Table Of Contents
Providing Protocol Support for Broadband Access Aggregation of PPPoE Sessions
Prerequisites for Providing Protocol Support for Broadband Access Aggregation of PPPoE Sessions
Restrictions for Providing Protocol Support for Broadband Access Aggregation of PPPoE Sessions
Information About Providing Protocol Support for Broadband Access Aggregation for PPPoE Sessions
PPPoE Specification Definition
PPPoE Profile Assignment to a VLAN Without Subinterfaces
PPPoE over VLAN Configuration Without Using Subinterfaces
PPPoE over VLAN Support on ATMs
Benefits of PPPoE over VLAN Scaling and ATM Support for PPPoE over VLANs
Benefits of Autosense for ATMs
Benefits of the Configurable MAC Address for PPPoE Feature
How to Provide Protocol Support for Broadband Access Aggregation of PPPoE Sessions
Assigning a PPPoE Profile to an Ethernet Interface
Assigning a PPPoE Profile to an ATM
Assigning a PPPoE Profile to an ATM Range and Within a Range
Assigning a PPPoE Profile to an ATM VC Class
Assigning a PPPoE Profile to a VLAN Subinterface
Configuring PPPoEoE on a Cisco 7600 SIP-400
Configuration Tasks for PPPoE over Ethernet
Enabling PPPoE over IEEE 802.1Q VLAN
Enabling an ATM to Support Encapsulated PPPoE over IEEE 802.1Q VLAN
Enabling Support for PPPoE over IEEE 802.1Q VLAN in a VC Class
Configuring MAC Addresses for PPPoEoA
Prerequisites for Configurable MAC Address for PPPoE
Configuring PPPoE Session Recovery After Reload
Monitoring and Maintaining PPPoE Profiles
PPPoE Profiles Configuration: Example
MAC Address of the PPPoEoA Session as the Burned-In MAC Address: Example
Address Autoselect Configured and MAC Address Not Configured: Example
PPPoE over 802.1Q VLAN Support on an Ethernet Interface: Example
PPPoE over 802.1Q VLAN Support on ATMs: Example
MAC Address Configured on the ATM Interface: Example
MAC Address Configured on the BBA Group: Example
PPPoE Session Recovery After Reload: Example
Providing Protocol Support for Broadband Access Aggregation of PPPoE Sessions
First Published: May 2, 2005Last Updated: November 27, 2009PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) profiles contain configuration information for a group of PPPoE sessions. Multiple PPPoE profiles can be defined for a device, allowing different virtual templates and other PPPoE configuration parameters to be assigned to different PPP interfaces, VLANs, and ATM permanent virtual circuits (PVCs) that are used in supporting broadband access aggregation of PPPoE sessions.
Note
This module describes the method to configure PPPoE sessions using profiles. If you have configured your PPPoE sessions using a release of Cisco IOS software earlier than Cisco IOS Release 12.4, see the documentation that corresponds to that release. Although the configuration methods used in Cisco IOS software releases prior to Release 12.4 are supported in Release 12.4, it is recommended that you use the configuration methods described in this module for new configurations and when upgrading to Cisco IOS Release 12.4.
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest feature information and caveats, see the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the"Feature Information for Providing Protocol Support for Broadband Access Aggregation for PPPoE Sessions" section.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco IOS and Catalyst OS software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Contents
•
Prerequisites for Providing Protocol Support for Broadband Access Aggregation of PPPoE Sessions
•
Restrictions for Providing Protocol Support for Broadband Access Aggregation of PPPoE Sessions
•
Information About Providing Protocol Support for Broadband Access Aggregation for PPPoE Sessions
•
How to Provide Protocol Support for Broadband Access Aggregation of PPPoE Sessions
Prerequisites for Providing Protocol Support for Broadband Access Aggregation of PPPoE Sessions
•
You must understand the concepts described in the "Understanding Broadband Access Aggregation" module.
•
You must perform the tasks contained in the "Preparing for Broadband Access Aggregation" module.
Restrictions for Providing Protocol Support for Broadband Access Aggregation of PPPoE Sessions
PPPoE profiles separate the configuration of PPPoE from the configuration of virtual private dialup networks (VPDNs). The legacy method of configuring PPPoE in VPDN groups is permitted, but you cannot configure PPPoE profiles and PPPoE in VPDN groups simultaneously.
Note
VPDN is not supported on the Cisco 7600 router in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRC.
If a PPPoE profile is assigned to a PPPoE port (Ethernet, interface, VLAN, or virtual circuit (VC) class), or ATM range and the profile has not yet been defined, the following restrictions are applicable:
•
The port, VC class, or range does not have any PPPoE parameters configured.
•
The port, VC class, or range does not use parameters from the global group.
Only PPPoE over 802.1Q VLAN support can be configured without using subinterfaces on the PPPoE server.
ATM support for PPPoE over 802.1Q VLANs can be configured only on the PPPoE server. Individual VLANs that are configured on subinterfaces can be shut down. Individual VLANs that are configured on the main interface cannot be shut down.
A VLAN range can be configured on a main interface at the same time that VLANs outside the range are configured on subinterfaces of the same main interface. However, you cannot configure a specific VLAN on the main interface and on a subinterface at the same time.
Note
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRC does not support VCs or ATMs.
Information About Providing Protocol Support for Broadband Access Aggregation for PPPoE Sessions
To provide protocol support for broadband access aggregation for PPPoE sessions, you should understand concepts described in the following sections:
•
PPPoE Specification Definition
•
PPPoE Profile Assignment to a VLAN Without Subinterfaces
PPPoE Specification Definition
PPPoE is a specification that defines how a host PC interacts with a common broadband medium (for example, a digital subscriber line (DSL), wireless modem or cable modem) to achieve access to a high-speed data network. Relying on two widely accepted standards, Ethernet and PPP, the PPPoE implementation allows users over the Ethernet to share a connection. The Ethernet principles supporting multiple users in a LAN, combined with the principles of PPP, which apply to serial connections, support this connection.
The base protocol is defined in RFC 2516.
Benefits of PPPoE Profiles
Before the introduction of the use of PPPoE profiles, PPPoE parameters were configured within a VPDN group. Configuring PPPoE in a VPDN group limited PPPoE configuration options because only one PPPoE VPDN group with one virtual template was permitted on a device. The PPPoE Profiles feature provides simplicity and flexibility in PPPoE configuration by separating PPPoE from VPDN configuration. The PPPoE Profiles feature allows multiple PPPoE profiles, each with a different configuration, to be used on a single device.
Note
VPDN is not supported on the Cisco 7600 router in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRC.
Note
This module describes the method for configuring PPPoE sessions using profiles. If you have configured your PPPoE sessions using a release of Cisco IOS software earlier than Cisco IOS Release 12.4, see the documentation that corresponds to that release. Although the configuration methods used in Cisco IOS software releases prior to Release 12.4 are supported in Release 12.4, it is recommended that you use the configuration methods described in the "Providing Protocol Support for Broadband Access Aggregation of PPPoE Sessions" module for new configurations and when upgrading to Cisco IOS Release 12.4.
PPPoE Connection Throttling
Repeated requests to initiate PPPoE sessions can adversely affect the performance of a router and RADIUS server. The PPPoE Connection Throttling feature limits PPPoE connection requests to help prevent intentional denial-of-service attacks and unintentional PPP authentication loops. This feature implements session throttling on the PPPoE server to limit the number of PPPoE session requests that can be initiated from a MAC address or VC during a specified period of time.
PPPoE Profile Assignment to a VLAN Without Subinterfaces
Use PPPoE profile assignment to a VLAN without subinterfaces to improve PPPoE over IEEE 802.Q VLAN functionality in the following two ways:
•
It removes the requirement for each PPPoE VLAN to be created on a subinterface. Removal of this requirement increases the number of VLANs that can be configured on a router from 1001 to 4000 VLANs per interface.
•
It adds ATM support for PPPoE over VLAN traffic that uses bridged RFC 1483 encapsulation.
Note
ATM is not supported on the Cisco 7600 router in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRC.
To configure PPPoE over 802.1Q VLAN support on an interface rather than a subinterface, and to configure ATM support for PPPoE over 802.1Q VLANs, you should understand the concepts described in the following sections:
•
PPPoE over VLAN Configuration Without Using Subinterfaces
•
PPPoE over VLAN Support on ATMs
•
Benefits of PPPoE over VLAN Scaling and ATM Support for PPPoE over VLANs
PPPoE over VLAN Configuration Without Using Subinterfaces
PPPoE profile assignment to a VLAN without subinterfaces removes the requirement for each PPPoE VLAN to be created on a subinterface. Allowing more than one PPPoE VLAN to be configured on a main interface increases the number of VLANs that can be configured on a router from 1001 to 4000 VLANs per interface.
Individual VLANs or a range of VLANs can be configured on an interface. You can configure a VLAN range on a main interface and at the same time configure VLANs outside the range on subinterfaces of the same interface.
PPPoE over VLAN Support on ATMs
PPPoE profile assignment to a VLAN without subinterfaces enables ATMs to process PPPoE over VLAN packets that use bridged RFC 1483 encapsulation. This capability allows PPPoE traffic from different 802.1Q VLANs to be multiplexed over the same ATM.
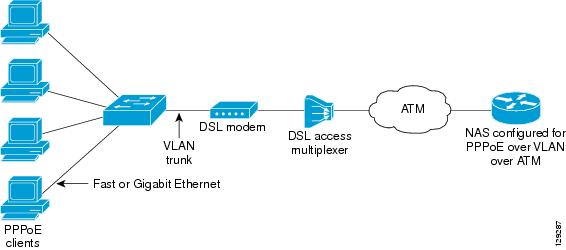
Figure 1 shows a sample network topology that implements PPPoE over VLAN on ATM. In this topology, a service provider is using an Ethernet switch to provide Ethernet service to home users and a single multiplexer to provide the switch with WAN access. The home users use PPPoE to access services on the network access server (NAS). Each port on the switch is assigned a separate VLAN, and the VLANs are trunked over a Fast Ethernet or Gigabit Ethernet interface that is connected to a DSL modem acting as a bridge.
The 802.1Q VLAN-encapsulated traffic coming in from the Ethernet switch trunk is encapsulated in RFC 1483 bridged encapsulation by the DSL modem and sent across the ATM WAN to the NAS. The NAS, which is configured to support PPPoE over VLAN over ATM, will extract the PPPoE packet from the PPPoE over 802.1Q VLAN over RFC 1483 bridged encapsulation and provide PPPoE services to the user.
In the downlink, the NAS sends packets in PPPoE over 802.1Q VLAN over RFC 1483 bridged encapsulation. The DSL modem strips off the RFC 1483 encapsulation and forwards the 802.1Q VLAN packets across the trunk to the switch. The switch then sends the Ethernet packets to the port associated with the 802.1 VLAN ID.
Figure 1 Sample Network Topology for PPPoE over 802.1Q VLAN over ATM
Benefits of PPPoE over VLAN Scaling and ATM Support for PPPoE over VLANs
PPPoE over VLAN scaling and ATM support for PPPoE over VLANs has the following benefits:
•
Increases the number of VLANs that can be configured on a router from 1001 to 4000 VLANs per interface by removing the requirement for each PPPoE VLAN to be configured on a subinterface.
•
Provides support for PPPoE over VLAN over ATM interfaces using RFC 1483 bridged encapsulation.
Autosense for ATMs
The PPPoA/PPPoE Autosense for ATM PVCs feature enables a router to distinguish between incoming PPP over ATM (PPPoA) and PPPoE and to create virtual access based on demand for both PPP types.
Note
The Preauthentication with ISDN PRI and Channel-Associated Signalling feature is supported on Subnetwork Access Protocol (SNAP)-encapsulated ATMs only. It is not supported on multiplexer (MUX)-encapsulated.
Benefits of Autosense for ATMs
Autosense for ATMs provides resource allocation on demand. For each autosense configured for both PPPoA and PPPoE, certain resources (including one virtual-access interface) are allocated upon configuration, regardless of the existence of a PPPoA or PPPoE session on that resource. The autosense for ATMs resources are allocated for PPPoA and PPPoE sessions only when a client initiates a session,thus reducing overhead on the NAS.
Note
Autosense for ATMs supports ATMs only. Switched virtual circuits (SVCs) are not supported.
MAC Address for PPPoEoA
Any change in the usage of MAC addresses will not happen unless it is explicitly configured. This will prevent you from experiencing unexpected behavior resulting from a system change.
Except for using a different MAC address, this feature does not change the way PPPoE works. This change is limited to ATM interfaces only—specifically, PPPoEoA—and will not be applied to other interfaces where PPPoE is operated such as Ethernet, Ethernet VLAN, and Data-over-Cable Service Interface Specifications (DOCSIS). Changing the PPPoE MAC address on those interfaces, which are broadcast in nature, requires placing the interface in promiscuous mode, thereby affecting the performance of the router because the router software has to receive all Ethernet frames and then discard unneeded frames in the software driver.
This feature is disabled by default and applies to all PPPoE sessions on an ATM interface configured in a BBA group.
When PPPoE and RBE are configured on two separate ATMs on the same DSL, the customer premises equipment (CPE) acts like a pure bridge, bridging from Ethernet to the two ATMs on the DSL. Because the CPE acts as a bridge, and because the aggregation router uses the same MAC address for both PPPoE and RBE, the CPE will not be able to bridge packets to the correct MAC address. The solution is to have a different MAC address for PPPoE only. The MAC address can be either configured or selected automatically.
The MAC address of the PPPoEoA session is either the value configured on the ATM interface using the mac-address command or the burned-in MAC address if a MAC address is not already configured on the ATM interface. This functionality is effective only when neither autoselect nor a MAC address is specified on a BBA group.
If the MAC address is specified on a BBA group, all PPPoEoA sessions use the MAC address specified on the BBA group, which is applied on the VC.
If the MAC address is selected automatically, 7 is added to the MAC address of the ATM interface.
Benefits of the Configurable MAC Address for PPPoE Feature
Because the Cisco IOS aggregation routers use the interface MAC address as the source MAC address for all broadband aggregation protocols on that interface, this feature solves problems that may occur when both RBE and PPPoE are deployed on the same ATM interface.
How to Provide Protocol Support for Broadband Access Aggregation of PPPoE Sessions
To provide protocol support for broadband access aggregation by assigning a profile, you must define the profile. The profile definition is required as described in the "Defining a PPPoE Profile" section, and an additional task makes an assignment of the profile to a protocol type.
•
Defining a PPPoE Profile (required)
•
Assigning a PPPoE Profile to an Ethernet Interface (optional)
•
Assigning a PPPoE Profile to an ATM (optional)
•
Assigning a PPPoE Profile to an ATM Range and Within a Range (optional)
•
Assigning a PPPoE Profile to an ATM VC Class (optional)
•
Configuring MAC Addresses for PPPoEoA (optional)
•
Assigning a PPPoE Profile to a VLAN Subinterface (optional)
•
Configuring PPPoEoE on a Cisco 7600 SIP-400
When assigning a PPPoE profile to a VLAN without a subinterface, choose from the following tasks:
•
Enabling PPPoE over IEEE 802.1Q VLAN (optional)
•
Enabling an ATM to Support Encapsulated PPPoE over IEEE 802.1Q VLAN (optional)
•
Enabling Support for PPPoE over IEEE 802.1Q VLAN in a VC Class (optional)
When configuring PPPoE session recovery after a system reload, perform the following task:
•
Configuring MAC Addresses for PPPoEoA (optional)
Defining a PPPoE Profile
Perform this task to define a PPPoE profile.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
bba-group pppoe {group-name | global}
4.
virtual-template template-number
5.
sessions max limit number-of-sessions [threshold threshold-value]
6.
sessions per-mac limit per-mac-limit
7.
sessions per-vlan limit per-vlan-limit [inner vlan-id]
8.
sessions per-vc limit per-vc-limit [threshold threshold-value]
9.
sessions {per-mac | per-vc} throttle session-requests session-request-period blocking-period
10.
ac name name
11.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Assigning a PPPoE Profile to an Ethernet Interface
Perform this task to assign a PPPoE profile to an Ethernet interface.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
interface ethernet number
4.
pppoe enable [group group-name]
5.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Assigning a PPPoE Profile to an ATM
Perform this task to assign a PPPoE profile to an ATM .
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
interface atm number[.subinterface-number {multipoint | point-to-point}]
4.
pvc [name] vpi/vci [ilmi | l2transport | qsaal]
5.
protocol pppoe [group group-name]
or
encapsulation aal5autoppp virtual-template number [group group-name]
6.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Assigning a PPPoE Profile to an ATM Range and Within a Range
Perform this task to assign a PPPoE profile to an ATM range and within a range.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
interface atm number [.subinterface-number {multipoint | point-to-point}]
4.
range [range-name] pvc [start-vpi/]start-vci [end-vpi/]end-vci
5.
protocol pppoe [group group-name]
or
encapsulation aal5autoppp virtual-template number [group group-name]
6.
pvc-in-range [-name] [[vpi/]vci]
7.
protocol pppoe [group group-name]
or
encapsulation aal5autoppp virtual-template number [group group-name]
8.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Assigning a PPPoE Profile to an ATM VC Class
Perform this task to assign a PPPoE profile to an ATM VC class.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
vc-class atm vc-class-name
4.
protocol pppoe [group group-name]
or
encapsulation aal5autoppp virtual-template number [group group-name]
5.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Assigning a PPPoE Profile to a VLAN Subinterface
Perform this task to assign a PPPoE profile to a VLAN subinterface.
Note
This configuration method requires the use of subinterfaces. One subinterface supports one VLAN.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
interface range {fastethernet interfacenumber - interfacenumber | gigabitethernet interfacenumber - interfacenumber | loopback number | tunnel number | port-channel number | vlan number | macro keyword}
4.
encapsulation dot1q vlan-id second-dot1q {any | vlan-id} [native]
5.
protocol pppoe [group group-name]
6.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring PPPoEoE on a Cisco 7600 SIP-400
PPP provides a standard method of communicating to peers over a point-to-point link. An Ethernet link provides multipoint communication between multiple peers. PPPoE allows point-to-point communication across multipoint Ethernet links.
The PPPoE over Ethernet interface (PPPoEoE) enables the Cisco 7600 series router with a Cisco 7600 SIP-400 to tunnel and terminate Ethernet PPP sessions over Ethernet links. The PPPoE over IEEE 802.1Q VLANs feature enables the router to tunnel and terminate Ethernet PPP sessions across VLAN links. IEEE 802.1Q encapsulation is used to interconnect a VLAN-capable router with another VLAN-capable networking device. The packets on the 802.1Q link contain a standard Ethernet frame and the VLAN information associated with that frame.
PPPoEoE on Cisco 7600 SIP-400 supports the following features:
•
PPPoE discovery packets (rate-limited), PPPoE PPP control packets, and PPPoE PPP IP data packets provide a per-user session on an Ethernet interface.
•
PPPoE is supported on main interfaces, 802.1q and QinQ access interfaces, and VLAN ranges (802.1q ranges and QinQ inner ranges).
•
8000 PPPoE sessions are supported.
•
PPPoE and IP sessions can be configured on the same subinterface.
Restrictions
•
PPPoA and any PPP feature on ATM interfaces are not supported.
•
Ambiguous VLANs and a range of VLANs for IP session interfaces are not supported. However, a range of VLANs is supported for PPPoE-configured interfaces.
•
Negotiated maximum transmission unit (MTU) value can only be 1492 or 1500 bytes.
•
If the ip tcp adjust-mss command is used, the only value supported is 1468.
•
PPPoE can be configured only on subinterfaces.
•
Layer 2 Tunnel Protocol (L2TP) tunneling of PPPoE sessions is not supported.
Configuration Tasks for PPPoE over Ethernet
To configure PPPoE over Ethernet, perform the following tasks:
•
Configuring a Virtual Template Interface (required)
•
Monitoring Virtual Access Interface (required)
•
Creating an Ethernet Interface and Enabling PPPoE (required)
•
Configuring a BBA Group to Establish PPPoE Sessions (required)
•
Configuring PPPoE over 802.1Q VLANs on a Cisco 7600 Router With a SIP-400 (required)
Configuring a Virtual Template Interface
Configure a virtual template interface before you configure PPPoE on an Ethernet interface. The virtual template interface is a logical entity that is applied dynamically as needed to an incoming PPP session request. Perform this task to create and configure a virtual template interface:
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
interface virtual-template number [type [ethernet | serial | tunnel]]
4.
ip unnumbered ethernet number
5.
mtu bytes
6.
ppp authentication chap
7.
ppp ipcp ip address required
8.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Examples
The following example shows the configuration of a virtual template interface:
Router(config)# interface virtual-template 1Router(config)# ip unnumbered21 Loopback1Router(config-if)# no peer default ip addressRouter(config-if)# ppp authentication chapRouter(config-if)# ppp authorizationRouter(config-if)# ppp accountingMonitoring Virtual Access Interface
When a virtual template interface is applied dynamically to an incoming user session, a virtual access interface (VAI) is created. You cannot use the command-line to directly create or configure a VAI. Perform this task to monitor the VAI and free the memory for other dial-in uses.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
show interfaces virtual-access number [configuration]
3.
clear interface virtual-access number
DETAILED STEPS
Examples
The following example shows how to display the active VAI configuration:
Router# show interfaces virtual-access 1.1 configuration!interface virtual-access1.1if vrf forwarding vrf-1ip unnumbered Loopback1no ip proxy-arppeer default ip address pool vrf-1ppp authentication chapend
Note
Virtual-access 1.1 is a PPPoE subinterface.
Creating an Ethernet Interface and Enabling PPPoE
Perform this task to create an Ethernet interface and enable PPPoE on it.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
interface GigabitEthernet number
4.
pppoe enable [group group-name]
5.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring a BBA Group to Establish PPPoE Sessions
Note
Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRC does not support the configuration of broadband aggregation (BBA) groups using RADIUS. You must configure BBA groups manually.
Perform this task to configure a BBA group to establish PPPoE sessions and link it to the appropriate virtual template interface.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
bba-group pppoe name
4.
virtual-template template-number
5.
sessions per-mac limit per-mac-limit
6.
sessions max limit number-of-sessions [threshold threshold-value]
7.
sessions per-vc limit per-vc-limit [threshold threshold-value]
8.
exit
9.
interface type-number
10.
encapsulation dot1q vlan-id
11.
protocol pppoe group group-name
12.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring PPPoE over 802.1Q VLANs on a Cisco 7600 Router With a SIP-400
PPPoE over IEEE 802.1Q VLANs enables the Cisco 7600 series router with a SIP-400 to support PPPoE over IEEE802.1Q encapsulated VLAN interfaces. IEEE 802.1Q encapsulation is used to interconnect a VLAN-capable router with another VLAN-capable networking device. The packets on the 802.1Q link contain a standard Ethernet frame and the VLAN information associated with that frame. Perform the following tasks to configure PPPoE on a Cisco 7600 router with a SIP-400:
•
Configuring a Virtual Template
•
Creating an Ethernet 802.1Q Encapsulated Subinterface and Enabling PPPoE
•
Verifying PPPoE over Ethernet
Note
PPPoE is disabled by default on a VLAN.
Configuring a Virtual Template
Before configuring PPPoE on an IEEE 802.1Q VLAN interface, configure a virtual template. See the "Configuring a Virtual Template Interface" section.
Creating an Ethernet 802.1Q Encapsulated Subinterface and Enabling PPPoE
Perform this task to create an Ethernet 802.1Q interface and enable PPPoE on it.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
interface gigabitethernet slot/subslot/port
4.
encapsulation dot1q vlan-id second-dot1q {any | vlan-id} [native]
5.
exit
6.
bba-group pppoe {bba-group-name | global}
7.
pppoe enable [group group-name]
8.
pppoe max-sessions number
9.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Verifying PPPoE over Ethernet
Perform this task to verify PPPoEoE.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
show pppoe session all
3.
show pppoe session packets
4.
show pppoe summary
DETAILED STEPS
Clearing PPPoE Sessions
Perform this task to clear the PPPoE sessions.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
clear pppoe all
3.
clear pppoe {interface type number [vc {[vpi/]vci | vc-name}]
4.
clear pppoe rmac mac-address [sid session-id]
5.
clear pppoe interface type number[vlan vlan -number]
DETAILED STEPS
Enabling PPPoE over IEEE 802.1Q VLAN
Perform this task to enable PPPoE over IEEE 802.1Q VLAN support on a main Ethernet interface.
The PPPoE over VLAN Enhancements: Configuration Limit Removal and ATM Support feature removes the requirement for each PPPoE VLAN to be created on a subinterface. Allowing more than one PPPoE VLAN to be configured on a main interface increases the number of VLANs that can be configured on a router from 1001 to 4000 VLANs per interface.
Individual VLANs or a range of VLANs can be configured on an interface. You can configure a VLAN range on a main interface and at the same time configure VLANs outside the range on subinterfaces of the same interface.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
interface type number
4.
vlan-id dot1q vlan-id
or
vlan-range dot1q start-vlan-id end-vlan-id
5.
pppoe enable [group group-name]
6.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Enabling an ATM to Support Encapsulated PPPoE over IEEE 802.1Q VLAN
Perform the following task to enable an ATM to support encapsulated PPPoE over IEEE 802.1Q VLAN traffic. The PPPoE over VLAN Enhancements: Configuration Limit Removal and ATM Support feature enables ATMs to process PPPoE over VLAN packets that use bridged RFC 1483 encapsulation. This capability allows PPPoE traffic from different 802.1Q VLANs to be multiplexed over the same ATM.
For more information, see the "PPPoE over VLAN Support on ATMs" section.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
interface atm number.subinterface-number {multipoint | point-to-point}
4.
pvc [name] vpi/vci
5.
protocol pppovlan dot1q {vlan-id | start-vlan-id end-vlan-id} [group group-name]
6.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Enabling Support for PPPoE over IEEE 802.1Q VLAN in a VC Class
Perform the following task to enable support for PPPoE over IEEE 802.1Q VLANs in a VC class.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
vc-class atm name
4.
protocol pppovlan dot1q {vlan-id | start-vlan-id end-vlan-id} [group group-name]
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring MAC Addresses for PPPoEoA
You can configure the MAC address on ATMs in a BBA group to use a different MAC address for PPP over Ethernet over ATM (PPPoEoA).
Perform this task to configure different MAC addresses on PPPoEoA and enable the aggregation router to bridge packets from Ethernet to the appropriate MAC addresses..
Prerequisites for Configurable MAC Address for PPPoE
A BBA group profile should already exist. The BBA group commands are used to configure broadband access on aggregation and client devices that use PPPoA, PPPoE, and Routed Bridge Encapsulation (RBE).
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
bba-group pppoe {bba-group-name | global}
4.
mac-address {autoselect | mac-address}
5.
exit
6.
show pppoe session
7.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Examples
The following example shows the display of the MAC address as LocMac:
Router# show pppoe session1 session in LOCALLY_TERMINATED (PTA) State1 session totalUniq ID PPPoE RemMAC Port VT VAStateSID LocMAC VA-st3 3 000b.fdc9.0001 ATM3/0.1 1 Vi2.1PTA0008.7c55.a054 VC: 1/50 UPLocMAC is burned in mac-address of ATM interface(0008.7c55.a054).Configuring PPPoE Session Recovery After Reload
Perform this task to configure the aggregation device to send PPPoE active discovery terminate (PADT) packets to the CPE device upon receipt of PPPoE packets on "half-active" PPPoE sessions (a PPPoE session that is active on the CPE end only).
If the PPP keepalive mechanism is disabled on a CPE device, a PPPoE session will pause indefinitely after an aggregation device reload. The PPPoE Session Recovery After Reload feature enables the aggregation device to attempt to recover PPPoE sessions that failed because of reload by notifying CPE devices about the PPPoE session failures.
The PPPoE protocol relies on the PPP keepalive mechanism to detect link or peer device failures. If PPP detects a failure, it terminates the PPPoE session. If the PPP keepalive mechanism is disabled on a CPE device, the CPE device has no way to detect link or peer device failures over PPPoE connections. When an aggregation router that serves as the PPPoE session endpoint reloads, the CPE device will not detect the connection failure and will continue to send traffic to the aggregation device. The aggregation device will drop the traffic for the failed PPPoE session.
The sessions auto cleanup command enables an aggregation device to attempt to recover PPPoE sessions that existed before a reload. When the aggregation device detects a PPPoE packet for a half-active PPPoE session, the device notifies the CPE of the PPPoE session failure by sending a PPPoE PADT packet. The CPE device is expected to respond to the PADT packet by taking failure recovery action.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
bba-group pppoe {group-name | global}
4.
virtual-template template-number
5.
sessions auto cleanup
6.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Troubleshooting Tips
Use the show pppoe session and debug pppoe commands to troubleshoot PPPoE sessions.
Monitoring and Maintaining PPPoE Profiles
Perform this task to monitor and maintain PPPoE profiles.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
show pppoe session [all | packets]
3.
clear pppoe {interface type number [vc {[vpi/]vci | vc-name}] | rmac mac-addr [sid session-id] | all}
4.
debug pppoe {data | errors | events | packets} [rmac remote-mac-address | interface type number [vc {[vpi/]vci | vc-name}]]
DETAILED STEPS
Configuration Examples for Providing Protocol Support for Broadband Access Aggregation of PPPoE Sessions
This section provides the following configuration examples:
•
PPPoE Profiles Configuration: Example
•
MAC Address of the PPPoEoA Session as the Burned-In MAC Address: Example
•
MAC Address Configured on the ATM Interface: Example
•
Address Autoselect Configured and MAC Address Not Configured: Example
•
MAC Address Configured on the BBA Group: Example
•
PPPoE over 802.1Q VLAN Support on an Ethernet Interface: Example
•
PPPoE over 802.1Q VLAN Support on ATMs: Example
•
MAC Address Configured on the BBA Group: Example
•
PPPoE Session Recovery After Reload: Example
PPPoE Profiles Configuration: Example
The following example shows how to configure the three PPPoE profiles: vpn1, vpn2, and a global PPPoE profile. The profiles vpn1 and vpn2 are assigned to VC classes, VLANs, and ranges. Any Ethernet interface, VLAN, range, or VC class that is configured for PPPoE but is not assigned either profile vpn1 or vpn (such as VC class class-pppoe-global) will use the global profile.
Note
The order in which the commands are configured can be changed.
vpdn enable!vpdn-group 1request-dialinprotocol l2tpdomain vpn1initiate-to ip 209.165.200.225 priority 1local name NAS1-1!vpdn-group 2request-dialinprotocol l2tpdomain vpn2initiate-to ip 209.165.201.1 priority 1local name NAS1-2!virtual-template 1 pre-clone 20virtual-template 2 pre-clone 20!bba-group pppoe globalvirtual-template 1sessions max limit 8000sessions per-mac limit 2sessions per-vc limit 8!bba-group pppoe vpn1virtual-template 1sessions per-vc limit 2sessions per-mac limit 1!bba-group pppoe vpn2virtual-template 2sessions per-mac limit 1sessions per-vc limit 2!vc-class atm class-pppoe-globalprotocol pppoe!vc-class atm class-pppox-autoencapsulation aal5autoppp virtual-template 1 group vpn1!vc-class atm class-pppoe-1protocol pppoe group vpn1!vc-class atm class-pppoe-2protocol pppoe group vpn2!interface Loopback 1ip address 209.165.201.1 255.255.255.0!interface ATM 1/0.10 multipointrange range-pppoe-1 100 109protocol pppoe group vpn1!interface ATM 1/0.20 multipointclass-int class-pppox-auto0/200encapsulation aal5autoppp virtual-template 1!0/201!0/202encapsulation aal5autoppp virtual-template 1 group vpn2!0/203class-vc class-pppoe-global!!interface Ethernet 2/3.1encapsulation dot1Q 1pppoe enable group vpn1!interface Ethernet 2/3.2encapsulation dot1Q 2pppoe enable group vpn2!interface ATM 6/0.101 point-to-pointip address 209.165.202.129 255.255.255.00/101!interface ATM 6/0.102 point-to-pointip address 209.165.201.1 255.255.255.00/102!interface virtual-template 1ip unnumbered loopback 1no logging event link-statusno keepalivepeer default ip address pool pool-1ppp authentication chap!interface virtual-template 2ip unnumbered loopback 1no logging event link-statusno keepalivepeer default ip address pool pool-2ppp authentication chap!ip local pool pool-1 10.10.1.1 10.10.1.250ip local pool pool-2 10.10.2.1 10.10.2.250!MAC Address of the PPPoEoA Session as the Burned-In MAC Address: Example
In the following example, neither address autoselect nor a MAC address is configured on the BBA group, and the MAC address is not configured on the ATM interface (the default condition). The show pppoe session command is used to confirm that the MAC address of the PPPoEoA session is the burned-in MAC address of the ATM interface.
bba-group pppoe onevirtual-template 1interface ATM 3/0no ip addressno ip route-cacheno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM 3/0.1 multipointno ip route-cache1/50encapsulation aal5snapprotocol pppoe group one!Router# show pppoe session1 session in LOCALLY_TERMINATED (PTA) State1 session totalUniq ID PPPoE RemMAC Port VT VAStateSID LocMAC VA-st3 3 000b.fdc9.0001 ATM3/0.1 1 Vi2.1PTA0008.7c55.a054 VC: 1/50 UPLocMAC is burned in mac-address of ATM interface(0008.7c55.a054).Address Autoselect Configured and MAC Address Not Configured: Example
The following example shows how to configure address autoselect in the BBA group. The MAC address is not configured on the ATM interface. The show pppoe session command displays the MAC address of the interface, plus 7.
bba-group pppoe onevirtual-template 1mac-address autoselect!interface ATM 3/0no ip addressno ip route-cacheno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM 3/0.1 multipointno ip route-cache1/50encapsulation aal5snapprotocol pppoe group oneRouter# show pppoe session1 session in LOCALLY_TERMINATED (PTA) State1 session totalUniq ID PPPoE RemMAC Port VT VAStateSID LocMAC VA-st5 5 000b.fdc9.0001 ATM3/0.1 1 Vi2.1PTA0008.7c55.a05b VC: 1/50 UPLocMAC = burned in mac-address of ATM interface + 7 (0008.7c55.a05b)PPPoE over 802.1Q VLAN Support on an Ethernet Interface: Example
The following example shows how to configure PPPoE over a range of 802.1Q VLANs on FastEthernet interface 0/0. The VLAN range is configured on the main interface, and therefore each VLAN will not use up a separate subinterface.
bba-group pppoe PPPOEvirtual-template 1sessions per-mac limit 1interface virtual-template 1ip address 209.165.201.1 255.255.255.0mtu 1492interface fastethernet 0/0no ip addressno ip mroute-cacheduplex halfvlan-range dot1q 20 30pppoe enable group PPPOEexit-vlan-configPPPoE over 802.1Q VLAN Support on ATMs: Example
The following example shows how to configure an ATM to support PPPoE over a range of 802.1Q VLANs:
bba-group pppoe PPPOEOAvirtual-template 1sessions per-mac limit 1interface virtual-template 1ip address 209.165.202.129 255.255.255.0mtu 1492interface atm 4/0.10 multipoint10/100protocol pppovlan dot1q 0 50 group PPPOEOAMAC Address Configured on the ATM Interface: Example
In the following example, neither autoselect nor the MAC address is configured on the BBA group, but the MAC address is configured on the ATM interface, as indicated by the report from the show pppoe session command:
bba-group pppoe onevirtual-template 1interface ATM 3/0mac-address 0001.0001.0001no ip addressno ip route-cacheno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM 3/0.1 multipointno ip route-cache1/50encapsulation aal5snapprotocol pppoe group one!Router# show pppoe session1 session in LOCALLY_TERMINATED (PTA) State1 session totalUniq ID PPPoE RemMAC Port VT VAStateSID LocMAC VA-st7 7 000b.fdc9.0001 ATM3/0.1 1 Vi2.1PTA0001.0001.0001 VC: 1/50 UPLocMAC = configured mac-address on atm interface(0001.0001.0001).MAC Address Configured on the BBA Group: Example
The following example shows how to configure the MAC address on the BBA group. The display from the show pppoe session command indicates that all PPPoEoA sessions on the ATM interface associated with the BBA group use the same MAC address as specified on the BBA group.
bba-group pppoe onevirtual-template 1mac-address 0002.0002.0002interface ATM 3/0mac-address 0001.0001.0001no ip addressno ip route-cacheno atm ilmi-keepalive!interface ATM 3/0.1 multipointno ip route-cache1/50encapsulation aal5snapprotocol pppoe group oneRouter# show pppoe session1 session in LOCALLY_TERMINATED (PTA) State1 session totalUniq ID PPPoE RemMAC Port VT VAStateSID LocMAC VA-st8 8 000b.fdc9.0001 ATM3/0.1 1 Vi2.1PTA0002.0002.0002 VC: 1/50 UPLocMac(Mac address of PPPoEoA session) is mac-address specified on bba-group one (0002.0002.0002)PPPoE Session Recovery After Reload: Example
The following example shows how the router attempts to recover failed PPPoE sessions in the ATM range called "range-pppoe-1":
bba-group pppoe group1virtual-template 1sessions auto cleanup!interface ATM1/0.10 multipointrange range-pppoe-1 100 109protocol pppoe group group1!interface virtual-template 1ip address negotiatedno peer default ip addressppp authentication chapWhere to Go Next
•
If you want to establish PPPoE session limits for sessions on a specific PVC or VLAN configured on an L2TP access concentrator, see the "Establishing PPPoE Session Limits per NAS Port" module.
•
If you want to use service tags to enable a PPPoE server to offer PPPoE clients a selection of service during call setup, see the "Offering PPPoE Clients a Selection of Services During Call Setup" module.
•
If you want to enable an L2TP access concentrator to relay active discovery and service selection functionality for PPPoE over an L2TP control channel to an L2TP network server (LNS) or tunnel switch, see the "Enabling PPPoE Relay Discovery and Service Selection Functionality" module.
Note
L2TP is not supported on the Cisco 7600 router in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRC.
•
If you want to configure the transfer upstream of the Point-to-Point Protocol over X (PPPoX, where X designates a family of encapsulating communications protocols such as pppoe, pppoa, pppoeoa, pppoeovlan implementing PPP), see the "Configuring Upstream Connections Speed Transfer" module.
•
If you want to use SNMP to monitor PPPoE sessions, see the "Monitoring PPPoE Sessions with SNMP" module.
•
If you want to identify a physical subscribe line for RADIUS communication with a RADIUS server, see the "Identifying a Physical Subscriber Line for RADIUS Access and Accounting" module.
•
If you want to configure a Cisco Subscriber Service Switch, see the "Configuring Cisco Subscriber Service Switch Policies" module.
Additional References
The following sections provide references related to the Providing Protocol Support for Broadband Access Aggregation of PPPoE Session feature.
Related Documents
Broadband access aggregation concepts
"Understanding Broadband Access Aggregation" module in
Cisc IOS Broadband and DSL Configuration GuideTasks for preparing for broadband access aggregation
"Preparing for Broadband Access Aggregation" module in
Cisco IOS Broadband and DSL Configuration GuideBroadband access commands: complete command syntax, command mode, command history, defaults, usage guidelines, and examples
Cisco IOS Broadband Access Aggregation and DSL Command Reference
Establishing PPPoE session limits for sessions on a specific permanent virtual circuit or VLAN configured on an L2TP access concentrator
"Establishing PPPoE Session Limits per NAS Port" module in
Cisco IOS Broadband Access Aggregation and DSL Configuration GuideUsing service tags to enable a PPPoE server to offer PPPoE clients a selection of service during call setup
"Offering PPPoE Clients a Selection of Services During Call Setup" module in Cisco IOS Broadband Access Aggregation and DSL Configuration Guide
Enabling an L2TP access concentrator to relay active discovery and service selection functionality for PPPoE over an L2TP control channel to an L2TP LNS or tunnel switch
"Enabling PPPoE Relay Discovery and Service Selection Functionality" module in Cisco IOS Broadband Access Aggregation and DSL Configuration Guide
Configuring the transfer upstream of the PPPoX session speed value
"Configuring Upstream Connections Speed Transfer" module in
Cisco IOS Broadband Access Aggregation and DSL Configuration GuideUsing SNMP to monitor PPPoE sessions
"Monitoring PPPoE Sessions with SNMP" in Cisco IOS Broadband Access Aggregation and DSL Configuration Guide
Identifying a physical subscribe line for RADIUS communication with a RADIUS server
"Identifying a Physical Subscriber Line for RADIUS Access and Accounting" module in Cisco IOS Broadband Access Aggregation and DSL Configuration Guide
Configuring a Cisco Subscriber Service Switch
"Configuring Cisco Subscriber Service Switch Policies" module in Cisco IOS Broadband Access Aggregation and DSL Configuration Guide
Standards
No new or modified standards are supported by this feature, and support for existing standards has not been modified by this feature.
—
MIBs
RFCs
RFC 1483
Multiprotocol Encapsulation over ATM Adaptation Layer 5
RFC 2516
A Method for Transmitting PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE)
Technical Assistance
Feature Information for Providing Protocol Support for Broadband Access Aggregation for PPPoE Sessions
Table 1 lists the features in this module and provides links to specific configuration information. Only features that were introduced or modified in Cisco IOS Releases 12.2(1) or 12.0(3)S or a later release appear in the table.
For information on a feature in this technology that is not documented here, see the "Configuring Broadband Access Aggregation Features Roadmap."
Not all commands may be available in your Cisco IOS software release. For release information about a specific command, see the command reference documentation.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and software image support. Cisco Feature Navigator enables you to determine which Cisco IOS and Catalyst OS software images support a specific software release, feature set, or platform. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to http://tools.cisco.com/ITDIT/CFN/jsp/index.jsp. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Note
Table 1 lists only the Cisco IOS software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given Cisco IOS software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that Cisco IOS software release train also support that feature.
Table 1 Feature Information for Providing Protocol Support for Broadband Access Aggregation of PPPoE Sessions
Configurable MAC Address for PPPoE
12.3(11)T
The Configurable MAC Address for PPPoE feature configures the MAC address on ATM PVCs in a broadband access (BBA) group to use a different MAC address for PPP over Ethernet over ATM (PPPoEoA).
The following section provides information about this feature:
•
"Configuring MAC Addresses for PPPoEoA" section
The following commands were introduced or modified: bba-group ppoe, mac-address.
Configuration Limit Removal and ATM Support
12.3(2)T
The Configuration Limit Removal and ATM Support feature provides two enhancements to PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) over IEEE 802.1Q VLAN functionality:
•
It removes the requirement for each PPPoE VLAN to be created on a subinterface. Removal of this requirement increases the number of VLANs that can be configured on a router from 1001 to 4000 VLANs per interface.
•
It adds ATM support for PPPoE over VLAN traffic that uses bridged RFC 1483 encapsulation.
The following sections provide information about this feature:
•
"Assigning a PPPoE Profile to a VLAN Subinterface" section
•
"Enabling PPPoE over IEEE 802.1Q VLAN" section
•
"Enabling an ATM to Support Encapsulated PPPoE over IEEE 802.1Q VLAN" section
The following commands were introduced or modified: encapsulation dot1q, interface atm, interface range, protocol pppoe, pppoe enable, protocol pppoe, vlan-id dot1q, vlan dot1q.
PPPoA/PPPoE Autosense for ATMs
12.1(1)DC
12.2(4)T
12.2(4)T3The PPPoA/PPPoE Autosense for ATMs feature enables a router to distinguish between incoming PPP over ATM (PPPoA) and PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) over ATMsessions and to create virtual access based on demand for both PPP types.
The following sections provide information about this feature:
•
"Assigning a PPPoE Profile to an ATM" section
•
"Assigning a PPPoE Profile to an ATM Range and Within a Range" section
The following commands were introduced or modified: encapsulation aal5 auto, interface ATM, ppp virtual-template, protocol pppoe, pvc-in-range, range.
PPPoE Connection Throttling
12.2 (15)T
12.2(33)SRC
The PPPoE Connection Throttling feature limits PPPoE connection requests to help prevent intentional denial-of-service attacks and unintentional PPP authentication loops. This feature implements session throttling on the PPPoE server to limit the number of PPPoE session requests that can be initiated from a MAC address or virtual circuit during a specified period of time.
The following sections provide information about this feature:
•
"PPPoE Connection Throttling" section
PPPoE Profiles
12.2(15)T
The PPPoE Profiles feature configures PPP over Ethernet profiles that contain configuration information for a group of PPPoE sessions.
The following sections provide information about this feature:
•
"How to Provide Protocol Support for Broadband Access Aggregation of PPPoE Sessions" section
PPPoE Session Recovery After Reload
12.3(2)T
12.2(33)SRCThe PPPoE Session Recovery After Reload feature enables the aggregation device to attempt to recover PPPoE sessions that failed because of reload by notifying CPE devices about the PPPoE session failures.
The following section provides information about this feature:
VLAN Range
12.0(7)XE
12.1(5)T
12.2(2)DD
12.2(4)B
12.2(8)T
12.2(13)TThe VLAN Range feature can be used to group VLAN subinterfaces so that any command entered in a group applies to every subinterface within the group. This capability simplifies configurations and reduces command parsing.
The following section provides information about this feature:
•
"PPPoE over VLAN Configuration Without Using Subinterfaces" section.
Cisco and the Cisco Logo are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. A listing of Cisco's trademarks can be found at www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1005R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
© 2005-2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.

 Feedback
Feedback