Table Of Contents
DLSw+ RSVP Bandwidth Reservation
Enable DLSw+ RSVP Bandwidth Reservation
Enable RSVP Support on Specific Peers
Verify DLSw+ RSVP Bandwidth Reservation feature
Disable the DLSw+ RSVP Bandwidth Reservation feature
DLSw+ RSVP Bandwidth Reservation
Feature Summary
The DLSw+ RSVP Bandwidth Reservation feature allows DLSw+ to reserve network bandwidth for the DLSw+ TCP connection between DLSw+ peers.
Benefits
Although it has been possible to reserve bandwidth for a particular existing DLSw+ peer connection through the RSVP command line interface (CLI) support in Cisco IOS software, the CLI required prior knowledge of the TCP ports for which the reservation was being made. Because DLSw+ used one well-known port and one randomly assigned port, the reservation could not be made until after the peer connection was active.
The DLSw+ RSVP Bandwidth Reservation feature permits new DLSw+ peer connections to request bandwidth reservations automatically upon connection, thereby removing the need for user intervention after the peer is connected. This feature ensures the reservation survives a network or device failure and that the DLSw+ traffic carried over a TCP connection is not affected by congestion.
List of Terms
Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP)—IETF standard for allowing applications to request specific Quality of Service (QOS) for specific flows (as specified in RFC 2205).
Platforms
The DLSw+ RSVP Bandwidth Reservation feature is supported on the following platforms:
•
Cisco 1600 series
•
Cisco 1700 series
•
Cisco 2500 series
•
Cisco 2600 series
•
Cisco 3600 series
•
Cisco 3800 series
•
Cisco 4000 series (Cisco 4000, 4000-M, 4500, 4500-M, 4700, 4700-M)
•
Cisco 7200 series
•
Cisco 7500 series
Supported MIBs and RFCs
No MIBs are supported by this feature.
The DLSw+ RSVP Bandwidth Reservation feature supports the following RFCs:
•
RFC 1795
•
RFC 2166
•
RFC 2205
Functional Description
The user specifies the amount of RSVP reserved bandwidth for DLSw+ in the following ways:
•
Globally—When the user configures the dlsw rsvp command, DLSw+ uses these values for initiating RSVP to all its peers.
•
Per peer —When the user configures the dlsw remote peer tcp command, DLSw+ configures the RSVP parameters specifically for this peer connection.
•
Type of peer connection—When the user configures either the dlsw peer-on-demand-defaults or dlsw prom-peer defaults command, DLSw+ uses the configured RSVP parameters for peer-on-demand and promiscuous peer connections, respectively.
In any of these situations, the user turns off RSVP by setting the average-bit-rate or maximum-burst values to 0.
Because RSVP requires both a sender and a receiver, the DLSw+ RSVP Bandwidth Reservation feature must be implemented on both devices of a DLSw+ connection. However, RSVP does not need to be configured on all devices that are in the IP routed path between two DLSw+ peers. In this type of configuration the devices in the middle must support only IP RSVP; they do not need to be configured for the new DLSw+ RSVP Bandwidth Reservation feature or of DLSw+. The devices between the peers prioritize the IP packets belonging to the DLSw+ session according to the IP TOS settings. If, however, the devices in the middle do not support IP RSVP, end-to-end bandwidth is not guaranteed.
In the case of priority peers, RSVP bandwidth reservation is done only for the highest priority connection to the peer (TCP port 2065). If the user configures priority queuing and RSVP on the same peer, the user must ensure that the RSVP designated traffic is assigned to the highest priority TCP peer connection.
If the users change the average-bit-rate or maximum-burst settings without removing the existing RSVP bandwidth reservation, a message warns the users that they are removing the existing reservation and that they need to request a new reservation with new values.
Configuration Tasks
Enable DLSw+ RSVP Bandwidth Reservation
Issuing the dlsw rsvp command enables the DLSw+ RSVP Bandwidth Reservation feature on the router and sets the RSVP parameters for all of its peer connections.
To enable the DLSw+ RSVP Bandwidth Reservation feature, use the following command in global configuration mode:
dlsw rsvp {default | [average-bit-rate maximum-burst]}
Enable DLSw+ RSVP Bandwidth Reservation feature on the local peer.
Enable RSVP Support on Specific Peers
After RSVP is globally enabled, the user must enable RSVP on specific peers. The user can retain the average-bit-rate and maximum-burst values set in the dlsw rsvp command or the user can override these values for any particular peer connection (remote, promiscuous, or peer-on-demand) by configuring the dlsw remote peer, dlsw prom-peer-defaults, or dlsw peer-on-demand-defaults command.
Remote Peers
To enable RSVP support for a remote peer connection, use the following command in global configuration mode:
dlsw remote peer [rsvp {global | [average-bit-rate maximum burst]}]
Configures RSVP parameters for a specific peer connection.
Promiscuous Peers
To enable RSVP support for a promiscuous peer connection, use the following command in global configuration mode:
dlsw prom-peer-defaults [rsvp {global | learn | [average-bit-rate maximum burst]}]
Configures RSVP parameters for this promiscuous peer's connection.
Peer-on-Demand Peers
To enable RSVP support for a peer-on-demand connection, use the following command in global configuration mode
dlsw peer-on-demand-defaults [global | average-bit-rate maximum burst]
Configures RSVP parameters for this peer-on-demand peer's connection.
Verify DLSw+ RSVP Bandwidth Reservation feature
To verify that the RSVP PATH messages for DLSw+ are sent and that the feature is working correctly, use the following command in global configuration mode:
To verify whether the RSVP RESV messages for DLSw+ are sent all the way through the RSVP network to the remote peer, issue the following command in global configuration mode:
To verify that the RSVP bandwidth reservations are in place for the DLSw+ peers, issue the following command in global configuration mode:
show ip rsvp reservation
Verifies that the RSVP reservations are configured for a peer.
Disable the DLSw+ RSVP Bandwidth Reservation feature
To disable the DLSw+ RSVP Bandwidth Reservation feature for all peers, issue the following command in global configuration mode:
Setting the average-bit-rate and maximum burst values to 0 in the dlsw remote peer tcp, dlsw prom-peer defaults, and dlsw peer-on-demand defaults commands turns off RSVP for a particular peer connection.
Note
The reservations made by the DLSw+ RSVP commands can be deleted by the global RSVP commands (for example, no ip rsvp reservation).
Configuration Examples
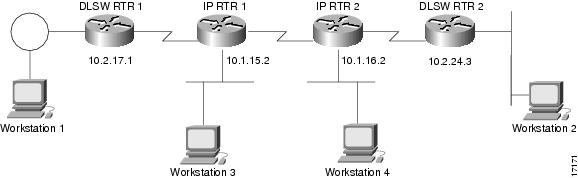
shows a DLSw+ network with the DLSw+ RSVP Bandwidth Reservation feature configured.
Figure 1 DLSw+ RSVP Bandwidth Reservation Feature Configured
DLSWRTR 1 and DLSWRTR 2 are configured for the DLSw+ RSVP Bandwidth Reservation feature with an average bit rate of 40 and a maximum-burst rate of 10.
DLSWRTR 1
dlsw local-peer peer id 10.2.17.1dlsw remote-peer 0 tcp 10.2.24.3dlsw rsvp 40 10DLSWRTR2
dlsw local-peer peer id 10.2.24.3dlsw remote-peer 0 tcp 10.2.17.1dlsw rsvp 40 10The following output of the show ip rsvp sender command on the DLSWRTR2 verifies that PATH messages are being sent from DLSWRTR2:
DLSWRTR2#show ip rsvp senderTo From Pro DPort Sport Prev Hop I/F BPS Bytes10.2.17.1 10.2.24.3 TCP 2065 11003 10K 28K10.2.24.3 10.2.17.1 TCP 11003 2065 10.2.17.1 Et1/1 10K 28KThe following output of the show ip rsvp req command on the DLSWRTR2 verifies that RESV messages are being sent from DLSWRTR2:
DLSWRTR2#show ip rsvp reqTo From Pro DPort Sport Next Hop I/F Fi Serv BPS Bytes10.2.24.3 10.2.17.1 TCP 11003 2065 10.2.17.1 Et1/1 FF RATE 10K 28KIf the IP cloud is able to guarantee the bandwidth requested and the show ip rsvp sender and show ip rsvp req commands are successful, issue the show ip rsvp res command to verify that a reservation was made from DLSWRTR1 to DLSWRTR2:
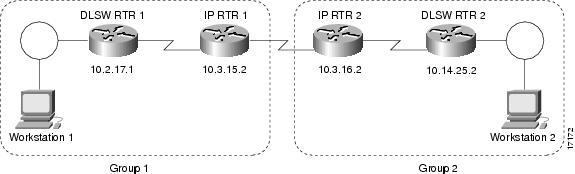
DLSWRTR2#show ip rsvp reseTo From Pro DPort Sport Next Hop I/F Fi Serv BPS Bytes10.2.17.1 10.2.24.3 TCP 2065 11003 10.2.17.1 Et1/1 FF RATE 10K 28K10.2.24.3 10.2.17.1 TCP 11003 2065 FF RATE 10K 28Kshows a DLSw+ border peer network configured with DLSw+ RSVP.
Figure 2 DLSw+ RSVP Bandwidth Reservation Feature and Border Peers
The following example configures DLSWRTR1 to send PATH messages at rates of 40 Kbps and 10KBps and DLSWRTR2 to send PATH messages at rates of
DLSWRTR1
dlsw local-peer peer-id 10.2.17.1 group 1 promiscuousdlsw rsvp defaultdlsw remote-peer 0 tcp 10.3.15.2dlsw peer-on-demand-defaults rsvp 40 10IPRTR1
dlsw local-peer peer-id 10.3.15.2 group 1 border promiscuousdlsw remote-peer 0 tcp 10.3.16.2IPRTR2
dlsw local-peer peer-id 10.3.16.2 group 2 border promiscuousdlsw remote-peer 0 tcp 10.3.15.2DLSWRTR2
dlsw local-peer peer-id 10.14.25.2 group 2 promiscuousdlsw rsvp defaultdlsw remote-peer 0 tcp 10.3.16.2The following output of the show ip rsvp sender command on DLSWRTR2 verifies that PATH messages are being sent from DLSWRTR2:
DLSWRT2#show ip rsvp senderTo From Pro DPort Sport Prev Hop I/F BPS Bytes10.2.17.1 10.14.25.2 TCP 2065 11003 10K 28K10.14.25.2 10.2.17.1 TCP 11003 2065 10.2.17.1 Et1/1 10K 28KThe following output of the show ip rsvp request command on DLSWRTR2 verifies that RESV messages are being sent from DLSWRTR 2:
DLSWRT2#show ip rsvp reqTo From Pro DPort Sport Next Hop I/F Fi Serv BPS Bytes10.14.25.2 10.2.17.1 TCP 11003 2065 10.2.17.1 Et1/1 FF RATE 10K 28KThe following output of the show ip rsvp res command on the DLSWRTR1 verifies that the RSVP reservation was successful:
DLSWRTR1#show ip rsvp reseTo From Pro DPort Sport Next Hop I/F Fi Serv BPS Bytes10.2.17.1 10.14.25.2 TCP 2065 11003 10.14.25.2 Et1/1 FF RATE 10K 28K10.14.25.2 10.2.17.1 TCP 11003 2065 FF RATE 10K 28KCommand Reference
This section documents new or modified commands. All other commands used with this feature are documented in the Cisco IOS Release 12.0 command references.
dlsw peer-on-demand-defaults
Use the dlsw peer-on-demand-defaults global configuration command to configure defaults for peer-on-demand transport. Use the no form of this command to disable the previous assignment.
dlsw peer-on-demand-defaults [fst] [bytes-netbios-out bytes-list-name] [cost cost]
[dest-mac destination-mac-address] [dmac-output-list access-list-number] [rsvp {global |
average-bit-rate maximum burst}] [host-netbios-out host-list-name] [inactivity minutes]
[keepalive seconds] [lf size] [lsap-output-list list] [port-list port-list-number] [priority]
[tcp-queue-max]
no dlsw peer-on-demand-defaults [fst] [bytes-netbios-out bytes-list-name] [cost cost]
[dest-mac destination-mac-address] [dmac-output-list access-list-number] [rsvp global |
average-bit-rate maximum burst] [host-netbios-out host-list-name] [inactivity minutes]
[keepalive seconds] [lf size] [lsap-output-list list] [port-list port-list-number] [priority]
[tcp-queue-max]
Syntax Description
Default
The default peer-on-demand transport is TCP.
Command Mode
Global configuration
Usage Guidelines
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 11.0.
Setting the average-bit-rate and maximum burst values to 0 disables the RSVP bandwidth reservation for the peer connections.
Example
The following example configures FST for peer-on-demand transport:
dlsw peer-on-demand-defaults fstdlsw prom-peer-defaults
Use the dlsw prom-peer-defaults global configuration command to configure defaults for promiscuous transport. Use the no form of this command to disable the previous assignment.
dlsw prom-peer-defaults [fst] [bytes-netbios-out bytes-list-name] [cost cost]
[dest-mac destination-mac-address] [dmac-output-list access-list-number]
[host-netbios-out host-list-name] [keepalive seconds] [lf size]
[lsap-output-list list] [rsvp {global | learn | [average-bit-rate
maximum burst]}] [tcp-queue-max size]
no dlsw prom-peer-defaults [fst] [bytes-netbios-out bytes-list-name] [cost cost]
[dest-mac destination-mac-address] [dmac-output-list access-list-number]
[host-netbios-out host-list-name] [keepalive seconds] [lf size]
[lsap-output-list list] [rsvp {global | learn | [average-bit-rate
maximum burst]}] [tcp-queue-max size]
Syntax Description
Default
The default promiscuous peer transport is TCP.
Command Mode
Global configuration
Usage Guidelines
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 11.0.
A promiscuous peer is a peer not configured as a remote peer on this DLSw+ device, but which initiated a peer connection that was accepted because promiscuous peering was enabled.
Setting the average-bit-rate and maximum burst values to 0 disables the RSVP bandwidth reservation for non-configured remote peers.
Example
The following example configures the cost for promiscuous peers:
dlsw prom-peer-defaults cost 4Related Commands
dlsw remote-peer tcp
Use the dlsw remote-peer tcp global configuration command to identify the IP address of a peer with which to exchange traffic using TCP. Use the no form of this command to remove a remote peer.
dlsw remote-peer list-number tcp ip-address [backup-peer [ip-address | frame-relay
interface serial number dlci-number | interface name]] [bytes-netbios-out bytes-list-name]
[cost cost] [dest-mac mac-address] [dmac-output-list access-list-number]
[host-netbios-out host-list-name] [inactivity minutes] [dynamic] [keepalive seconds]
[lf size] [linger minutes] [lsap-output-list list] [no-llc minutes] [passive] [priority]
[rif-passthru virtual-ring-number] [rsvp {global | [average-bit-rate maximum
burst]}] [tcp-queue-max size] [timeout seconds]
no dlsw remote-peer list-number tcp ip-address [backup-peer [ip-address | frame-relay
interface serial number dlci-number | interface name]] [bytes-netbios-out bytes-list-name]
[cost cost] [dest-mac mac-address] [dmac-output-list access-list-number]
[host-netbios-out host-list-name] [inactivity minutes] [dynamic] [keepalive seconds]
[lf size] [linger minutes] [lsap-output-list list] [no-llc minutes] [passive] [priority]
[rif-passthru virtual-ring-number] [rsvp {global | [average-bit-rate maximum
burst]}] [tcp-queue-max size] [timeout seconds]Syntax Description
Defaults
No peer IP address is identified.
The linger option is inactive. If the linger option is added with no minutes specified, the default is 5 minutes.
The dynamic option is not on by default. If the dynamic option is added without either the inactivity or no-llc argument specified, the default is to terminate the TCP connection to the remote peer after 5 minutes of no active LLC2 connection.
Command Mode
Global configuration
Usage Guidelines
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 10.3. The following keywords and arguments first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 11.1: dynamic, inactivity minutes, linger minutes, no-llc minutes and timeout seconds. The following keywords and arguments first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 11.2: dest-mac mac-address, dmac-output-list access-list-number, linger minutes.
SNA Dial-on-Demand Routing allows switched links to be closed during idle periods. To enable this feature, set the keepalive option to 0 and configure the timeout option. When the dynamic option is configured, the keepalive option is automatically set to 0.
To enhance DDR cost savings, configure the TCP connection to a remote peer to be dynamically established (that is, established only when there is DLSw data to send). You can also configure the TCP connection to terminate after a specified period of idle time on the peer or after a specified period of no active LLC sessions on the peer.
You cannot use both no-llc and inactivity in a command specifying a dynamic peer.
When you need to permit access to a single MAC address, the dest-mac option is an easier option than the dmac-output-list option.
Use the linger option to specify that a backup peer will remain connected for a specified period of time after the primary connection is gone.
When the priority option on the dlsw remote-peer command is configured, DLSw+ automatically activates four TCP ports to that remote peer (ports 2065, 1981, 1982, and 1983) and assigns traffic to specific ports. Furthermore, if APPN is running with DLSw+ and you specify the priority option on the dlsw remote-peer command, then the SNA TOS maps APPN COS to TCP TOS and will preserve the APPN COS characteristics throughout the network.
The rif passthru option works only on Token Ring LANs via SRB. Other LAN types, such as SDLC and QLLC, are not supported. The RIF passthru feature is supported with TCP encapsulation and it disables local acknowledgment.
The following features are not supported with the DLSw+ RIF Passthru feature:
•
Border peers
•
Peer-on-demand peers
•
Dynamic peers
•
Backup peers
Setting the average-bit-rate or maximum burst rate to 0 turns off RSVP for this peer.
Examples
The following example specifies a TCP encapsulation connection for remote peer transport:
dlsw remote-peer 0 tcp 10.2.17.8The following example specifies a TCP peer as backup to a primary FST peer:
dlsw remote-peer 0 fst 10.2.18.9dlsw remote-peer 0 tcp 10.2.17.8 backup-peer 10.2.18.9Related Commands
dlsw rsvp
Use the dlsw rsvp global configuration command to enable the DLSw+ RSVP Bandwidth Reservation feature on the local peer. Use the no form of this command to disable the DLSw+ RSVP Bandwidth Reservation feature for all peers in the router.
dlsw rsvp {default | [average-bit-rate maximum burst]}
no dlsw rsvp {default | [average-bit-rate maximum burst]}Syntax Description
Default
The default values for the average-bit-rate and maximum burst rate are 10 Kbps and 28 KBps, respectively.
Command Mode
Global configuration
Usage Guidelines
This command first appeared in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(3)T.
The DLSw+ RSVP Bandwidth Reservation feature does not require that all peers in a network have RSVP configured. However, the feature does require that the end peer devices are configured with RSVP and that all devices in the middle are IP RSVP capable.
The default value assumes that the DLSw+ peer is connected via a 56 Kbps link. If this is not the case, then the default values will likely not produce optimal results. Even if the line speed is 56 Kbps, the default values (10 Kbps average-bit-rate and 28 KBps maximum burst rate) may not be optimal in a particular network environment and should be changed accordingly.
Example
The following example configures the DLSw+ RSVP Bandwidth Reservation feature with an average-bit-rate of 10 Kbps and a maximum-burst rate of 28 KBps:
dlsw rsvp defaultRelated Commands
dlsw peer-on-demand-defaults
dlsw prom-peer defaults
dlsw remote-peer tcp
show ip rsvp sender
show ip rsvp req
show ip rsvp res