Contents
- IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Tunnel Protection
- Finding Feature Information
- Prerequisites for IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Tunnel Protection
- Restrictions for IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Tunnel Protection
- Information About IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Tunnel Protection
- GRE Tunnels with IPsec
- How to Configure IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Tunnel Protection
- Configuring IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Encryption Using a Crypto Map
- Configuring IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Encryption Using Tunnel Protection
- Configuration Examples for IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Tunnel Protection
- Example: Configuring IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Encryption Using a Crypto Map
- Example: Configuring IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Encryption Using Tunnel Protection
- Additional References
- Feature Information for IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Tunnel Protection
IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Tunnel Protection
The IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Tunnel Protection feature allows both IPv6 unicast and multicast traffic to pass through a protected generic routing encapsulation (GRE) tunnel.
- Finding Feature Information
- Prerequisites for IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Tunnel Protection
- Restrictions for IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Tunnel Protection
- Information About IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Tunnel Protection
- How to Configure IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Tunnel Protection
- Configuration Examples for IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Tunnel Protection
- Additional References
- Feature Information for IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Tunnel Protection
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Toolkit and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Information About IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Tunnel Protection
GRE Tunnels with IPsec
Generic routing encapsulation (GRE) tunnels sometimes are combined with IPSec, because IPSec does not support IPv6 multicast packets. This function prevents dynamic routing protocols from running successfully over an IPSec VPN network. Because GRE tunnels do support IPv6 multicast , a dynamic routing protocol can be run over a GRE tunnel. Once a dynamic routing protocol is configured over a GRE tunnel, you can encrypt the GRE IPv6 multicast packets using IPSec.
IPSec can encrypt GRE packets using a crypto map or tunnel protection. Both methods specify that IPSec encryption is performed after GRE encapsulation is configured. When a crypto map is used, encryption is applied to the outbound physical interfaces for the GRE tunnel packets. When tunnel protection is used, encryption is configured on the GRE tunnel interface.
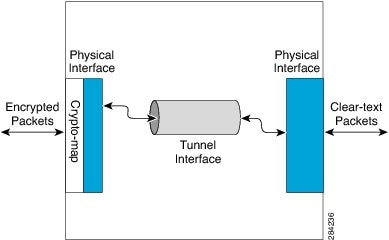
The following figure shows encrypted packets that enter a router through a GRE tunnel interface using a crypto map on the physical interface. Once the packets are decrypted and decapsulated, they continue to their IP destination as clear text.
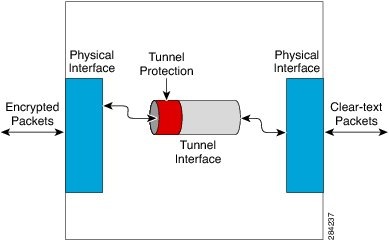
The following figure shows encryption using tunnel protection command on the GRE tunnel interface. The encrypted packets enter the router through the tunnel interface and are decrypted and decapsulated before they continue to their destination as clear text.
There are two key differences in using the crypto map and tunnel protection methods:
- The IPSec crypto map is tied to the physical interface and is checked as packets are forwarded out through the physical interface. At this point, the GRE tunnel has already encapsulated the packet.
- Tunnel protection ties the encryption functionality to the GRE tunnel and is checked after the packet is GRE encapsulated but before the packet is handed to the physical interface.
How to Configure IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Tunnel Protection
- Configuring IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Encryption Using a Crypto Map
- Configuring IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Encryption Using Tunnel Protection
Configuring IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Encryption Using a Crypto Map
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Encryption Using Tunnel Protection
DETAILED STEPS
Configuration Examples for IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Tunnel Protection
- Example: Configuring IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Encryption Using a Crypto Map
- Example: Configuring IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Encryption Using Tunnel Protection
Example: Configuring IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Encryption Using a Crypto Map
Router> enable Router# configure terminal Router(config)# ipv6 multicast-routing Router(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing Router(config)# interface tunnel 10 Router(config-if)# ipv6 address my-prefix 0:0:0:7272::72/64 Router(config-if)# tunnel mode gre ip Router(config-if)# tunnel source ethernet0 Router(config-if)# tunnel destination 172.16.0.12 Router(config-if)# exit Router(config)# crypto isakmp policy 15 Router(config-isakmp-policy)# authentication pre-share Router(config-isakmp-policy)# hash md5 Router(config-isakmp-policy)# group 2 Router(config-isakmp-policy)# encryption 3des Router(config-isakmp-policy)# exit Router(config)# crypto isakmp key cisco-10 address 172.16.0.12 255.240.0.0 Router(config)# crypto ipsec transform-set myset0 ah-sha-hmac esp-3des Router(config)# access-list 110 permit gre host 192.168.0.16 host 172.16.0.12 Router(config)# crypto map mymap 10 ipsec-isakmp Router(config-crypto-map)# set peer 10.0.0.1 Router(config-crypto-map)# set transform-set myset0 Router(config-crypto-map)# match address 102 Router(config-crypto-map)# exit Router(config)# interface ethernet1 Router(config-if)# crypto map mymap Router(config-if)# end
Example: Configuring IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Encryption Using Tunnel Protection
Router> enable Router# configure terminal Router(config)# ipv6 multicast-routing Router(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing Router(config)# crypto isakmp policy 15 Router(config-isakmp-policy)# authentication pre-share Router(config-isakmp-policy)# hash md5 Router(config-isakmp-policy)# group 2 Router(config-isakmp-policy)# encryption 3des Router(config-isakmp-policy)# exit Router(config)# crypto isakmp key cisco-10 address 172.16.0.12 255.240.0.0 Router(config)# crypto ipsec transform-set myset0 ah-sha-hmac esp-3des Router(config)# crypto ipsec profile ipsecprof Router(ipsec-profile)# set transform-set myset0 Router(ipsec-profile)# exit Router(config)# interface tunnel 1 Router(config-if)# ipv6 address 3ffe:b00:c18:1::3/127 Router(config-if)# tunnel mode gre ip Router(config-if)# tunnel source 10.0.0.1 Router(config-if)# tunnel destination 172.16.0.12 Router(config-if)# tunnel protection ipsec profile ipsecprof Router(config-if)# end
Additional References
Related Documents
Technical Assistance
|
Description |
Link |
|---|---|
|
The Cisco Support and Documentation website provides online resources to download documentation, software, and tools. Use these resources to install and configure the software and to troubleshoot and resolve technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support and Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Tunnel Protection
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
| Table 1 | Feature Information for IPv6 over IPv4 GRE Tunnel Protection |
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.

 Feedback
Feedback