-
User Guide for Cisco Secure Access Control Server 4.1
-
Preface
-
Overview
-
Using the Web Interface
-
Network Configuration
-
Shared Profile Components
-
User Group Management
-
User Management
-
System Configuration: Basic
-
System Configuration: Advanced
-
System Configuration: Authentication and Certificates
-
Logs and Reports
-
Administrators and Administrative Policy
-
User Databases
-
Posture Validation
-
Network Access Profiles
-
Unknown User Policy
-
User Group Mapping and Specification
-
Troubleshooting
-
TACACS+ Attribute-Value Pairs
-
RADIUS Attributes
-
CSUtil Database Utility
-
VPDN Processing
-
RDBMS Synchronization Import Definitions
-
Internal Architecture
-
Index
-
Table Of Contents
Administrators and Administrative Policy
Administration Control Privilege
Password Expirations and Account Lockouts
Support for Regulatory Compliance
Adding, Editing, and Deleting Accounts
Administration Control Pages Reference
Add Administrator and Edit Administrator Pages
Administrator Password Policy Page
Administrators and Administrative Policy
This chapter addresses the features in the Administration Control section of the Cisco Secure Access Control Server Release 4.1, hereafter referred to as ACS.
This chapter contains the following topics:
•
Adding, Editing, and Deleting Accounts
•
Administration Control Pages Reference
Administrator Accounts
Administrator accounts provide the only access to the ACS web interface.
This section contains the following topics:
•
Password Expirations and Account Lockouts
•
Support for Regulatory Compliance
About Administrator Accounts
From the Administration Control page, you can link to pages that establish the names, passwords, and privileges for individual administrators or groups of administrators.
ACS administrator accounts are:
•
Unique to ACS and not related to other accounts, such as Windows administrator accounts, ACS TACACS+ accounts, or any other ACS user accounts.
•
Unrelated to external ACS users because ACS stores ACS administrator accounts in a separate internal database.
Privileges
The privileges that you grant to each administrator determine access to areas of the web interface. By default, new administrators do not have any privileges.
Administration Control Privilege
Administrators who have the Administration Control privilege can access the complete Administration Control page. For these administrators, this page provides management of administrators and access to pages that control administrative access policy. Restricted administrators can update their passwords. Figure 11-1 shows the access granted by the administration control privilege.
Figure 11-1 The Administration Control Privilege
Examples of privileges that you can grant to administrators or groups of administrators include:
•
Shared profile components
•
Network, system, and interface configuration
•
Administration control
•
External user databases, posture validation, and network access profiles (NAPs)
•
Reports and activities
For example, you are an administrator with the Administration Control privilege who wants to configure access to the Network Configuration section of the web interface for administrators whose responsibilities include network management. Therefore, you check only the Network Configuration privilege for the applicable administrator accounts.
However, you might want to configure all privileges for an administrator or an administrative group. In this case, you click the Grant All (privileges) option.
The web interface also includes a filter that can control the type of access granted to administrators. For example, you can configure an administrator for read-only access to groups of users, or you can grant them add and edit access to the same groups.
Note
See Chapter 10, "Logs and Reports," for information on generating reports of privileges granted to administrators.
The Influence of Policy
The Administration Control page also includes links to access, session, and password policy configuration pages. These policies influence all account logins and include the following configuration options:
•
Access Policy—IP address limitations, HTTP port restrictions, and secure socket layer (SSL) setup.
•
Session Policy—Timeouts, automatic local logins, and response to invalid IP address connections.
•
Password Policy—Password validation, lifetime, inactivity, and incorrect attempts.
Group Access Privileges
ACS includes options that determine the type of administrator access to groups or users in groups. When enabled, these options grant an administrator the following privileges with respect to any available group:
•
Add or edit user pages
•
Edit group pages
•
Read access to user pages
•
Read access to the group pages
Table 11-1 describes the interaction of the options:
Password Expirations and Account Lockouts
Successful logins take administrators to the main ACS web interface page. However, all logins are subject to the restrictions that have been configured in Administration Control, including expiration, account lockout, and password configuration options.
Limits set for password lifetime and password inactivity can force password change or account lockout. In addition, the limit set for failed attempts can force password change, and privileged administrators can manually lock accounts. In the case of an account lockout, a privileged administrator must unlock the account.
ACS includes the Account Never Expires option that can globally override automatic account lockouts and password configuration options. If the Account Never Expires option is enabled for a specific administrator, all administrator lockout options are ignored.
In the case of an account lockout, ACS displays the Login Process Fail page. Depending on the options, ACS displays the following pages for changing passwords:
•
A password update page appears when you attempt to log in.
•
The Change Password page appears when you click the Administration Control button in the navigation bar, if you do not have the Administration Control privilege. The Change Password page includes a list of the password criteria.
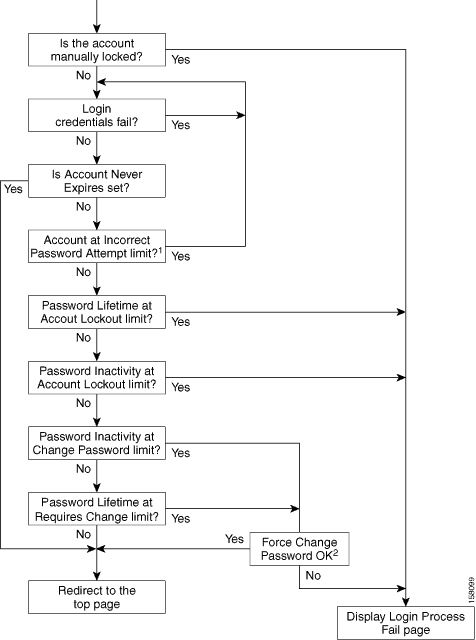
Figure 11-2 shows the process flow at login time.
Figure 11-2 Login Process Flow
1 When the administrator reaches the Incorrect Password Attempts limit, ACS locks the account. At this point, successful attempts will fail. However, if Account Never Expires is set, then the account cannot be locked out.
2 The administrator has successfully logged in. Therefore, if only the password has been incorrectly used, ACS allows retries even though the administrator has exceeded the Incorrect Password Attempt limit.
Support for Regulatory Compliance
ACS includes options that can support regulatory compliance. For example, an administrator with the Administration Control privilege can decide whether to grant the Administration Control privilege to other administrators. Administrators who do not have this privilege cannot access the administrator configuration details.
All administrator logins are subject to the policy that you configure for passwords and accounts, unless you check the Account Never Expires option. For example, ACS provides configurable limits on password lifetime, activity, and incorrect password attempts. These options can force password change and can result in automatic account lockout. Privileged administrators can also lock out an account. In addition, you can monitor the last password change and last account activity for each administrator.
In addition, you can restrict access to reports. For example, you can enable or disable an administrator's ability to change the Administration Audit report configuration.
You can also configure administrator access to user groups. You can selectively choose to allow administrators to setup groups and add or edit users. ACS also provides configuration of administrator read access to users and groups.
Logging In
The ACS login page is the access point for the web interface. If your valid password expires, or if a change in policy affects a password, ACS forces you to change your password when you log in. If you are locked out, contact an administrator who has the Administration Control privilege.
Note
Administrators must have a Windows domain administrator account in order to log in and manage ACS services. However, Windows domain administrators cannot log in to ACS. Only administrators with valid ACS accounts can log in to ACS. For information, see the Installation Guide for Cisco Secure ACS for Windows Release 4.1 or the Installation Guide for Cisco Secure ACS Solution Engine Release 4.1.
ACS for Windows
To log in from a client, you must have an administrator account. However, the Session Policy includes an Allow automatic local login option. If this option is enabled, you can bypass the login page on the server that is running ACS. This option is available for unintentional lockouts. For more information about automatic local logins, see Configuring Session Policy.
ACS Solution Engine
To access the ACS web interface from a browser, log in to ACS by using an administrator account.
The first administrator to log in must create an administrator name and password by using the Add ACS Admin command in the Command Line Interface (CLI) to create the administrator name and password for the first account. For complete information on the CLI, see the "Administering Cisco Secure ACS Solution Engine" chapter of the Installation Guide for Cisco Secure ACS Solution Engine Release 4.1.
In cases where ACS has locked out all administrators, use the Unlock <administrator name> command from the CLI. Only an administrator with the Administration Control privilege can use this command. For complete information on the CLI, see the "Administering Cisco Secure ACS Solution Engine" chapter of the Installation Guide for Cisco Secure ACS Solution Engine Release 4.1.
To log in:
Step 1
To start ACS, click the ACS Admin button in the Cisco Secure ACS program group.
The Cisco Secure ACS login page appears.
Step 2
Type your Username and Password.
Step 3
Click the Login button.
The Cisco Secure ACS main page appears.
Adding, Editing, and Deleting Accounts
Administrators with the Administration Control privilege can add, edit, and delete administrator accounts.
This section contains the following topics:
Adding or Editing Accounts
To add or edit an administrator account:
Step 1
In the navigation bar, click Administration Control.
The Administration Control Page appears if the current account has the Administration Control privilege. Otherwise, a Change Password page appears.
Step 2
Click Add Administrator, and the Add Administrator page appears; or, click the name of the administrator account that you want to edit and the Edit Administrator administrator_name page appears.
Step 3
Type the Administrator Name, Password, and Password Confirmation for new accounts. If necessary, change the Password and Password Confirmation fields for an existing account. For information about these fields, see Add Administrator and Edit Administrator Pages.
Step 4
Check Account Never Expires to prevent the account for this administrator from expiring. For information, see Add Administrator and Edit Administrator Pages.
Step 5
Check the Account Locked check box to lock this account. If the Account Locked check box is checked, uncheck the box to unlock the account.
Step 6
Click Grant All or Revoke All to globally add or remove all privileges. For information on these commands, see Add Administrator and Edit Administrator Pages. Removing privileges from an existing account disables the account.
Step 7
Move the group names between the Available groups and Editable groups list boxes. Groups in the Editable groups list, and associated users, will be available to the current administrator according to the access options that you check.
Step 8
Check the appropriate options to grant access privileges to the Editable groups and associated users. For information on these options, see Add Administrator and Edit Administrator Pages.
Step 9
Check the appropriate options in the Shared Profile Components area to grant access to specific areas of the Shared Profile Components section of the web interface. For information on these options, see Add Administrator and Edit Administrator Pages. For information on shared profile components, see Chapter 4, "Shared Profile Components."
Step 10
Check Network Configuration to grant access to the Network Configuration section of the web interface. For information on network configuration, see Chapter 3, "Network Configuration."
Step 11
Check options in the System Configuration area to grant access to pages in the System Configuration section of the web interface. For information on these options, see Add Administrator and Edit Administrator Pages. For information on system configuration, see Chapter 7, "System Configuration: Basic," Chapter 8, "System Configuration: Advanced," and Chapter 10, "Logs and Reports."
Step 12
Check the Interface Configuration option to grant access to the Interface Configuration section of the web interface. For information on interface configuration, see Chapter 2, "Using the Web Interface."
Step 13
Check the Administration Control option to grant access to the Administration Control section of the web interface.
Step 14
Check the External User Databases option to grant access to the External User Databases section of the web interface. For information on external user databases, see Chapter 12, "User Databases."
Step 15
Check the Posture Validation option to grant access to the Posture Validation section of the web interface. For information on posture validation, see Chapter 13, "Posture Validation."
Step 16
Check the Network Access Profiles option to grant access to the Network Access Profiles section of the web interface. For information on network access profiles, see Chapter 14, "Network Access Profiles."
Step 17
Check options in the Reports and Activities area to grant access to pages in the Reports and Activities section of the web interface. For information on these options, see Add Administrator and Edit Administrator Pages. For information on reports, see Chapter 10, "Logs and Reports."
Step 18
Click Submit.
ACS saves the new administrator account. The new account appears in the list of administrator accounts on the Administration Control page.
Deleting an Account
You use this feature to delete administrator accounts. You can disable an account by clicking the Revoke All button. However, we recommend that you delete any unused administrator accounts.
To delete an account:
Step 1
In the navigation bar, click Administration Control.
ACS displays the Administration Control page.
Step 2
Click the name of the administrator account that you want to delete.
The Edit Administrator administrator_name page appears, where administrator_name is the name of the administrator account that you have selected.
Step 3
Click the Delete button.
ACS displays a confirmation dialog box.
Step 4
Click OK.
ACS deletes the administrator account. The Administrators list on the Administration Control page no longer contains the administrator account.
Configuring Policy Options
The options on these pages control access, session, and password policies.
This section contains the following options:
Configuring Access Policy
If you have the Administration Control privilege, you can use the Access Policy feature to limit access by IP address and by the TCP port range used for administrative sessions. You can also enable the secure socket layer (SSL) for access to the web interface.
Before You Begin
If you want to enable the SSL for administrator access, you must have completed the steps in Installing an ACS Server Certificate, page 9-21, and Adding a Certificate Authority Certificate, page 9-24. After you have enabled SSL, ACS begins using the SSL at the next administrator login. This change does not affect current administrator sessions. In the absence of a certificate, ACS displays an error message when you attempt to configure SSL.
To set up an ACS Access Policy:
Step 1
In the navigation bar, click Administration Control.
ACS displays the Administration Control page.
Step 2
Click Access Policy.
The Access Policy Setup page appears.
Step 3
Click the appropriate IP Address Filtering option. For information on these options, see Access Policy Setup Page.
Step 4
Type the appropriate IP address ranges in accordance with the IP Address Filtering option.
Step 5
Click the appropriate HTTP Port Allocation option to allow all ports or restrict access to certain ports. If you restrict access, type the range of the restricted ports. For information on these options, see Access Policy Setup Page.
Step 6
Check this option if you want ACS to use the SSL. For information on this option, see Access Policy Setup Page.
Step 7
Click Submit.
ACS saves and begins enforcing the access policy settings.
Configuring Session Policy
If you have the Administration Control privilege, you can use the Session Policy controls that enable or disable:
•
Local logins
•
Responses to invalid IP address connections
To set up ACS session policy:
Step 1
In the navigation bar, click Administration Control.
ACS displays the Administration Control page.
Step 2
Click Session Policy.
The Session Policy Setup page appears.
Step 3
Click the appropriate policies and type the appropriate information to set up the policy. For information on these options and fields, see Session Policy Setup Page.
Step 4
Click Submit.
ACS saves and begins enforcing the session policy settings.
Configuring Password Policy
You can access the Administrator Password Policy page from the Password Policy button on the Add Administrator page. If you do not configure the password policy, any administrator can log in, create administrators, and assign privileges.
The Administrator Password Policy provides controls that:
•
Constrain complexity
•
Restrict lifetime
•
Restrict inactive accounts
•
Limit incorrect login attempts
To set up a password policy:
Step 1
In the navigation bar, click Administration Control.
ACS displays the Administration Control page.
Step 2
Click Password Policy.
The Administrator Password Policy page appears.
Step 3
Click the appropriate options and type the appropriate values. For information on these options and fields, see Administrator Password Policy Page.
Step 4
Click Submit.
ACS saves and begins enforcing the password policy settings at the next login.
Administration Control Pages Reference
The following topics describe the pages accessed from the Administration Control button on the navigation bar:
•
Add Administrator and Edit Administrator Pages
•
Administrator Password Policy Page
Administration Control Page
The Administration Control page is the starting point for configuring administrator accounts and policies. Only administrators with the Administration Control privilege can access this page.
To open this page, click the Administration Control button in the navigation bar.
Table 11-2 Administration Control (Privileged Administrator)
Administrators
Lists all configured administrators.
<administrator_name>
Opens the Edit Administrator <administrator_name> page. For information, see the Add Administrator and Edit Administrator Pages.
Add Administrator
Opens the Add Administrator page. For information, see the Add Administrator and Edit Administrator Pages.
Access Policy
Opens the Access Policy Setup page, which controls network access for browsers. For information, see the Administrator Password Policy Page.
Session Policy
Opens the Session Policy Setup page, which provides configuration details for HTTP sessions. For information, see the Session Policy Setup Page.
Password Policy
Opens the Administrator Password Policy page. For information, see the Administrator Password Policy Page.
Related Topics
Add Administrator and Edit Administrator Pages
Use the areas on the Add Administrator and Edit Administrator pages to:
•
Add an administrator (Add Administrator page only)
•
Add, edit, and monitor passwords
•
Monitor and reenable locked out accounts
•
Enable or disable privileges
To open these pages, click Administration Control, and then click Add Administrator or click <administrator_name> to edit an administrator.
Table 11-3 describes the following options:
Related Topics
•
Date Format Control, page 7-3
•
Local Password Management, page 7-4
•
ACS System Restore, page 7-13
•
ACS Active Service Management, page 7-17
•
VoIP Accounting Configuration, page 7-20
•
Appliance Configuration (ACS Solution Engine Only), page 7-20
•
Support Page (ACS Solution Engine Only), page 7-23
•
Viewing or Downloading Diagnostic Logs (ACS Solution Engine Only), page 7-25
•
Appliance Upgrade Status (ACS Solution Engine Only), page 7-26
•
ACS Internal Database Replication, page 8-1
•
RDBMS Synchronization, page 8-17
•
IP Pools Address Recovery, page 8-37
•
Global Authentication Setup, page 9-19
•
ACS Certificate Setup, page 9-20
•
NAC Attribute Management (ACS Solution Engine Only), page 8-37
•
Appliance Configuration (ACS Solution Engine Only), page 7-20
•
About ACS Logs and Reports, page 10-1
•
Password Expirations and Account Lockouts
•
Adding, Editing, and Deleting Accounts
Administrator Password Policy Page
Use the Administrator Password Policy page to set password validation, lifetime, inactivity, and incorrect attempt options. If you do not configure the password policy, any administrator can log in, create administrators, and assign privileges.
To open this page, click Administration Control and then click Password Policy.
ACS returns an error when:
•
The specification is out of range.
•
Users do not meet the criteria on this page.
Table 11-4 describes the following options:
•
Incorrect Password Attempt Options
Access Policy Setup Page
Use the Access Policy Setup page to configure access for IP addresses and ranges, to configure HTTP access, and to set up the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL).
To open the Access Policy Setup page, click Administration Control, and then click Access Policy.
Table 11-5 describes the following options:
Related Topics
•
Installing an ACS Server Certificate, page 9-21
•
Adding a Certificate Authority Certificate, page 9-24
Session Policy Setup Page
Use the Session Policy Setup page to configure session attributes that include timeout, automatic local logins (ACS for Windows only), and response to invalid IP address connections.
To open this page, click Administration Control, and then click Session Policy.
Table 11-6 describes the session configuration options.

 Feedback
Feedback