-
Cisco MDS 9020 Fabric Switch Configuration Guide and Command Reference, Release 2.x
-
Index
-
Preface
-
Product Overview
-
Before You Begin
-
Initial Configuration
-
Software Images
-
Managing System Hardware
-
Configuring Interfaces
-
Configuring and Managing Zones
-
Managing FLOGI and FDMI
-
Configuring Switch Security
-
Configuring SNMP
-
Configuring Fibre Channel Routing Services and Protocols
-
Configuring IP Services
-
Configuring Domain Parameters
-
Configuring System Message Logging
-
Advanced Features and Concepts
-
Monitoring System Processes and Logs
-
Cisco SAN-OS Features Supported in CiscoFabricWare
-
Command Reference
-
Table Of Contents
Configuring Fibre Channel Routing Services and Protocols
Displaying Global FSPF Information
Configuring Fibre Channel Routing Services and Protocols
Fabric Shortest Path First (FSPF) is the standard path selection protocol used by Fibre Channel fabrics. The FSPF feature is enabled by default on all Fibre Channel switches. Except in configurations that require special consideration, you do not need to configure any FSPF services. FSPF automatically calculates the best path between any two switches in a fabric. Specifically, FSPF is used to do the following:
•
Dynamically compute routes throughout a fabric by establishing the shortest and quickest path between any two switches.
•
Select an alternative path in the event of the failure of a given path. FSPF supports multiple paths and automatically computes an alternative path around a failed link. It provides a preferred route when two equal paths are available.
This chapter provides details on Fibre Channel routing services and protocols. It includes the following sections:
•
Displaying Global FSPF Information
FSPF Features
FSPF is the protocol currently standardized by the T11 committee for routing in Fibre Channel networks. The FSPF protocol has the following characteristics and features:
•
Supports multipath routing.
•
Bases path status on a link state protocol.
•
Routes hop by hop, based only on the domain ID.
•
Runs only on E ports and provides a loop free topology.
•
Uses a topology database to keep track of the state of the links on all switches in the fabric and associates a cost with each link.
•
Guarantees a fast reconvergence time in case of a topology change. It uses the standard Dijkstra's algorithm, but there is a static dynamic option for a more robust, efficient, and incremental Dijkstra's algorithm.
FSPF Examples
Note
The FSPF feature can be used on any topology.
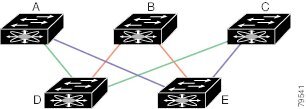
Fault Tolerant Fabric
Figure 11-1 Fault Tolerant Fabric
For example, if all links are of equal speed, the FSPF calculates two equal paths from A to C: A-D-C (green) and A-E-C (blue).
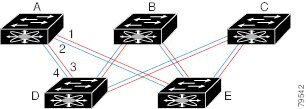
Redundant Links
To further improve on the topology in Figure 11-1, each connection between any pair of switches can be replicated; two or more links can be present between a pair of switches. Figure 11-2 shows this arrangement.
Figure 11-2 Fault Tolerant Fabric with Redundant Links
For example, if all links are of equal speed, the FSPF calculates four equal paths from A to C: A1-E-C, A2-E-C, A3-D-C, and A4-D-C.
Link State Record Defaults
Each time a new switch enters the fabric, a link state record (LSR) is sent to the neighboring switches and then flooded throughout the fabric. Table 11-1 displays the default settings for switch responses.
Clearing FSPF Counters
To clear the FSPF statistics counters for one interface, perform this task:
Displaying Global FSPF Information
Example 11-1 displays global FSPF information:
•
Domain number of the switch.
•
Autonomous region for the switch.
•
Min_LS_arrival: minimum time that must elapse before the switch accepts LSR updates.
•
Min_LS_interval: minimum time that must elapse before the switch can transmit an LSR.
Tip
If the Min_LS_interval is higher than 10 seconds, the graceful shutdown feature is not implemented.
•
LS_refresh_time: interval time lapse between refresh LSR transmissions.
•
Max_age: maximum time aa LSR can stay before being deleted.
Example 11-1 Displays FSPF Information
switch# show fspfFSPF routing administration status is enabledFSPF routing operational status is UPMinLsArrival = 1000 msec , MinLsInterval = 5000 msecLocal Domain is 0x61(97)Number of LSRs = 0Protocol constants :LS_REFRESH_TIME = 30 minutes (1800 sec)MAX_AGE = 60 minutes (3600 sec)Statistics counters :Number of LSR that reached MaxAge = 0Number of SPF computations = 0Number of Checksum Errors = 0Number of Transmitted packets : LSU 0 LSA 0 Hello 0 Retranmsitted LSU 0Number of Received packets : LSU 0 LSA 0 Hello 0 Error Packets 0Displaying FSPF Interfaces
Example 11-2 displays the following information for each selected interface.
•
Link cost
•
Timer values
•
Neighbor's domain ID (if known)
•
Local interface number
•
Remote interface number (if known)
•
FSPF state of the interface
•
Interface counters
Example 11-2 Displays FSPF Interface Information
switch# show fspf interfaceFSPF interface fc1/1FSPF routing administrative state is activeInterface cost is 0Timer intervals configured, Hello 20 s, Dead 80 s, Retransmit 5 sFSPF State is DOWNNeighbor Domain Id is 0x0(0), Neighbor Interface index is 0x00000000Statistics counters :Number of packets received : LSU 0 LSA 0 Hello 0 Error packets 0Number of packets transmitted : LSU 0 LSA 0 Hello 0 Retransmitted LSU 0FSPF interface fc1/2FSPF routing administrative state is activeInterface cost is 0Timer intervals configured, Hello 20 s, Dead 80 s, Retransmit 5 sFSPF State is DOWNNeighbor Domain Id is 0x0(0), Neighbor Interface index is 0x00000000Statistics counters :Number of packets received : LSU 0 LSA 0 Hello 0 Error packets 0Number of packets transmitted : LSU 0 LSA 0 Hello 0 Retransmitted LSU 0FSPF interface fc1/3FSPF routing administrative state is activeInterface cost is 0Timer intervals configured, Hello 20 s, Dead 80 s, Retransmit 5 sFSPF State is DOWNNeighbor Domain Id is 0x0(0), Neighbor Interface index is 0x00000000Statistics counters :Number of packets received : LSU 0 LSA 0 Hello 0 Error packets 0Number of packets transmitted : LSU 0 LSA 0 Hello 0 Retransmitted LSU 0Default Settings
Table 11-2 lists the default settings for FSPF features.

 Feedback
Feedback