-
Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager Configuration Guide, Release 3.4(1a)
-
Index
-
New and Changed Information
-
Preface
- Getting Started
- Installation and Switch Management
- Switch Configuration
-
Fabric Configuration
-
Configuring and Managing VSANs
-
SAN Device Virtualization
-
Creating Dynamic VSANs
-
Configuring Inter-VSAN Routing
-
Configuring and Managing Zones
-
Distributing Device Alias Services
-
Configuring Fibre Channel Routing Services and Protocols
-
Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing
-
Managing FLOGI, Name Server, FDMI, and RSCN Databases
-
Discovering SCSI Targets
-
Configuring FICON
-
Advanced Features and Concepts
-
-
Security
-
Configuring FIPS
-
Configuring Users and Common Roles
-
Configuring SNMP
-
Configuring RADIUS and TACACS+
-
Configuring IPv4 Access Control Lists
-
Configuring Certificate Authorities and Digital Certificates
-
Configuring IPsec Network Security
-
Configuring FC-SP and DHCHAP
-
Configuring Port Security
-
Configuring Fabric Binding
-
- IP Services
- Intelligent Storage Services
- Network and Switch Monitoring
- Traffic Management
- Troubleshooting
-
Launching Fabric Manager in Cisco SAN-OS Releases Prior to 3.2(1)
-
Cisco Fabric Manager Unsupported Feature List
-
Interface Nonoperational Reason Codes
-
Managing Cisco FabricWare
-
Configuration Limits for Cisco MDS SAN-OS Release 3.1(x) and 3.2(x)
-
Table Of Contents
Configuring DPVM with the DPVM Wizard
Configuring DPVM Config and Pending Databases
Activating DPVM Config Databases
About DPVM Database Distribution
Disabling DPVM Database Distribution
Comparing Database Differences
Creating Dynamic VSANs
Port VSAN membership on the switch is assigned on a port-by-port basis. By default each port belongs to the default VSAN.
You can dynamically assign VSAN membership to ports by assigning VSANs based on the device WWN. This method is referred to as Dynamic Port VSAN Membership (DPVM). DPVM offers flexibility and eliminates the need to reconfigure the port VSAN membership to maintain fabric topology when a host or storage device connection is moved between two Cisco MDS switches or two ports within a switch. It retains the configured VSAN regardless of where a device is connected or moved. To assign VSANs statically, see Chapter 1, "Configuring and Managing VSANs."
This chapter includes the following sections:
•
DPVM
DPVM
DPVM configurations are based on port world wide name (pWWN) and node world wide name (nWWN) assignments. A DPVM database contains mapping information for each device pWWN/nWWN assignment and the corresponding VSAN. The Cisco SAN-OS software checks the database during a device FLOGI and obtains the required VSAN details.
The pWWN identifies the host or device and the nWWN identifies a node consisting of multiple devices. You can assign any one of these identifiers or any combination of these identifiers to configure DPVM mapping. If you assign a combination, then preference is given to the pWWN.
DPVM uses the Cisco Fabric Services (CFS) infrastructure to allow efficient database management and distribution. DPVM uses the application driven, coordinated distribution mode and the fabric-wide distribution scope (see Chapter 13, "Using the CFS Infrastructure").
Note
DPVM does not cause any changes to device addressing. DPVM only pertains to the VSAN membership of the device, ensuring that the host gets same VSAN membership on any port on the switch. For example, if a port on the switch has a hardware failure, you can move the host connection to another port on the switch and not need to update the VSAN membership manually.
Note
DPVM is not supported on FL ports. DPVM is supported only on F ports.
This section describes DPVM and includes the following topics:
•
Configuring DPVM with the DPVM Wizard
•
Configuring DPVM Config and Pending Databases
•
Activating DPVM Config Databases
About DPVM Configuration
To use the DPVM feature as designed, be sure to verify the following requirements:
•
The interface through which the dynamic device connects to the Cisco MDS 9000 Family switch must be configured as an F port.
•
The static port VSAN of the F port should be valid (not isolated, not suspended, and in existence).
•
The dynamic VSAN configured for the device in the DPVM database should be valid (not isolated, not suspended, and in existence).
Note
The DPVM feature overrides any existing static port VSAN membership configuration. If the VSAN corresponding to the dynamic port is deleted or suspended, the port is shut down.
To begin configuring DPVM, you must explicitly enable DPVM on the required switches in the fabric. By default, this feature is disabled in all switches in the Cisco MDS 9000 Family.
Configuring DPVM with the DPVM Wizard
To use the DPVM Setup Wizard in Fabric Manager to set up dynamic port VSAN membership, follow these steps:
Step 1
Click the DPVM Setup Wizard icon in the Fabric Manager toolbar (See Figure 28-1).
Figure 28-1 DPVM Wizard Icon
You see the Select Master Switch page.
Step 2
Click the switch you want to be the master switch. This switch controls the distribution of the DPVM database to other switches in the fabric.
Step 3
Click Next.
You see the AutoLearn Current End Devices page.
Step 4
Optionally, click the Create Configuration From Currently Logged In End Devices check box if you want to turn on autolearning.
Step 5
Click Next.
You see the Edit and Activate Configuration page.
Step 6
Verify the current or autolearned configuration. Optionally, click Insert to add more entries into the DPVM config database.
Step 7
Click Finish to update the DPVM config database, distribute the changes using CFS, and activate the database, or click Cancel to exit the DPVM Setup Wizard without saving changes.
About DPVM Databases
The DPVM database consists of a series of device mapping entries. Each entry consists of a device pWWN/nWWN assignment along with the dynamic VSAN to be assigned. You can configure a maximum of 16,000 DPVM entries in the DPVM database. This database is global to the whole switch (and fabric) and is not maintained for each VSAN.
The DPVM feature uses three databases to accept and implement configurations.
•
Configuration (config) database—All configuration changes are stored in the configuration database when distribution is disabled.
•
Active database—The database currently enforced by the fabric.
•
Pending database—All configuration changes are stored in the DPVM pending database when distribution is enabled (see the "DPVM Database Distribution" section).
Changes to the DPVM config database are not reflected in the active DPVM database until you activate the DPVM config database. Changes to the DPVM pending database are not reflected in the config/active DPVM database until you commit the DPVM pending database. This database structure allows you to create multiple entries, review changes, and let the DPVM config and pending databases take effect.
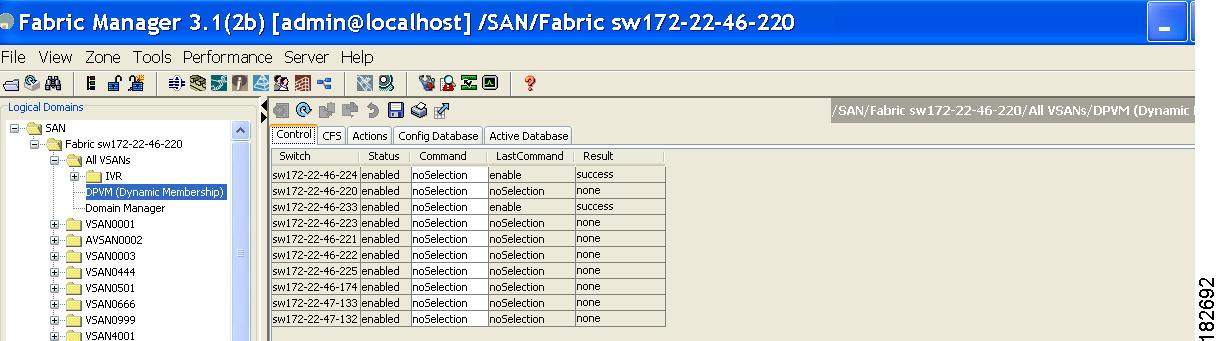
Figure 28-2 shows an example of the DPVM databases in the Information pane in Fabric Manager.
Figure 28-2 DPVM Configuration in Fabric Manager
Configuring DPVM Config and Pending Databases
To create and populate the config and pending databases using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand Fabricxx> All VSANs and then select DPVM in the Logical Attributes pane.
You see the DPVM configuration in the Information pane.
Step 2
Click the CFS tab and select a master switch by checking a check box in the Master column.
Step 3
Click the Config Database tab and then click the Create Row to insert a new entry.
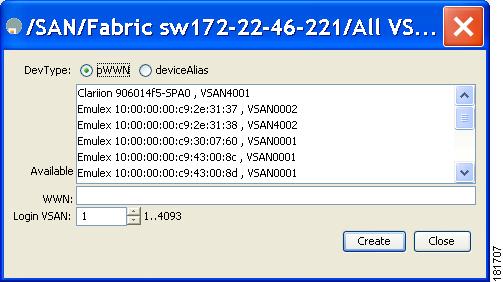
You see the Create Config Database dialog box shown in Figure 28-3.
Figure 28-3 Create Config Database
Step 4
Choose an available WWN and VSAN combination or fill in the pWWN and Login VSAN fields.
Step 5
Click Create to save these changes in the config or pending database or click Close to discard any unsaved changes.
Step 6
Click the CFS tab and select the Config Action drop-down menu for the master database.
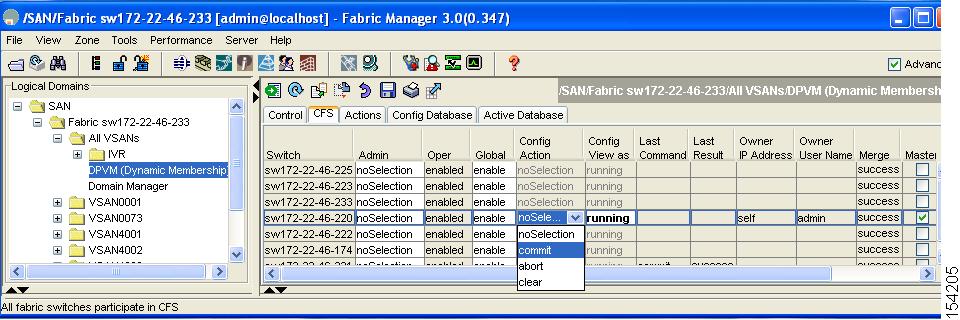
You see the options shown in Figure 28-4.
Figure 28-4 Config Action Drop-down Menu
Step 7
Select commit from the drop-down menu to distribute these changes or abort to discard the changes.
Activating DPVM Config Databases
When you explicitly activate the DPVM config database, the DPVM config database becomes the active DPVM database. Activation may fail if conflicting entries are found between the DPVM config database and the currently active DPVM database. However, you can force activation to override conflicting entries.
To activate the DPVM config database using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand Fabricxx> All VSANs and then select DPVM from the Logical Attributes pane.
You see the DPVM configuration in the Information pane.
Step 2
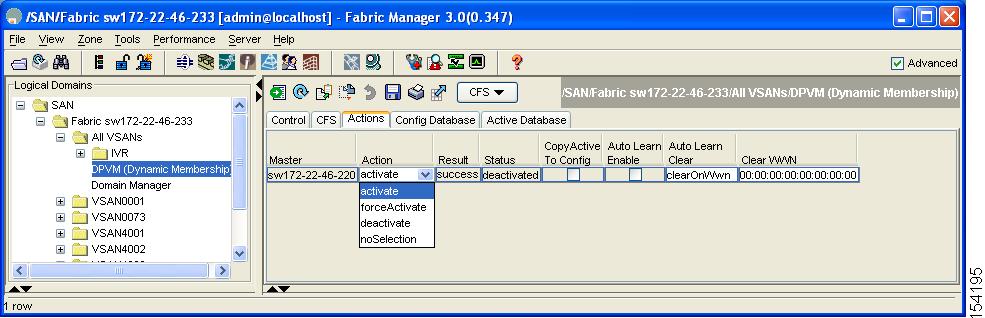
Click the Action tab and set the Action drop-down menu to activate or forceActivate to activate the DPVM config database (see Figure 28-5).
Figure 28-5 Activate a Configured Database
Step 3
Click the CFS tab and select the Config Action drop-down menu for the master database.
You see the options shown in Figure 28-6.
Figure 28-6 Config Action Drop-down Menu
Step 4
Select commit from the drop-down menu to distribute these changes or abort to discard the changes.
Note
To disable DPVM, you must explicitly deactivate the currently active DPVM database.
Viewing the Pending Database
To view the pending database using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand Fabricxx> All VSANs and then select DPVM from the Logical Attributes pane.
You see the DPVM configuration in the Information pane.
Step 2
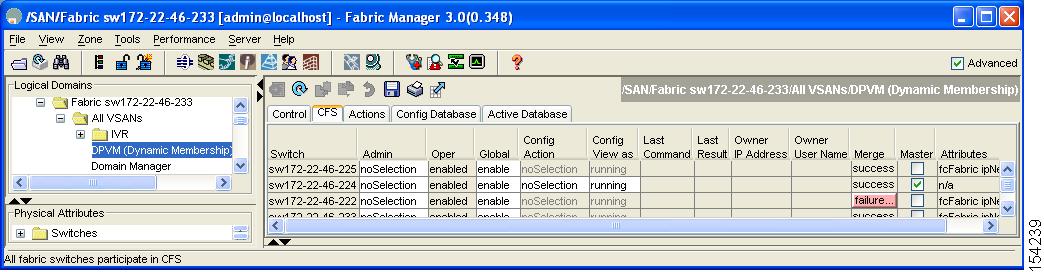
Click the CFS tab and set the Config View drop-down menu to pending (see Figure 28-7).
Figure 28-7 CFS Tab with Master Switch Checked
Step 3
Click Apply Changes.
Step 4
Click the Config Database tab.
You see the pending database entries.
About Autolearned Entries
The DPVM database can be configured to automatically learn (autolearn) about new devices within each VSAN. The autolearn feature can be enabled or disabled at any time. Learned entries are created by populating device pWWNs and VSANs in the active DPVM database. The active DPVM database should already be available to enable autolearn.
You can delete any learned entry from the active DPVM database when you enable autolearn. These entries only become permanent in the active DPVM database when you disable autolearn.
Note
Autolearning is only supported for devices connected to F ports. Devices connected to FL ports are not entered into the DPVM database because DPVM is not supported on FL ports.
The following conditions apply to learned entries:
•
If a device logs out while autolearn is enabled, that entry is automatically deleted from the active DPVM database.
•
If the same device logs multiple times into the switch through different ports, then the VSAN corresponding to last login is remembered.
•
Learned entries do not override previously configured and activated entries.
•
Learning is a two-part process—enabling autolearning followed by disabling autolearning.When the auto-learn option is enabled, the following applies:
–
Learning currently logged-in devices—occurs from the time learning is enabled.
–
Learning new device logins— occurs as and when new devices log in to the switch.
Enabling Autolearning
To enable autolearning using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand Fabricxx> All VSANs and then select DPVM from the Logical Attributes pane.
You see the DPVM configuration in the Information pane.
Step 2
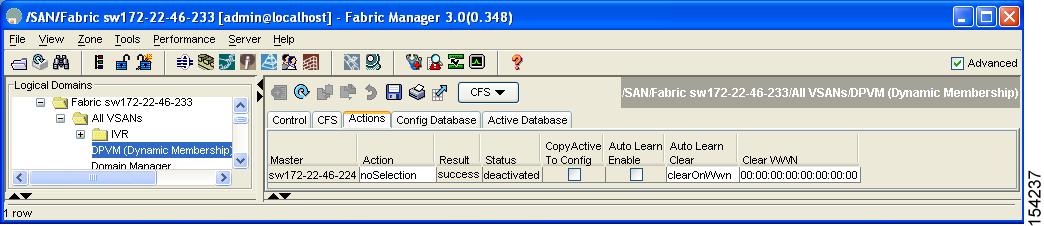
Click the Actions tab and check the Auto Learn Enable check box to enable autolearning (see Figure 28-8).
Figure 28-8 DPVM Actions Tab
Step 3
Click the CFS tab and select commit to distribute these changes or abort to discard the changes.
Clearing Learned Entries
You can clear DPVM entries from the active DPVM database (if autolearn is still enabled) using one of two methods.
To clear a single autolearn entry using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand Fabricxx> All VSANs and then select DPVM from the Logical Attributes pane.
You see the DPVM configuration in the Information pane.
Step 2
Click the Actions tab and select clearOnWWN from the Auto Learn Clear drop-down men.
Step 3
Check the clear WWN check box next to the WWN of the autolearned entry that you want to clear.
Step 4
Click CFS and select commit to distribute these changes or abort to discard the changes.
To clear all autolearn entries using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand Fabricxx> All VSANs and then select DPVM from the Logical Attributes pane.
You see the DPVM configuration in the Information pane.
Step 2
Click the Actions tab.
You see the DPVM Actions menu shown in Figure 28-9.
Figure 28-9 DPVM Actions Tab
Step 3
Select clear from the Auto Learn Clear drop-down menu.
Step 4
Click the CFS tab and select commit to distribute these changes or abort to discard the changes.
Note
These two procedures do not start a session and can only be issued in the local switch.
DPVM Database Distribution
If the DPVM database is available on all switches in the fabric, devices can be moved anywhere and offer the greatest flexibility. To enable database distribution to the neighboring switches, the database should be consistently administered and distributed across all switches in the fabric. The Cisco SAN-OS software uses the Cisco Fabric Services (CFS) infrastructure to achieve this requirement (see Chapter 13, "Using the CFS Infrastructure").
This section describes how to distribute the DPVM database and includes the following topics:
•
About DPVM Database Distribution
•
Disabling DPVM Database Distribution
About DPVM Database Distribution
Using the CFS infrastructure, each DPVM server learns the DPVM database from each of its neighboring switches during the ISL bring-up process. If you change the database locally, the DPVM server notifies its neighboring switches, and that database is updated by all switches in the fabric.
If fabric distribution is enabled, all changes to the configuration database are stored in the DPVM pending database. These changes include the following tasks:
•
Adding, deleting, or modifying database entries.
•
Activating, deactivating, or deleting the configuration database.
•
Enabling or disabling autolearning.
These changes are distributed to all switches in a fabric when you commit the changes. You can also discard (abort) the changes at this point.
Tip
See the "Viewing the Pending Database" section to view the contents of the of the pending database.
Disabling DPVM Database Distribution
These changes are distributed to all switches in a fabric when you commit the changes. You can also discard (abort) the changes at this point.
Tip
See the "Viewing the Pending Database" section to view the contents of the pending database.
To disable DPVM database distribution to the neighboring switches using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand Fabricxx> All VSANs and then select DPVM from the Logical Attributes pane.
You see the DPVM configuration in the Information pane.
Step 2
Click the CFS tab and select disable from the Admin drop-down menu.
Step 3
Click Apply Changes to save this change or click Undo Changes to discard the change.
About Locking the Fabric
The first action that modifies the existing configuration creates the DPVM pending database and locks the feature in the fabric. Once you lock the fabric, the following conditions apply:
•
No other user can make any configuration changes to this feature.
•
A copy of the configuration database becomes the DPVM pending database. Modifications from this point on are made to the DPVM pending database. The DPVM pending database remains in effect until you commit the modifications to the DPVM pending database or discard (abort) the changes to the DPVM pending database.
Locking the Fabric
To lock the fabric and apply changes to the DPVM pending database using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand Fabricxx> All VSANs and then select DPVM from the Logical Attributes pane.
You see the DPVM configuration in the Information pane.
Step 2
Click the Config Database tab and Create Row.
You see the Create Config Database dialog box shown in Figure 28-10.
Figure 28-10 Create Config Database
Step 3
Choose an available pWWN and login VSAN.
Step 4
Click Create to save this change to the pending database or click Close to discard any unsaved change.
Committing Changes
If you commit the changes made to the configuration, the configuration in the DPVM pending database are distributed to other switches. On a successful commit, the configuration change is applied throughout the fabric and the lock is released.
To commit the DPVM pending database using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand Fabricxx> All VSANs and then select DPVM from the Logical Attributes pane.
You see the DPVM configuration in the Information pane.
Step 2
Click the CFS tab and select commit from the Config Action drop-down menu.
Step 3
Click Apply Changes to save this change or click Undo Changes to discard the change.
Discarding Changes
If you discard (abort) the changes made to the DPVM pending database, the configurations remain unaffected and the lock is released.
To discard the DPVM pending database using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand Fabricxx> All VSANs and then select DPVM from the Logical Attributes pane.
You see the DPVM configuration in the Information pane.
Step 2
Click the CFS tab and select abort from the Config Action drop-down menu.
Step 3
Click Apply Changes to save this change or click Undo Changes to discard the change.
Clearing a Locked Session
If you have performed a DPVM task and have forgotten to release the lock by either committing or discarding the changes, an administrator can release the lock from any switch in the fabric. If the administrator performs this task, your changes to the DPVM pending database are discarded and the fabric lock is released.
Tip
The DPVM pending database is only available in the volatile directory and are subject to being discarded if the switch is restarted.
To use administrative privileges and release a locked DPVM session using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand Fabricxx> All VSANs and then select DPVM from the Logical Attributes pane.
You see the DPVM configuration in the Information pane.
Step 2
Click the CFS tab and select clear from the Config Action drop-down menu.
Step 3
Click Apply Changes to save this change or click Undo Changes to discard the change.
Database Merge Guidelines
A database merge refers to a union of the configuration database and static (unlearned) entries in the active DPVM database. See the "CFS Merge Support" section on page 13-9 for detailed concepts.
When merging the DPVM database between two fabric, follow these guidelines:
•
Verify that the activation status and the auto-learn status is the same is both fabrics.
•
Verify that the combined number of device entries in each database does not exceed 16K.
CautionIf you do not follow these two conditions, the merge will fail. The next distribution will forcefully synchronize the databases and the activation states in the fabric.
This section describes how to merge DPVM databases and includes the following topics:
•
Comparing Database Differences
About Copying DPVM Databases
The following circumstances may require the active DPVM database to be copied to the DPVM config database:
•
If the learned entries are only added to the active DPVM database.
•
If the DPVM config database or entries in the DPVM config database are accidently deleted.
Note
If you copy the DPVM database and fabric distribution is enabled, you must commit the changes.
Copying DPVM Databases
To copy the currently active DPVM database to the DPVM config database using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand Fabricxx> All VSANs and then select DPVM in the Logical Attributes pane.
You see the DPVM configuration in the Information pane.
Step 2
Click the Actions tab and check the CopyActive to Config check box.
Step 3
Click the CFS tab and select commit from the Config Action drop-down menu.
Comparing Database Differences
To compare the currently active database entries to the DPVM config database using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand Fabricxx> All VSANs and then select DPVM from the Logical Attributes pane.
You see the DPVM configuration in the Information pane.
Step 2
Click the Active Database tab.
You see the DPVM active database in the Information pane.
Step 3
Select Config from the Compare With drop-down menu.
You see the comparison dialog box.
Step 4
Select Close to close the comparison dialog box.
Default Settings
Table 28-1 lists the default settings for DPVM parameters.
Table 28-1 Default DPVM Parameters
DPVM
Disabled.
DPVM distribution
Enabled.
Autolearning
Disabled.

 Feedback
Feedback