19.
In the Cisco CallManager Administration, choose Features > Phone Services and enter the new IP address in all URLs. This applies to any URLs that point to the server that is being changed. Services can (and in many cases should) point to other servers/www sites.
20.
Change the Server IP address to the new IP address in Network Properties.
21.
Change LMHOST and HOSTS files on all servers in a cluster to the new IP address.
22.
Change the DHCP Option 150 to the new IP address.
23.
Open the SQL Enterprise Manager and change the IP addresses in the URLs in the PlugIn table by choosing Start > Programs Microsoft SQL Server 2000 > Enterprise Manager.
24.
Choose the tree server name > Databases > latest CCM03xx database.
25.
Choose Tables > PlugIn.
26.
Right-click PlugIn to open the table and choose Return All Rows.
Note
Modifications occur immediately. You cannot cancel changes.
27.
Open the stiBackup configuration by choosing Start > Programs Administrative Tools > Services Console > stiBack for Cisco IP Telephony Applications and enter the new IP address in all the appropriate tabs.
28.
In C:\TAPS\TAPSCCM.txt, enter the new IP address
Default Web Site Under IIS Has Improper Setting
Symptom
One of the following error messages displays when you try to access the following URL:
http://your-cm-server-name/ccmadmin
•
Internet Explorer: This page cannot be displayed
•
Netscape: Not Found. The requested URL /ccmadmin was not found on this server.
If you try to access the same page using the Cisco CallManager IP address (http://10.48.23.2/ccmadmin) instead of the name, the page displays.
Possible Cause
An incorrect setting in the Default Web Site tab for the IIS has been set on the server.
Recommended Action
1.
Verify in the Internet Service Manager on the Cisco CallManager machine the Default Web Site. In the Web Site tab, choose All Unassigned and not the IP address of the machine.
You can verify that setting by choosing
Start > Programs > Administrative tools/Internet Service Manager.
Expand the icon that shows your server name.2.
Right-click Default Web Site. You have option properties that you must choose. Look for the Web Site tab and verify the All Unassigned setting.
Note
If you need to keep the specific IP address setting for any reason, you cannot use the name instead of IP address from a remote web browser.
Port 80 Is Blocked in One or More Routers Between Your Local Browser and the Cisco CallManager Server
Symptom
One of the following error messages displays when a firewall blocks the port that is used by the web server or the http traffic:
•
Internet Explorer: This page cannot be displayed
•
Netscape: There was no response. The server could be down or is not responding
Possible Cause
For security reasons, the system blocked the http access from your local network to the server network.
Recommended Action
1.
Verify whether other types of traffic to the Cisco CallManager server, such as ping or Telnet, are allowed. If any are successful, it will show that http access to the Cisco CallManager Web server has been blocked from your remote network.
2.
Check the security policies with your network administrator.
3.
Try again from the same network where the Server is located.
You Attempt to Access a Machine Where Access Is Explicitly Denied
Symptom
One of the following error messages displays:
•
Internet Explorer: This page cannot be displayed
•
Netscape: Not Found. The requested URL / ccmadmin was not found on this server.
•
From both browsers without the show friendly http error messages advance setting configured: Access to this server is forbidden.
Possible Cause
This represents a security policy that is applied by the network administrator.
Recommended Action
1.
Check the security policies with your network administrator. Try again from a different machine.
2.
If you are the network administrator, check the Directory Security tab of the Default Web Site in the Internet Service Manager on the Cisco CallManager server.
3.
You can verify the setting by choosing
Start > Programs > Administrative tools/Internet Service Manager.4.
Expand the icon that shows your server name.
5.
Right-click Default Web Site. You have the option properties from which you must choose.
6.
Look for the Directory Security tab and verify the setting.
Improper Network Setting Exists in the Remote Machine Where You Are Browsing
Symptom
There is no connectivity, or there is no connectivity to other devices in the same network as the Cisco CallManager.
When you attempt the same action from other remote machines, the Cisco CallManager Administration Page displays.
Possible Cause
Improper network configuration settings on a station or on the default Gateway can cause a web page not to display because partial or no connectivity to that network exists.
Recommended Action
1.
Try pinging the IP address of the Cisco CallManager server and other devices to confirm that you cannot connect.
2.
If the connectivity to any other device out of your local network is failing, check the network setting on your station, as well as the cable and connector integrity.
3.
If the connectivity to any other device out of your local network is failing, check the network setting on your station, as well as the cable and connector integrity. Refer to the appropriate hardware documentation for detailed information.
If you are using TCP-IP over a LAN to connect, continue with the following steps to verify the network settings on the remote station.
4.
Choose Start > Setting > Network and Dial-up connections.
5.
Choose Local Area Connection, then Properties.
The list of communication protocols displays as checked.
6.
Choose Internet Protocol (TCP-IP) and click Properties again.
7.
Depending on your network, choose either Obtain an ip address automatically or set manually your address, mask and default Gateway.
The possibility exists that a browser-specific setting could be improperly configured.
8.
Choose the Internet Explorer browser Tools > Internet Options.
9.
Choose the Connections tab and then verify the LAN settings or the dial-up settings.
By default, the LAN settings and the dial-up settings are not configured. The generic network setting from Windows is used.
10.
If the connectivity is failing only to the Cisco CallManager network, a routing issue probably exists in the network. Contact the network administrator to verify the routing that is configured in your default gateway.
Note
If you cannot browse from the remote server after following this procedure, contact TAC to have the issue investigated in more detail.
Refer to the following URL for more information on configuration settings:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk331/tk336/tk542/tsd_technology_support_sub-protocol_home.html
Replication Fails Between the Publisher and the Subscriber
Replicating the SQL database is a core function of Cisco CallManager clusters. The server with the master copy of the database is called the publisher, while the servers replicating the database are called subscribers.
Cannot Update Data Because the Publisher Is Not Available
Symptom
The following error message displays:
Error Message Cannot update data because the publisher is not available. Please try again later. (58)Possible Cause
The subscriber build failed.
Recommended Action
1.
Ensure that the NetBIOS name resolution is working between all servers.
2.
Ensure (by editing) that the hosts and LMHOSTS are filled in on the publisher and subscriber servers, so each one can resolve the other's host name and NetBIOS name.
Hosts is used for DNS resolution. LMHOSTS uses NetBIOS for name resolution. Also, SQL uses NetBIOS for name resolution.
If the Cisco CallManager fails to update, the database layer on the subscriber cannot find the publisher.
3.
Check the SQL "distribution agent" on the publisher for history and errors.
4.
Choose Start > Programs > Administrative Tools > Local Security Policy.
5.
Choose Audit Policy.
6.
Enable Failure auditing for all events.
For SQL, enable Authentication.
Note
Users get replicated in the DC Directory, not in SQL.
7.
From the web, upgrade the Cisco CallManager for the software version on your publisher.
The software will download the SQL database to the subscriber(s).
Subscriber Stops Replicating Data From the Publisher
Symptom
Changes made on the publisher are not reflected on phones that are registered with the subscriber.
Possible Cause
Replication fails between the publisher and subscriber.
Recommended Action
Complete the following steps to reestablish the relationship between the two systems. First, the subscriber subscription will need to be recreated on the publisher. Then, delete the subscription and re-create it on the subscriber system.
Recreating the Subscription on the Publisher
1.
Choose Programs > Microsoft SQL Server 2000 > Enterprise Manager from the publisher to start the SQL Enterprise Manager.
2.
The subscription can be re-created from the publisher. Under Microsoft SQL Server, select New SQL Server Registration...
The Register SQL Server Wizard displays. Make sure the From now on I want to perform the task without using a wizard checkbox is not checked.
3.
Click Next.
The other SQL servers that reside on the Cisco CallManagers should display in the Additional Servers box.
4.
Choose all servers and Add them to the Added servers box.
5.
Click Next.
Click The SQL Server login information that was assigned to me by the system administrator.
6.
Click Next.
7.
On the next screen, use the "sa" account and password for the subscriber system.
Note
This is the sa account and password from the SUBSCRIBER system. The password was selected when the subscriber system was installed.
8.
In the Select SQL Server Group window, choose the option to Add the SQL server(s) to the existing SQL Server group.
9.
Click Finish.
After selecting finish, the wizard will display status of the addition of the added server(s).
The display should read "Registered successfully."
10.
Click Close.
The listing of the two servers in the display means they are recognized by the publisher, so data can be shared with them.
Deleting the Subscription on the Publisher
Use the following procedure to delete the subscription on the publisher.
1.
Choose Microsoft SQL Servers > SQL Server Group > Machine_name > Databases > CCM0301 > Publications from the Enterprise Manager to locate the Publication for the CCM0301 database.
2.
Choose the Cisco CallManager subscription that is failing and delete the entry.
Note
Select the area on the right. Do not delete the book icon on the left.
A warning displays indicating the subscription has been removed at the publisher, but not the subscriber and if you want to connect to the subscriber and delete the subscription.
3.
Click Yes.
The next message indicates that the subscription has been deleted but the data has not.
4.
Click OK.
Re-creating the Subscription on the Subscriber
Next, the subscription must be added back into the subscriber SQL server. Use the following procedure to re-create the subscription on the subscriber.
1.
Select the SQL server name of the subscriber that you just deleted from the publisher.
2.
Right-click to get the menu.
3.
Choose New > Pull Subscription from the menu.
Note
Always choose the latest version of the database, not the earlier version
The Pull Subscription Wizard displays.
4.
Click Next.
5.
On the Choose Publication screen expand the publisher (which should be listed) and select the database.
6.
Click Next.
7.
On the Specify Synchronization Agent Login screen, Choose Using SQL Server Authentication of this account.
The login name will be sa and the password will be the same password for the publisher sa account.
8.
On the Specify Immediate-Updating Subscription(s) popup, Click Yes, make this an immediate-updating subscription(s).
9.
Click Next.
10.
On the Initialize Subscription screen, Click Yes, initialize the schema and data at the Subscriber.
11.
Click Next.
12.
On the Set Distribution Agent Schedule popup, Choose Continuously.
13.
Click Next.
14.
The next step will verify that both the SQL server agent and the Microsoft DTC services are running.
15.
Click Next.
16.
Click Finish in the Completing the Pull Subscription Wizard screen.
The Wizard will set up the subscription and display a success when completed.
A display indicating success should appear when the process is completed.
17.
Now that the subscription has been created, the snapshot agent must be run to get the data out to the subscriber for synchronization.
18.
Choose the publisher SQL server and choose Replication Monitor > Publishers > Machine_name >CCM0301 subscription.
19.
Choose the Snapshot entry and choose Start.
The snapshot agent will run at this point. It will take about 3-5 minutes to complete the task. Once the snapshot agent completes, the pull agent will start to apply the snapshot to the subscriber. This will take another 3-5 minutes.
20.
Once the pull subscription has completed, on the publisher, select the subscriber SQL server and open the pull subscriptions for the CCM0301 database.
The subscription should be in a running state and waiting for updates.
Note
If the last action still reads "Waiting for snapshot agent to become available," press F5 to refresh the screen.
At this time, the subscriber is now resynchronized with the publisher and updates are getting recorded in the local subscriber SQL database.
Verification
Use the following procedure to verify that the SQL Subscription is working.
1.
To test the propogation of data, create a device on the publishing server that is easily recognizable.
Note
The more recognizable the device is, the easier it will be to find.
2.
Click Insert.
The device does not need to be functional.
3.
Click Update and Close.
4.
Go into the SQL Enterprise Manager, expand the SQL subscriber in question and look in the database table to see if the new device is present.
Slow Server Response
This section addresses a problem related to a slow response from the server: Mismatched Duplex Port Settings.
Mismatched Duplex Port Settings
Symptom
Slow response from the server occurs.
Possible Cause
Slow response could result if the duplex of the switch does not match the duplex port setting on the Cisco CallManager server.
Recommended Action
1.
For optimal performance, set both switch and server to 100/Full.
Cisco does not recommend using the Auto setting on either the switch or the server.
2.
You must restart the Cisco CallManager server for this change to take effect.
JTAPI Subsystem Startup Problems
The JTAPI (Java Telephony API) subsystem is a very important component of the Cisco Customer Response Solutions (CRS) platform. JTAPI is the component that communicates with the Cisco CallManager, and is responsible for telephony call control. The CRS platform hosts telephony applications, such as Cisco AutoAttendant, Cisco IP ICD, and Cisco IP-IVR. This section is not specific to any of these applications; the JTAPI subsystem is an underlying component that is used by all of them.
Before starting the troubleshooting process, ensure that the software versions that you are using are compatible. To verify compatibility, read the Cisco CallManager Release Notes for the version of Cisco CallManager that you are using.
To check the version of CRS, log in to the AppAdmin page by typing http://servername/appadmin, where servername is the name of the server on which CRS is installed. The current version is located in the lower-right corner of the main menu.
JTAPI Subsystem is OUT_OF_SERVICE
Symptom
The JTAPI subsystem does not start.
Possible Cause
One of the following exceptions displays in the trace file:
–
MIVR-SS_TEL-4-ModuleRunTimeFailure
–
MIVR-SS_TEL-1-ModuleRunTimeFailure
MIVR-SS_TEL-4-ModuleRunTimeFailure
Search for the MIVR-SS_TEL-1-ModuleRunTimeFailure string in the trace file. At the end of the line, an exception reason is given.
The following are the most common errors:
•
Unable to create provider—bad login or password
•
Unable to create provider -- Connection refused
•
Unable to create provider -- login=
•
Unable to create provider -- hostname
•
Unable to create provider -- Operation timed out
•
Unable to create provider -- null
Unable to create provider—bad login or password
Possible Cause
The user name or password entered in the JTAPI configuration is incorrect.
Full Text of Error Message
%MIVR-SS_TEL-4-ModuleRunTimeFailure:Real-timefailure in JTAPI subsystem: Module=JTAPISubsystem,Failure Cause=7,FailureModule=JTAPI_PROVIDER_INIT,Exception=com.cisco.jtapi.PlatformExceptionImpl:Unable to create provider -- bad login or password.%MIVR-SS_TEL-7-EXCEPTION:com.cisco.jtapi.PlatformExceptionImpl:Unable to create provider -- bad login or password.Recommended Action
Verify that the user name and password are correct. Try logging into the CCMuser page (http://servername/ccmuser) on the Cisco CallManager to ensure that the Cisco CallManager is able to authenticate correctly.
Unable to create provider -- Connection refused
Possible Cause
The JTAPI connection to the Cisco CallManager is refused by the Cisco CallManager.
Full Text of Error Message
%MIVR-SS_TEL-4-ModuleRunTimeFailure:Real-timefailure in JTAPI subsystem: Module=JTAPI Subsystem,Failure Cause=7,Failure Module=JTAPI_PROVIDER_INIT,Exception=com.cisco.jtapi.PlatformExceptionImpl: Unableto create provider -- Connection refused%MIVR-SS_TEL-7-EXCEPTION:com.cisco.jtapi.PlatformExceptionImpl:Unable to create provider -- Connection refusedRecommended Action
Verify that the CTI Manager service is running in the Cisco CallManager Control Center.
Unable to create provider -- login=
Possible Cause
Nothing has been configured in the JTAPI configuration page.
Full Text of Error Message
%MIVR-SS_TEL-4-ModuleRunTimeFailure:Real-timefailure in JTAPI subsystem: Module=JTAPI Subsystem,Failure Cause=7,Failure Module=JTAPI_PROVIDER_INIT,Exception=com.cisco.jtapi.PlatformExceptionImpl:Unable to create provider -- login=%MIVR-SS_TEL-7-EXCEPTION:com.cisco.jtapi.PlatformExceptionImpl:Unable to create provider -- login=Recommended Action
Configure a JTAPI provider in the JTAPI configuration page on the CRS server.
Unable to create provider -- hostname
Possible Cause
The CRS engine is not able to resolve the host name of the Cisco CallManager.
Full Text of Error Message
%M%MIVR-SS_TEL-4-ModuleRunTimeFailure:Real-timefailure in JTAPI subsystem: Module=JTAPI Subsystem,Failure Cause=7,Failure Module=JTAPI_PROVIDER_INIT,Exception=com.cisco.jtapi.PlatformExceptionImpl:Unable to create provider -- dgrant-mcs7835.cisco.com%MIVR-SS_TEL-7-EXCEPTION:com.cisco.jtapi.PlatformExceptionImpl:Unable to create provider -- dgrant-mcs7835.cisco.comRecommended Action
Verify that DNS resolution is working correctly from the CRS engine. Try using an IP address instead of the DNS name.
Unable to create provider -- Operation timed out
Possible Cause
The CRS engine does not have IP connectivity with the Cisco CallManager.
Full Text of Error Message
101: Mar 24 11:37:42.153 PST%MIVR-SS_TEL-4-ModuleRunTimeFailure:Real-timefailure in JTAPI subsystem: Module=JTAPI Subsystem,Failure Cause=7,Failure Module=JTAPI_PROVIDER_INIT,Exception=com.cisco.jtapi.PlatformExceptionImpl:Unable to create provider -- Operation timed out102: Mar 24 11:37:42.168 PST %MIVR-SS_TEL-7-EXCEPTION:com.cisco.jtapi.PlatformExceptionImpl:Unable to create provider -- Operation timed outRecommended Action
Check the IP address that is configured for the JTAPI provider on the CRS server. Check the default gateway configuration on the CRS server and the Cisco CallManager. Make sure there are no IP routing problems. Test connectivity by pinging the Cisco CallManager from the CRS server.
Unable to create provider -- null
Possible Cause
There is no JTAPI provider IP address or host name configured, or when the JTAPI client is not using the correct version.
Full Text of Error Message
%MIVR-SS_TEL-4-ModuleRunTimeFailure:Real-timefailure in JTAPI subsystem: Module=JTAPI Subsystem,Failure Cause=7,Failure Module=JTAPI_PROVIDER_INIT,Exception=com.cisco.jtapi.PlatformExceptionImpl:Unable to create provider -- nullRecommended Action
Verify that a host name or IP address is configured in the JTAPI configuration. If the JTAPI version is incorrect, download the JTAPI client from the Cisco CallManager Plugins page and install it on the CRS server.
MIVR-SS_TEL-1-ModuleRunTimeFailure
Symptom
This exception usually occurs when the JTAPI subsystem is unable to initialize any ports.
Possible Cause
The CRS server can communicate with the Cisco CallManager, but is unable to initialize any CTI ports or CTI route points through JTAPI. This error occurs if the CTI ports and CTI route points are not associated with the JTAPI user.
Full Text of Error Message
255: Mar 23 10:05:35.271 PST %MIVR-SS_TEL-1-ModuleRunTimeFailure:Real-time failure in JTAPI subsystem: Module=JTAPI Subsystem,Failure Cause=7,Failure Module=JTAPI_SS,Exception=nullRecommended Action
Check the JTAPI user on the Cisco CallManager, and verify that CTI ports and CTI route points that are configured on the CRS server are associated with the user.
JTAPI Subsystem is in PARTIAL_SERVICE
Symptom
The following exception displays in the trace file:
MIVR-SS_TEL-3-UNABLE_REGISTER_CTIPORT
Possible Cause
The JTAPI subsystem is unable to initialize one or more CTI ports or route points.
Full Text of Error Message
1683: Mar 24 11:27:51.716 PST%MIVR-SS_TEL-3-UNABLE_REGISTER_CTIPORT:Unable to register CTI Port: CTI Port=4503,Exception=com.cisco.jtapi.InvalidArgumentExceptionImpl:Address 4503 is not in provider's domain.1684: Mar 24 11:27:51.716 PST %MIVR-SS_TEL-7-EXCEPTION:com.cisco.jtapi.InvalidArgumentExceptionImpl:Address 4503 is not in provider's domain.Recommended Action
The error message in the trace will tell you which CTI port or route point was unable to be initialized. Verify that this device exists in the Cisco CallManager configuration, and is also associated with the JTAPI user on the Cisco CallManager.
Security
This section covers the following security issues and provides information on where to find detailed documentation regarding the security process:
•
Changing IIS Parameters for Security
Changing IIS Parameters for Security
Symptom
You lose settings for locking down the IIS servers to protect the Cisco CallManager from hackers, attacks, or threats.
Possible Cause
Whenever you upgrade or reinstall the Cisco CallManager, all the IIS settings revert to the Cisco CallManager defaults.
Recommended Action
Test all your settings on a non-production Cisco CallManager before changing the settings on your production server.
Make note of the settings because they will change every time that you perform an upgrade or reinstall, and you will have to reset them.
Note
Ensure that you do not change any settings within the Cisco web directory, or you run the risk of losing a Cisco CallManager service due to a missing or moved file.
Near-Term Security Solutions
Refer to the following documents to ensure that you have quality of service (QoS) configured properly throughout your network to help ensure voice quality is affected as little as possible during the remainder of cleanup operations:
•
Cisco IP Telephony QoS Design Guide
•
Cisco IP Telephony Network Design Guide
•
IP Telephony Solutions Guide
The following URL provides the guides:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/voice/ip_tele/index.htm
Refer to the Cisco IP Telephony Network Design Guide to establish separate Voice/Data VLANs.
Note
This could provide a long-term solution depending on the size and complexity of the network involved.
Long-Term Security Solutions
Refer to documentation located at and below the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/voice/ip_tele/index.htm
Related Information
The following URL provides Cisco CallManager Security Patch Process:
http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/cc/pd/nemnsw/callmn/prodlit/cmspp_qa.pdf
Cisco highly recommends that you do not install any patches from Microsoft. Download the wrapped versions from CCO.
You can sign up for Microsoft security patch alerts at the following URL:
http://www.microsoft.com/technet/treeview/default.asp?url=/technet/security/
bulletin/notify.aspThe alerts include an associated rating, which gives you an estimated time of a HotFix posting to CCO.
Refer to the following URL for security considerations for an IP telephony network:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/voice/ip_tele/index.htm
Virus Protection
Refer to the following URL for procedures for stopping an active security attack or preventing an imminent security risk:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/partner/products/sw/voicesw/ps556/prod_security_advisories_list.html
To verify that the server has the latest patches, refer to the following documents:
•
Installing Cisco CallManager
•
Upgrading Cisco CallManager
•
Using Cisco CallManager Upgrade Assistant Utility

 Feedback
Feedback