Troubleshooting de Problemas de Conexión de Vecindad BGP
Opciones de descarga
-
ePub (86.3 KB)
Visualice en diferentes aplicaciones en iPhone, iPad, Android, Sony Reader o Windows Phone -
Mobi (Kindle) (88.1 KB)
Visualice en dispositivo Kindle o aplicación Kindle en múltiples dispositivos
Lenguaje no discriminatorio
El conjunto de documentos para este producto aspira al uso de un lenguaje no discriminatorio. A los fines de esta documentación, "no discriminatorio" se refiere al lenguaje que no implica discriminación por motivos de edad, discapacidad, género, identidad de raza, identidad étnica, orientación sexual, nivel socioeconómico e interseccionalidad. Puede haber excepciones en la documentación debido al lenguaje que se encuentra ya en las interfaces de usuario del software del producto, el lenguaje utilizado en función de la documentación de la RFP o el lenguaje utilizado por un producto de terceros al que se hace referencia. Obtenga más información sobre cómo Cisco utiliza el lenguaje inclusivo.
Acerca de esta traducción
Cisco ha traducido este documento combinando la traducción automática y los recursos humanos a fin de ofrecer a nuestros usuarios en todo el mundo contenido en su propio idioma. Tenga en cuenta que incluso la mejor traducción automática podría no ser tan precisa como la proporcionada por un traductor profesional. Cisco Systems, Inc. no asume ninguna responsabilidad por la precisión de estas traducciones y recomienda remitirse siempre al documento original escrito en inglés (insertar vínculo URL).
Contenido
Introducción
Este documento describe los problemas que evitan que la vecindad BGP se establezca correctamente.
Prerequisites
Requirements
No hay requisitos específicos para este documento.
Componentes Utilizados
Este documento no tiene restricciones específicas en cuanto a versiones de software y de hardware.
La información que contiene este documento se creó a partir de los dispositivos en un ambiente de laboratorio específico. Todos los dispositivos que se utilizan en este documento se pusieron en funcionamiento con una configuración verificada (predeterminada). Si tiene una red en vivo, asegúrese de entender el posible impacto de cualquier comando.
Convenciones
Consulte Convenciones de Consejos TécnicosCisco para obtener más información sobre las convenciones del documento.
Antecedentes
Los routers BGP pueden intercambiar información de ruteo solamente cuando establecen una conexión de peer entre ellos.
El establecimiento del peer BGP comienza con la creación de una conexión TCP entre los dispositivos.
Una vez establecida la conexión TCP, los dispositivos BGP intentan crear una sesión BGP mediante el intercambio de mensajes BGP Open, donde intercambian la versión de BGP, el número AS, el tiempo de espera y el identificador BGP.
En el proceso de establecimiento de peer BGP, varias cosas pueden evitar que una vecindad BGP se establezca correctamente. Este documento trata algunas de las posibles razones de este problema:
-
Un error al escribir dio como resultado una dirección IP incorrecta en la instrucción de vecino o el número de sistema autónomo incorrecto. Compruebe las configuraciones.
-
La unidifusión está dañada. Algunas de las razones son:
-
Asignación errónea del circuito virtual (VC) en un Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) o entorno de Frame Relay en una red altamente redundante.
-
La lista de acceso está bloqueando el paquete de unidifusión o TCP.
-
La traducción de direcciones de red (NAT) se está ejecutando en el router y está traduciendo el paquete de unidifusión.
-
La capa 2 está inactiva.
-
-
La falta del comando ebgp-multihop es un error común que impide que aparezcan los peers. Este problema se analiza en el segundo ejemplo.
Diagrama de la red
Utilice este diagrama de red como ejemplo para las primeras tres causas:
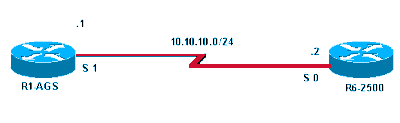 Diagrama de la red
Diagrama de la red
Problema
La Declaración De Vecino Es Incorrecta
El comando show ip bgp summary en el Router R1-AGS muestra que la sesión está activa.
R1-AGS(9)#show ip bgp summary
BGP table version is 1, main routing table version 1 Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd 10.10.10.2 4 400 0 0 0 0 0 never Active
Las configuraciones son:
| R1-AGS | R6-2500 |
|---|---|
interface Loopback0 ip address 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 ! interface Serial1 ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0 ! router bgp 400 neighbor 10.10.10.2 remote-as 400 neighbor 10.10.10.2 update-source Loopback0 ! ip route 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 10.10.10.2 |
interface Loopback0 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 ! interface Serial0 ip address 10.10.10.2 255.255.255.0 ! router bgp 400 neighbor 10.10.10.1 remote-as 400 neighbor 10.10.10.1 update-source Loopback0 ! ip route 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 10.10.10.1 |
Los comandos debug ip bgp y debug ip tcp transactions muestran la falla de la conexión TCP.
Depuraciones en el Router R1-AGS:
BGP: 10.10.10.2 open active, local address 10.2.2.2 TCB00135978 created TCB00135978 setting property 0 16ABEA TCB00135978 bound to 10.2.2.2.11039 TCP: sending SYN, seq 3797113156, ack 0 TCP0: Connection to 10.10.10.2:179, advertising MSS 1460 TCP0: state was CLOSED -> SYNSENT [11039 -> 10.10.10.2(179)] TCP0: state was SYNSENT -> CLOSED [11039 -> 10.10.10.2(179)] TCP0: bad seg from 10.10.10.2 -- closing connection: seq 0 ack 3797113157 rcvnxt 0 rcvwnd 0 TCP0: connection closed - remote sent RST TCB00135978 destroyed BGP: 10.10.10.2 open failed: Connection refused by remote host TCP: sending RST, seq 0, ack 1965664223 TCP: sent RST to 10.1.1.1:11016 from 10.10.10.1:179
Depuraciones en el Router R6-2500:
TCP: sending RST, seq 0, ack 3797113157 TCP: sent RST to 10.2.2.2:11039 from 10.10.10.2:179 BGP: 10.10.10.1 open active, local address 10.1.1.1 TCB001E030C created TCB001E030C setting property TCP_WINDOW_SIZE (0) 194F7A TCB001E030C setting property TCP_TOS (11) 194F79 TCB001E030C bound to 10.10.1.1.11016 TCP: sending SYN, seq 1965664222, ack 0 TCP0: Connection to 10.10.10.1:179, advertising MSS 1460 TCP0: state was CLOSED -> SYNSENT [11016 -> 10.10.10.1(179)] TCP0: state was SYNSENT -> CLOSED [11016 -> 10.10.10.1(179)] TCP0: bad seg from 10.10.10.1 -- closing connection: seq 0 ack 1965664223 rcvnxt 0 rcvwnd 0 TCP0: connection closed - remote sent RST TCB 0x1E030C destroyed BGP: 10.10.10.1 open failed: Connection refused by remote host
Solución
Para remediar esta situación, corrija la dirección de loopback en la sentencia neighbor o quite el comando update-source de la configuración.
En este ejemplo, se corrige la dirección.
| R1-AGS | R6-2500 |
|---|---|
router bgp 400 neighbor 10.1.1.1 remote-as 400 neighbor 10.1.1.1 update-source Loopback0 ! ip route 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 10.10.10.2 |
router bgp 400 neighbor 10.2.2.2 remote-as 400 neighbor 10.2.2.2 update-source Loopback0 ! ip route 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 10.10.10.1 |
Una mirada al comando show ip bgp summary muestra que el Router R1-AGS se encuentra en el estado establecido.
R1-AGS(9)#show ip bgp summary
BGP table version is 1, main routing table version 1 Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd 10.1.1.1 4 400 3 3 1 0 0 00:00:26 0
Problema
No hay rutas a la dirección vecina o se utiliza la ruta predeterminada para llegar a la entidad par
El comando show ip bgp summary en el Router R1-AGS muestra que la sesión está actualmente activa.
R1-AGS(9)#show ip bgp summary
BGP table version is 1, main routing table version 1 Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd 10.1.1.1 4 400 0 0 0 0 0 never Active
Las configuraciones son:
| R1-AGS | R6-2500 |
|---|---|
interface Loopback0 ip address 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 ! interface Serial1 ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0 ! router bgp 300 neighbor 10.1.1.1 remote-as 400 neighbor 10.1.1.1 ebgp-multihop 2 neighbor 10.1.1.1 update-source Loopback0 |
interface Loopback0 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 ! interface Serial0 ip address 10.10.10.2 255.255.255.0 ! router bgp 400 neighbor 10.2.2.2 remote-as 300 neighbor 10.2.2.2 ebgp-multihop 2 neighbor 10.2.2.2 update-source Loopback0 |
Si ejecuta los comandos debug, muestra que no hay ruta al vecino.
Depuraciones en el Router R1-AGS:
BGP: 10.1.1.1 open active, delay 9568ms BGP: 10.1.1.1 multihop open delayed 19872ms (no route) BGP: 10.1.1.1 multihop open delayed 12784ms (no route)
Depuraciones en el Router R6-2500:
BGP: 10.2.2.2 open active, delay 6531ms BGP: 10.2.2.2 multihop open delayed 14112ms (no route) BGP: 10.2.2.2 multihop open delayed 15408ms (no route)
Solución
La solución es incluir una ruta al salto siguiente en la sentencia de vecino BGP. Utilice una ruta estática o dinámica según la situación.
En un entorno de BGP interno (iBGP) en el que tenga más control, puede propagar la ruta de forma dinámica mediante un protocolo de routing.
En una situación de BGP externo (eBGP), se recomienda configurar una ruta estática para alcanzar el salto siguiente.

Nota: Utilice el comando neighbor ebgp-multihop sólo cuando la dirección IP con la que está haciendo peering en su peer eBGP no esté conectada directamente.
En este ejemplo, se utiliza una ruta estática.
| R1-AGS | R6-2500 |
|---|---|
router bgp 300 neighbor 10.1.1.1 remote-as 400 neighbor 10.1.1.1 ebgp-multihop 2 neighbor 10.1.1.1 update-source Loopback0 ! ip route 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 10.10.10.2 |
router bgp 400 neighbor 10.2.2.2 remote-as 300 neighbor 10.2.2.2 ebgp-multihop 2 neighbor 10.2.2.2 update-source Loopback0 ! ip route 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 10.10.10.1 |
El comando show ip bgp summary muestra que el router R1-AGS se encuentra en el estado fijado.
R1-AGS(9)#show ip bgp summary
BGP table version is 1, main routing table version 1 Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd 10.1.1.1 4 400 3 3 1 0 0 00:00:26 0

Nota: Una ruta predeterminada nunca se va a utilizar para establecer una sesión BGP (iBGP/eBGP), y se ve la misma salida (sin ruta) en los debugs, aunque se puede hacer ping al vecino BGP. Nuevamente, la solución es agregar una ruta hacia el vecino BGO.
Problema
Falta el comando Update-source en BGP
El comando show ip bgp summary en el Router R1-AGS muestra que la sesión está activa.
R1-AGS(9)#show ip bgp summary
BGP table version is 1, main routing table version 1 Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd 10.1.1.1 4 400 0 0 0 0 0 never Active
Las configuraciones son:
| R1-AGS | R6-2500 |
|---|---|
interface Loopback0 ip address 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 ! interface Serial1 ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0 ! router bgp 400 neighbor 10.1.1.1 remote-as 400 ! ip route 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 10.10.10.2 |
interface Loopback0 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 ! interface Serial0 ip address 10.10.10.2 255.255.255.0 ! router bgp 400 neighbor 10.2.2.2 remote-as 400 ! ip route 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 10.10.10.1 |
Si ejecuta los comandos debug, muestra que la conexión TCP falla.
Depuraciones en el Router R1-AGS:
TCP: sending RST, seq 0, ack 2248020754 TCP: sent RST to 10.10.10.2:11018 from 10.2.2.2:179 BGP: 10.1.1.1 open active, local address 10.10.10.1 TCB0016B06C created TCB0016B06C setting property 0 16ADEA TCB0016B06C bound to 10.10.10.1.11042 TCP: sending SYN, seq 4099938541, ack 0 TCP0: Connection to 10.1.1.1:179, advertising MSS 536 TCP0: state was CLOSED -> SYNSENT [11042 -> 10.1.1.1(179)] TCP0: state was SYNSENT -> CLOSED [11042 -> 10.1.1.1(179)] TCP0: bad seg from 10.1.1.1 -- closing connection: seq 0 ack 4099938542 rcvnxt 0 rcvwnd 0 TCP0: connection closed - remote sent RST TCB0016B06C destroyed BGP: 10.1.1.1 open failed: Connection refused by remote host
Depuraciones en el Router R6-2500:
BGP: 10.2.2.2 open active, local address 10.10.10.2 TCB00194800 created TCB00194800 setting property TCP_WINDOW_SIZE (0) E6572 TCB00194800 setting property TCP_TOS (11) E6571 TCB00194800 bound to 10.10.10.2.11018 TCP: sending SYN, seq 2248020753, ack 0 TCP0: Connection to 10.2.2.2:179, advertising MSS 556 TCP0: state was CLOSED -> SYNSENT [11018 -> 10.2.2.2(179)] TCP0: state was SYNSENT -> CLOSED [11018 -> 10.2.2.2(179)] TCP0: bad seg from 10.2.2.2 -- closing connection: seq 0 ack 2248020754 rcvnxt 0 rcvwnd 0 TCP0: connection closed - remote sent RST TCB 0x194800 destroyed BGP: 10.2.2.2 open failed: Connection refused by remote host TCP: sending RST, seq 0, ack 4099938542 TCP: sent RST to 10.10.10.1:11042 from 10.1.1.1:179
Solución
Para resolver este problema, configure el comando update-source en ambos routers o quite el comando update-source y cambie la sentencia de vecino en ambos routers.
Estos son ejemplos de ambas soluciones.
El comando update-source se configura en ambos routers:
| R1-AGS | R6-2500 |
|---|---|
interface Loopback0 ip address 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 ! interface Serial1 ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0 ! router bgp 400 neighbor 10.1.1.1 remote-as 400 neighbor 10.1.1.1 update-source Loopback0 ! ip route 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 10.10.10.2 |
interface Loopback0 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 ! interface Serial0 ip address 10.10.10.2 255.255.255.0 ! router bgp 400 neighbor 10.2.2.2 remote-as 400 neighbor 10.2.2.2 update-source Loopback0 ! ip route 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 10.10.10.1 |
El comando show ip bgp summary muestra que el router R1-AGS se encuentra en el estado fijado.
R1-AGS(9)# show ip bgp summary
BGP table version is 1, main routing table version 1 Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd 10.2.2.2 4 400 3 3 1 0 0 00:00:26 0
Cuando alguien se está conectando a su dirección de loopback, simplemente tiene que utilizar el comando update-source. Esto es cierto en relación con un par iBGP y un par eBGP.
Aquí, se quita el comando update-source y se cambia la sentencia de vecino en ambos routers.
| R1-AGS | R6-2500 |
|---|---|
interface Loopback0 ip address 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 ! interface Serial1 ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0 ! router bgp 400 neighbor 10.10.10.2 remote-as 400 |
interface Loopback0 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 ! interface Serial0 ip address 10.10.10.2 255.255.255.0 ! router bgp 400 neighbor 10.10.10.1 remote-as 400 |
El comando show ip bgp summary muestra que el router R1-AGS se encuentra en el estado fijado.
R1-AGS(9)#show ip bgp summary
BGP table version is 1, main routing table version 1 Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd 10.10.10.2 4 400 3 3 1 0 0 00:00:26 0
Información Relacionada
Historial de revisiones
| Revisión | Fecha de publicación | Comentarios |
|---|---|---|
2.0 |
30-Nov-2023
|
Recertificación |
1.0 |
10-Dec-2001
|
Versión inicial |
Con la colaboración de ingenieros de Cisco
Contacte a Cisco
- Abrir un caso de soporte

- (Requiere un Cisco Service Contract)
 Comentarios
Comentarios