ASA/PIX: Configuración y resolución de problemas de la inyección de ruta inversa (RRI)
Contenido
Introducción
Este documento describe cómo configurar y resolver problemas RRI (Reverse Route Injection) en Cisco Security Appliance (ASA/PIX).
Nota: Consulte Ejemplo de Configuración de Autenticación PIX/ASA 7.x y Cisco VPN Client 4.x con Windows 2003 IAS RADIUS (contra Active Directory) para obtener más información sobre la configuración de VPN de acceso remoto en ASA/PIX y Cisco VPN Client.
Prerequisites
Requirements
No hay requisitos específicos para este documento.
Componentes Utilizados
La información que contiene este documento se basa en las siguientes versiones de software y hardware.
-
Cisco 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) que ejecuta la versión de software 8.0
-
Software Cisco VPN Client versión 5.0
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Productos Relacionados
Esta configuración también se puede utilizar con Cisco 500 Series PIX Firewall que ejecuta la versión de software 7.x y posteriores.
Convenciones
Antecedentes
Reverse Route Injection (RRI) se utiliza para rellenar la tabla de routing de un router interno que ejecuta el protocolo Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) o el protocolo de información de routing (RIP) para clientes VPN remotos o sesiones LAN®.
Configurar
En esta sección encontrará la información para configurar las funciones descritas en este documento.
Nota: Utilice la herramienta Command Lookup (sólo para clientes registrados) para obtener más información sobre los comandos utilizados en esta sección.
Diagrama de la red
En este documento, se utiliza esta configuración de red:
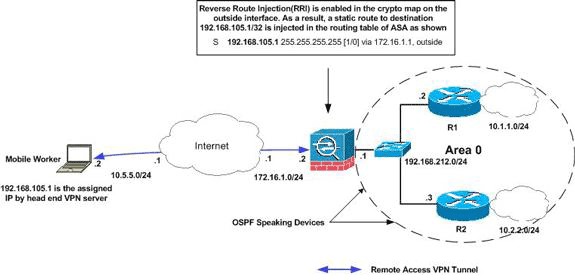
Nota: Los esquemas de direccionamiento IP utilizados en esta configuración no son legalmente enrutables en Internet. Son las direcciones RFC1918 que se han utilizado en un entorno de laboratorio.
Nota: Puede utilizar RRI en los escenarios de túnel VPN de LAN a LAN y de Easy VPN.
Configuraciones
En este documento, se utilizan estas configuraciones:
| Cisco ASA |
|---|
ciscoasa(config)#access-list split extended permit ip 192.168.212.0 255.255.255.0
192.168.105.0 255.255.255.00
ciscoasa(config)#access-list redistribute standard permit 192.168.105.0 255.255.255.0
ciscoasa(config)#ip local pool clients 192.168.105.1-192.168.105.10 mask 255.255.255.0
ciscoasa(config)#route-map redistribute permit 1
ciscoasa(config-route-map)#match ip address redistribute
ciscoasa(config-route-map)#exit
ciscoasa(config)#group-policy clientgroup internal
ciscoasa(config)#group-policy clientgroup attributes
ciscoasa(config-group-policy)#split-tunnel-policy tunnelspecified
ciscoasa(config-group-policy)#split-tunnel-network-list value split
ciscoasa(config-group-policy)#exit
ciscoasa(config)#isakmp nat-traversal 10
ciscoasa(config)#isakmp enable outside
ciscoasa(config)#isakmp policy 10 authentication pre-share
ciscoasa(config)#isakmp policy 10 encryption 3des
ciscoasa(config)#isakmp policy 10 hash sha
ciscoasa(config)#isakmp policy 10 group 2
ciscoasa(config)#isakmp policy 10 lifetime 86400
ciscoasa(config)#crypto ipsec transform-set ESP-3DES-SHA esp-3des esp-sha-hmac
ciscoasa(config)#crypto dynamic-map outside_dyn_map 20 set transform-set ESP-3DES-SHA
ciscoasa(config)#crypto dynamic-map outside_dyn_map 20 set reverse-route
!--- Command to enable RRI
ciscoasa(config)#crypto map outside_map 65535 ipsec-isakmp dynamic outside_dyn_map
ciscoasa(config)#crypto map outside_map interface outside
ciscoasa(config)#tunnel-group vpn-test type ipsec-ra
ciscoasa(config)#tunnel-group vpn-test general-attributes
ciscoasa(config-tunnel-general)#address-pool clients
ciscoasa(config-tunnel-general)#default-group-policy clientgroup
ciscoasa(config-tunnel-general)#tunnel-group vpn-test ipsec-attributes
ciscoasa(config-tunnel-ipsec)#pre-shared-key cisco123
ciscoasa(config-tunnel-ipsec)#exit |
| Cisco ASA |
|---|
ciscoasa#show running-config
: Saved
:
ASA Version 8.0(2)
!
hostname ciscoasa
enable password 8Ry2YjIyt7RRXU24 encrypted
names
!
interface Ethernet0
nameif outside
security-level 0
ip address 172.16.1.2 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet1
nameif inside
security-level 100
ip address 192.168.212.1 255.255.255.0
!
!---Output Suppressed
!
passwd 2KFQnbNIdI.2KYOU encrypted
ftp mode passive
access-list split extended permit ip 192.168.212.0 255.255.255.0
192.168.105.0 255.255.255.0
!--- Split-tunneling ACL
access-list redistribute standard permit 192.168.105.0 255.255.255.0
!--- Match the traffic sourced from 192.168.105.0 network
pager lines 24
mtu outside 1500
mtu insi 1500
ip local pool clients 192.168.105.1-192.168.105.10 mask 255.255.255.0
no failover
icmp unreachable rate-limit 1 burst-size 1
no asdm history enable
arp timeout 14400
!
route-map redistribute permit 1
match ip address redistribute
!
!
router ospf 1
network 192.168.212.0 255.255.255.0 area 0
log-adj-changes
redistribute static subnets route-map redistribute
!--- Redistribute the static routes sourced from 192.168.105.0 !--- network into OSPF Autonomous System (AS).
!
route outside 10.5.5.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.1.1 1
!---Output Suppressed
crypto ipsec transform-set ESP-3DES-SHA esp-3des esp-sha-hmac
crypto dynamic-map outside_dyn_map 20 set transform-set ESP-3DES-SHA
crypto dynamic-map outside_dyn_map 20 set reverse-route
!--- Command to enable RRI
crypto map outside_map 65535 ipsec-isakmp dynamic outside_dyn_map
crypto map outside_map interface outside
crypto isakmp enable outside
crypto isakmp policy 10
authentication pre-share
encryption 3des
hash sha
group 2
lifetime 86400
crypto isakmp policy 65535
authentication pre-share
encryption 3des
hash sha
group 2
lifetime 86400
!---Output Suppressed
service-policy global_policy global
group-policy clientgroup internal
group-policy clientgroup attributes
split-tunnel-policy tunnelspecified
split-tunnel-network-list value split
username vpnuser password gKK.Ip0zetpjju4R encrypted
tunnel-group vpn-test type remote-access
tunnel-group vpn-test general-attributes
address-pool clients
default-group-policy clientgroup
tunnel-group vpn-test ipsec-attributes
pre-shared-key *
prompt hostname context
Cryptochecksum:d41d8cd98f00b204e9800998ecf8427e
: end |
Troubleshoot
En esta sección encontrará información que puede utilizar para solucionar problemas de configuración.
Resultado de la tabla de ruteo antes de que RRI esté Habilitado en ASA
Nota: Suponga que un usuario móvil remoto establece el túnel VPN y que 192.168.105.1 es la dirección IP asignada por ASA.
Tabla de routing ASA
ciscoasa#show route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
S 192.168.105.1 255.255.255.255 [1/0] via 172.16.1.1, outside
C 192.168.212.0 255.255.255.0 is directly connected, insi
C 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 is directly connected, outside
S 10.5.5.0 255.255.255.0 [1/0] via 172.16.1.1, outside
O 10.2.2.1 255.255.255.255 [110/11] via 192.168.212.3, 2:09:24, insi
O 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 [110/11] via 192.168.212.2, 2:09:24, insi
Consejo: Incluso si RRI no está configurado, la ruta estática del cliente conectado se inyecta en la tabla de ruteo del servidor VPN (ASA/PIX). Sin embargo, no se redistribuye al router interno, que ejecuta protocolos de ruteo dinámicos, como OSPF, EIGRP (si ejecuta ASA 8.0).
Tabla de Ruteo R1 del Router
R1#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
C 192.168.212.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 10.1.1.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback0
O 10.2.2.1/32 [110/11] via 192.168.212.3, 02:11:52, Ethernet0
Tabla de ruteo del router R2
R2#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
C 192.168.212.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 10.2.2.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback0
O 10.1.1.1/32 [110/11] via 192.168.212.2, 02:13:03, Ethernet0
Resultado de la tabla de ruteo después de que RRI esté Habilitado en ASA
Nota: Suponga que un usuario móvil remoto establece el túnel VPN y que 192.168.105.1 es la dirección IP asignada por ASA.
Tabla de routing ASA
ciscoasa#show route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
S 192.168.105.1 255.255.255.255 [1/0] via 172.16.1.1, outside
C 192.168.212.0 255.255.255.0 is directly connected, insi
C 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 is directly connected, outside
S 10.5.5.0 255.255.255.0 [1/0] via 172.16.1.1, outside
O 10.2.2.1 255.255.255.255 [110/11] via 192.168.212.3, 2:09:24, insi
O 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 [110/11] via 192.168.212.2, 2:09:24, insi
Tabla de Ruteo R1 del Router
R1#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
192.168.105.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O E2 192.168.105.1 [110/20] via 192.168.212.1, 00:03:06, Ethernet0
!--- Redistributed route
C 192.168.212.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 10.1.1.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback0
O 10.2.2.1/32 [110/11] via 192.168.212.3, 02:11:52, Ethernet0
Tabla de ruteo del router R2
R2#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
192.168.105.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O E2 192.168.105.1 [110/20] via 192.168.212.1, 00:04:17, Ethernet0
!--- Redistributed route
C 192.168.212.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 10.2.2.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback0
O 10.1.1.1/32 [110/11] via 192.168.212.2, 02:13:03, Ethernet0
Información Relacionada
Contacte a Cisco
- Abrir un caso de soporte

- (Requiere un Cisco Service Contract)
 Comentarios
Comentarios