Hardware and VMware Hosting Requirements (top)
The Packaged CCE deployment at the customer site must run in a duplexed environment with a pair of Unified Computing System (UCS) servers. These servers are referred to as Side A Host and Side B Host.
The two Packaged CCE servers must use the same server model.
- Co-residency support = None
- Supported Versions of VMWare vSphere ESXi
- 5.1 update 3, 5.5 update 2 on VM Version 9 for all Unified CVP and Unified CCE components
- 5.1 update 3, 5.5 update 2 on VM Version 8 for all other
Packaged CCE components
Note: Release 11.0(2) and later also supports ESXi 6.0 update 1.
- Supported Hardware
- UCS Tested Reference Configurations for fresh installs or
technology refreshes
- Cisco UCS B200 M4 TRC#1
- Cisco UCS C240 M3S TRC#1
-
Cisco UCS C240 M4SX TRC#1 / BE7000H
Note: Packaged CCE 11.0(2) and ICM11.0(2) ES2 are required to support UCS C240 M4SX TRC#1. The supported firmware version for the UCS C240 M4 hardware is 2.0(9c) or later. - UCS Tested Reference Configurations for common ground
upgrades
- Cisco UCS B200 M3 TRC#1
- Cisco UCS C260 M2 TRC#1
- Cisco UCS C240 M3S TRC#1
- UCS or 3rd-party Specs-based on Intel Xeon = Not supported
- UCS Tested Reference Configurations for fresh installs or
technology refreshes
- Supported Versions of Cisco Nexus 1000V: Refer to the Host Software Version Compatibility matrix for Cisco Nexus 1000V to determine the version that is compatible with the ESXi version that you are running.
When ordering Packaged CCE with the UCS B200 M4, customers must either already have a supported UCS B-Series platform infrastructure and SAN in their data center or must purchase these separately. UCS B-Series blades are not standalone servers and have no internal storage.
For information on the Packaged CCE UCS B Series Fabric Interconnects
Validation Tool, which performs checks on currently deployed UCS B-Series
Fabric Interconnect clusters to determine compliance with Packaged CCE
requirements, refer to
Packaged CCE UCS B-Series Fabric Interconnects Validation Tool. This
tool does not test all UCS B-Series requirements.
UCS-B Series Platform and Hardware Requirements (top)
| UCS-B Platform Series Component | Models Supported | Notes and Additional Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| UCS Blade Server | Cisco UCS B200 M3
Cisco UCS B200 M4 |
If using existing blades, the specification must match either: |
| UCS Blade Server Chassis | Cisco UCS 5108 | |
| UCS Fabric Interconnects |
|
Minimum two matching UCS fabric interconnects per Data Center site. UCS Manager version 2.2(1) minimum. Ethernet End Host mode is required. |
| UCS Fabric Extenders |
|
Two matching UCS fabric extenders per Cisco UCS 5108 Blade Server Chassis. Minimum two 10G connections per Fabric Extender to Fabric Interconnect. |
UCS B-Series Platform Storage Area Network Hardware and Transport Requirements (top)
Packaged CCE deployments on a UCS B-Series platform require a supported Storage Area Network (SAN). Packaged CCE blade servers do not come with internal storage and must use Boot from SAN.
Packaged CCE supports the following SAN transports in FibreChannel (FC) End Host or Switch Mode:
- FibreChannel (FC): FC 2/4/8G
- FibreChannel over Ethernet (FCoE): 10G Ethernet
Packaged CCE requirements for SAN:
- Compatibility with the VMware HCL and UCSM Manager Server
Interoperability list for UCSM version deployed
- Low latency, where VMware realtime performance statistic disk.totalLatency.average does not exceed 60 (milliseconds) for any Packaged CCE datastore (SAN LUN).
- Conforms with Application IOPS and bandwidth requirements met by provisioned LUNs and SAN transport. Refer to the Bandwidth Provisioning and Network QoS Considerations section in this wiki for details on application IOPS and bandwidth requirements.
The following SAN/NAS storage technologies are not supported:
- NFS
- iSCSI
- Infiniband SAN
- Deduplication
SAN LUNs with SATA/SAS 7200 RPM and slower disk drives are only supported where used in Tiered Storage Pools containing SSD (Solid State) and 10000 and/or 15000 RPM SAS/FC HDDs.
While customers may use thin provisioned LUNs, Packaged CCE VMs must be deployed Thick-provisioned, thus SAN LUNs must have sufficient storage space to accommodate all applications VMs on deployment.
UCS B-Series LAN Requirements (top)
| Topology | Requirements | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Common-L2 |
10G Ethernet Uplinks required Each Fabric Interconnect must connect to both of two common-L2 10GE switches (cross-connect) |
Single-link, PortChannel, vPC and VSS uplinks are supported. Visible and Private networks are allowed to be converged northbound of Fabric Interconnects (pinning is not required). |
Side A Server Component Configurations (top)
| Components | vCPU* | RAM (in GB) | HDD (in GB) | CPU Reservation (in MHz) |
Virtual Network Adapter Type | RAM Reservation (in MB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unified CCE Call Server | 4 | 8 | 80 | 5000 | VMXNet3 | 8192 |
| Unified CCE Data Server | 4 | 8 | 80 + 750 | 5100 | VMXNet3 | 8192 |
| Unified CVP Server 1A | 4 | 6 | 150 | 1800 | VMXNet3 | 6144 |
| Unified CVP Server 2A | 4 | 6 | 150 | 1800 | VMXNet3 | 6144 |
| Finesse | 4 | 8 | 146 | 8000 | VMXNet3 | 8192 |
| Unified CVP OAMP Server | 2 | 2 | 80 | 400 | VMXNet3 | 2048 |
| Unified Intelligence Center Publisher | 4 | 10 | 146 | 900 | VMXNet3 | 10GB (10240MB) |
| Unified Communications Manager Publisher | 2 | 8 | 110 | 3600 | VMXNet3 | 8192 |
| Unified Communications Manager Subscriber 1 | 2 | 8 | 110 | 3600 | VMXNet3 | 8192 |
- vCPUs are oversubscribed by design.
Side B Server Component Configurations (top)
| Components | vCPU* | RAM (in GB) | HDD (in GB) | CPU Reservation (in MHz) | Virtual Network Adapter Type | RAM Reservation (in MB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unified CCE Call Server | 4 | 8 | 80 | 5000 | VMXNet3 | 8192 |
| Unified CCE Data Server | 4 | 8 | 80 + 750 | 5100 | VMXNet3 | 8192 |
| Unified CVP Server 1B | 4 | 6 | 150 | 1800 | VMXNet3 | 6144 |
| Unified CVP Server 2B | 4 | 6 | 150 | 1800 | VMXNet3 | 6144 |
| Unified CVP Reporting Server (optional) | 4 | 4 | 72 + 438 | 1800 | VMXNet3 | 4096 |
| Finesse | 4 | 8 | 146 | 8000 | VMXNet3 | 8192 |
| Unified Intelligence Center Subscriber | 4 | 10 | 146 | 900 | VMXNet3 | 10GB (10240MB) |
| Unified Communications Manager Subscriber 2 |
2 | 8 | 110 | 3600 | VMXNet3 | 8192 |
- vCPUs are oversubscribed by design.
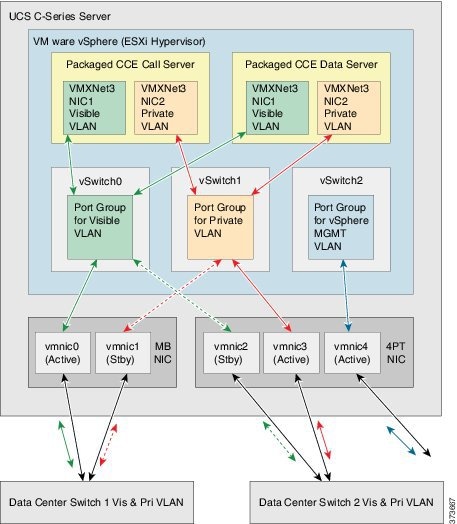
Network Requirements for Cisco UCS C-Series Servers (top)
The illustration below shows the reference design for all Packaged CCE deployments on UCS C-Series servers and the network implementation of the vSphere vSwitch design.
This design calls for using the VMware NIC Teaming (without load balancing) of virtual machine network interface controller (vmnic) interfaces in an Active/Standby configuration through alternate and redundant hardware paths to the network.
The network side implementation does not have to exactly match this illustration, but it must allow for redundancy and must not allow for single points of failure affecting both Visible and Private network communications.
Note: The customer also has the option, at their discretion, to configure VMware NIC Teaming on the Management vSwitch on the same or separate switch infrastructure in the data center.
Requirements:
- Ethernet interfaces must be Gigabit speed and connected to Gigabit Ethernet switches. 10/100 Ethernet is not supported.
- No single point of failure is allowed to affect both the Active and
Standby Visible network links or both the Visible and Private network
communications between Packaged CCE Side A and Side B servers at the
same time.
- Cisco Stacking technology does not meet the high availability
requirements of Packaged CCE network communications.
- A switch stack may not be used for both the Active and Standby Visible network uplinks from a single Packaged CCE server, even if those uplinks connect to separate physical switches within a stack.
- A switch stack may not be used for both the Active Visible and
Active Private network uplinks from a single Packaged CCE server,
even if those uplinks connect to separate physical switches within a
stack.
- Network switches must be configured properly for connection to VMware. Refer to the VMware Knowledge Base for details on ensuring proper switch configuration to prevent Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) delay in failover/fallback scenarios.
VMware vSwitch Design for Cisco UCS C-Series Servers(top)
This figure illustrates a configuration for the vSwitches and vmnic adapters on a UCS C-Series server using the redundant Active/Standby vSwitch NIC Teaming design. The configuration is the same for the Side A server and the Side B server.
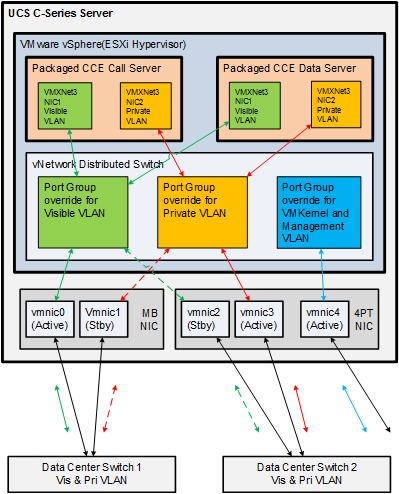
VMware vNetwork Distributed Switch for UCS-C Series Servers (top)
The illustration below shows the reference design for Packaged CCE deployments on UCS C-Series servers with the VMware vNetwork Distributed Switch.
You must use Port Group override, similar to the configuration for the
UCS-B series servers. See the
VMware vSwitch Design for Cisco UCS B-Series Servers section below.
Data Center Switch Configuration for UCS C-Series Server Ethernet Uplinks (top)
Reference and required design for UCS C-Series server Packaged CCE Visible and Private networks Ethernet uplinks uses the VMware default of IEEE 802.1Q (dot1q) trunking, which is referred to as the Virtual Switch VLAN Tagging (VST) mode. This design requires that specific settings be used on the uplink data center switch, as described in the example below.
Improper configuration of up-link ports can directly and negatively impact system performance, operation, and fault handling.
Note: All VLAN settings are given for example purposes. Customer VLANs may vary according to their specific network requirements.
Example: Virtual Switch VLAN Tagging (top)
C3750-A1 interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1 description PCCE_Visible_A_Active switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk allowed vlan 10 switchport mode trunk switchport nonegotiate spanning-tree portfast trunk interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2 description PCCE_Private_A_Standby switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk allowed vlan 100 switchport mode trunk switchport nonegotiate spanning-tree portfast trunk C3750-A2 interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1 description PCCE_Visible_A_Standby switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk allowed vlan 10 switchport mode trunk switchport nonegotiate spanning-tree portfast trunk interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2 description PCCE_Private_A_Active switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk allowed vlan 100 switchport mode trunk switchport nonegotiate spanning-tree portfast trunk C3750-B1 interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1 description PCCE_Visible_B_Active switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk allowed vlan 20 switchport mode trunk switchport nonegotiate spanning-tree portfast trunk interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2 description PCCE_Private_A_Standby switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk allowed vlan 200 switchport mode trunk switchport nonegotiate spanning-tree portfast trunk C3750-B2 interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1 description PCCE_Visible_B_Standby switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk allowed vlan 20 switchport mode trunk switchport nonegotiate spanning-tree portfast trunk interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2 description PCCE_Private_B_Active switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk allowed vlan 200 switchport mode trunk switchport nonegotiate spanning-tree portfast trunk
Note:
- ESXi supports dotlq only.
- DTP is not supported.
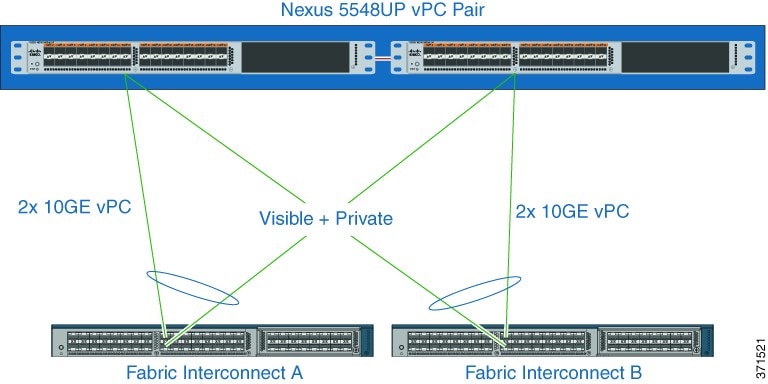
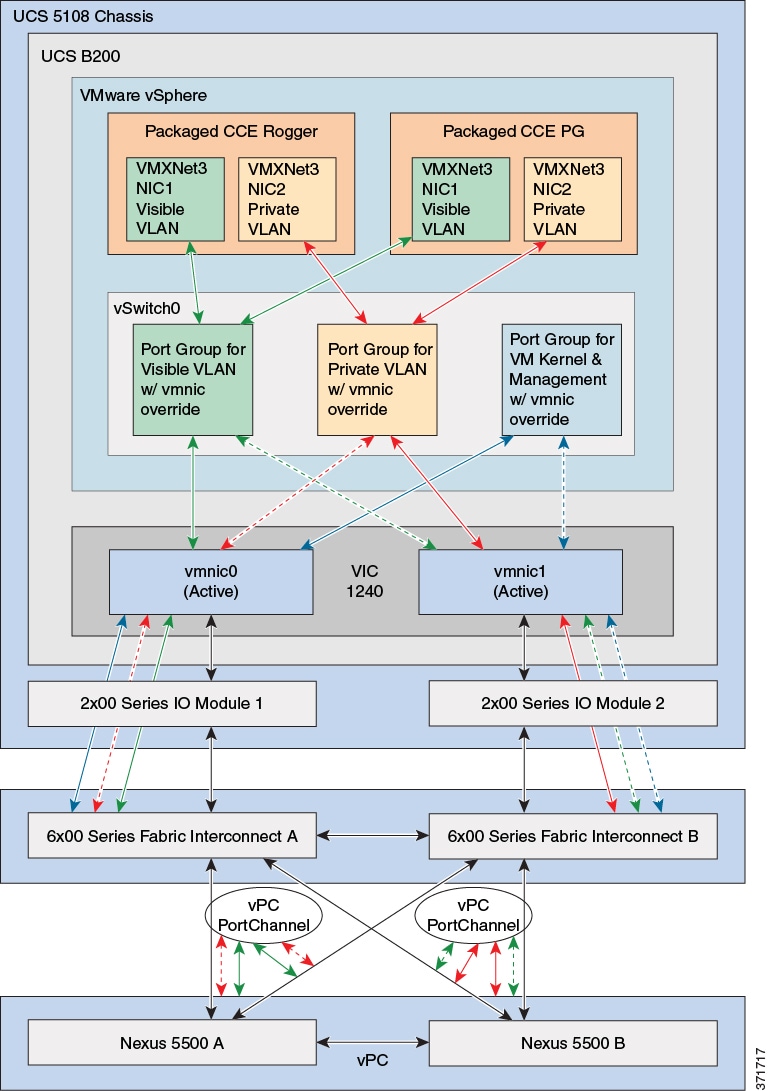
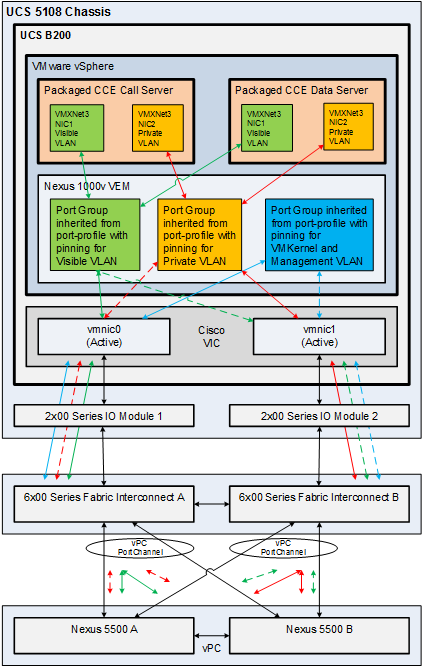
Network Requirements for Cisco UCS B-Series Servers (top)
The figure below shows the virtual to physical Packaged CCE
communications path from application local OS NICs to the data center
network switching infrastructure.
The reference design depicted uses a single virtual switch with two vmnics
in Active/Active mode, with Visible and Private network path diversity
aligned through the Fabric Interconnects using the Port Group vmnic override
mechanism of the VMware vSwitch.
Alternate designs are allowed, such as those resembling that of UCS C-Series servers where each Port Group (VLAN) has its own vSwitch with two vmnics in Active/Standby configuration. In all designs, path diversity of the Visible and Private networks must be maintained so that both networks do not fail in the event of a single path loss through the Fabric Interconnects.
VMware vSwitch Design for Cisco UCS B-Series Servers (top)
The figures in this topic illustrate the two vmnic interfaces with Port
Group override for the VMware vSwitch on a UCS B-Series server using an
Active/Active vmnic teaming design. The configuration is the same for the
Side A and Side B servers.
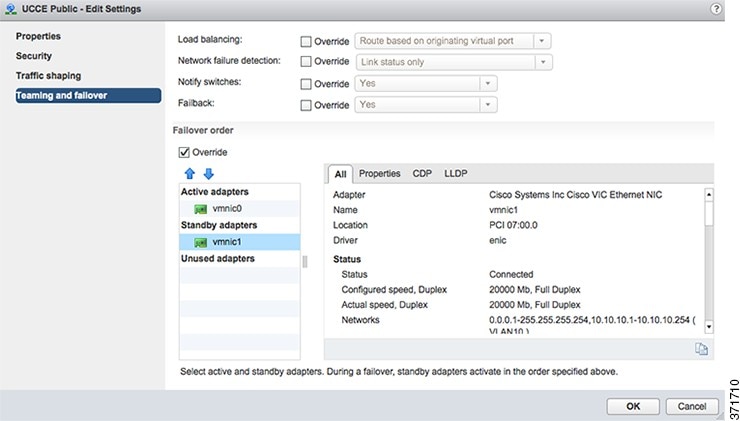
The following figure shows the Public network alignment (preferred path via
override) to the vmnic0 interface.
TThe following figure shows the Private networks alignment to the vmnic1 interface.
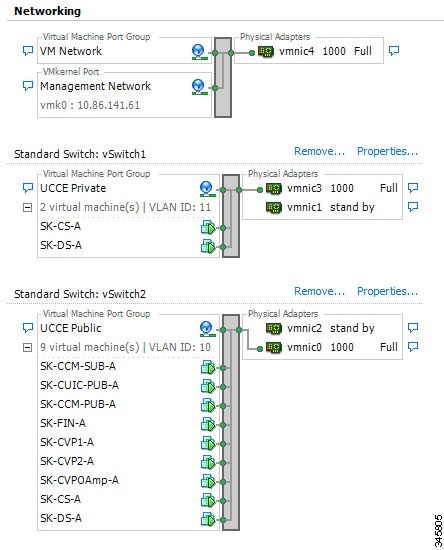
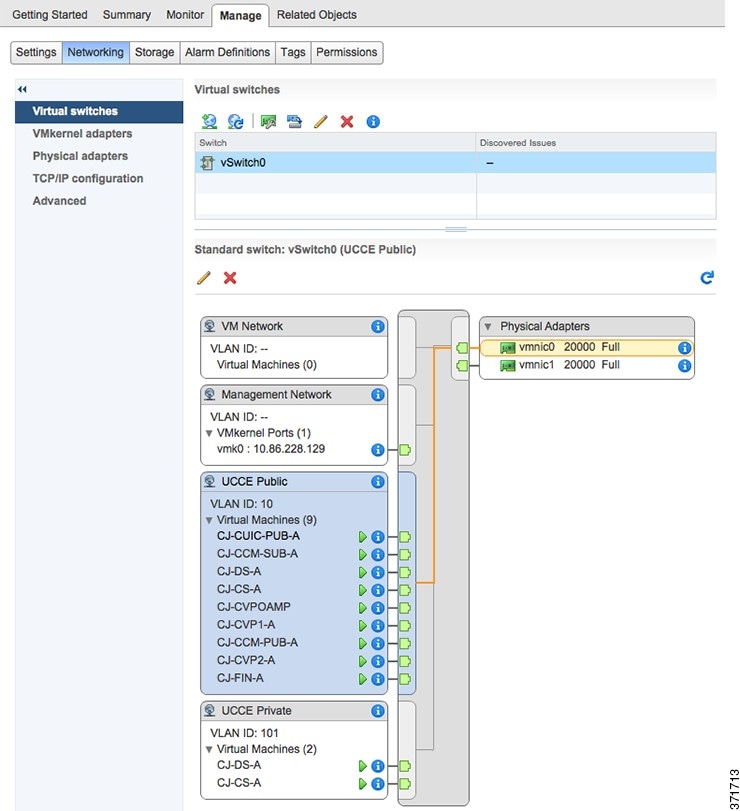
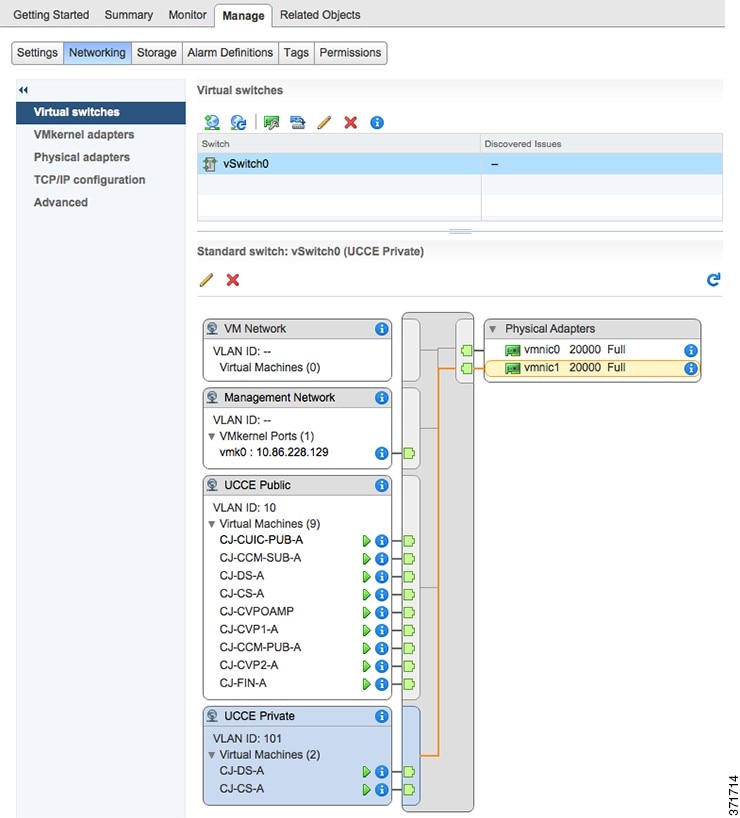
When using Active/Active vmnic interfaces, Active/Stanby can be set per Port Group (VLAN) in the vSwitch dialog in the vSphere Web Client, as shown:
Ensure that the Packaged CCE Visible and Private networks Active and Standby vmnics are alternated through Fabric Interconnects so that no single path failure will result in a failover of both network communication paths at one time. In order to check this, you may need to compare the MAC addresses of the vmnics in vSphere to the MAC addresses assigned to the blade in UCS Manager to determine the Fabric Interconnect to which each vmnic is aligned.
UCS B-Series servers may also be designed to have 6 or more vmnic interfaces with separate vSwitch Active/Standby pairs similar to the design used for UCS C-Series servers. This design still requires that active path for Visible and Private networks be alternated between the two Fabric Interconnects.
VMware vNetwork Distributed Switch Design for Cisco UCS B-Series Servers (top)
Use the UCS B-series example configuration as a guideline for configuring the UCS B-series with a VMware vNetwork Distributed Switch.
Cisco Nexus 1000V Design for Cisco UCS B-Series Servers (top)
The figure below shows the Packaged CCE reference design for Nexus 1000V with UCS B-Series servers.
Except for the reference diagram, the requirements and configuration for the
Nexus 1000V are the same for Packaged CCE and Unified CCE. For details on
using the Nexus 1000V, see
Nexus 1000v Support in Unified CCE.
Data Center Switch Configurations for Cisco UCS B-Series Fabric Interconnect Ethernet Uplink (top)
This topic provides examples of data center switch uplink port configurations for connecting to UCS B-series Fabric Interconnects.
There are several supported designs for configuring Ethernet uplinks from
UCS B-Series Fabric Interconnects to the data center switches for Packaged
CCE. Virtual Switch VLAN Tagging is required, with EtherChannel / Link
Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) and Virtual PortChannel (vPC) being
options depending on data center switch capabilities.
The required and reference design for Packaged CCE Visible and Private
network uplinks from UCS Fabric Interconnects uses a Common-L2 design, where
both Packaged CCE VLANs are trunked to a pair of data center switches.
Customer also may choose to trunk other management (including VMware) and
enterprise networks on these same links, or use a Disjoint-L2 model to
separate these networks from Packaged CCE.Both designs are supported, though
only the Common-L2 model is used here.
Note: All VLAN, vPC and PortChannel IDs and configuration settings are given for example purposes. Customer VLANs, IDs and any vPC timing and priority settings may vary according to their specific network requirements.
Improper configuration of up-link ports can directly and negatively impact system performance, operation, and fault handling.
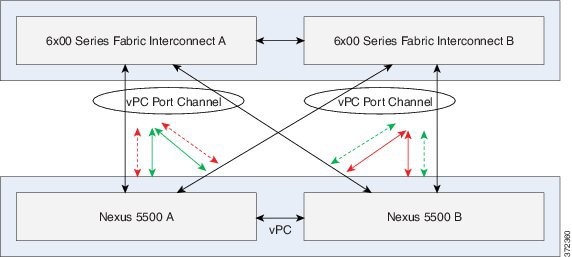
Example 1: vPC Uplinks (top)
In this example, UCS Fabric Interconnect Ethernet uplinks to a pair of Cisco Nexus 5500 series switches using LACP and vPC. UCS Fabric Interconnects require LACP where PortChannel uplinks are used, regardless of whether they are vPC.
Note: Cisco Catalyst 10G switches with VSS also may be used in a similar uplink topology with VSS (MEC) uplinks to the Fabric Interconnects. That IOS configuration is not described here, and differs from the configuration of NX-OS.
N5KA cfs ipv4 distribute cfs eth distribute feature lacp feature vpc feature lldp vlan 1-10,100 vpc domain 1 role priority 1000 system-priority 4000 peer-keepalive destination 10.0.0.2 delay restore 180 peer-gateway auto-recovery interface port-channel1 description vPC_to_FabricA switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 1-10,100 spanning-tree port type edge trunk vpc 1 interface port-channel2 description vPC_to_FabricB switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 1-10,100 spanning-tree port type edge trunk vpc 2 interface port-channel100 description vPC_Peer_Link switchport mode trunk spanning-tree port type network vpc peer-link interface Ethernet1/1 description Uplink-To-FabricA switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 1-10,100 channel-group 1 mode active interface Ethernet1/2 description Uplink-To-FabricB switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 1-10,100 channel-group 2 mode active interface Ethernet1/5 description Interswitch_Link switchport mode trunk channel-group 100 interface Ethernet1/6 description Interswitch_Link switchport mode trunk channel-group 100 interface mgmt0 ip address 10.0.0.1/24 no ip igmp snooping mrouter vpc-peer-link vpc bind-vrf default vlan 4048 N5KB cfs ipv4 distribute cfs eth distribute feature lacp feature vpc feature lldp vlan 1-10,100 vpc domain 1 role priority 2000 system-priority 4000 peer-keepalive destination 10.0.0.1 delay restore 180 peer-gateway auto-recovery interface port-channel1 description vPC_to_FabricA switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 1-10,100 spanning-tree port type edge trunk vpc 1 interface port-channel2 description vPC_to_FabricB switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 1-10,100 spanning-tree port type edge trunk vpc 2 interface port-channel100 description vPC_Peer_Link switchport mode trunk spanning-tree port type network vpc peer-link interface Ethernet1/1 description Uplink-To-FabricA switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 1-10,100 channel-group 1 mode active interface Ethernet1/2 description Uplink-To-FabricB switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 1-10,100 channel-group 2 mode active interface Ethernet1/5 description Interswitch_Link switchport mode trunk channel-group 100 interface Ethernet1/6 description Interswitch_Link switchport mode trunk channel-group 100 interface mgmt0 ip address 10.0.0.2/24 no ip igmp snooping mrouter vpc-peer-link vpc bind-vrf default vlan 4048
Note: Additional interfaces can be added to the vPCs (channel-groups) to increase the aggregate uplink bandwidth. These interfaces must be added symmetrically on both Nexus 5500 switches.
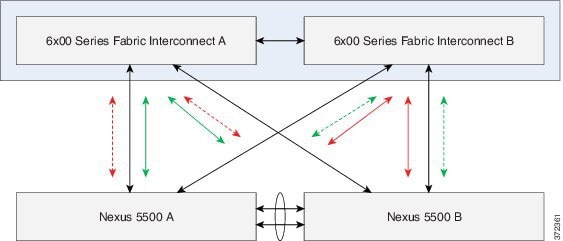
Example 2: Standard Uplinks (top)
In this example, a pair of Cisco Nexus 5500 series switches uplinked to the UCS Fabric Interconnects without PortChannels or vPC (the Nexus 5500 pair may still be vPC enabled).
Note: CCisco Catalyst switches capable of 10G Ethernet also may use a similar uplink topology. That IOS configuration is not described here, and may differ from NX-OS configuration.
N5KA cfs ipv4 distribute cfs eth distribute feature lldp vlan 1-10,100 interface port-channel100 description L2-Interswitch-Trunk switchport mode trunk spanning-tree port type network interface Ethernet1/1 description Uplink-To-FabricA switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 1-10,100 spanning-tree port type edge trunk interface Ethernet1/2 description Uplink-To-FabricB switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 1-10,100 spanning-tree port type edge trunk interface Ethernet1/5 description Interswitch_Link switchport mode trunk channel-group 100 interface Ethernet1/6 description Interswitch_Link switchport mode trunk channel-group 100 N5KB cfs ipv4 distribute cfs eth distribute feature lldp vlan 1-10,100 interface port-channel100 description L2-Interswitch-Trunk switchport mode trunk spanning-tree port type network interface Ethernet1/1 description Uplink-To-FabricA switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 1-10,100 spanning-tree port type edge trunk interface Ethernet1/2 description Uplink-To-FabricB switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 1-10,100 spanning-tree port type edge trunk interface Ethernet1/5 description Interswitch_Link switchport mode trunk channel-group 100 interface Ethernet1/6 description Interswitch_Link switchport mode trunk channel-group 100
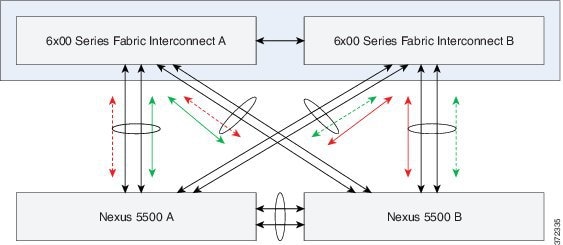
Example 3:EtherChannel Uplinks (top)
In this example, a Nexus 5500 pair with non-vPC PortChannel (EtherChannel
with LACP) uplinks to the UCS Fabric Interconnects.
Note: Cisco Catalyst switches capable of 10G Ethernet also may use a
similar uplink topology. That IOS configuration is not described here, and
may differ from NX-OS
configuration.
N5KA cfs ipv4 distribute cfs eth distribute feature lacp feature lldp vlan 1-10,100 interface port-channel1 description PC_to_FabricA switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 1-10,100 spanning-tree port type edge trunk interface port-channel2 description PC_to_FabricB switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 1-10,100 spanning-tree port type edge trunk interface port-channel100 description Interswitch_Peer_Link switchport mode trunk spanning-tree port type network interface Ethernet1/1 description Uplink-To-FabricA switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 1-10,100 channel-group 1 mode active interface Ethernet1/2 description Uplink-To-FabricA switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 1-10,100 channel-group 1 mode active interface Ethernet1/3 description Uplink-To-FabricB switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 1-10,100 channel-group 2 mode active interface Ethernet1/4 description Uplink-To-FabricB switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 1-10,100 channel-group 2 mode active interface Ethernet1/5 description Interswitch_Link switchport mode trunk channel-group 100 interface Ethernet1/6 description Interswitch_Link switchport mode trunk channel-group 100 N5KB cfs ipv4 distribute cfs eth distribute feature lacp feature lldp vlan 1-10,100 interface port-channel1 description PC_to_FabricA switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 1-10,100 spanning-tree port type edge trunk interface port-channel2 description vPC_to_FabricB switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 1-10,100 spanning-tree port type edge trunk interface port-channel100 description PC_Peer_Link switchport mode trunk spanning-tree port type network interface Ethernet1/1 description Uplink-To-FabricA switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 1-10,100 channel-group 1 mode active interface Ethernet1/2 description Uplink-To-FabricA switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 1-10,100 channel-group 1 mode active interface Ethernet1/3 description Uplink-To-FabricB switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 1-10,100 channel-group 2 mode active interface Ethernet1/4 description Uplink-To-FabricB switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 1-10,100 channel-group 2 mode active interface Ethernet1/5 description Interswitch_Link switchport mode trunk channel-group 100 interface Ethernet1/6 description Interswitch_Link switchport mode trunk channel-group 100
Packaged CCE Application IOPS for SAN Provisioning (top)
This section details the Packaged CCE application IO requirements to be used for Storage Area Networks (SAN) provisioning. You must use these data points to properly size and provision LUNs to be mapped to datastores in vSphere to then host the Packaged CCE applications. Partners and Customers should work closely with their SAN vendor to size LUNs to these requirements.
Packaged CCE on UCS B-Series does not require a fixed or set number of LUNs/Datatores. Instead, customers may use as few as a single, or use a 1 to 1 mapping of application VM to LUN, provided that the Packaged CCE applications IOPS throughput and latency requirements are met. Any given LUN design will vary from vendor to vendor, and SAN model to model. Work closely with your SAN vendor to determine the best solution to meet the given requirements here.
The IOPS provided in this topic are for Packaged CCE on-box components only. For any off-box applications, refer to each application's documentation for IOPS requirements.
Requirements and restrictions for SAN LUN Provisioning include the following:
- VMware vSphere Boot from SAN LUN may not be shared with any Packaged CCE application VMs.Consult VMware and SAN vendor best practices for boot from SAN.
- Thin provisioned LUNs are supported. They must start with sufficient space to house the total required space of all Packaged CCE application VMs, as those VMs vDisks do not support Thin Provisioning.
- Data de-duplication is not supported on the SAN.
- RAID 0 or RAID 1 are not supported for the SANs disk arrays used to house the LUNs created. RAID 0 lacks redundancy and RAID 1 negatively impacts application performance. RAID levels 5, 6, 10 are most common. Other advanced RAID levels offered by your SAN vendor are supported, provided that application IOPS, throughput, and latency requirements are met.
- Tiered storage is supported.
- 7200 RPM or slower drives are not supported for Packaged CCE use in a SAN due to poor latency. The one exception to this requirement is if the drive is used in a Tiered storage pool with 10,000/15,000 RPM drives and with SSD tiers in the same pool.
Note: In the following IOPS and KBps tables:
- Numbers given for 95th Pct, Average, and Peak are totals of Read + Write.
- Requirements are per instance of the given application.
- Any application VM that has multiple vDisks is inclusive of those multiple devices in the sum total values given, and those devices should be deployed on same LUN/Datastore with sufficient resources to meet those requirements.
- Unified CVP Reporting Server IOPS does not include on-box VXML reporting being enabled. If VXML reporting is enabled, see the Unified CVP Reporting Server IOPS requirements on the "Virtualization for Cisco Unified Customer Voice Portal" wiki page, available at Virtualization for Cisco Unified Customer Voice Portal.
| Packaged CCE Component | IOPS | KBps | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 95th Pct | Average | Peak | Write % | 95th Pct | Average | Peak | Write % | |
| Unified CCE Call Server | 67 | 58 | 235 | 90 | 3396 | 2727 | 12023 | 90 |
| Unified CCE Data Server | 671 | 590 | 2715 | 90 | 3360 | 3362 | 353623 | 70 |
| Unified CVP Server | 17 | 13 | 259 | 90 | 462 | 408 | 7448 | 90 |
| Finesse Server | 34 | 30 | 112 | 90 | 1699 | 1404 | 2848 | 90 |
| Unified CVP OAMP Server | 7 | 6 | 82 | 90 | 51 | 35 | 7481 | 90 |
| Unified Intelligence Center | 533 | 436 | 894 | 90 | 3894 | 2446 | 11750 | 90 |
| Unified Communications Manager Publisher | 37 | 34 | 555 | 90 | 577 | 482 | 2786 | 90 |
| Unified Communications Manager Subscriber | 35 | 32 | 564 | 90 | 1174 | 973 | 3409 | 90 |
| Unified CVP Reporting Server | 78 | 23 | 3843 | 90 | 1555 | 306 | 8703 | 90 |
| Unified CCE AW/HDS | 743 | 636 | 6507 | 90 | 3565 | 4999 | 484334 | 30 |
| Packaged CCE Component | IOPS | KBps | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 95th Pct | Average | Peak | Write % | 95th Pct | Average | Peak | Write % | |
| Unified CCE Call Server | 64 | 58 | 89 | 90 | 3200 | 2744 | 3927 | 90 |
| Unified CCE Data Server | 683 | 598 | 4758 | 90 | 5928 | 3406 | 236176 | 70 |
| Unified CVP Server | 17 | 12 | 36 | 90 | 430 | 387 | 1029 | 90 |
| Finesse Server | 33 | 28 | 55 | 90 | 1738 | 1430 | 2576 | 90 |
| Unified CVP OAMP Server | 7 | 6 | 973 | 60 | 35 | 22 | 1437 | 90 |
| Unified Intelligence Center | 612 | 467 | 1066 | 90 | 4158 | 2582 | 13297 | 90 |
| Unified Communications Manager Publisher | 48 | 41 | 450 | 90 | 602 | 531 | 3274 | 90 |
| Unified Communications Manager Subscriber | 37 | 33 | 628 | 90 | 1110 | 979 | 4339 | 90 |
| Unified CVP Reporting Server | 88 | 19 | 2634 | 60 | 1638 | 472 | 68588 | 75 |