Introdução
Este documento descreve problemas que impedem que a vizinhança BGP seja estabelecida corretamente.
Pré-requisitos
Requisitos
Não existem requisitos específicos para este documento.
Componentes Utilizados
Este documento não se restringe a versões de software e hardware específicas.
As informações neste documento foram criadas a partir de dispositivos em um ambiente de laboratório específico. Todos os dispositivos utilizados neste documento foram iniciados com uma configuração (padrão) inicial. Se a rede estiver ativa, certifique-se de que você entenda o impacto potencial de qualquer comando.
Conventions
Consulte as Convenções de Dicas Técnicas da Cisco para obter mais informações sobre convenções de documentos.
Informações de Apoio
Os roteadores BGP podem trocar informações de roteamento somente quando estabelecem uma conexão de peer entre eles.
O estabelecimento de peer do BGP começa com a criação de uma conexão TCP entre os dispositivos.
Após o estabelecimento da conexão TCP, os dispositivos BGP tentam criar uma sessão BGP pela troca de mensagens BGP Open, onde trocam a versão BGP, o número AS, o tempo de espera e o identificador BGP.
No processo de estabelecimento de peer de BGP, várias coisas podem impedir que uma vizinhança de BGP seja corretamente estabelecida. Este documento discute algumas das possíveis razões para esse problema:
Diagrama de Rede
Use esse diagrama de rede como um exemplo para as primeiras três causas:
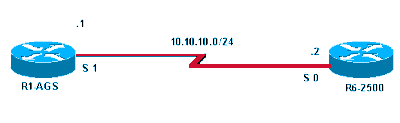 Diagrama de Rede
Diagrama de Rede
Problema
Instrução De Vizinho Incorreta
O comando show ip bgp summary no Roteador R1-AGS mostra a sessão ativa.
R1-AGS(9)#show ip bgp summary
BGP table version is 1, main routing table version 1
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
10.10.10.2 4 400 0 0 0 0 0 never Active
As configurações são:
| R1-AGS |
R6-2500 |
interface Loopback0
ip address 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
!
interface Serial1
ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 400
neighbor 10.10.10.2 remote-as 400
neighbor 10.10.10.2 update-source Loopback0
!
ip route 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 10.10.10.2 |
interface Loopback0
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
!
interface Serial0
ip address 10.10.10.2 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 400
neighbor 10.10.10.1 remote-as 400
neighbor 10.10.10.1 update-source Loopback0
!
ip route 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 10.10.10.1 |
Os comandos debug ip bgp e debug ip tcp transactions mostram a falha da conexão de TCP.
Depurações no roteador R1-AGS:
BGP: 10.10.10.2 open active, local address 10.2.2.2
TCB00135978 created
TCB00135978 setting property 0 16ABEA
TCB00135978 bound to 10.2.2.2.11039
TCP: sending SYN, seq 3797113156, ack 0
TCP0: Connection to 10.10.10.2:179, advertising MSS 1460
TCP0: state was CLOSED -> SYNSENT [11039 -> 10.10.10.2(179)]
TCP0: state was SYNSENT -> CLOSED [11039 -> 10.10.10.2(179)]
TCP0: bad seg from 10.10.10.2 -- closing connection: seq 0 ack 3797113157 rcvnxt 0 rcvwnd 0
TCP0: connection closed - remote sent RST
TCB00135978 destroyed
BGP: 10.10.10.2 open failed: Connection refused by remote host
TCP: sending RST, seq 0, ack 1965664223
TCP: sent RST to 10.1.1.1:11016 from 10.10.10.1:179
Depurações no roteador R6-2500:
TCP: sending RST, seq 0, ack 3797113157
TCP: sent RST to 10.2.2.2:11039 from 10.10.10.2:179
BGP: 10.10.10.1 open active, local address 10.1.1.1
TCB001E030C created
TCB001E030C setting property TCP_WINDOW_SIZE (0) 194F7A
TCB001E030C setting property TCP_TOS (11) 194F79
TCB001E030C bound to 10.10.1.1.11016
TCP: sending SYN, seq 1965664222, ack 0
TCP0: Connection to 10.10.10.1:179, advertising MSS 1460
TCP0: state was CLOSED -> SYNSENT [11016 -> 10.10.10.1(179)]
TCP0: state was SYNSENT -> CLOSED [11016 -> 10.10.10.1(179)]
TCP0: bad seg from 10.10.10.1 -- closing connection: seq 0 ack 1965664223 rcvnxt 0 rcvwnd 0
TCP0: connection closed - remote sent RST
TCB 0x1E030C destroyed
BGP: 10.10.10.1 open failed: Connection refused by remote host
Solução
Para corrigir essa situação, corrija o endereço de loopback na instrução de vizinho ou remova o comando update-source da configuração.
Neste exemplo, o endereço é corrigido.
| R1-AGS |
R6-2500 |
router bgp 400
neighbor 10.1.1.1 remote-as 400
neighbor 10.1.1.1 update-source Loopback0
!
ip route 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 10.10.10.2
|
router bgp 400
neighbor 10.2.2.2 remote-as 400
neighbor 10.2.2.2 update-source Loopback0
!
ip route 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 10.10.10.1
|
Uma olhada no comando show ip bgp summary mostra que o roteador R1-AGS está no estado estabelecido.
R1-AGS(9)#show ip bgp summary
BGP table version is 1, main routing table version 1
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
10.1.1.1 4 400 3 3 1 0 0 00:00:26 0
Problema
Não há rotas para o endereço vizinho ou a rota padrão é usada para alcançar o peer
O comando show ip bgp summary no roteador R1-AGS mostra que a sessão está ativa no momento.
R1-AGS(9)#show ip bgp summary
BGP table version is 1, main routing table version 1
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
10.1.1.1 4 400 0 0 0 0 0 never Active
As configurações são:
| R1-AGS |
R6-2500 |
interface Loopback0
ip address 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
!
interface Serial1
ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 300
neighbor 10.1.1.1 remote-as 400
neighbor 10.1.1.1 ebgp-multihop 2
neighbor 10.1.1.1 update-source Loopback0 |
interface Loopback0
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
!
interface Serial0
ip address 10.10.10.2 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 400
neighbor 10.2.2.2 remote-as 300
neighbor 10.2.2.2 ebgp-multihop 2
neighbor 10.2.2.2 update-source Loopback0 |
Se você executar os comandos debug, ele mostrará que não há rota para o vizinho.
Depurações no roteador R1-AGS:
BGP: 10.1.1.1 open active, delay 9568ms
BGP: 10.1.1.1 multihop open delayed 19872ms (no route)
BGP: 10.1.1.1 multihop open delayed 12784ms (no route)
Depurações no roteador R6-2500:
BGP: 10.2.2.2 open active, delay 6531ms
BGP: 10.2.2.2 multihop open delayed 14112ms (no route)
BGP: 10.2.2.2 multihop open delayed 15408ms (no route)
Solução
A solução é incluir uma rota para o próximo salto na instrução do vizinho BGP. Use uma rota estática ou dinâmica dependendo da situação.
Em um ambiente de BGP interno (iBGP) onde você tem mais controle, você pode propagar a rota dinamicamente usando um protocolo de roteamento.
Em uma situação de BGP externo (eBGP), recomenda-se configurar uma rota estática para alcançar o próximo salto.

Note: Use o comando neighbor ebgp-multihop somente quando o endereço IP para o qual você está fazendo o peering no peer do eBGP não estiver conectado diretamente.
Neste exemplo, uma rota estática é usada.
| R1-AGS |
R6-2500 |
router bgp 300
neighbor 10.1.1.1 remote-as 400
neighbor 10.1.1.1 ebgp-multihop 2
neighbor 10.1.1.1 update-source Loopback0
!
ip route 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 10.10.10.2
|
router bgp 400
neighbor 10.2.2.2 remote-as 300
neighbor 10.2.2.2 ebgp-multihop 2
neighbor 10.2.2.2 update-source Loopback0
!
ip route 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 10.10.10.1
|
O comando show ip bgp summary mostra que o Roteador R1-AGS está no estado estabelecido.
R1-AGS(9)#show ip bgp summary
BGP table version is 1, main routing table version 1
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
10.1.1.1 4 400 3 3 1 0 0 00:00:26 0

Note: Uma rota padrão nunca será usada para estabelecer uma sessão BGP (iBGP/eBGP), e você verá a mesma saída (sem rota) nas depurações, embora seja possível fazer ping no vizinho BGP. A solução é novamente adicionar uma rota ao vizinho de BGP.
Problema
O comando Update-source está ausente no BGP
O comando show ip bgp summary no Roteador R1-AGS mostra a sessão ativa.
R1-AGS(9)#show ip bgp summary
BGP table version is 1, main routing table version 1
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
10.1.1.1 4 400 0 0 0 0 0 never Active
As configurações são:
| R1-AGS |
R6-2500 |
interface Loopback0
ip address 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
!
interface Serial1
ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 400
neighbor 10.1.1.1 remote-as 400
!
ip route 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 10.10.10.2 |
interface Loopback0
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
!
interface Serial0
ip address 10.10.10.2 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 400
neighbor 10.2.2.2 remote-as 400
!
ip route 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 10.10.10.1 |
Se você executar os comandos debug, ele mostrará a conexão TCP falhar.
Depurações no roteador R1-AGS:
TCP: sending RST, seq 0, ack 2248020754
TCP: sent RST to 10.10.10.2:11018 from 10.2.2.2:179
BGP: 10.1.1.1 open active, local address 10.10.10.1
TCB0016B06C created
TCB0016B06C setting property 0 16ADEA
TCB0016B06C bound to 10.10.10.1.11042
TCP: sending SYN, seq 4099938541, ack 0
TCP0: Connection to 10.1.1.1:179, advertising MSS 536
TCP0: state was CLOSED -> SYNSENT [11042 -> 10.1.1.1(179)]
TCP0: state was SYNSENT -> CLOSED [11042 -> 10.1.1.1(179)]
TCP0: bad seg from 10.1.1.1 -- closing connection: seq 0 ack 4099938542 rcvnxt 0 rcvwnd 0
TCP0: connection closed - remote sent RST
TCB0016B06C destroyed
BGP: 10.1.1.1 open failed: Connection refused by remote host
Depurações no roteador R6-2500:
BGP: 10.2.2.2 open active, local address 10.10.10.2
TCB00194800 created
TCB00194800 setting property TCP_WINDOW_SIZE (0) E6572
TCB00194800 setting property TCP_TOS (11) E6571
TCB00194800 bound to 10.10.10.2.11018
TCP: sending SYN, seq 2248020753, ack 0
TCP0: Connection to 10.2.2.2:179, advertising MSS 556
TCP0: state was CLOSED -> SYNSENT [11018 -> 10.2.2.2(179)]
TCP0: state was SYNSENT -> CLOSED [11018 -> 10.2.2.2(179)]
TCP0: bad seg from 10.2.2.2 -- closing connection: seq 0 ack 2248020754 rcvnxt 0 rcvwnd 0
TCP0: connection closed - remote sent RST
TCB 0x194800 destroyed
BGP: 10.2.2.2 open failed: Connection refused by remote host
TCP: sending RST, seq 0, ack 4099938542
TCP: sent RST to 10.10.10.1:11042 from 10.1.1.1:179
Solução
Para resolver esse problema, configure o comando update-source em ambos os roteadores ou remova o comando update-source e altere a instrução vizinha em ambos os roteadores.
Esses são exemplos de ambas as soluções.
O comando update-source é configurado em ambos os roteadores:
| R1-AGS |
R6-2500 |
interface Loopback0
ip address 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
!
interface Serial1
ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 400
neighbor 10.1.1.1 remote-as 400
neighbor 10.1.1.1 update-source Loopback0
!
ip route 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 10.10.10.2 |
interface Loopback0
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
!
interface Serial0
ip address 10.10.10.2 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 400
neighbor 10.2.2.2 remote-as 400
neighbor 10.2.2.2 update-source Loopback0
!
ip route 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 10.10.10.1 |
O comando show ip bgp summary mostra que o Roteador R1-AGS está no estado estabelecido.
R1-AGS(9)#
show ip bgp summary
BGP table version is 1, main routing table version 1
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
10.2.2.2 4 400 3 3 1 0 0 00:00:26 0
Você só precisa usar o comando atualizar-fonte quando alguém corresponder ao seu endereço de circuito fechado. Isso acontece com peers iBGP e eBGP.
Aqui, o comando update-source é removido e a instrução de vizinho é alterada em ambos os roteadores.
| R1-AGS |
R6-2500 |
interface Loopback0
ip address 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
!
interface Serial1
ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 400
neighbor 10.10.10.2 remote-as 400
|
interface Loopback0
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
!
interface Serial0
ip address 10.10.10.2 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 400
neighbor 10.10.10.1 remote-as 400
|
O comando show ip bgp summary mostra que o Roteador R1-AGS está no estado estabelecido.
R1-AGS(9)#show ip bgp summary
BGP table version is 1, main routing table version 1
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
10.10.10.2 4 400 3 3 1 0 0 00:00:26 0
Informações Relacionadas

 Feedback
Feedback