Ejemplo de Configuración de IPsec LAN-to-LAN Tunnel entre un Catalyst 6500 con el Módulo de Servicio VPN y un Cisco IOS Router
Contenido
Introducción
Este documento describe cómo crear un túnel de LAN a LAN IPSec entre un switch Catalyst de Cisco serie 6500 con el módulo de servicio de aceleración de VPN y un router Cisco IOS®.
Prerequisites
Requirements
No hay requisitos específicos para este documento.
Componentes Utilizados
La información que contiene este documento se basa en las siguientes versiones de software y hardware.
-
Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2(14)SY2 para Catalyst 6000 Supervisor Engine, con el módulo de servicio VPN IPSec
-
Cisco 3640 Router que ejecuta Cisco IOS Software Release 12.3(4)T
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Convenciones
Para obtener más información sobre las convenciones del documento, consulte Convenciones de Consejos Técnicos de Cisco.
Antecedentes
El módulo de servicio VPN Catalyst 6500 tiene dos puertos Gigabit Ethernet (GE) sin conectores visibles externamente. Estos puertos son direccionables sólo con fines de configuración. El puerto 1 es siempre el puerto interior. Este puerto gestiona todo el tráfico desde y hacia la red interna. El segundo puerto (puerto 2) gestiona todo el tráfico desde y hacia la WAN o las redes externas. Estos dos puertos siempre se configuran en el modo de enlace troncal 802.1Q. El módulo de servicio VPN utiliza una técnica denominada Bump In The Wire (BITW) para el flujo de paquetes.
Los paquetes son procesados por un par de VLAN, una Capa 3 dentro de VLAN y una Capa 2 fuera de VLAN. Los paquetes, desde el interior hasta el exterior, se enrutan a través de un método denominado Lógica de reconocimiento de direcciones codificadas (EARL) a la VLAN interna. Después de cifrar los paquetes, el módulo de servicio VPN utiliza la VLAN exterior correspondiente. En el proceso de descifrado, los paquetes del exterior al interior se puentean al módulo de servicio VPN usando la VLAN externa. Después de que el módulo de servicio VPN descifra el paquete y mapea la VLAN a la VLAN interna correspondiente, EARL enruta el paquete al puerto LAN apropiado. La Capa 3 dentro de la VLAN y la Capa 2 fuera de las VLAN se unen ejecutando el comando crypto connect vlan. Hay tres tipos de puertos en los switches Catalyst serie 6500:
-
Puertos enrutados: de forma predeterminada, todos los puertos Ethernet son puertos enrutados. Estos puertos tienen una VLAN oculta asociada con ellos.
-
Puertos de acceso: estos puertos tienen una VLAN de protocolo de enlace troncal (VTP) externa o VLAN asociada a ellos. Puede asociar más de un puerto a una VLAN definida.
-
Puertos troncales: estos puertos llevan muchas VLAN externas o VTP, en las que todos los paquetes se encapsulan con un encabezado 802.1Q.
Configurar
En esta sección encontrará la información para configurar las funciones descritas en este documento.
Nota: Use la Command Lookup Tool (sólo clientes registrados) para obtener más información sobre los comandos utilizados en este documento.
Diagrama de la red
Este documento utiliza la configuración de red que se muestra en este diagrama:
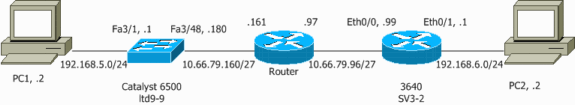
Configuración para IPSec Usando un Acceso de Capa 2 o Puerto Troncal
Realice estos pasos para configurar IPsec con la ayuda de un puerto trunk o de acceso de Capa 2 para la interfaz física externa.
-
Agregue las VLAN internas al puerto interno del módulo de servicio VPN.
Suponga que el módulo de servicio VPN está en la ranura 4. Utilice VLAN 100 como VLAN interna y VLAN 209 como VLAN externa. Configure los puertos GE del módulo de servicio VPN de la siguiente manera:
interface GigabitEthernet4/1 no ip address flowcontrol receive on flowcontrol send off switchport switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,100,1002-1005 switchport mode trunk cdp enable interface GigabitEthernet4/2 no ip address flowcontrol receive on flowcontrol send off switchport switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,209,1002-1005 switchport mode trunk cdp enable spanning-tree portfast trunk
-
Agregue la interfaz VLAN 100 y la interfaz donde se termina el túnel (que, en este caso, es la interfaz Vlan 209, como se muestra aquí).
interface Vlan100 ip address 10.66.79.180 255.255.255.224 interface Vlan209 no ip address crypto connect vlan 100
-
Configure el puerto físico externo como un puerto de acceso o troncal (que, en este caso, es FastEthernet 3/48, como se muestra aquí).
!--- This is the configuration that uses an access port. interface FastEthernet3/48 no ip address switchport switchport access vlan 209 switchport mode access !--- This is the configuration that uses a trunk port. interface FastEthernet3/48 no ip address switchport switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport mode trunk
-
Cree la NAT de omisión. Agregue estas entradas a la sentencia no nat para eximir el nating entre estas redes:
access-list inside_nat0_outbound permit ip 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.6.0 0.0.0.255 global (outside) 1 interface nat (inside) 0 access-list inside_nat0_outbound nat (inside) 1 192.168.5.0 255.255.255.0
-
Cree la configuración de criptografía y la lista de control de acceso (ACL) que define el tráfico que se va a cifrar.
-
Cree una ACL (en este caso, ACL 100) que defina el tráfico desde la red interna 192.168.5.0/24 a la red remota 192.168.6.0/24, de la siguiente manera:
access-list 100 permit ip 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.6.0 0.0.0.255
-
Defina sus propuestas de políticas de protocolo ISAKMP (Asociación de seguridad de Internet) y protocolo de administración de claves (Key Management Protocol), como las siguientes:
crypto isakmp policy 1 hash md5 authentication pre-share group 2
-
Ejecute este comando (en este ejemplo) para utilizar y definir claves previamente compartidas.
crypto isakmp key cisco address 10.66.79.99
-
Defina sus propuestas de IPSec de la siguiente manera:
crypto ipsec transform-set cisco esp-des esp-md5-hmac
-
Cree su declaración de mapa criptográfico de la siguiente manera:
crypto map cisco 10 ipsec-isakmp set peer 10.66.79.99 set transform-set cisco match address 100
-
-
Aplique el mapa crypto a la interfaz VLAN 100, de la siguiente manera:
interface vlan100 crypto map cisco
Estas configuraciones se utilizan.
| Catalyst 6500 |
|---|
!--- Define the Phase 1 policy. crypto isakmp policy 1 hash md5 authentication pre-share group 2 crypto isakmp key cisco address 10.66.79.99 ! ! !--- Define the encryption policy for this setup. crypto ipsec transform-set cisco esp-des esp-md5-hmac ! !--- Define a static crypto map entry for the peer !--- with mode ipsec-isakmp. !--- This indicates that Internet Key Exchange (IKE) !--- is used to establish the IPsec !--- security associations (SAs) to protect the traffic !--- specified by this crypto map entry. crypto map cisco 10 ipsec-isakmp set peer 10.66.79.99 set transform-set cisco match address 100 ! ! no spanning-tree vlan 100 ! ! ! interface FastEthernet3/1 ip address 192.168.5.1 255.255.255.0 ! !--- This is the outside Layer 2 port that allows VLAN !--- 209 traffic to enter. interface FastEthernet3/48 no ip address switchport switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport mode trunk ! interface GigabitEthernet4/1 no ip address flowcontrol receive on flowcontrol send off switchport switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q !--- VLAN 100 is defined as the Interface VLAN (IVLAN). switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,100,1002-1005 switchport mode trunk cdp enable ! interface GigabitEthernet4/2 no ip address flowcontrol receive on flowcontrol send off switchport switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q !--- The Port VLAN (PVLAN) configuration is handled transparently by !--- the VPN service module without user configuration !--- or involvement. It also is not shown in the configuration. !--- Note: For every IVLAN, a corresponding PVLAN exists. switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,209,1002-1005 switchport mode trunk cdp enable spanning-tree portfast trunk ! interface Vlan1 no ip address shutdown ! !--- This is the IVLAN that is configured to intercept the traffic !--- destined to the secure port on which the inside port !--- of the VPN service module is the only port present. interface Vlan100 ip address 10.66.79.180 255.255.255.224 crypto map cisco !--- This is the secure port that is a virtual Layer 3 interface. !--- This interface purposely does not have a Layer 3 IP address !--- configured. This is normal for the BITW process. !--- The IP address is moved from this interface to VLAN 100 to !--- accomplish BITW. This brings the VPN service module into !--- the packet path. interface Vlan209 no ip address crypto connect vlan 100 ! ip classless !--- Configure the routing so that the device !--- is directed to reach its destination network. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.66.79.161 global (outside) 1 interface !--- NAT 0 prevents NAT for networks specified in the ACL inside_nat0_outbound. nat (inside) 0 access-list inside_nat0_outbound nat (inside) 1 192.168.5.0 255.255.255.0 !--- This access list (inside_nat0_outbound) is used with the nat zero command. !--- This prevents traffic which matches the access list from undergoing !--- network address translation (NAT). The traffic specified by this ACL is !--- traffic that is to be encrypted and !--- sent across the VPN tunnel. This ACL is intentionally !--- the same as (100). !--- Two separate access lists should always be used in this configuration. access-list inside_nat0_outbound permit ip 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.6.0 0.0.0.255 !--- This is the crypto ACL. access-list 100 permit ip 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.6.0 0.0.0.255 |
| Router del Cisco IOS |
|---|
SV3-2#show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 1268 bytes ! version 12.3 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption ! hostname SV3-2 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! ! no aaa new-model ip subnet-zero ! ip audit notify log ip audit po max-events 100 ip ssh break-string no ftp-server write-enable ! !--- Define the Phase 1 policy. crypto isakmp policy 1 hash md5 authentication pre-share group 2 crypto isakmp key cisco address 10.66.79.180 ! ! !--- Define the encryption policy for this setup. crypto ipsec transform-set cisco esp-des esp-md5-hmac ! !--- Define a static crypto map entry for the peer !--- with mode ipsec-isakmp. This indicates that IKE !--- is used to establish the IPsec !--- SAs to protect the traffic !--- specified by this crypto map entry. crypto map cisco 10 ipsec-isakmp set peer 10.66.79.180 set transform-set cisco match address 100 ! ! !--- Apply the crypto map to the interface. interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 10.66.79.99 255.255.255.224 half-duplex crypto map cisco ! interface Ethernet0/1 ip address 192.168.6.1 255.255.255.0 half-duplex no keepalive ! ! ip http server no ip http secure-server ip classless !--- Configure the routing so that the device !--- is directed to reach its destination network. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.66.79.97 ! ! !--- This is the crypto ACL. access-list 100 permit ip 192.168.6.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 ! ! control-plane ! ! line con 0 line aux 0 line vty 0 4 ! end |
Configuración para IPsec con un Puerto Ruteado
Realice estos pasos para configurar IPsec con la ayuda de un puerto ruteado de Capa 3 para la interfaz física externa.
-
Agregue las VLAN internas al puerto interno del módulo de servicio VPN.
Suponga que el módulo de servicio VPN está en la ranura 4. Utilice VLAN 100 como VLAN interna y VLAN 209 como VLAN externa. Configure los puertos GE del módulo de servicio VPN de la siguiente manera:
interface GigabitEthernet4/1 no ip address flowcontrol receive on flowcontrol send off switchport switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,100,1002-1005 switchport mode trunk cdp enable interface GigabitEthernet4/2 no ip address flowcontrol receive on flowcontrol send off switchport switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,209,1002-1005 switchport mode trunk cdp enable spanning-tree portfast trunk
-
Agregue la interfaz VLAN 100 y la interfaz donde se termina el túnel (que, en este caso, es FastEthernet3/48, como se muestra aquí).
interface Vlan100 ip address 10.66.79.180 255.255.255.224 interface FastEthernet3/48 no ip address crypto connect vlan 100
-
Cree la NAT de omisión. Agregue estas entradas a la sentencia no nat para eximir el nating entre estas redes:
access-list inside_nat0_outbound permit ip 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.6.0 0.0.0.255 global (outside) 1 interface nat (inside) 0 access-list inside_nat0_outbound nat (inside) 1 192.168.5.0 255.255.255.0
-
Cree su configuración de criptografía y la ACL que define el tráfico que se cifrará.
-
Cree una ACL (en este caso, ACL 100) que defina el tráfico desde la red interna 192.168.5.0/24 a la red remota 192.168.6.0/24, de la siguiente manera:
access-list 100 permit ip 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.6.0 0.0.0.255
-
Defina las propuestas de políticas ISAKMP, como esta:
crypto isakmp policy 1 hash md5 authentication pre-share group 2
-
Ejecute este comando (en este ejemplo) para utilizar y definir claves previamente compartidas:
crypto isakmp key cisco address 10.66.79.99
-
Defina sus propuestas de IPSec de la siguiente manera:
crypto ipsec transform-set cisco esp-des esp-md5-hmac
-
Cree su declaración de mapa criptográfico de la siguiente manera:
crypto map cisco 10 ipsec-isakmp set peer 10.66.79.99 set transform-set cisco match address 100
-
-
Aplique el mapa crypto a la interfaz VLAN 100, de la siguiente manera:
interface vlan100 crypto map cisco
Estas configuraciones se utilizan.
| Catalyst 6500 |
|---|
!--- Define the Phase 1 policy. crypto isakmp policy 1 hash md5 authentication pre-share group 2 crypto isakmp key cisco address 10.66.79.99 ! ! !--- Define the encryption policy for this setup. crypto ipsec transform-set cisco esp-des esp-md5-hmac ! !--- Define a static crypto map entry for the peer !--- with mode ipsec-isakmp. This indicates that IKE !--- is used to establish the IPsec !--- SAs to protect the traffic !--- specified by this crypto map entry. crypto map cisco 10 ipsec-isakmp set peer 10.66.79.99 set transform-set cisco match address 100 ! ! no spanning-tree vlan 100 ! ! ! interface FastEthernet3/1 ip address 192.168.5.1 255.255.255.0 !--- This is the secure port that is configured in routed port mode. !--- This routed port mode does not have a Layer 3 IP address !--- configured. This is normal for the BITW process. !--- The IP address is moved from this interface to the VLAN 100 to !--- accomplish BITW. This brings the VPN service module into !--- the packet path. This is the Layer 2 port VLAN on which the !--- outside port of the VPN service module also belongs. interface FastEthernet3/48 no ip address crypto connect vlan 100 ! interface GigabitEthernet4/1 no ip address flowcontrol receive on flowcontrol send off switchport switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q !--- VLAN 100 is defined as the IVLAN. switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,100,1002-1005 switchport mode trunk cdp enable ! interface GigabitEthernet4/2 no ip address flowcontrol receive on flowcontrol send off switchport switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q !--- The PVLAN configuration is handled transparently by the !--- VPN service module without user configuration !--- or involvement. It also is not shown in the configuration. !--- Note: For every IVLAN, a corresponding PVLAN exists. switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,209,1002-1005 switchport mode trunk cdp enable spanning-tree portfast trunk ! interface Vlan1 no ip address shutdown ! !--- This is the IVLAN that is configured to intercept the traffic !--- destined to the secure port on which the inside port of the !--- VPN service module is the only port present. interface Vlan100 ip address 10.66.79.180 255.255.255.224 crypto map cisco ! ip classless !--- Configure the routing so that the device !--- is directed to reach its destination network. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.66.79.161 ! global (outside) 1 interface !--- NAT 0 prevents NAT for networks specified in the ACL inside_nat0_outbound. nat (inside) 0 access-list inside_nat0_outbound nat (inside) 1 192.168.5.0 255.255.255.0 !--- This access list (inside_nat0_outbound) is used with the nat zero command. !--- This prevents traffic which matches the access list from undergoing !--- network address translation (NAT). The traffic specified by this ACL is !--- traffic that is to be encrypted and !--- sent across the VPN tunnel. This ACL is intentionally !--- the same as (100). !--- Two separate access lists should always be used in this configuration. access-list inside_nat0_outbound permit ip 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.6.0 0.0.0.255 !--- This is the crypto ACL. access-list 100 permit ip 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.6.0 0.0.0.255 |
| Router del Cisco IOS |
|---|
SV3-2# show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 1268 bytes ! version 12.3 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption ! hostname SV3-2 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! ! no aaa new-model ip subnet-zero ! ip audit notify log ip audit po max-events 100 ip ssh break-string no ftp-server write-enable ! !--- Define the Phase 1 policy. crypto isakmp policy 1 hash md5 authentication pre-share group 2 crypto isakmp key cisco address 10.66.79.180 ! ! !--- Define the encryption policy for this setup. crypto ipsec transform-set cisco esp-des esp-md5-hmac ! !--- Define a static crypto map entry for the peer !--- with mode ipsec-isakmp. This indicates that IKE !--- is used to establish the IPsec !--- SAs to protect the traffic !--- specified by this crypto map entry. crypto map cisco 10 ipsec-isakmp set peer 10.66.79.180 set transform-set cisco match address 100 ! ! !--- Apply the crypto map to the interface. interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 10.66.79.99 255.255.255.224 half-duplex crypto map cisco ! interface Ethernet0/1 ip address 192.168.6.1 255.255.255.0 half-duplex no keepalive ! ! ip http server no ip http secure-server ip classless !--- Configure the routing so that the device !--- is directed to reach its destination network. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.66.79.97 ! ! !--- This is the crypto ACL. access-list 100 permit ip 192.168.6.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 ! ! control-plane ! ! line con 0 line aux 0 line vty 0 4 ! end |
Verificación
En esta sección encontrará información que le permitirá confirmar que su configuración funcione correctamente.
La herramienta Output Interpreter Tool (clientes registrados solamente) (OIT) soporta ciertos comandos show. Utilice la OIT para ver un análisis del resultado del comando show.
-
show crypto ipsec sa: muestra la configuración utilizada por las SAs IPsec actuales.
-
show crypto isakmp sa—Muestra todas las SA IKE actuales en un par.
-
show crypto vlan—Muestra la VLAN asociada con la configuración crypto.
-
show crypto eli—Muestra las estadísticas del módulo de servicio VPN.
Para obtener información adicional sobre la verificación y resolución de problemas de IPsec, consulte Solución de problemas de seguridad IP - Introducción y uso de los comandos debug.
Troubleshoot
Esta sección proporciona la información para resolver problemas de su configuración.
Comandos para resolución de problemas
Nota: Antes de ejecutar comandos debug, consulte Información Importante sobre Comandos Debug.
-
depuración crypto ipsec — Muestra los IPSec Negotiations de la Fase 2.
-
debug crypto isakmp — muestra las negociaciones ISAKMP para la fase 1.
-
debug crypto engine — muestra el tráfico codificado.
-
clear crypto isakmp: borra las SA relacionadas con la Fase 1.
-
clear crypto sa: borra las SA relacionadas con la Fase 2.
Para obtener información adicional sobre la verificación y resolución de problemas de IPsec, consulte Solución de problemas de seguridad IP - Introducción y uso de los comandos debug.
Información Relacionada
Contacte a Cisco
- Abrir un caso de soporte

- (Requiere un Cisco Service Contract)
 Comentarios
Comentarios