Feedback Feedback
|
Table Of Contents
QSIG/DPNSS Phone System with Cisco EGW 2200 Integration Guide for Cisco Unity Connection 2.0
Task List to Create the Integration
Integrations with Multiple Phone Systems
Planning How the Voice Messaging Ports Will Be Used by Cisco Unity Connection
Programming the QSIG/DPNSS Phone System
Creating a New Integration with the QSIG/DPNSS Phone System
(Multiple Integrations Only) Adding New User Templates
Appendix: Documentation and Technical AssistanceObtaining Documentation, Obtaining Support, and Security Guidelines
QSIG/DPNSS Phone System with Cisco EGW 2200 Integration Guide for Cisco Unity Connection 2.0
Published May 30, 2007
This document provides instructions for integrating a QSIG/DPNSS phone system with Cisco Unity Connection through a Cisco EGW 2200.
Integration Tasks
Before doing the following tasks to integrate Cisco Unity Connection with a QSIG/DPNSS phone system through a Cisco EGW 2200, confirm that the Cisco Unity Connection server is ready for the integration by completing the appropriate tasks in the Cisco Unity Connection Installation Guide.
The following task lists describe the process for creating, changing, and deleting integrations.
Task List to Create the Integration
Use the following task list to set up a new integration with a QSIG/DPNSS phone system. If you are installing a new Cisco Unity Connection server by using the Cisco Unity Connection Installation Guide, you may have already completed some of the following tasks.
1.
Review the system and equipment requirements to confirm that all phone system and Cisco Unity Connection server requirements have been met. See the "Requirements" section.
2.
Plan how the voice messaging ports will be used by Cisco Unity Connection. See the "Planning How the Voice Messaging Ports Will Be Used by Cisco Unity Connection" section.
3.
Program the QSIG/DPNSS phone system. See the "Programming the QSIG/DPNSS Phone System" section.
4.
Set up the Cisco EGW 2200. See the "Setting Up the Cisco EGW 2200" section.
5.
Create the integration. See the "Creating a New Integration with the QSIG/DPNSS Phone System" section.
6.
Test the integration. See the "Testing the Integration" section.
7.
If this integration is a second or subsequent integration, add the applicable new user templates for the new phone system. See the (Multiple Integrations Only) Adding New User Templates.
Requirements
The QSIG/DPNSS integration supports configurations of the following components:
Phone System
•
A QSIG/DPNSS phone system.
•
The phone system ready for the integration as described in the installation guide for the phone system and the Cisco EGW 2200 documentation.
•
A VoIP gateway configured and connected to the QSIG/DPNSS phone system.
Cisco Unity Connection Server
•
Cisco Unity Connection installed and ready for the integration, as described in the Cisco Unity Connection Installation Guide at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6509/prod_installation_guides_list.html.
•
A license that enables the applicable number of voice messaging ports.
•
A Cisco EGW 2200 ready for the integration as described in the Cisco EGW 2200 documentation.
•
The Cisco EGW 2200 connected to the LAN and configured for a QSIG/DPNSS backhaul signaling stream from the VoIP gateway.
Integration Description
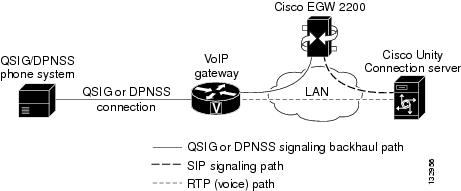
The QSIG/DPNSS integration uses a Cisco EGW 2200, which translates QSIG or DPNSS call signaling into SIP, a VoIP gateway, and the LAN to connect Cisco Unity Connection and a QSIG/DPNSS phone system. Figure 1 shows the required connections.
Figure 1 Connections Between a QSIG/DPNSS Phone System and Cisco Unity Connection
Call Information
The QSIG/DPNSS integration sends the following information with forwarded calls:
•
The extension of the called party
•
The extension of the calling party (for internal calls) or the phone number of the calling party (if it is an external call and the system uses caller ID)
•
The reason for the forward (the extension is busy, does not answer, or is set to forward all calls)
Cisco Unity Connection uses this information to answer the call appropriately. For example, a call forwarded to Cisco Unity Connection is answered with the personal greeting of the user. If the phone system routes the call to Cisco Unity Connection without this information, Cisco Unity Connection answers with the opening greeting.
Integration Functionality
The QSIG/DPNSS integration with Cisco Unity Connection provides the following features:
•
Call forward to personal greeting
•
Call forward to busy greeting
•
Caller ID
•
Easy message access (a subscriber can retrieve messages without entering an ID because Cisco Unity Connection identifies the subscriber based on the extension from which the call originated; a password may be required)
•
Identified subscriber messaging (Cisco Unity Connection identifies the subscriber who leaves a message during a forwarded internal call, based on the extension from which the call originated)
•
Message waiting indication (MWI)
Integrations with Multiple Phone Systems
When Cisco Unity Connection is installed as Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition (CMBE)—on the same server with Cisco CallManager—Cisco Unity Connection cannot be integrated with multiple phone systems at one time.
When Cisco Unity Connection is not installed as Cisco Unified Communications Suite, Cisco Unity Connection can be integrated with multiple phone systems at one time. For information on and instructions for integrating Cisco Unity Connection with multiple phone systems, refer to the Multiple Phone System Integration Guide for Cisco Unity Connection 2.0 at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6509/products_installation_and_configuration_guides_list.html.
Planning How the Voice Messaging Ports Will Be Used by Cisco Unity Connection
Before programming the phone system, you need to plan how the voice messaging ports will be used by Cisco Unity Connection.
Unlike other integrations, the hunt group mechanism for a QSIG/DPNSS phone system integration is implemented on the Cisco Unity Connection server. Within a port group, each incoming call hunts for an available voice messaging port among all the ports in a round-robin (or circular) fashion. If a voice messaging port in the cluster is set not to answer calls or is not enabled, a call reaching that port may receive a busy signal.
The following table describes the voice messaging port settings in Cisco Unity Connection that can be set on Telephony Integrations > Port of Cisco Unity Connection Administration.
The Number of Voice Messaging Ports to Install
The number of voice messaging ports to install depends on numerous factors, including:
•
The number of calls Cisco Unity Connection will answer when call traffic is at its peak.
•
The expected length of each message that callers will record and that users will listen to.
•
The number of users.
•
The number of calls made for message notification.
•
The number of MWIs that will be activated when call traffic is at its peak.
•
The number of TRAP connections needed when call traffic is at its peak. (TRAP connections are used by Cisco Unity Connection web applications to play back and record over the phone.)
•
The number of calls that will use the automated attendant and call handlers when call traffic is at its peak.
It is best to install only the number of voice messaging ports that are needed so that system resources are not allocated to unused ports.
The Number of Voice Messaging Ports That Will Answer Calls
The calls that the voice messaging ports answer can be incoming calls from unidentified callers or from users. Assign all of the voice messaging ports to answer calls.
You can set voice messaging ports to both answer calls and to dial out (for example, to set MWIs).
The Number of Voice Messaging Ports That Will Dial Out
Ports that will dial out can do one or more of the following:
•
Notify users by phone, pager, or e-mail of messages that have arrived.
•
Turn MWIs on and off for user extensions.
•
Make a TRAP connection so that users can use the phone as a recording and playback device in Cisco Unity Connection web applications.
Preparing for Programming the Phone System
Record your decisions about the voice messaging ports to guide you in programming the phone system.
Programming the QSIG/DPNSS Phone System
For information on provisioning a QSIG or DPNSS phone system to integrate with Cisco Unity Connection, refer to the Cisco EGW 2200 documentation.
CautionIn programming the phone system, do not send calls to voice messaging ports in Cisco Unity Connection that cannot answer calls (voice messaging ports that are not set to Answer Calls). For example, if a voice messaging port is set only to Dialout MWI, do not send calls to it.
Setting Up the Cisco EGW 2200
For information on setting up the Cisco EGW 2200, refer to the Cisco EGW 2200 documentation.
Creating a New Integration with the QSIG/DPNSS Phone System
After ensuring that the QSIG/DPNSS phone system and Cisco Unity Connection are ready for the integration, do the following procedures to set up the integration and to enter the port settings.
To Create an Integration
Step 1
Log on to Cisco Unity Connection Administration.
Step 2
In Cisco Unity Connection Administration, expand Telephony Integrations, then click Phone System.
Step 3
On the Search Phone Systems page, on the Phone System menu, click New Phone System. The Phone System Integration Wizard appears.
Step 4
On the Select Phone System Manufacturer page, in the Manufacturer field, click QSIG/DPNSS and click Next.
Step 5
On the Select Phone System Model page, in the Model field, click QSIG/DPNSS and click Next.
Step 6
On the Set Up Phone System page, in the Phone System Name field, accept the default name or enter the descriptive name that you want, and click Next.
Step 7
On the Select Port Group Template page, in the Port Group Template field, click Cisco 2200 EGW to QSIG/DPNSS PBX and click Next.
Step 8
On the Set Up Port Group page, enter the following settings and click Next.
Step 9
On the Confirm Phone System Settings page, confirm the settings that you have entered and click Finish.
Step 10
On the Phone System Creation Summary page, click Close.
Step 11
In Cisco Unity Connection Administration, expand Telephony Integrations, then click Port Group.
Step 12
On the Search Port Groups page, click the display name of the port group that you created for the QSIG/DPNSS integration.
Note
By default, the display name for a port group is composed of the phone system display name followed by an incrementing number.
Step 13
On the Port Group Basics page, on the Edit menu, click Servers.
Step 14
On the Edit Servers page, do the following substeps if there is a secondary Cisco EGW 2220 or SIP proxy server. Otherwise, continue to Step 15.
a.
Under SIP Proxy Servers, click Add.
b.
Enter the following settings for the secondary Cisco EGW 2220 or SIP proxy server and click Save.
Note
You can click Ping to verify the IP address (or host name) of the Cisco EGW 2220 or SIP proxy server.
c.
Repeat Step 14a. and Step 14b. for any remaining secondary Cisco EGW 2220 or SIP proxy server in the cluster.
Step 15
In Cisco Unity Connection Administration, expand Telephony Integrations, then click Port.
Step 16
On the Search Ports page, click the display name of the first voice messaging port that you created for this phone system integration.
Note
By default, the display names for the voice messaging ports are composed of the port group display name followed by incrementing numbers.
Step 17
On the Port Basics page, enter the following settings. The fields in the following table are the ones that you can change.
Step 18
Click Save.
Step 19
Click Next.
Step 20
Repeat Step 17 through Step 19 for all remaining voice messaging ports for the phone system.
Step 21
If another phone system integration exists, in Cisco Unity Connection Administration, expand Telephony Integrations, then click Trunk. Otherwise, skip to Step 25.
Step 22
On the Search Phone System Trunks page, on the Phone System Trunk menu, click New Phone System Trunk.
Step 23
On the New Phone System Trunk page, enter the following settings for the phone system trunk and click Save.
Step 24
Repeat Step 22 and Step 23 for all remaining phone system trunks that you want to create.
Step 25
If prompted to restart the Connection Conversation Manager service, do the following substeps. Otherwise, continue to Step 26.
a.
In the Navigation drop-down list, click Cisco Unity Connection Serviceability and click Go.
b.
On the Cisco Unity Connection Serviceability page, on the Tools menu, click Control Center - Feature Services.
c.
On the Control Center - Feature Services page, in the Server drop-down list, click the name of the Cisco Unity Connection server and click Go.
d.
Under Cisco Unity Connection Services, click Connection Conversation Manager.
e.
At the top of the page, click Restart.
f.
When prompted to confirm restarting the service, click Yes.
g.
In the Navigation drop-down list, click Cisco Unity Connection Administration and click Go.
h.
In Cisco Unity Connection Administration, expand Telephony Integrations, then click Phone System.
Step 26
In the Related Links drop-down list, click Check Telephony Configuration and click Go to confirm the phone system integration settings.
If the test is not successful, the Task Execution Results displays one or more messages with troubleshooting steps. After correcting the problems, test the connection again.
Step 27
In the Task Execution Results window, click Close.
Step 28
Log off Cisco Unity Connection Administration.
Testing the Integration
To test whether Cisco Unity Connection and the phone system are integrated correctly, do the following procedures in the order listed.
If any of the steps indicate a failure, refer to the following documentation as applicable:
•
The installation guide for the phone system.
•
The setup information earlier in this guide.
To Set Up the Test Configuration
Step 1
Set up two test extensions (Phone 1 and Phone 2) on the same phone system that Cisco Unity Connection is connected to.
Step 2
Set Phone 1 to forward calls to the Cisco Unity Connection pilot number when calls are not answered.
CautionThe phone system must forward calls to the Cisco Unity Connection pilot number in no fewer than four rings. Otherwise, the test may fail.
Step 3
To create a test user for testing, in Cisco Unity Connection Administration, expand Users, then click Users.
Step 4
On the Search Users page, on the User menu, click Add New.
Step 5
On the New User page, enter the following settings.
Step 6
Click Save.
Step 7
On the Edit User Basics page, in the Voice Name field, record a voice name for the test user.
Step 8
In the Phone System field, confirm that the phone system selected is the phone system that Phone 1 is connected to.
Step 9
Uncheck the Set for Self-enrollment at Next Login check box.
Step 10
Click Save.
Step 11
On the Edit menu, click Message Waiting Indicators.
Step 12
On the Message Waiting Indicators page, click the message waiting indicator. If no message waiting indication is in the table, click Add New.
Step 13
On the Edit Message Waiting Indicator page, enter the following settings.
Step 14
Click Save.
Step 15
On the Edit menu, click Transfer Options.
Step 16
On the Transfer Options page, click the active option.
Step 17
On the Edit Transfer Option page, under Transfer Action, click the Extension option and enter the extension of Phone 1.
Step 18
In the Transfer Type field, click Release to Switch.
Step 19
Click Save.
Step 20
Minimize the Cisco Unity Connection Administration window.
Do not close the Cisco Unity Connection Administration window because you will use it again in a later procedure.
Step 21
Log on to Real-Time Monitoring Tool (RTMT).
Step 22
On the Unity Connection menu, click Port Monitor. The Port Monitor tool appears in the right pane.
Step 23
In the right pane, click Start Polling. The Port Monitor will display which port is handling the calls that you will make.
To Test an External Call with Release Transfer
Step 1
From Phone 2, enter the access code necessary to get an outside line, then enter the number outside callers use to dial directly to Cisco Unity Connection.
Step 2
In the Port Monitor, note which port handles this call.
Step 3
When you hear the opening greeting, enter the extension for Phone 1. Hearing the opening greeting means that the port is configured correctly.
Step 4
Confirm that Phone 1 rings and that you hear a ringback tone on Phone 2. Hearing a ringback tone means that Cisco Unity Connection correctly released the call and transferred it to Phone 1.
Step 5
Leaving Phone 1 unanswered, confirm that the state of the port handling the call changes to "Idle." This state means that release transfer is successful.
Step 6
Confirm that, after the number of rings that the phone system is set to wait, the call is forwarded to Cisco Unity Connection and that you hear the greeting for the test user. Hearing the greeting means that the phone system forwarded the unanswered call and the call-forward information to Cisco Unity Connection, which correctly interpreted the information.
Step 7
On the Port Monitor, note which port handles this call.
Step 8
Leave a message for the test user and hang up Phone 2.
Step 9
In the Port Monitor, confirm that the state of the port handling the call changes to "Idle." This state means that the port was successfully released when the call ended.
Step 10
Confirm that the MWI on Phone 1 is activated. The activated MWI means that the phone system and Cisco Unity Connection are successfully integrated for turning on MWIs.
To Test Listening to Messages
Step 1
From Phone 1, enter the internal pilot number for Cisco Unity Connection.
Step 2
When asked for your password, enter the password for the test user. Hearing the request for your password means that the phone system sent the necessary call information to Cisco Unity Connection, which correctly interpreted the information.
Step 3
Confirm that you hear the recorded voice name for the test user (if you did not record a voice name for the test user, you will hear the extension number for Phone 1). Hearing the voice name means that Cisco Unity Connection correctly identified the user by the extension.
Step 4
Listen to the message.
Step 5
After listening to the message, delete the message.
Step 6
Confirm that the MWI on Phone 1 is deactivated. The deactivated MWI means that the phone system and Cisco Unity Connection are successfully integrated for turning off MWIs.
Step 7
Hang up Phone 1.
Step 8
On the Port Monitor, confirm that the state of the port handling the call changes to "Idle." This state means that the port was successfully released when the call ended.
To Set Up Supervised Transfer on Cisco Unity Connection
Step 1
In Cisco Unity Connection Administration, on the Edit Transfer Option page for the test user, in the Transfer Type field, click Supervise Transfer.
Step 2
In the Rings to Wait For field, enter 3.
Step 3
Click Save.
Step 4
Minimize the Cisco Unity Connection Administration window.
Do not close the Cisco Unity Connection Administration window because you will use it again in a later procedure.
To Test Supervised Transfer
Step 1
From Phone 2, enter the access code necessary to get an outside line, then enter the number outside callers use to dial directly to Cisco Unity Connection.
Step 2
On the Port Monitor, note which port handles this call.
Step 3
When you hear the opening greeting, enter the extension for Phone 1. Hearing the opening greeting means that the port is configured correctly.
Step 4
Confirm that Phone 1 rings and that you do not hear a ringback tone on Phone 2. Instead, you should hear the indication your phone system uses to mean that the call is on hold (for example, music).
Step 5
Leaving Phone 1 unanswered, confirm that the state of the port handling the call remains "Busy." This state and hearing an indication that you are on hold mean that Cisco Unity Connection is supervising the transfer.
Step 6
Confirm that, after three rings, you hear the greeting for the test user. Hearing the greeting means that Cisco Unity Connection successfully recalled the supervised-transfer call.
Step 7
During the greeting, hang up Phone 2.
Step 8
On the Port Monitor, confirm that the state of the port handling the call changes to "Idle." This state means that the port was successfully released when the call ended.
Step 9
Click Stop Polling.
Step 10
Exit RTMT.
To Delete the Test User
Step 1
In Cisco Unity Connection Administration, expand Users, then click Users.
Step 2
On the Search Users page, check the check box to the left of the test user.
Step 3
Click Delete Selected.
(Multiple Integrations Only) Adding New User Templates
When you create the first phone system integration, this phone system is automatically selected in the default user template. The users that you add after creating this phone system integration will be assigned to this phone system by default.
However, for each additional phone system integration that you create, you must add the applicable new user templates that will assign users to the new phone system. You must add the new templates before you add new users who will be assigned to the new phone system.
For details on adding new user templates, refer to the "Adding, Changing, or Deleting an Account Template" chapter in the Cisco Unity Connection User Moves, Adds, and Changes Guide at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6509/prod_maintenance_guides_list.html.
For details on selecting a user template when adding a new user, refer to the applicable chapter for adding user accounts in the Cisco Unity Connection User Moves, Adds, and Changes Guide at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6509/prod_maintenance_guides_list.html.
Appendix: Documentation and Technical Assistance
Conventions
The QSIG/DPNSS Phone System with Cisco EGW 2200 Integration Guide for Cisco Unity Connection 2.0 uses the following conventions.
The QSIG/DPNSS Phone System with Cisco EGW 2200 Integration Guide for Cisco Unity Connection 2.0 also uses the following conventions:
Note
Means reader take note. Notes contain helpful suggestions or references to material not covered in the document.
CautionMeans reader be careful. In this situation, you might do something that could result in equipment damage or loss of data.
For descriptions and URLs of Cisco Unity Connection documentation on Cisco.com, see the About Cisco Unity Connection Documentation. The document is shipped with Cisco Unity Connection and is available at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6509/products_documentation_roadmaps_list.html.
Obtaining Documentation, Obtaining Support, and Security Guidelines
For information on obtaining documentation, obtaining support, providing documentation feedback, security guidelines, and also recommended aliases and general Cisco documents, see the monthly What's New in Cisco Product Documentation, which also lists all new and revised Cisco technical documentation, at:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses. Any examples, command display output, and figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
© 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.