Comprendre le protocole Spanning Tree rapide (802.1w)
Options de téléchargement
-
ePub (332.9 KB)
Consulter à l’aide de différentes applications sur iPhone, iPad, Android ou Windows Phone -
Mobi (Kindle) (523.4 KB)
Consulter sur un appareil Kindle ou à l’aide d’une application Kindle sur plusieurs appareils
Langage exempt de préjugés
Dans le cadre de la documentation associée à ce produit, nous nous efforçons d’utiliser un langage exempt de préjugés. Dans cet ensemble de documents, le langage exempt de discrimination renvoie à une langue qui exclut la discrimination en fonction de l’âge, des handicaps, du genre, de l’appartenance raciale de l’identité ethnique, de l’orientation sexuelle, de la situation socio-économique et de l’intersectionnalité. Des exceptions peuvent s’appliquer dans les documents si le langage est codé en dur dans les interfaces utilisateurs du produit logiciel, si le langage utilisé est basé sur la documentation RFP ou si le langage utilisé provient d’un produit tiers référencé. Découvrez comment Cisco utilise le langage inclusif.
À propos de cette traduction
Cisco a traduit ce document en traduction automatisée vérifiée par une personne dans le cadre d’un service mondial permettant à nos utilisateurs d’obtenir le contenu d’assistance dans leur propre langue. Il convient cependant de noter que même la meilleure traduction automatisée ne sera pas aussi précise que celle fournie par un traducteur professionnel.
Table des matières
Introduction
Ce document décrit les informations sur les améliorations ajoutées par RSTP à la norme 802.1D précédente.
Fond
La norme Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)/802.1D a été conçue à un moment où la reprise de la connectivité après une panne dans un délai d'environ une minute était considérée comme des performances adéquates. Avec l'avènement de la commutation de couche 3 dans les environnements LAN, le pont est désormais en concurrence avec les solutions routées où des protocoles, tels qu'OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) et EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol), sont capables de fournir un chemin alternatif en moins de temps.
Cisco a amélioré la spécification 802.1D originale avec des fonctionnalités, telles que Uplink Fast, Backbone Fast et Port Fast pour accélérer le temps de convergence d'un réseau ponté. L'inconvénient est que ces mécanismes sont propriétaires et ont besoin d'une configuration supplémentaire.
Le protocole Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP ; IEEE 802.1w) peut être considéré comme une évolution de la norme 802.1D plutôt qu'une révolution. La terminologie 802.1D reste principalement la même. La plupart des paramètres ont été laissés inchangés, de sorte que les utilisateurs familiarisés avec le protocole 802.1D peuvent rapidement et facilement configurer le nouveau protocole. Dans la plupart des cas, RSTP est plus performant que les extensions propriétaires de Cisco sans configuration supplémentaire. La norme 802.1w peut également revenir à la norme 802.1D pour assurer l'interopérabilité avec les ponts existants, par port. Cela réduit les avantages qu'il introduit.
La nouvelle édition de la norme 802.1D, IEEE 802.1D-2004, intègre les normes IEEE 802.1t-2001 et IEEE 802.1w.
Support de RSTP pour les commutateurs Catalyst
Ce tableau montre la prise en charge de RSTP dans certaines familles de commutateurs Catalyst, et le logiciel minimum requis pour cette prise en charge.
| Plate-forme Catalyst | MST avec RSTP | RPVST+ (également connu sous le nom de PVRST+) |
|---|---|---|
| Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL | Non disponible. | Non disponible. |
| Catalyst 2940 | 12.1(20)EA2 | 12.1(20)EA2 |
| Catalyst 2950/2955/3550 | 12.1(9)EA1 | 12.1(13)EA1 |
| Catalyst 2970/3750 | 12.1(14)EA1 | 12.1(14)EA1 |
| Catalyst 3560 | 12.1(19)EA1 | 12.1(19)EA1 |
| Catalyst 3750 Metro | 12.1(14)AX | 12.1(14)AX |
| Catalyst 2948G-L3/4908G-L3 | Non disponible. | Non disponible. |
| Catalyst 4000/4500 (Cisco IOS®) | 12.1(12c)EW | 12.1(19)EW |
| Catalyst 6000/6500 (Cisco IOS) | 12.1(11b)EX, 12.1(13)E, 12.2(14)SX | 12.1(13)E |
| Catalyst 8500 | Non disponible. | Non disponible. |
Nouveaux états de port et rôles de port
Le protocole 802.1D définit les cinq états de port suivants :
-
désactivé
-
écouter
-
apprendre
-
bloquer
-
transmettre
Consultez le tableau de la section États des ports de ce document pour plus d'informations sur les états des ports.
L'état du port est mixte, qu'il bloque le trafic ou le transmette, et quel que soit son rôle dans la topologie active (port racine, port désigné, etc.). Par exemple, du point de vue opérationnel, il n'y a aucune différence entre un port à l'état blocking et un port à l'état listening. Les deux ports écartent les trames et n'apprennent pas les adresses MAC. La vraie différence réside dans le rôle que le Spanning Tree attribue au port. Il peut être supposé sans risque qu'un port à l'état listening est désigné ou racine et va passer à l'état forwarding. Malheureusement, une fois à l'état forwarding, il n'y a aucun moyen de savoir avec l'état du port si le port est racine ou désigné. Cela contribue à démontrer les failles de cette terminologie basée sur l'état. RSTP dissocie le rôle et l'état d'un port pour résoudre ce problème.
États du port
Il y a seulement trois états de port dans RSTP qui correspondent aux trois états opérationnels possibles. Les états 802.1D disabled, blocking et listening sont fusionnés en un état unique discarding 802.1w.
| État de port STP (802.1D) | État de port RSTP (802.1w) | Le port est-il inclus dans la topologie active ? | Le port apprend-il les adresses MAC ? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Désactivé | Rejeter | Non | Non |
| Bloquer | Rejeter | Non | Non |
| Écouter | Rejeter | Oui | Non |
| Apprendre | Apprendre | Oui | Oui |
| Transmettre | Transmettre | Oui | Oui |
Rôles de port
Le rôle de port est désormais une variable attribuée à un port donné. Les rôles de port racine et de port désigné demeurent, alors que le rôle de port blocking est réparti en rôles de port de secours et alternatifs. L'algorithme Spanning Tree (STA) détermine le rôle d'un port, en fonction des unités BPDU (Bridge Protocol Data Unit). Afin de simplifier les choses, la chose à retenir à propos d'une BPDU est qu'il y a toujours une méthode pour comparer deux d'entre eux et décider si l'un est plus utile que l'autre. Cela se base sur la valeur enregistrée dans le BPDU et parfois sur le port sur lequel les BPDU sont reçus. Ceci vu, les informations de cette section expliquent les approches pratiques des rôles de port.
Rôles de port racine
-
Le port qui reçoit le meilleur BPDU sur un pont est le port racine. Il s’agit du port le plus proche du pont racine en termes de coût de chemin. Le STA élit un seul pont racine dans le réseau ponté total (par VLAN). Le pont racine envoie les BPDU qui sont plus utiles que ceux qu'envoie tout autre pont. Le pont racine est le seul pont du réseau qui n'a pas de port racine. Tous les autres ponts reçoivent les BPDU sur au moins un port.

Rôle du port désigné
-
Le port est dit désigné s'il peut envoyer le meilleur BPDU sur le segment auquel il est connecté. Les ponts 802.1D relient différents segments, tels que des segments Ethernet pour créer un domaine ponté. Sur un segment donné, il peut seulement y avoir un chemin vers le pont racine. S’il existe deux chemins, il existe une boucle de pont dans le réseau. Tous les ponts connectés à un segment donné écoutent les BPDU de chacun et conviennent du pont qui envoie le meilleur BPDU en tant que pont désigné pour le segment. Le port du pont qui correspond est le port désigné pour ce segment.

Rôles des ports alternatifs et de secours
-
Ces deux rôles de port correspondent à l'état blocking de la norme 802.1D. Un port bloqué est défini comme n'étant pas le port désigné ou le port racine. Un port bloqué reçoit un BPDU plus utile que celui qu'il envoie sur son segment. N’oubliez pas qu’un port doit recevoir des unités BPDU pour rester bloqué. RSTP introduit ces deux rôles à cet effet.
-
Un port alternatif reçoit plus de BPDU utiles d'un autre pont et est un port bloqué. Ceci est montré dans le schéma suivant :

-
Un port de secours reçoit plus de BPDU utiles du pont où il est et est un port bloqué. Ceci est montré dans le schéma suivant :

Cette distinction est déjà faite intérieurement dans la norme 802.1D. C'est essentiellement comme cela que fonctionne Cisco UplinkFast. Le raisonnement est qu'un port alternatif fournit un autre chemin au pont racine et peut donc remplacer le port racine s'il a une défaillance. Naturellement, un port de secours fournit une connectivité redondante au même segment et ne peut pas garantir une connectivité alternative au pont racine. Par conséquent, il est exclu du groupe de liaisons ascendantes.
En conséquence, RSTP calcule la topologie finale pour le spanning-tree qui utilise les mêmes critères que la norme 802.1D. Il n'y a aucun changement dans la façon dont les différentes priorités de pont et de port sont utilisées. L'adjectif blocking est utilisé pour l'état discarding dans l'implémentation Cisco. CatOS versions 7.1 et ultérieures affichent encore les états listening et learning. Cela donne plus d'informations sur un port que ne l'exige la norme IEEE. Cependant, la nouvelle caractéristique est il y a maintenant une différence entre le rôle que le protocole détermine pour un port et son état actuel. Par exemple, il est désormais possible de désigner et de bloquer simultanément un port. Bien que cela se produise généralement pendant de très courtes périodes, cela signifie que ce port est dans un état transitoire vers l'état de transmission désigné.
Nouveau format BPDU
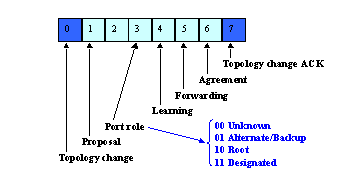
Peu de modifications ont été introduites par RSTP au format BPDU. Seulement deux indicateurs, Topology Change (TC) et TC Acknowledgment (TCA), sont définis dans 802.1D. Cependant, le protocole RSTP utilise les six bits de l’octet d’indicateur qui restent afin d’effectuer les opérations suivantes :
-
Encoder le rôle et l'état du port qui initie le BPDU
-
gérer le mécanisme de proposition/d'accord
Affichage complet des diagrammes Cisco BPDU, IEEE BPDU et BPDU
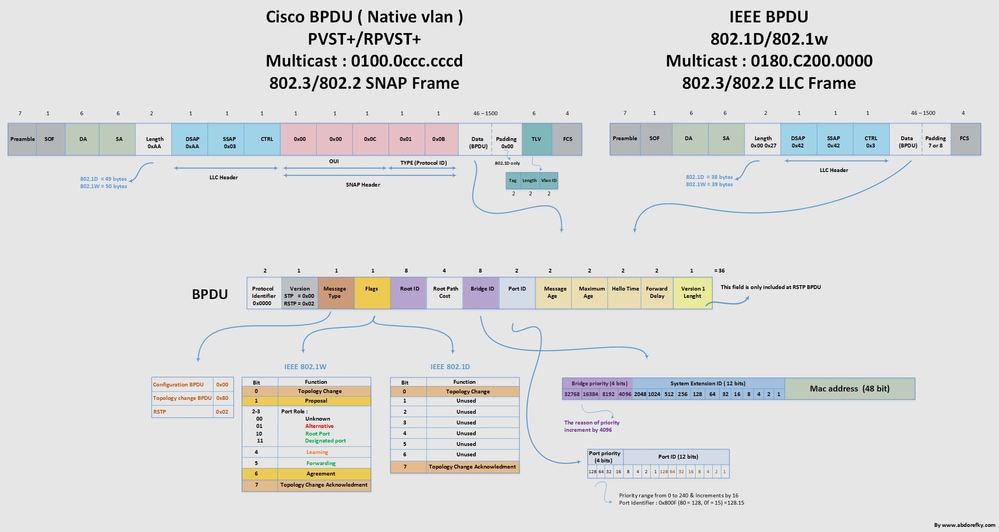
Pour obtenir une image de résolution supérieure, reportez-vous aux diagrammes Cisco BPDU, IEEE BPDU et BPDU.
Remarque : le bit 0 (modification de topologie) est le bit le moins significatif.
Une autre modification importante est que le BPDU RSTP est maintenant de type 2, version 2. Cela implique que les ponts existants doivent supprimer cette nouvelle BPDU. Cette propriété permet à un pont 802.1w de détecter facilement les ponts hérités qui lui sont connectés.
Nouvelle gestion des BPDU
Les unités BPDU sont envoyées à chaque Hello-Time
Les trames BPDU sont envoyées à chaque Hello Time et ne sont plus simplement relayées. Avec la norme 802.1D, un pont non racine ne génère des BPDU que quand il en reçoit une sur le port racine. Un pont relaie les unités BPDU plus qu’il ne les génère réellement. Ce n'est pas le cas avec la norme 802.1w. Un pont envoie une trame BPDU avec ses informations actuelles toutes les <hello-time> secondes (2 par défaut), même s’il n’en reçoit aucune du pont racine.
Vieillissement plus rapide des informations
Sur un port donné, si les hellos ne sont pas reçus trois fois consécutives, les informations de protocole peuvent être immédiatement périmées (ou si max_age expire). En raison de la modification de protocole précédemment mentionnée, les BPDU sont maintenant utilisées comme mécanisme keep-alive entre les ponts. Un pont considère qu'il perd la connectivité avec sa racine voisine directe ou le pont désigné s'il manque trois BPDU sur une ligne. Ce vieillissement rapide des informations permet une détection rapide des défaillances. Si un pont manque de recevoir les BPDU d'un voisin, il est certain que la connexion à ce voisin est perdue. Cela est contraire à 802.1D, où le problème peut se situer n'importe où sur le chemin vers la racine.
Remarque : les pannes sont détectées encore plus rapidement en cas de pannes de liaison physique.
Accepte des BPDU inférieures
Ce concept est ce qui compose le noyau du moteur BackboneFast. Le comité IEEE 802.1w a incorporé un mécanisme similaire dans le protocole RSTP. Quand un pont reçoit des informations inférieures de son pont désigné ou racine, il les accepte immédiatement et remplace celles enregistrées précédemment.
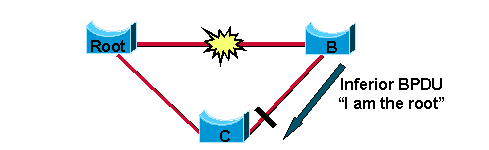
Puisque le pont C sait encore que la racine est vivante et opérationnelle, il envoie immédiatement une BPDU au pont B qui contient les informations sur le pont racine. En conséquence,le pont B n'envoie pas ses propres BPDU et accepte le port qui mène au pont C comme nouveau port racine.
Transition rapide vers l'état forwarding
La transition rapide est la fonctionnalité la plus importante introduite par 802.1w. Le STA existant a attendu passivement que le réseau converge avant de passer un port à l'état forwarding. La réalisation d'une convergence plus rapide a été le résultat de modifications apportées aux paramètres par défaut conservateurs (délais de transmission et minuteurs max_age) et a souvent mis en jeu la stabilité du réseau. Le nouveau protocole STP rapide est capable de confirmer activement qu'un port peut passer en toute sécurité à l'état de transmission sans avoir à se fier à une configuration de minuteur. Il y a maintenant un mécanisme de feedback réel qui a lieu entre les ponts compatibles RSTP. Afin d'obtenir une convergence rapide sur un port, le protocole s'appuie sur deux nouvelles variables : les ports de périphérie et le type de liaison.
Ports d'extrémité
Le concept de port de périphérie est déjà connu des utilisateurs de Spanning Tree Cisco, car il correspond essentiellement à la fonctionnalité PortFast. Tous les ports directement connectés aux stations d’extrémité ne peuvent pas créer de boucles de pont dans le réseau. Par conséquent, le port d'extrémité passe directement à l'état forwarding, et saute les états listening et learning. Ni les ports d'extrémité ni les ports PortFast activés ne produisent de modifications de topologie quand la liaison bascule. Un port d'extrémité qui reçoit une BPDU perd immédiatement l'état de port d'extrémité et devient un port spanning-tree normal. À ce stade, il y a une valeur configurée par l'utilisateur et une valeur opérationnelle pour l'état de port d'extrémité. L'implémentation Cisco maintient que le mot clé PortFast soit utilisé pour la configuration de port d'extrémité. Cela simplifie le passage à RSTP.
Type de liaison
RSTP peut seulement réaliser le passage rapide à l'état forwarding sur les ports d'extrémité et les liaisons point à point. Le type de liaison est automatiquement dérivé du mode duplex d'un port. Un port qui fonctionne en mode duplex est supposé être point à point, alors qu'un port semi-duplex est considéré par défaut comme un port partagé. Cette valeur de type de lien automatique peut être remplacée par une configuration explicite. Dans les réseaux commutés actuels, la plupart des liaisons fonctionnent en mode duplex intégral et sont traitées comme des liaisons point à point par RSTP. Cela leur permet de passer rapidement à l'état forwarding.
La convergence avec le protocole 802.1D
Ce diagramme illustre comment le protocole 802.1D traite une nouvelle liaison ajoutée à un réseau ponté :
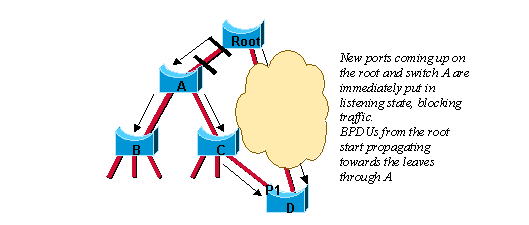
Dans ce scénario, une liaison est ajoutée entre le pont racine et le pont A. Supposons qu'il existe déjà une connexion indirecte entre le pont A et le pont racine (par C - D dans le schéma). L’algorithme STA bloque un port et désactive la boucle du pont. Lorsqu'ils sont activés, les deux ports sur la liaison entre la racine et le pont A passent à l'état listening. Le pont A peut maintenant entendre la racine directement. Il propage immédiatement ses BPDU sur les ports désignés vers les feuilles de l'arbre. Dès que les ponts B et C reçoivent cette nouvelle information supérieure du pont A, ils transmettent immédiatement l'information vers les feuilles. En quelques secondes, le pont D reçoit une BPDU de la racine et bloque immédiatement le port P1.
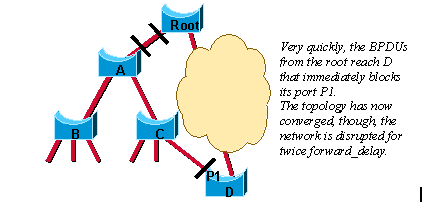
Le spanning-tree est très efficace dans la façon dont il calcule la nouvelle topologie du réseau. Le seul problème est maintenant que deux fois le délai de transmission doit s'écouler avant que la liaison entre la racine et le pont A finisse par passer à l'état forwarding. Ceci signifie 30 secondes d'interruption de trafic (la partie entière A, B et C du réseau est isolée) car l'algorithme 8021.D manque de mécanisme de feedback pour informer clairement que le réseau converge dans quelques secondes.
La convergence avec le protocole 802.1w
Maintenant, vous pouvez voir comment RSTP traite une situation semblable. Rappelez-vous que la topologie finale est exactement identique à celle calculée par la norme 802.1D (c'est-à-dire, un port bloqué au même endroit qu'avant). Seules les étapes utilisées pour atteindre cette topologie ont changé.
Les deux ports de la liaison entre le commutateur A et la racine sont placés en blocage désigné dès qu’ils sont activés. Jusqu'ici, tout se comporte comme dans un environnement 802.1D pur. Cependant, à ce stade, une négociation a lieu entre le commutateur A et le pont racine. Dès que le commutateur A reçoit la trame BPDU de la racine, il bloque les ports désignés non périphériques. Cette opération s'appelle la synchronisation. Une fois ceci fait, le pont A autorise explicitement le pont racine à passer son port à l'état forwarding. Ce schéma illustre le résultat de ce processus sur le réseau. La liaison entre le commutateur A et le pont racine est bloquée et les deux ponts échangent des BPDU.
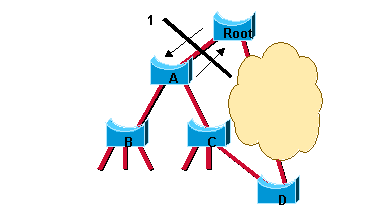
Lorsque le commutateur A bloque ses port désignés qui ne sont pas des ports d'extrémité, la liaison entre le commutateur A et la racine passe à l'état forwarding et la situation suivante apparaît :
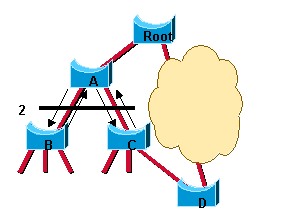
Il ne peut pas encore y avoir de boucle. Au lieu de bloquer avant le commutateur A, le réseau bloque maintenant après le commutateur A. Cependant, la boucle de pont potentielle est coupée à un emplacement différent. Cette coupe descend dans l'arborescence avec les nouvelles unités BPDU provenant de la racine via le commutateur A. À ce stade, les ports nouvellement bloqués sur le commutateur A négocient également une transition rapide vers l'état de transmission avec leurs ports voisins sur le commutateur B et le commutateur C qui lancent tous deux une opération de synchronisation. Outre le port racine vers A, le commutateur B ne dispose que de ports désignés en périphérie. Par conséquent, il n'a aucun port à bloquer pour autoriser le commutateur A à passer à l'état forwarding. De même, seul le commutateur C doit bloquer son port désigné vers D. L'état montré dans ce schéma est maintenant atteint :
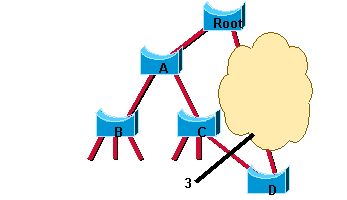
Rappelez-vous que la topologie finale est exactement identique à l'exemple 802.1D, ce qui signifie que le port P1 sur D finit par se bloquer. Cela signifie que la topologie finale du réseau est atteinte, juste dans le temps nécessaire pour que les nouveaux BPDU descendent l'arborescence. Aucun temporisateur n'est impliqué dans cette convergence rapide. Le seul nouveau mécanisme introduit par RSTP est l'accusé de réception qu'un commutateur peut envoyer à son nouveau port racine pour permettre son passage immédiat à l'état forwarding et qui contourne les délais des états listening et learning qui sont deux fois plus longs que le délai de l'état forwarding. L'administrateur n'a besoin de se soucier que des points suivants pour tirer parti de la convergence rapide :
-
Cette négociation entre les ponts n'est possible que lorsque les ponts sont connectés par des liaisons point à point (c'est-à-dire des liaisons bidirectionnelles simultanées, sauf si la configuration de port est explicite).
-
Les ports d'extrémité jouent un rôle encore plus important maintenant que PortFast est activé sur les ports en 802.1D. Par exemple, si l’administrateur réseau ne parvient pas à configurer correctement les ports de périphérie sur le commutateur B, leur connectivité est affectée par la liaison entre le commutateur A et la racine qui s’active.
BPDU de proposition/message d'entente
Lorsqu'un port est sélectionné par l'algorithme STA pour devenir un port désigné, 802.1D attend toujours deux fois <délai de transmission> secondes (2 x 15 par défaut) avant de passer à l'état de transmission. Avec RSTP, cette condition correspond à un port désigné à l'état bloqué. Les schémas ci-dessous illustrent comment la transition rapide est réalisée étape par étape. Supposons qu'un nouveau lien est créé entre le pont racine et le commutateur A. Chaque port de ce lien passe à l'état désigné bloqué jusqu'à ce qu'il reçoive une BPDU de l'autre port.
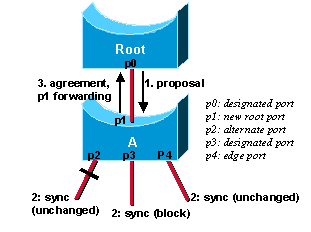
Quand un port désigné est à l'état discarding ou learning (et seulement dans ce cas), il active le bit de proposition des BPDU qu'il envoie. C'est ce qui se produit pour le port p0 du pont racine, comme le montre l'étape 1 du schéma ci-dessus. Étant donné que le commutateur A reçoit des informations supérieures, il sait immédiatement que p1 est le nouveau port racine. Le commutateur A démarre alors une synchronisation pour vérifier que tous ses ports sont synchronisés avec ces nouvelles informations. Un port est dit synchrone s'il remplit l'une ou l'autre des conditions suivantes :
-
Le port est à l'état bloqué, ce qui veut dire mis à l'écart dans une topologie stable.
-
Le port est un port d'extrémité.
Afin d'illustrer l'effet du mécanisme de synchronisation sur différents types de ports, supposons qu'il existe un port alternatif p2, un port de transfert désigné p3 et un port de périphérie p4 sur le commutateur A. Notez que p2 et p4 répondent déjà à l'un des critères. Pour être synchronisé (voir l’étape 2 du schéma précédent), le commutateur A doit simplement bloquer le port p3 et lui attribuer l’état d’abandon. Maintenant que tous ses ports sont synchrones, le commutateur peut débloquer son port racine p1 nouvellement sélectionné et lui envoyer en réponse un message d'entente. (voir l'étape 3). Ce message est une copie de la BPDU de proposition, avec le bit d'entente activé au lieu du bit de proposition. Cela garantit que le port p0 sait exactement à quelle proposition correspond l'entente qu'il reçoit.
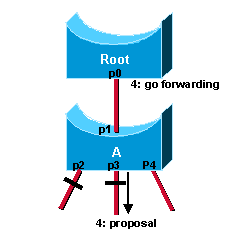
Une fois que le port p0 a reçu cette entente, il peut immédiatement passer à l'état forwarding. Il s'agit de l'étape 4 de la figure précédente. Notez que le port p3 est laissé à l'état désigné mis à l'écart après la synchronisation. À l'étape 4, ce port est exactement dans la même situation que le port p0 à l'étape 1. Il lance alors une proposition à son voisin et tente de passer rapidement à l'état forwarding.
-
Le mécanisme de proposition/entente est très rapide, car il ne repose pas sur les temporisateurs. Cette vague d’échanges se propage rapidement vers la périphérie du réseau et restaure rapidement la connectivité après une modification de la topologie.
-
Si un port désigné mis à l'écart ne reçoit pas d'accord après avoir envoyé une proposition, il passe lentement à l'état forwarding en retrouvant les mécanisme classiques du protocole 802.1D avec la séquence écoute-apprentissage. Cela peut se produire si le pont distant ne comprend pas les BPDU RSTP ou que le port du pont distant se bloque.
-
Cisco a introduit une amélioration dans le mécanisme de synchronisation, qui permet à un pont de passer seulement son ancien port racine à l'état mis à l'écart quand il synchronise. Détailler le fonctionnement de ce mécanisme sort du cadre de ce document. Cependant, on peut sans risque supposer qu'il est appelé dans la plupart des cas communs de reconvergence. Le scénario décrit dans la section La convergence avec le protocole 802.1w de ce document devient extrêmement efficace, car seuls les ports sur le chemin qui mène au port bloqué final sont temporairement perturbés.
UplinkFast
Une autre forme de passage immédiat à l'état forwarding inclus dans le RSTP est semblable à l'extension propriétaire de Cisco du STP appelée UplinkFast. Fondamentalement, quand un pont perd son port racine, il peut mettre son meilleur port alternatif directement en mode de transmission (l'apparence d'un nouveau port racine est également gérée par RSTP). La commutation d’un port alternatif en nouveau port racine provoque un changement de topologie du réseau. Le mécanisme de modification de topologie du protocole 802.1w efface les entrées appropriées des tables de mémoire adressable (CAM : Content Addressable Memory) du pont en amont. Cela évite la propagation d’un « multicast » issue du mécanisme d’UplinkFast.
Uplinkfast n'a pas besoin d'être configuré, car il est inclus nativement et activé automatiquement dans RSTP.
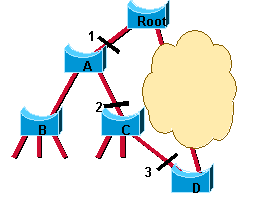
Nouveaux mécanismes de modification de topologie
Quand un pont 802.1D détecte une modification de topologie, il utilise un mécanisme fiable pour en informer d'abord le pont racine. Ceci est montré dans le schéma suivant :
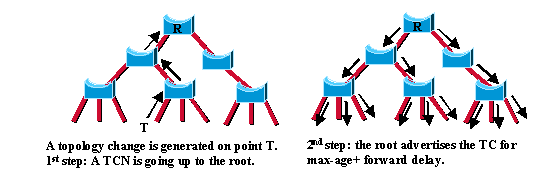
Une fois que le pont racine a connaissance d’une modification de la topologie du réseau, il définit l’indicateur TC sur les BPDU qu’il envoie, qui sont ensuite relayés à tous les ponts du réseau. Lorsqu’un pont reçoit une trame BPDU avec le bit d’indicateur TC défini, il réduit le temps de vieillissement de sa table de pontage en secondes de délai de transmission. Cela garantit une actualisation rapide des informations périmées. Ce mécanisme de modification de topologie a été profondément remanié avec RSTP. La détection d'une modification de topologie et sa propagation sur le réseau ont évolué.
Détection d'une modification de topologie
Avec RSTP, seuls les ports autres que des ports d'extrémité qui passent à l'état forwarding provoquent une modification de topologie. Cela signifie qu'une perte de connectivité n'est plus considérée comme une modification de topologie, contrairement au protocole 802.1D (c'est-à-dire, un port qui passe à l'état bloqué ne génère plus de TC). Quand un pont RSTP détecte une modification de topologie, il procède de la façon suivante :
-
Il lance le temporisateur TC avec une valeur égale à deux fois l'intervalle hello pour tous ses ports désignés autres que des ports d'extrémité et pour son port racine s'il y a lieu.
-
Il actualise les adresses MAC associées à tous ces ports.
Remarque : tant que le temporisateur TC s'exécute sur un port, les BPDU envoyées à partir de ce port ont le bit TC défini. Des BPDU sont également envoyées sur le port racine lorsque le temporisateur est actif.
Propagation d'une modification de topologie
Quand un pont reçoit une BPDU avec le bit TC activé depuis un voisin, il procède comme suit :
-
Il efface les adresses MAC apprises sur tous ses ports, sauf sur celui qui reçoit la modification de topologie.
-
Il démarre le temporisateur TC While et envoie des BPDU avec le bit TC défini sur tous ses ports désignés et sur son port racine (RSTP n'utilise plus la BPDU TCN spécifique, sauf si un pont hérité nécessite une notification).
De cette façon, la TCN circule se répand très rapidement sur tout le réseau. La propagation TC est désormais un processus en une étape. En fait, l’initiateur de la modification de topologie diffuse ces informations sur l’ensemble du réseau, contrairement à la norme 802.1D où seul le pont racine l’a fait. Ce mécanisme est beaucoup plus rapide que le mécanisme équivalent 802.1D. Il n'y a aucun besoin d'attendre que le pont racine soit prévenu et de maintenir ensuite la modification de topologie pour l'intégralité du réseau pendant une durée égale à <max age plus forward delay> secondes.
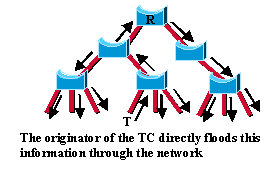
En seulement quelques secondes (un petit multiple des intervalles hello), la plupart des entrées des tables CAM du réseau entier (VLAN) s'actualisent. Cette approche a pour conséquence une inondation temporaire du réseau, mais d'un autre côté, elle efface les éventuelles informations périmées pouvant limiter la convergence rapide du réseau.
Compatibilité avec le protocole 802.1D
RSTP peut interagir avec les protocoles STP existants. Cependant, il est important de noter que les avantages de convergence rapide inhérents au protocole 802.1w sont perdus quand il interagit avec les ponts existants.
Chaque port met à jour une variable qui définit le protocole à exécuter sur le segment correspondant. Un temporisateur de délai de migration de trois secondes démarre également lorsque le port est activé. Quand ce temporisateur est exécuté, le mode STP ou RSTP en cours associé au port est verrouillé. Dès que le délai de migration expire, le port s'adapte au mode correspondant à la prochaine BPDU qu'il reçoit. Si le port change de mode de fonctionnement suite à la BPDU reçue, le délai de migration est relancé. Cela limite la fréquence de changement de mode possible.
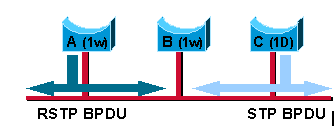
Par exemple, supposons que les ponts A et B de la figure précédente exécutent tous deux le protocole RSTP, le commutateur A étant désigné pour le segment. Un pont C STP existant est introduit sur cette liaison. Étant donné que les ponts 802.1D ignorent les BPDU RSTP et les suppriment, C pense qu'il n'y a aucun autre pont sur le segment et se met à envoyer ses BPDU inférieures de format 802.1D. Le commutateur A reçoit ces BPDU et, après un délai maximal égal à deux fois l'intervalle hello, remplace son mode par 802.1D sur ce seul port. En conséquence, C comprend maintenant les BPDU du commutateur A et accepte celui-ci comme pont désigné pour ce segment.
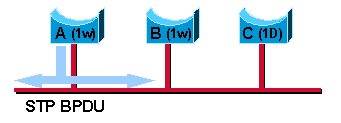
Notez que, dans ce cas particulier, si le pont C est supprimé, le pont A fonctionne en mode STP sur ce port même s'il peut mieux fonctionner en mode RSTP avec son seul voisin B. C'est parce que le pont A ne sait pas que le pont C est supprimé du segment. Pour ce cas (rare) particulier, l'intervention de l'utilisateur est nécessaire pour relancer manuellement la détection du protocole du port.
Lorsqu'un port est en mode de compatibilité 802.1D, il peut également gérer des BPDU TCN (Topology Change Notification) et des BPDU avec un bit TC ou TCA défini.
Conclusion
RSTP (IEEE 802.1w) inclut dans sa version native la plupart des améliorations propriétaires Cisco du protocole Spanning Tree 802.1D, par exemple BackboneFast, UplinkFast et PortFast. RSTP peut réaliser une convergence beaucoup plus rapide sur un réseau correctement configuré, parfois dans un délai de quelques centaines de millisecondes. Les minuteurs 802.1D classiques, tels que le délai de transmission et max_age, sont uniquement utilisés comme sauvegarde et ne sont pas nécessaires si les liaisons point à point et les ports de périphérie sont correctement identifiés et définis par l'administrateur. En outre, les minuteurs ne sont pas nécessaires s'il n'y a aucune interaction avec les ponts hérités.
Informations connexes
Historique de révision
| Révision | Date de publication | Commentaires |
|---|---|---|
2.0 |
09-Feb-2023
|
Première publication |
1.0 |
28-May-2002
|
Première publication |
Contribution d’experts de Cisco
Contacter Cisco
- Ouvrir un dossier d’assistance

- (Un contrat de service de Cisco est requis)
 Commentaires
Commentaires