Introducción
En este documento se describe cómo configurar y verificar la función de anuncio condicional del protocolo de puerta de enlace de frontera (BGP, Border Gateway Protocol).
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco le recomienda que tenga conocimiento acerca de este tema:
Componentes Utilizados
Este documento no tiene restricciones específicas en cuanto a versiones de software y de hardware.
La información que contiene este documento se creó a partir de los dispositivos en un ambiente de laboratorio específico. Todos los dispositivos que se utilizan en este documento se pusieron en funcionamiento con una configuración verificada (predeterminada). Si tiene una red en vivo, asegúrese de entender el posible impacto de cualquier comando.
Antecedentes
La Función de aviso condicional de BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) proporciona control adicional sobre el anuncio de ruteo, dependiendo de la existencia de otros prefijos en la tabla BGP.
La función de anuncio condicional de BGP que se describe en este documento se introdujo en las versiones 11.1 y 11.2 del software Cisco IOS® y está disponible en versiones posteriores.
Generalmente, las rutas se propagan independientemente de la existencia de una trayectoria diferente. La función de anuncio condicional de BGP usa las palabras clave non-exist-map y advertise-map del comando neighbor advertise-map para hacer un seguimiento de rutas según el prefijo de ruta. Si un prefijo de ruta no estuviese presente en el resultado del comando non-exist-map, entonces la ruta especificada por el comando advertise-map se encuentra anunciada. Esta función es útil para redes multilocalizadas, en las que algunos prefijos se anuncian a uno de los proveedores solo si falta la información del otro proveedor (lo que indica una falla en la sesión de interconexión o una accesibilidad parcial).
Además de los anuncios normales de BGP que un router envía a sus pares, también se envían anuncios condicionales de BGP.
Convenciones
For more information on document conventions, refer to the Cisco Technical Tips Conventions.
Configurar
En esta sección encontrará la información para configurar las funciones descritas en este documento.

Nota: Para encontrar información adicional sobre los comandos utilizados en este documento, utilice la herramienta de búsqueda de comandos de Cisco IOS. Solo los usuarios registrados de Cisco pueden tener acceso a las herramientas y la información para el uso interno de Cisco.
Diagrama de la red
Este documento utiliza la configuración de red que se muestra en el siguiente diagrama.
Aquí, la interfaz de loopback de R103 se utiliza para anunciar 192.168.50.0/24 a R102. R102 tiene una red BGP, 172.16.16.0/24, que se anuncia a sus pares BGP externos (eBGP), R101 y R103, de forma predeterminada.
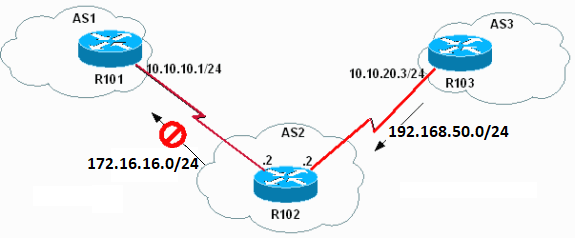 Configuración de la red
Configuración de la red
Gracias a la función de anuncio condicional de BGP, ahora puede realizar estas tareas en R102:
-
Si 192.168.50.0/24 existe en la tabla BGP de R102, no anuncie la red 172.16.16.0/24 a R101.
-
Si 192.168.50.0/24 no existe en la tabla BGP de R102, anuncie la red 172.16.16.0/24 a R101.
Con Cisco IOS 12.2T o versiones posteriores, la palabra clave exist-map también se puede usar para realizar estas tareas:
-
Si 192.168.50.0/24 existe en la tabla R102 BGP, anuncie la red 172.16.16.0/24 a R101.
-
Si 192.168.50.0/24 no existe en la tabla R102 BGP, no anuncie la red 172.16.16.0/24 a R101.
Configurar la función de anuncio condicional
En este documento, se utilizan estas configuraciones:

Nota: El ejemplo aquí trata la palabra clave non-exist-map. El uso de la palabra clave exist-map es similar a este.
| R102 |
hostname R102
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 172.16.16.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Serial8/0
ip address 10.10.10.2 255.255.255.0
!
interface Serial9/0
ip address 10.10.20.2 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 2
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 172.16.16.0 mask 255.255.255.0
network 172.31.130.0
neighbor 10.10.10.1 remote-as 1
neighbor 10.10.10.1 advertise-map ADVERTISE non-exist-map NON-EXIST
!--- Advertises the routes matched in the route-map ADVERTISE (172.16.16.0/24)
!--- only if the routes matched in route-map NON-EXIST (192.168.50.0/24)
!--- do not exist in the BGP table.
neighbor 10.10.20.3 remote-as 3
!
ip route 172.31.130.0 255.255.0.0 Null0
!
access-list 60 permit 172.16.16.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 65 permit 192.168.50.0 0.0.0.255
!
route-map NON-EXIST permit 10
match ip address 65
!
route-map ADVERTISE permit 10
match ip address 60
!
|
| R103 |
hostname R103
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 192.168.50.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Serial9/0
ip address 10.10.20.3 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 3
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 192.168.50.0
neighbor 10.10.20.2 remote-as 2
!
|
| R101 |
hostname R101
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 10.200.200.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Serial8/0
ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 1
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 10.200.200.0
neighbor 10.10.10.2 remote-as 2
!
|
Verifique la Configuración
Ejemplo 1
Este ejemplo confirma cómo se ve BGP cuando 192.168.50.0/24 está en la tabla BGP de R102:
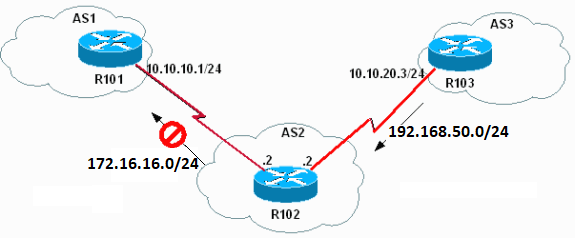 Verifique la Configuración
Verifique la Configuración
Primero verifique si 192.168.50.0/24 está en la tabla BGP de R102:
R102#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 6, local router ID is 172.16.16.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 172.16.16.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 172.31.130.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 192.168.50.0 10.10.20.3 0 0 3 i
*> 10.200.200.0 10.10.10.1 0 0 1 i
Debido a que 192.168.50.0/24 está en la tabla R102 BGP, R102 no debe anunciar 172.16.16.0/24 a R101.
R102#show ip bgp neighbors 10.10.10.1 advertised-routes
BGP table version is 6, local router ID is 172.16.16.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 172.31.130.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 192.168.50.0 10.10.20.3 0 0 3 i
!--- Note 172.16.16.0/24 is not advertised to neighbor 10.10.10.1.
R102#show ip bgp 172.16.16.0
BGP routing table entry for 172.16.16.0/24, version 6
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table)
Advertised to non peer-group peers:
!--- This is not advertised to R101.
10.10.20.3
Local
0.0.0.0 from 0.0.0.0 (172.16.16.1)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, weight 32768, valid, sourced, local, best
Luego revise el estado del anuncio condicional en R102:
R102#show ip bgp neighbors 10.10.10.1
BGP neighbor is 10.10.10.1, remote AS 1, external link
BGP version 4, remote router ID 10.200.200.1
BGP state = Established, up for 02:27:07
Last read 00:00:07, hold time is 180, keepalive interval is 60 seconds
!--- Output suppressed.
For address family: IPv4 Unicast
BGP table version 6, neighbor version 6
Index 1, Offset 0, Mask 0x2
Condition-map NON-EXIST, Advertise-map ADVERTISE, status: Withdraw
1 accepted prefixes consume 36 bytes
Prefix advertised 3, suppressed 0, withdrawn 1
Number of NLRIs in the update sent: max 1, min 0
!--- Output suppressed.
El resultado muestra que el anuncio condicional se retiró y que las redes que coinciden con el mapa de ruta ADVERTISE no se anuncian al par 10.10.10.1.
Para confirmar que las rutas que coinciden con el mapa de ruta ADVERTISE no se anuncien a R101, verifique la tabla BGP en R101:
R101#show ip bgp 172.16.16.0
% Network not in table
Ejemplo 2
En este ejemplo se muestra cómo se ve BGP cuando la red 192.168.50.0/24 no existe en la tabla BGP de R102.
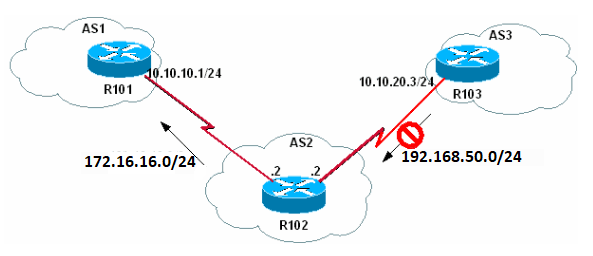 192.168.50.0/24 no existe en la tabla BGP de R102
192.168.50.0/24 no existe en la tabla BGP de R102
Los pasos son:
1. Cierre la interfaz de loopback 0 en R103 para que R103 ya no anuncie 192.168.50.0/24 a R102.
R103(config)#interface loopback 0
R103(config-if)#shutdown
R103(config-if)#
03:29:36: %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Loopback0, changed state to administratively down
2. Verifique que R102 no aprenda 192.168.50.0/24 y que la red no esté incluida en la tabla R102 BGP.
R102#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 8, local router ID is 172.16.16.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 172.16.16.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 172.31.130.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 10.200.200.0 10.10.10.1 0 0 1 i
!--- Note 192.168.50.0/24 is not present.
3. Observe cuánto tiempo tarda en comenzar el anuncio condicional:
R102#debug ip bgp updates
*Mar 1 02:39:18.059: BGP(0): 10.10.20.3 rcv UPDATE about 192.168.50.0/24
-- withdrawn
*Mar 1 02:39:18.059: BGP(0): no valid path for 192.168.50.0/24
*Mar 1 02:39:18.079: BGP(0): nettable_walker 192.168.50.0/24 no best path
*Mar 1 02:39:18.219: BGP(0): 10.10.10.1 computing updates, afi 0, neighbor
version 10, table version 11, starting at 0.0.0.0
*Mar 1 02:39:18.219: BGP(0): 10.10.10.1 send unreachable 192.168.50.0/24
*Mar 1 02:39:18.219: BGP(0): 10.10.10.1 send UPDATE 192.168.50.0/24
-- unreachable
*Mar 1 02:39:18.219: BGP(0): 10.10.10.1 1 updates enqueued (average=27, maximum=27)
*Mar 1 02:39:18.219: BGP(0): 10.10.10.1 update run completed, afi 0, ran for 0ms,
neighbor version 10, start version 11, throttled to 11
*Mar 1 02:40:04.747: BPG(0): Condition NON-EXIST changes to Advertise
*Mar 1 02:40:04.747: BGP(0): net 172.16.16.0/24 matches ADV MAP ADVERTISE:
bump version to 12
*Mar 1 02:40:05.187: BGP(0): nettable_walker 172.16.16.0/24 route sourced
locally
*Mar 1 02:40:05.187: BGP(0): 10.10.10.1 computing updates, afi 0, neighbor
version 11, table version 12, starting at 0.0.0.0
*Mar 1 02:40:05.187: BGP(0): 10.10.10.1 172.16.16.0/24 matches advertise map
ADVERTISE, state: Advertise
*Mar 1 02:40:05.187: BGP(0): 10.10.10.1 send UPDATE (format) 172.16.16.0/24,
next 10.10.10.2, metric 0, path
*Mar 1 02:40:05.187: BGP(0): 10.10.10.1 1 updates enqueued (average=52, maximum=52)
*Mar 1 02:40:05.187: BGP(0): 10.10.10.1 update run completed, afi 0, ran for 0ms,
neighbor version 11, start version 12, throttled to 12

Nota: El resultado de la depuración puede variar un poco dependiendo de la versión de software utilizada.
El proceso del escáner de BGP, que se ejecuta cada 60 segundos, acciona el proceso de anuncio condicional. Esto significa que el tiempo máximo para que surta efecto el anuncio condicional es de 60 segundos. El anuncio condicional puede tener efecto antes, según cuándo se elimina la ruta a la que se hizo seguimiento de la tabla BGP y cuándo se produce la siguiente instancia del escáner de BGP.
Ejecute estos comandos en R102 para verificar el estado de anuncio condicional en R102 para el vecino 10.10.10.1:
R102#show ip bgp neighbors 10.10.10.1
BGP neighbor is 10.10.10.1, remote AS 1, external link
BGP version 4, remote router ID 10.200.200.1
BGP state = Established, up for 02:45:27
Last read 00:00:27, hold time is 180, keepalive interval is 60 seconds
!--- Output suppressed.
For address family: IPv4 Unicast
BGP table version 12, neighbor version 12
Index 1, Offset 0, Mask 0x2
Condition-map NON-EXIST, Advertise-map ADVERTISE, status: Advertise
1 accepted prefixes consume 36 bytes
Prefix advertised 6, suppressed 0, withdrawn 4
Number of NLRIs in the update sent: max 1, min 0
!--- Output suppressed.
La tabla de routing y la tabla BGP de R101 tienen 172.16.16.0/24, como se muestra aquí:

Nota: En este ejemplo de salida, se envían los anuncios BGP condicionales (red 172.16.16.0/24), además de los anuncios BGP normales (red 172.31.130.0/16) que un router BGP envía a sus peers.
R101#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 18, local router ID is 10.200.200.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 172.16.16.0/24 10.10.10.2 0 0 2 i
*> 172.31.130.0 10.10.10.2 0 0 2 i
*> 10.200.200.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
R101#show ip route bgp
172.16.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
B 172.16.16.0 [20/0] via 10.10.10.2, 00:09:32
B 172.31.130.0/16 [20/0] via 10.10.10.2, 02:48:46
Ejemplo 3
Este ejemplo incluye la reinstalación de la red 192.168.50.0/24 en R102 para ver cómo BGP cambia de Advertise (anunciar) a Withdraw (retirar).
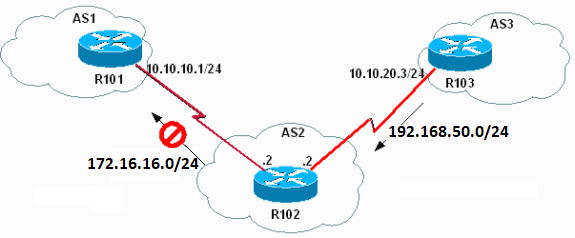 Cómo BGP cambia de Advertise (anunciar) a Withdraw (retirar)
Cómo BGP cambia de Advertise (anunciar) a Withdraw (retirar)
Para reinstalar 192.168.50.0/24, ejecute el no shutdown comando para hacer que el loopback de interfaz 0 en R103 funcione.
R103(config)#interface loopback 0
R103(config-if)#no shutdown
R103(config-if)#
03:49:06: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Loopback0,
changed state to up
03:49:07: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on
Interface Loopback0, changed state to up
!--- R102 kicks in conditional advertisement the moment the
!--- conditional network is received again.
*Mar 1 02:51:42.227: BGP(0): 10.10.20.3 rcvd UPDATE w/ attr:
nexthop 10.10.20.3, origin i, metric 0, path 3
*Mar 1 02:51:42.227: BGP(0): 10.10.20.3 rcvd 192.168.50.0/24
*Mar 1 02:51:42.247: BGP(0): Revise route installing 192.168.50.0/24 ->
10.10.20.3 to main IP table
*Mar 1 02:51:42.379: BGP(0): 10.10.10.1 computing updates, afi 0,
neighbor version 12, table version 13, starting at 0.0.0.0
*Mar 1 02:51:42.379: BGP(0): 10.10.10.1 send UPDATE (format)
192.168.50.0/24, next 10.10.10.2, metric 0, path 3
*Mar 1 02:51:42.379: BGP(0): 10.10.10.1 1 updates enqueued
(average=47, maximum=47)
*Mar 1 02:51:42.379: BGP(0): 10.10.10.1 update run completed, afi 0,
ran for 0ms, neighbor version 12, start version 13, throttled to 13
*Mar 1 02:52:09.159: BPG(0): Condition NON-EXIST changes to Withdraw
*Mar 1 02:52:09.159: BGP(0): net 172.16.16.0/24 matches ADV MAP
ADVERTISE: bump version to 14
*Mar 1 02:52:09.499: BGP(0): nettable_walker 172.16.16.0/24 route
sourced locally
*Mar 1 02:52:11.559: BGP(0): 10.10.10.1 computing updates, afi 0,
neighbor version 13, table version 14, starting at 0.0.0.0
*Mar 1 02:52:11.559: BGP(0): 10.10.10.1 172.16.16.0/24 matches advertise
map ADVERTISE, state: Withdraw
*Mar 1 02:52:11.559: BGP(0): 10.10.10.1 send unreachable 172.16.16.0/24
*Mar 1 02:52:11.559: BGP(0): 10.10.10.1 send UPDATE 172.16.16.0/24 -- unreachable
*Mar 1 02:52:11.559: BGP(0): 10.10.10.1 1 updates enqueued (average=27, maximum=27)
*Mar 1 02:52:11.559: BGP(0): 10.10.10.1 update run completed, afi 0, ran for 0ms,
neighbor version 13, start version 14, throttled to 14
R102 ya no anuncia 172.16.16.0/24 a R101.
R102#show ip bgp neighbors 10.10.10.1 advertised-routes
BGP table version is 14, local router ID is 172.16.16.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 172.31.130.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 192.168.50.0 10.10.20.3 0 0 3 i
!--- Note 172.16.16.0/24 is not advertised.
R102#show ip bgp neighbors 10.10.10.1
BGP neighbor is 10.10.10.1, remote AS 1, external link
BGP version 4, remote router ID 10.200.200.1
BGP state = Established, up for 03:01:32
Last read 00:00:31, hold time is 180, keepalive interval is 60 seconds
Neighbor capabilities:
!--- Output supressed.
For address family: IPv4 Unicast
BGP table version 14, neighbor version 14
Index 1, Offset 0, Mask 0x2
Condition-map NON-EXIST, Advertise-map ADVERTISE, status: Withdraw
1 accepted prefixes consume 36 bytes
Prefix advertised 7, suppressed 0, withdrawn 5
Number of NLRIs in the update sent: max 1, min 0
!--- Output supressed.

Nota: En un escenario real, AS1 y AS3 están conectados a Internet (BGP global). Por lo tanto, la red 192.168.50.0/24 podría propagarse a través de una malla BGP global de AS3 a la tabla BGP de AS1 (R101). AS1, a su vez, podría propagar el prefijo 192.168.50.0 a R102 (según el acuerdo de políticas entre AS1 y AS2). Si R101 propaga rutas AS3 aprendidas de la malla BGP global a R102, el anuncio condicional puede fallar si no se colocan comprobaciones adicionales en non-exist map.
Para entender mejor por qué falla el anuncio condicional, tenga en cuenta esta situación. AS1 aprende 192.168.50.0/24 de la malla BGP global y anuncia 192.168.50.0/24 a AS2 (R102). R102 también aprende el prefijo 192.168.50.0/24 de su par directo a R103 (por el link R102 a R103). Cuando falla el link directo entre R102 y R103, se espera que el prefijo 192.168.50.0/24 deje de existir en la tabla BGP de R102 y el anuncio condicional se inicie y anuncie el prefijo 172.16.16.0/24 a R101. Sin embargo, dado que el prefijo 192.168.50.0/24 sigue existiendo en la tabla BGP de R102 (aprendida de R101), el anuncio condicional se interrumpe porque el prefijo en el mapa no existente aún existe en el Tabla R102 BGP.
Para asegurarse de que el prefijo 192.168.50.0/24 se aprenderá únicamente de la conexión directa a AS3 (R102 a R103) a fin de que se activen los anuncios condicionales, agregue una sentencia match as_path en non-exist map que coincida con el AS_PATH del prefijo 192.168.50.0/24 aprendido de la conexión directa (que en este caso es AS3). La expresión regular en este caso es ^3. Para más información sobre las expresiones regulares, consulte Uso de expresiones regulares en BGP. Tenga en cuenta que no puede haber coincidencia solo en el as-path y no en el prefijo. Match as_path solo puede complementar los criterios de coincidencia para el prefijo coincidente. En otras palabras, no puede anunciar algunos prefijos a un vecino si no existe ningún prefijo de un determinado número de AS.
Aquí se muestra la nueva configuración de R102. Las inclusiones están en negrita.
| R101 |
hostname R102
!
interface Loopback0
ip address 172.16.16.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Serial8/0
ip address 10.10.10.2 255.255.255.0
!
interface Serial9/0
ip address 10.10.20.2 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 2
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 172.16.16.0 mask 255.255.255.0
network 172.31.130.0
neighbor 10.10.10.1 remote-as 1
neighbor 10.10.10.1 advertise-map ADVERTISE non-exist-map NON-EXIST
neighbor 10.10.20.3 remote-as 3
!
ip route 172.31.130.0 255.255.0.0 Null0
!
ip as-path access-list 1 permit ^3
!
access-list 60 permit 172.16.16.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 65 permit 192.168.50.0 0.0.0.255
!
route-map NON-EXIST permit 10
match ip address 65
match as-path 1
!
route-map ADVERTISE permit 10
match ip address 60
!
|
Información Relacionada





 Comentarios
Comentarios